Blink Reflex Baby

Rooting Reflex In Babies Why It Is So Important
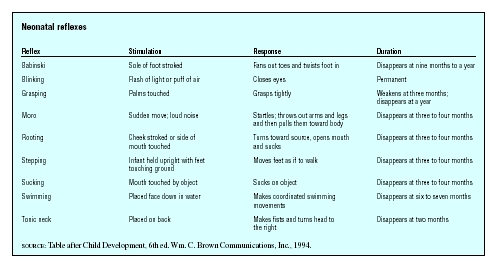
Neonatal Reflexes Baby Definition Description Common Problems

Understanding Your Child S Reflexes Suffolk Center For Speech

Baby S First Month Development Stages Of Development Baby

Child Development Ppt Download
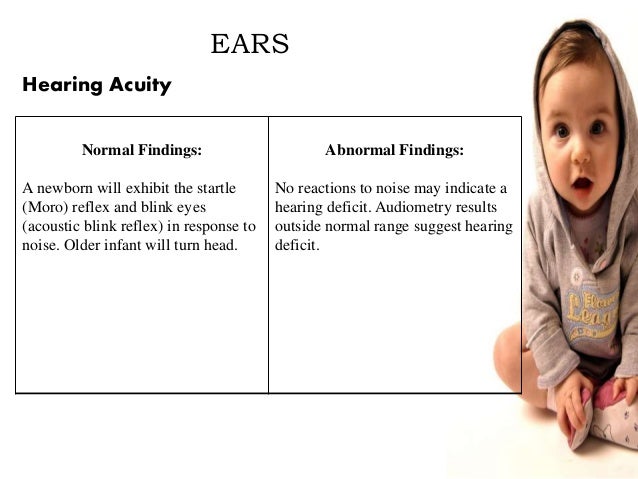
Infant Physical Assessment
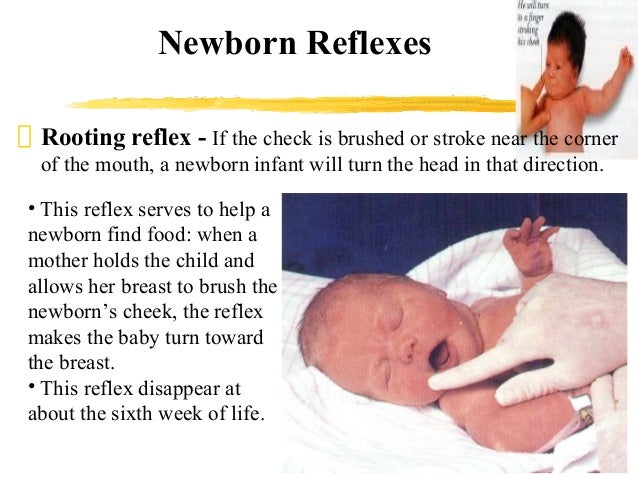
"The rooting reflex ensures that your baby gets her nutrition," says Tanya Remer Altmann, MD, a pediatrician in Westlake Village, California, and author of Mommy Calls Dr Tanya Answers Parents.
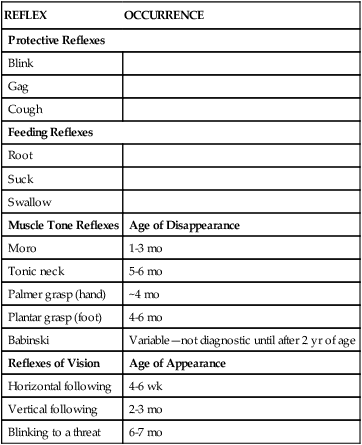
Blink reflex baby. Blink Baby closes both eyes Remains throughout life Moro or startle Making a loud noise or changing baby’s position causes baby to extend both arms outward with fingers spread, then bring them together in a tense, quivery embrace Present at 28 weeks of gestation;. These reflexes are somewhat automatic and not in his control To give an example if one strokes a newborn's hand or foot on either the top or back then whole arm or leg withdraws slightly and then the feet or hands flex and turn They turn as a mechanism to grasp your finger. Alzheimer's Disease https//youtube/OS8O5yrSP_chttps//youtube/beM9H5Eyve8LIKE👍SUBSCRIBE 🔔COMMENT 📝SHARE 🤝Video Showing Neonatal reflexesReflexes In.
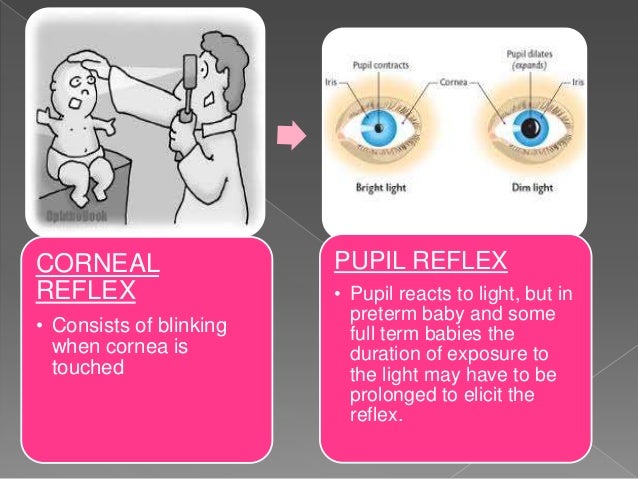
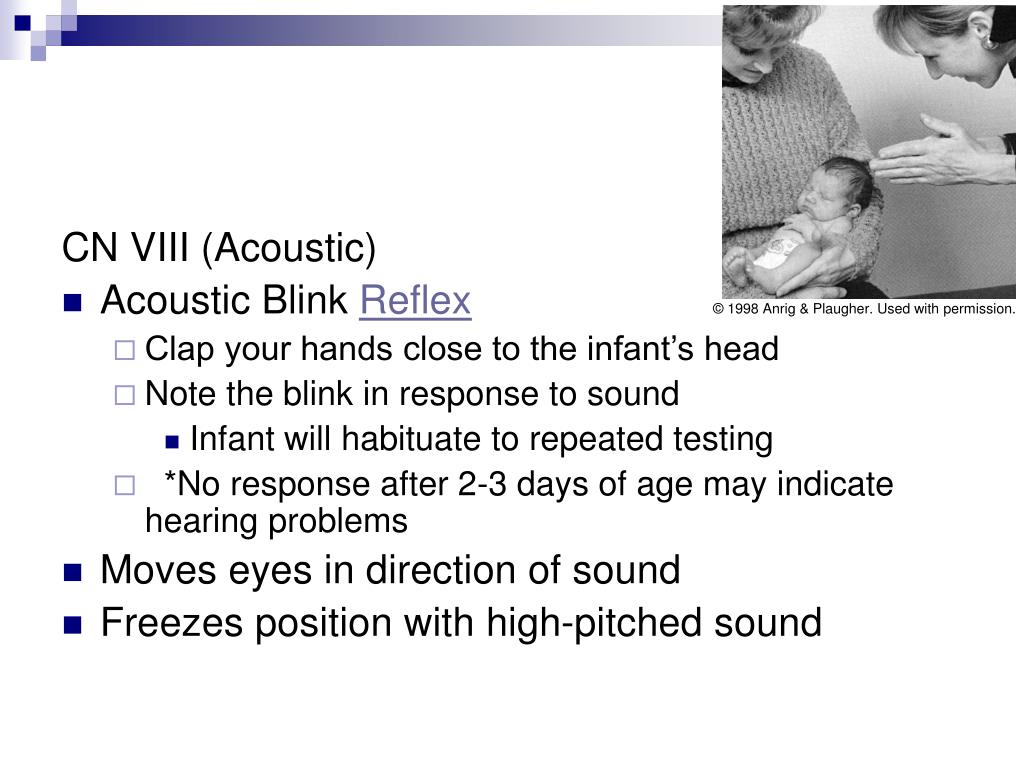
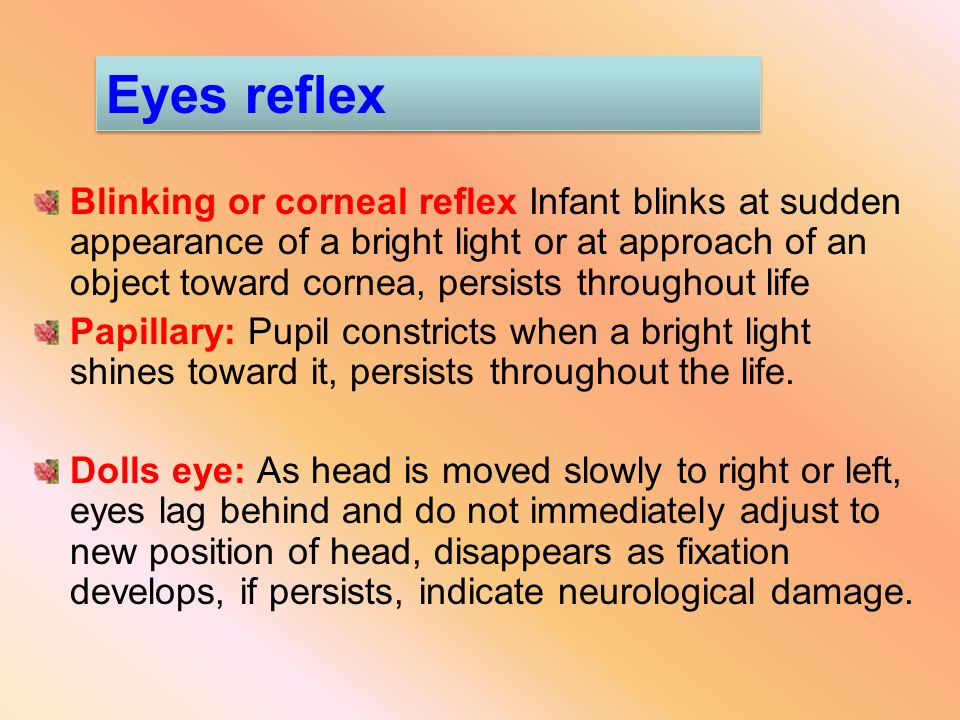
Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibited by newborns upon coming of objects near it Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye It can be elicited by shining a strong light (eg flashlight, otoscope light, etc) on the eyes. Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibited by newborns upon coming of objects near it Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye It can be elicited by shining a strong light (eg flashlight, otoscope light, etc) on the eyes Blink reflex can also be elicited by a sudden movement of an object towards the eye. The Neonatal or Newborn Baby Reflexes include Moro or Startle reflex, Babinski reflex, Galant reflex, Rooting reflex, Tonic Neck reflex, Swimming reflex, Pupillary reflex, Sucking reflex, Palmar Grasp reflex, etc Check out the video that explains all reflex found in babies.
R2 responses, especially contralateral ones, were more difficult to elicit under 9 months of age R1 latency and VIIth motor nerve conduction variations were a good witness of the peripheral nervous system maturation The influence of the different states of waking and sleeping on these reflex responses was studied. As the blink reflex It is an involuntary bli nking of The oculocephalic reflex was suppressed in 75% of babies by the age of 115 weeks and in more than 95% of babies aged weeks. In some babies, it may still be seen during sleep!.
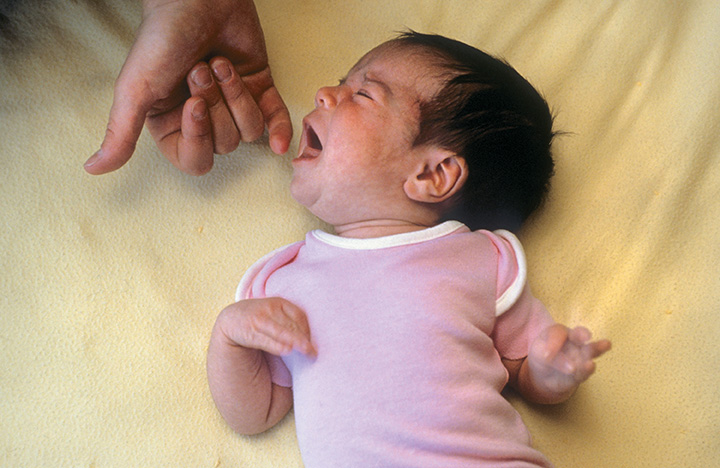
Blink reflex testes in neonates by habituation good indicator of CNS function in auditory tests cortical damage exists When the baby is turned face down towards the table, the arms will extend as if the baby is trying to catch himself 810 months parachute reflex appears. Disappears at 4–7 months Withdrawing Baby removes hand or foot from painful stimuli. In human behaviour The newborn infant with his eyes and will blink or close them at the sudden appearance of a bright light or at a sharp, sudden sound nearby The newborn infant will suck a nipple or almost any other object (eg, a finger) inserted into his mouth or touching his lips He will also.
Startle reflex Remains in different form An infant, in response to a sudden noise, flings out its arms, arches its back, and spreads its fingers Protection Eyeblink reflex Remains Rapid shutting and opening of eye on exposure to direct light Protection of eye from direct light Sucking reflex Remains. 2 Sucking reflex Like the rooting reflex, the sucking reflex helps a baby to seek food It causes an automatic sucking when the nipple of a breast or bottle, or even a finger, stimulates the lips This reflex appears at birth and becomes voluntary at 3 months 3 Moro reflex. The eyeblink reflex , also known as the blink reflex or corneal reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation (such as touching or a foreign body) of the cornea, or bright light, though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye).
This is due to the lack of maturity of the infants neurological system This is a normal reflex and may disappear as early as 6 months and as late as 2 years Functional significance A Babinski reflex in an older child or adult is atypical and is a sign of a problem in the brain or spinal cord. A reflex you may notice in your baby’s first months is the Moro reflex—a startle response If your baby’s head falls back abruptly or if he is startled, he will respond by throwing his arms and legs outward, extending his neck, and quickly bringing his arms together. The blink reflex is a reflex which is designed to naturally protect the eyes Most animals with eyes have some form of this reflex, and the reflex is present from the time that an animal first opens its eyes Abnormalities in this reflex can indicate that there is a neurological problem and may increase the risk of incurring eye damage because.
Last Modified Date December 06, The blink reflex is a reflex which is designed to naturally protect the eyes Most animals with eyes have some form of this reflex, and the reflex is present from the time that an animal first opens its eyes. Blink Baby closes both eyes Remains throughout life Moro or startle Making a loud noise or changing baby’s position causes baby to extend both arms outward with fingers spread, then bring them together in a tense, quivery embrace Present at 28 weeks of gestation;. The first one that I want to talk about is the breathing reflex The muscles required for inhalation and exhalation do their work on their own without any conscious awareness on the part of the newborn Or the conscious awareness of adults, for that matter There is also the eye blink reflex.
The sucking reflex often develops in premature babies over the first few weeks , even by the time they reach their original due date Until then, they're fed via feeding tubes Researchers continue to look at the sucking reflex and its relationship to swallowing and breathing The hope is to develop possible therapies that can help premature babies better develop this essential skill. Imagine trying to teach your baby how to suck or poop Thankfully, you don’t have to because babies are born with about 70 newborn reflexes tucked away in their jampacked brains. Blinking or Glabella reflex Glabella is lightly tapped and both eyes blink Habituation occurs with multiple attempts of the tapping Present at birth Disappears by 1 year Asymmetric tonic neck reflex With infant in supine position, head is gently rotated to one side Extension of the lateral arm and flexion of the contralateral arm occur.
These reflexes are somewhat automatic and not in his control To give an example if one strokes a newborn's hand or foot on either the top or back then whole arm or leg withdraws slightly and then the feet or hands flex and turn They turn as a mechanism to grasp your finger. This reflex is especially visible in patients with Bell palsy, an acute disorder of the facial nerve, due to failure of adequate eyelid closure The presence or absence of Bell’s reflex can be useful in diagnosis of many systemic and local diseases In supranuclear palsy, which can occur with SteeleRichardson syndrome, Parinaud’s syndrome, and double elevator palsy, patients cannot elevate their eyes but can do so on attempting the Bell’s phenomenon. Much of your baby’s activity in her first weeks of life is reflexive For instance, when you put your finger in her mouth, she doesn’t think about what to do, but sucks by reflex When confronted by a bright light, she will tightly shut her eyes, because that’s what her reflexes make her do.
When this reflex is triggered, the baby’s arms and legs open up and away from the body simultaneously, stress hormones release, breathing shallows, heart rate increases, and blood moves toward the limbs As this reflex repeats, babies learn to filter which stimuli are true threats warranting a response and which stimuli can be ignored. The blink reflex is a contraction of the eyelids in response to stimulation of the skin of the face The afferent pathway of the reflex is formed by sensory fibers in the trigeminal nerve supplying the skin of the head Motor fibers in the facial nerve innervating the orbicularis oculi muscles constitute the efferent pathway15 18. If your baby's eye blinking is accompanied by him rubbing his eyes and his eyes becoming red, it may be an allergy, so take your baby to the doctor Blinking Due To Tics Although more common in older children, some babies' eye blinking is due to a nervous tic, which causes them to blink excessively.
Auditory orienting reflex A sudden loud and unpleasant noise May produce the blink reflex Infant may remain still and show increased alertness Quieter sounds usually cause reflex eye and head turning to theside of the sound, as if to locate it Seen first at about 4 months of age Thereafter, head turning towards sound stimuli occurs and. Cranial nerves (CN) II and III can be tested by the pupillary reflex, which appears consistently at 32 to 35 weeks gestation A 28week infant will blink to light shone into the eyes, testing CN II and VII Beginning at 34 weeks of gestation, an infant will be able to fix and follow on an object, thus testing CN II, III, IV, and VI. The blink reflex was elicited in 50 children from birth to 3 years of age In the awake state, the R1 response was always obtained;.
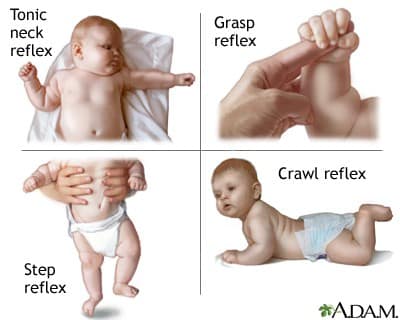
We also have the Babinski Reflex, which describes how a baby will curl and uncurl his or her toes when the bottom of the foot is stroked But unlike the Rooting Reflex, we really don't know why this might be. Gripping Reflex Babies will grasp anything that is placed in their palm The strength of this grip is strong, and most babies can support their entire weight in their grip Toe Curling Reflex When the inner sole of a baby’s foot is stroked, the infant will respond by curling his or her toes When the outer sole of a baby’s foot is stroked. Baby Reflexes Crying, Moro Reflex, Sneezing, Rooting and more!.
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). Corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex V VII Glabellar reflex V VII Vestibuloocular reflex VIII III, IV, VI Gag reflex IX X Reflexes usually only observed in human infants Grasp reflex Newborn babies have a number of other reflexes which are not seen in adults, referred to as primitive reflexes These automatic reactions to. Startle reflex The startle or “moro” reflex is a newborn reflex that doesn’t have a clear explanation as a survival tactic “The startle reflex occurs when a baby’s head shifts position suddenly.
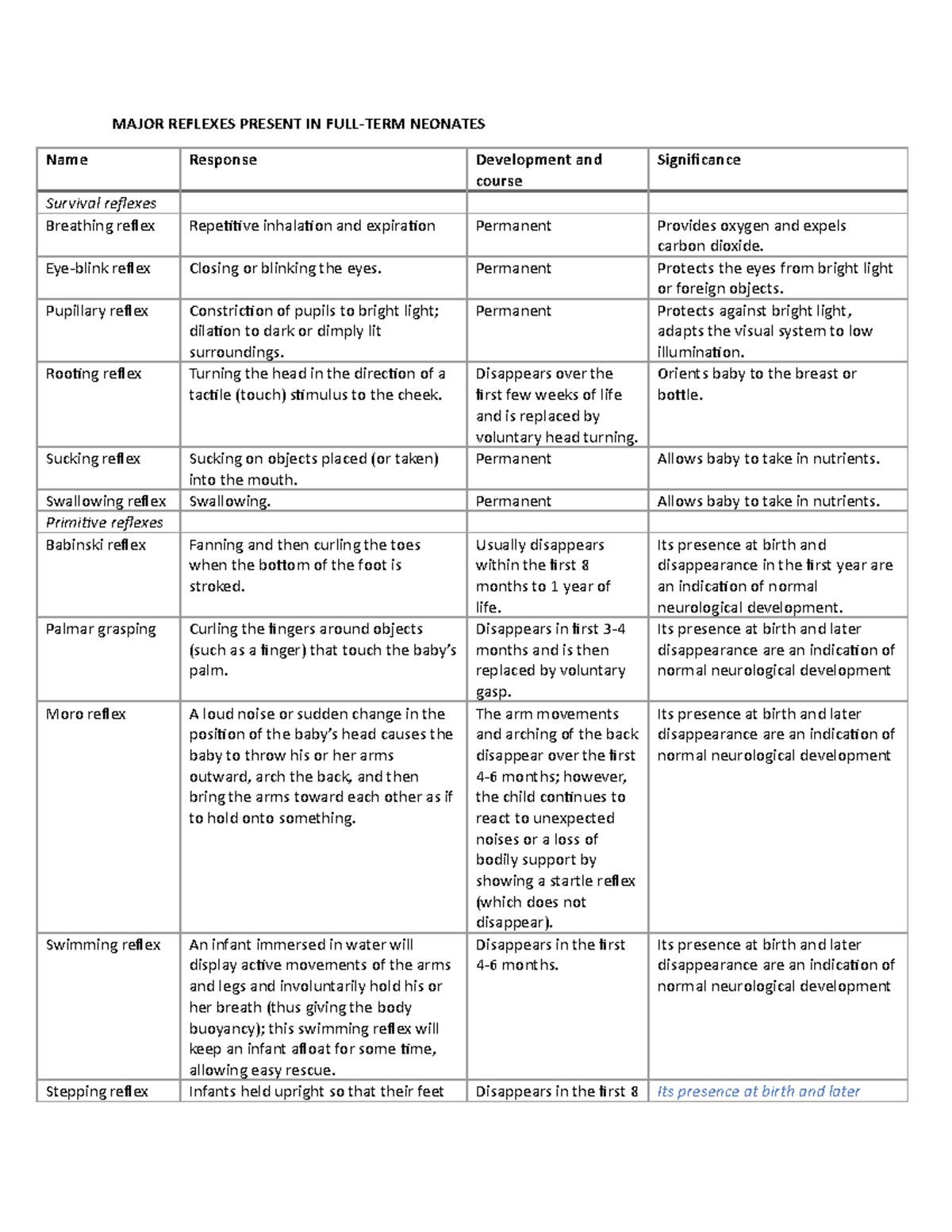
Definition Neonatal reflexes or primitive reflexes are the inborn behavioral patterns that develop during uterine life They should be fully present at birth and are gradually inhibited by higher centers in the brain during the first three to 12 months of postnatal life These reflexes, which are essential for a newborn's survival immediately after birth, include sucking, swallowing, blinking, urinating, hiccupping, and defecating. Startle reflex Remains in different form An infant, in response to a sudden noise, flings out its arms, arches its back, and spreads its fingers Protection Eyeblink reflex Remains Rapid shutting and opening of eye on exposure to direct light Protection of eye from direct light Sucking reflex Remains. At about 912 weeks after conception, the first of the primitive reflexes begins to develop and progresses throughout the pregnancy and is fully present at birth Symptoms if Retained Total body reaction;.
The eyeblink reflex , also known as the blink reflex or corneal reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation (such as touching or a foreign body) of the cornea, or bright light, though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). But newborns and infants blink far less often — only a handful of times every minute, with some babies blinking as infrequently as once a minute "The average is two or three blinks a minute. Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibited by newborns upon coming of objects near it Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye It can be elicited by shining a strong light (eg flashlight, otoscope light, etc) on the eyes Blink reflex can also be elicited by a sudden movement of an object towards the eye.
The complete blink rate was lower in newborn infants (62 blinks⁄min) than in preschool children (80 blinks⁄minute) Eyelid closing, opening and compete blink times were longer in newborn infants than in preschool children at all observation times Conclusions Newborn infants had a different pattern of eyelid movement com. Disappears at 4–7 months Withdrawing Baby removes hand or foot from painful. This is due to the lack of maturity of the infants neurological system This is a normal reflex and may disappear as early as 6 months and as late as 2 years Functional significance A Babinski reflex in an older child or adult is atypical and is a sign of a problem in the brain or spinal cord.
Introduction It is an electrodiagnostic test that evokes the corneal reflex It evaluates the integrity of the trigeminal and facial nerve Neuroanatomy The supraorbital branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve constitutes the afferent arm, while the motor fibers of the facial nerve form the efferent arm of this reflex The diagram below depicts the pathway of the blink reflex. This page includes the following topics and synonyms Newborn Reflexes, Primitive Stepping Reflex, Rooting Reflex, Moro Reflex, Startle Reflex. Babinski sign, also known as the plantar reflex, is one of the reflexes that doctors check for in newborns It’s a reaction to stroking the sole of a baby’s foot — but how the baby reacts is crucial Read on to learn what a normal response to the stimulation is.
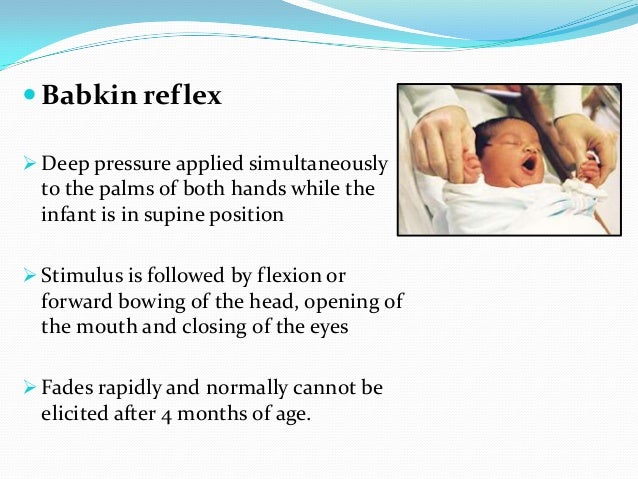
That flyingbaby stunt is an example of the parachute reflex in action "It occurs when you hold your child facing downward and suspended over the floor and then you swoosh him down," explains Dr. Normal Stepping Reflex Abnormal Stepping Reflex newborn_n_25mov newborn_ab_25mov Landau’s Reflex • When neonate is placed on stomach, their back arches and head raises • Emerges at 3 months postnatally and lasts until the child is 12 months old • If this reflex does not occur, it. •Stimulated when an object is placed into the baby’s palm •A normally developing neonate responds by grasping the object •This reflex emerges 11 wks in utero, and is inhibited 23 months after birth •A persistent palmar grasp reflex may cause issues such as swallowing problems and delayed speech (Grupen).
The blink reflex, the electrical version of the corneal reflex, represents a polysynaptic reflex Electrical stimulation of the supraorbital branch of the trigeminal nerve on one side results in a reflexive activation of the facial nucleus, causing contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle bilaterally. This reflex begins when the corner of the baby's mouth is stroked or touched The baby will turn his or her head and open his or her mouth to follow and "root" in the direction of the stroking This helps the baby find the breast or bottle to begin feeding. Teachers introducing children to reflexes in biology classes often use the blink reflex as an example because it is easy to demonstrate One way to demonstrate the reflex is to position a student behind a clear barrier and to throw a lightweight soft object like a cotton ball or a wad of paper at the barrier.
You take your baby for the first pediatric evaluation and, among other things, your pediatrician checks for the normal baby reflexes, including the presence of Moro reflex an important indication of a normal and developing nervous system in your newborn Everything is normal and you don't give this Moro reflex much thought, until it starts waking up your baby mid sleep and the troubles with. This page includes the following topics and synonyms Newborn Reflexes, Primitive Stepping Reflex, Rooting Reflex, Moro Reflex, Startle Reflex. The sucking reflex often develops in premature babies over the first few weeks , even by the time they reach their original due date Until then, they're fed via feeding tubes Researchers continue to look at the sucking reflex and its relationship to swallowing and breathing The hope is to develop possible therapies that can help premature babies better develop this essential skill.
The Moro or startle reflex causes your baby to extend their arms, legs, and fingers and arch when startled by the feeling of falling, a loud noise, or other environmental stimuli Babies will typically exhibit a "startled" look Pediatricians will typically check for this response right after birth and at the first baby checkups.

Baby Glabellar Reflex Reaction 0 4th Month Youtube

Childhood Eye Examination American Family Physician

Neonatology

Press Ads For J J Baby Wash Whatever Whatevers

Understanding Your Child S Reflexes The Cfy Diaries

Reflexes Present In Infants
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iStock_3573671_MEDIUM-582570425f9b58d5b178dd6f.jpg)
Strange Reflexes And What They Say About Your Health

Primitive Reflexes
Neonatal Reflexes By Baneet

Reflexes Present In Infants

How To Give Your Baby Medicine Babycenter Australia

Press Ads For J J Baby Wash Whatever Whatevers

Types Of Newborn S Reflexes And When Do They Disappear
Neonatal Eye Reflexes
Reflexes Present At Birth

Neonatal Nursing Care Part2 Neonatal Assessment Ppt Video Online Download

Reflexes

Newborn Baby Reflexes Ppt Newborn Baby
Psych Notes 350 101 Dw Studocu
Reflex Wikipedia
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf
Is Newborn Smiling Really Just A Reflex Research Is Challenging The Textbooks

Understanding Your Child S Reflexes Suffolk Center For Speech

Blink Reflex Is Characterized By The Involuntary Blink Of Nervous System Human Anatomy
Ppt Neurologic System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2615

Image Result For Primitive Reflex Primitive Reflexes Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatrics
Why Do You Blink Wonderopolis

Newborn Reflexes Nursing Assessment And Care

Childhood Eye Examination American Family Physician

Reflexes Present In Infants

Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Corneal Reflex Wikipedia

The Claim Babies Blink Less Than Adults Do The New York Times

The Primitive Reflexes Primitive Reflexes Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatrics

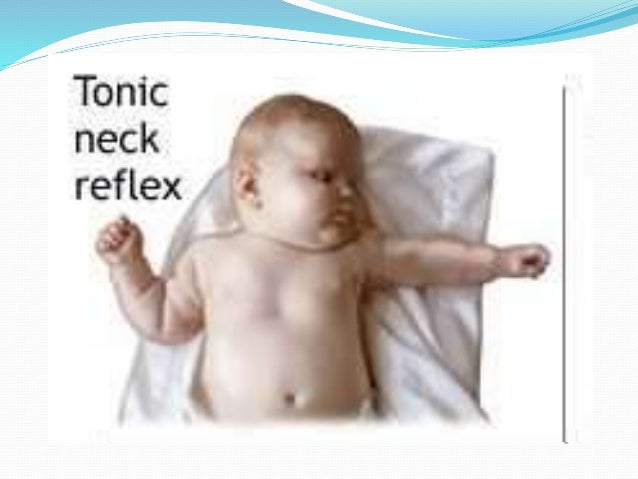
Tonic Neck Reflex Fencing Reflex Definition And Purpose

Baby Reflexes Things Newborn Infants Can Do From Infancy Happiest Baby

Newborn Reflexes

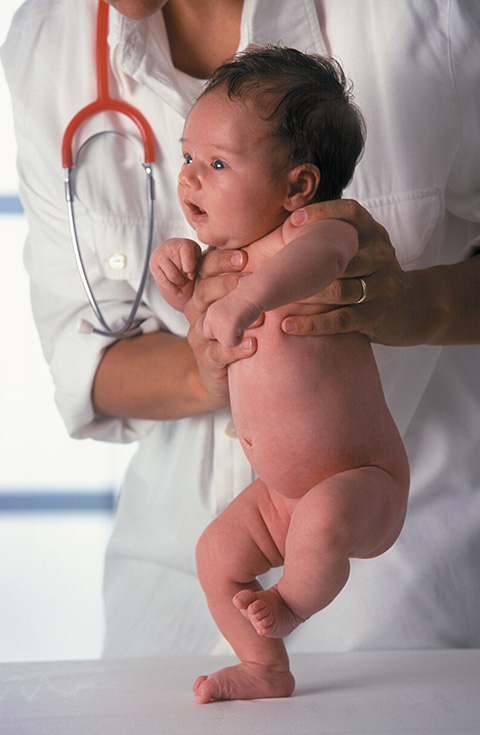
Stepping Reflex In Babies Definition Disappearance More

Untitled Document
Reflexes Present In Infants
Reflexes Our Inborn Physical Skills

Wkipb1no0xz69m
Www Pedscases Com Sites Default Files Pediatric eye exam slides Pdf

The Jewish Vues The Reflexes Part Ii
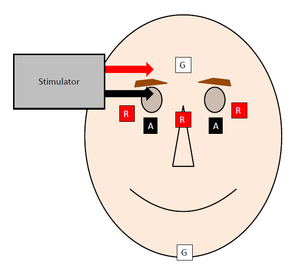
Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Infant Reflexes Information Mount Sinai New York
/GettyImages-958169622-5a2927441ac54c7b9f6944d09578cb4a.jpg)
The Different Types Of Newborn Reflexes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/200113930-001-56a059813df78cafdaa126a4.jpg)
Infant Vision Development From Birth To 2 Months

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
/174149172-56aafc3c5f9b58b7d0092a68.jpg)
Infant Vision Development From Birth To 2 Months
Wps Prenhall Com Wps Media Objects 6356 Tools Table9 3 Pdf

Infant Reflexes Baby Care Advice

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
Q Tbn And9gcr1bc3f7ratvy1zw0e Eoabwdwuvfpjms86h9zuto6f4oznssqa Usqp Cau
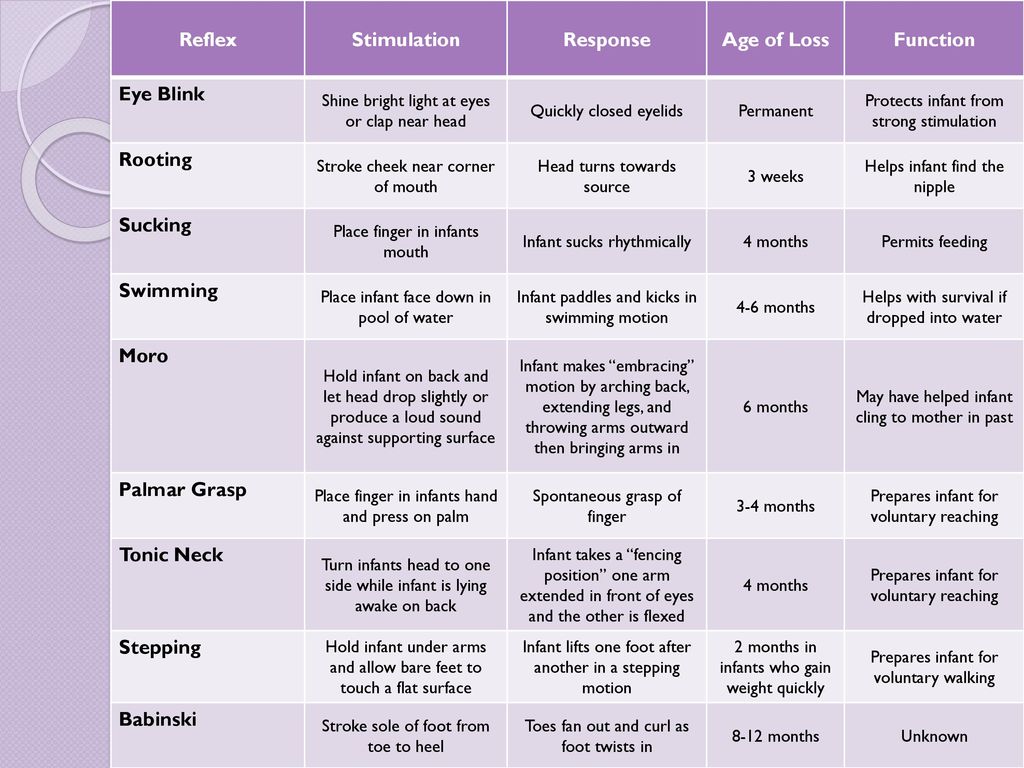
Reflexes Present In Infants
Http Www Sciencedirect Com Science Article Pii S Pdf Md5 1b67fab0bb23fccc3fb2afdd4 Pid 1 S2 0 S Main Pdf

When Do Babies Smile
Q Tbn And9gctpwmheniumeaq90gpdzx2jivertdblx53 Ykyemjh6g9cqeds9 Usqp Cau
Reflexes Our Inborn Physical Skills

Why Do Babies Blink Less Than Adults A Medical Explanation

Stepping Reflex In Babies Definition Disappearance More

Teach Neurology The Corneal Or Blink Reflex

Reflexes Present In Infants
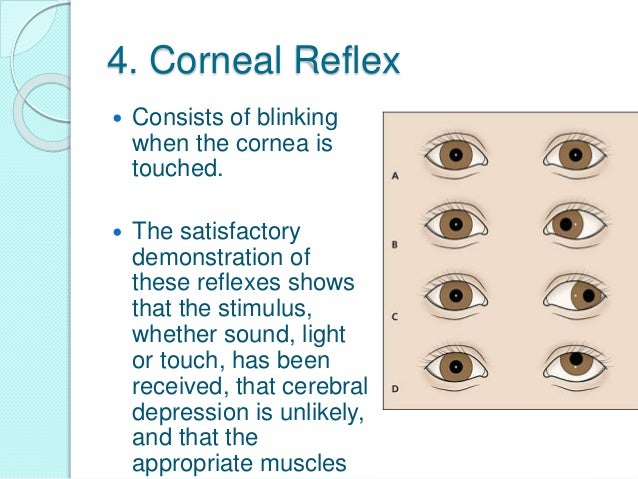
Reflexes Ppt Download
Newborn Baby Reflexes Ppt Newborn Baby

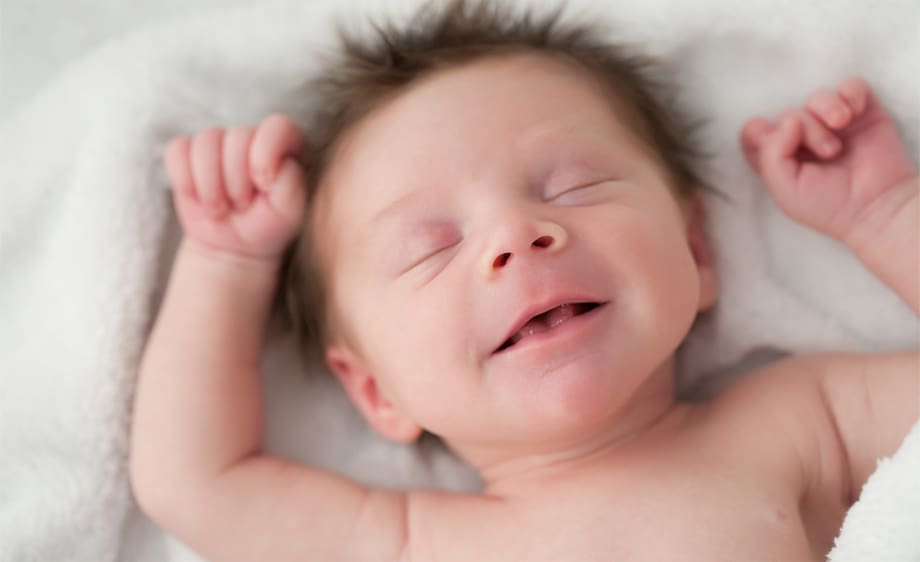
Why Do Babies Barely Blink Live Science

Light Blink Hearing Reflex Youtube
1

c 4 Predictable Newborn Patterns Ppt Video Online Download
Neonatal Reflexes Definition Patient Education

Blinking Reflex Youtube
Newborn Reflexes Nursing Assessment And Care
Reflexes Of Newborn Babies Newborn Baby

Tonic Neck Reflex Fencing Reflex Definition And Purpose

Rooting Reflex An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Excessive Eye Blinking Treatment What It Means And What To Do For Toddlers Mom Com

Understanding Your Child S Reflexes The Cfy Diaries

Understanding Your Child S Reflexes The Cfy Diaries
Q Tbn And9gctosogrkwe7yhk Bemea5qbf Uacwhtdzl2tnxxumdihpxpdxky Usqp Cau
The Newborn Infant Nurse Key
Corneal Reflex Wikipedia

Pin On Pregnancy

Neonatal Reflexes Baby Definition Description Common Problems

Newborn Reflexes Healthychildren Org

Test Bank Ch4 Pdf Oneclass

Neonatal Reflexes Video Behavior Khan Academy

Examination Of The Newborn Infant Ppt Video Online Download

Startle Reflex In Babies How Long Does It Last

Your Newborn Baby S Reflexes Essential Parent
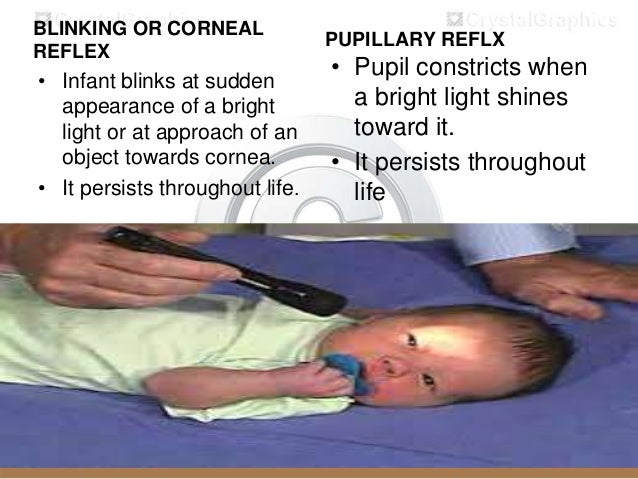
Newborn Assessment

Physiologic And Behavioral Adaptions Of Newborn Ch 23 Test 3 Ob Flashcards Quizlet

Physical Development Human Development Matrix Jennifer Simmons

Innate Reflex Biology Britannica

The Newborn

12 Fascinating Facts About The Human Body Self Care Lov4africa
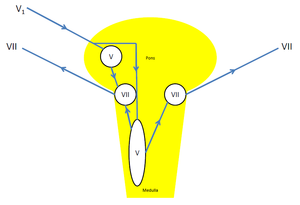
Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Know Your Baby S Newborn Reflexes Everyday Health

Blink Reflex Is Characterized By The Involuntary Blink Of Nervous System Human Anatomy



