Adenocarcinoma In Situ Cytology
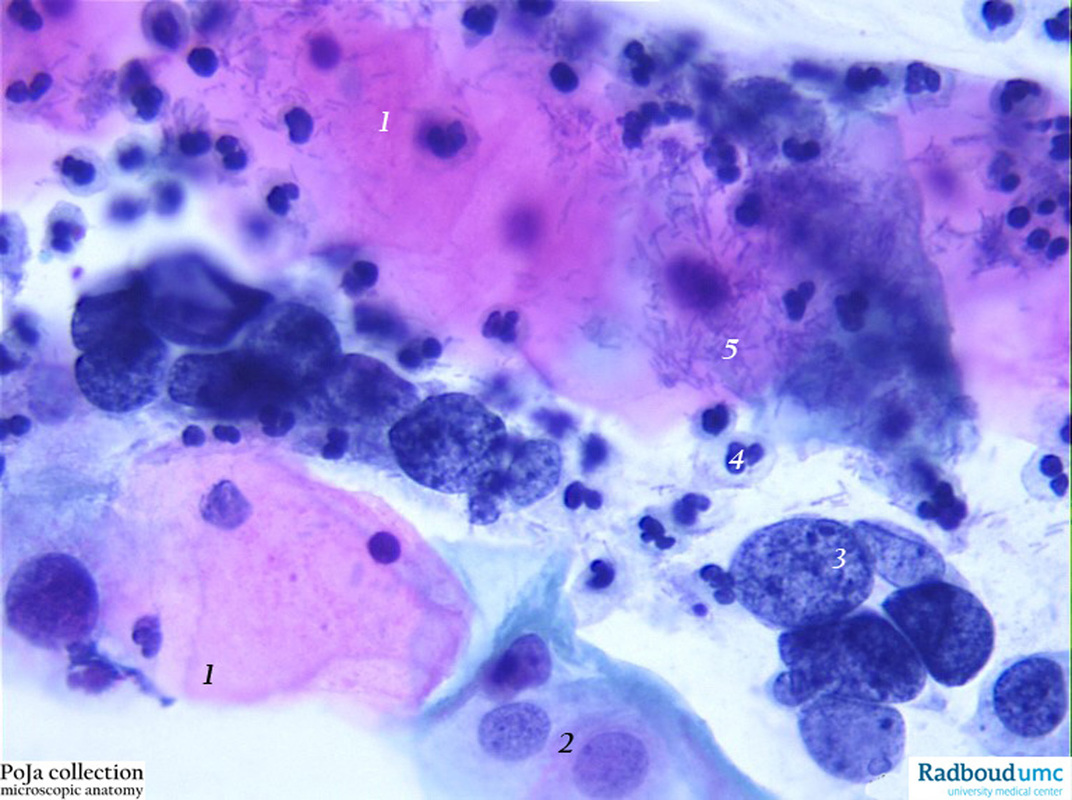
Carcinoma In Situ Cervix Cytology Human Poja Collection Microscopic Anatomy

Myoepithelial Cells In Cytology Smear Of Carcinoma In Situ May Download Scientific Diagram
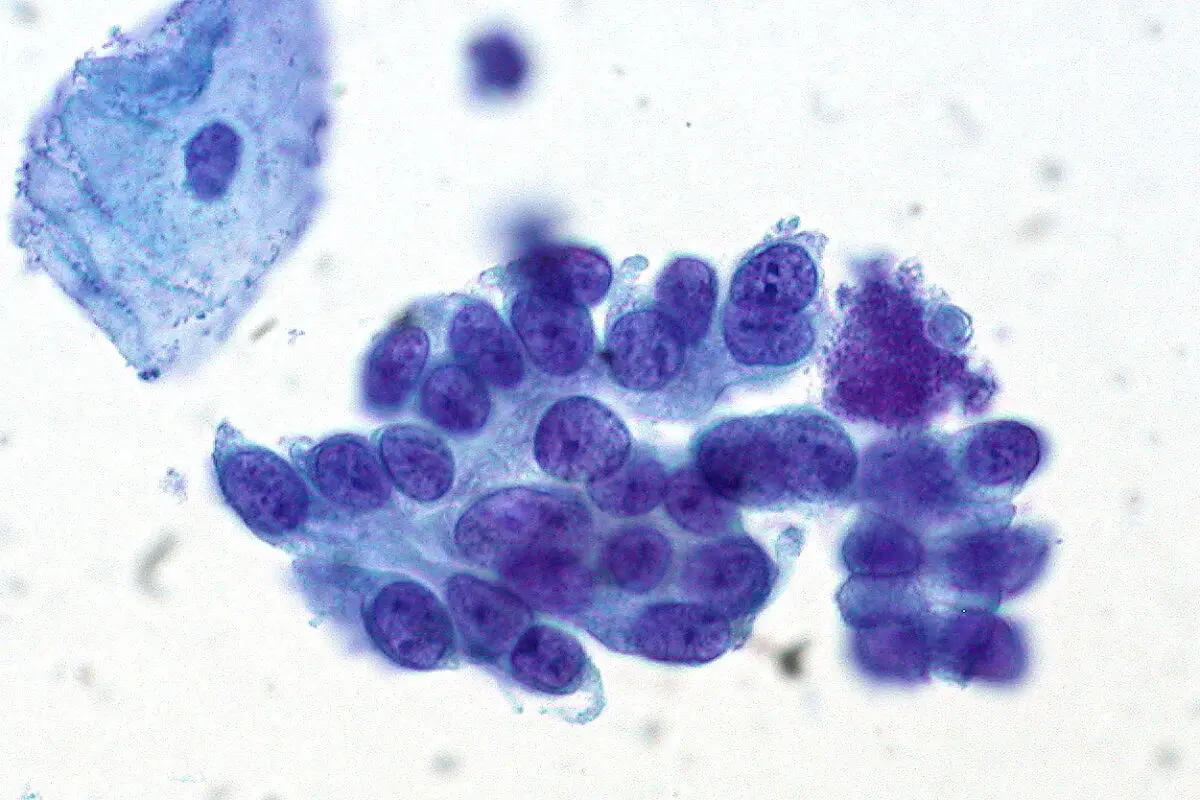
Cervical Cancer Screening Concise Medical Knowledge
Cytopathology Glowm
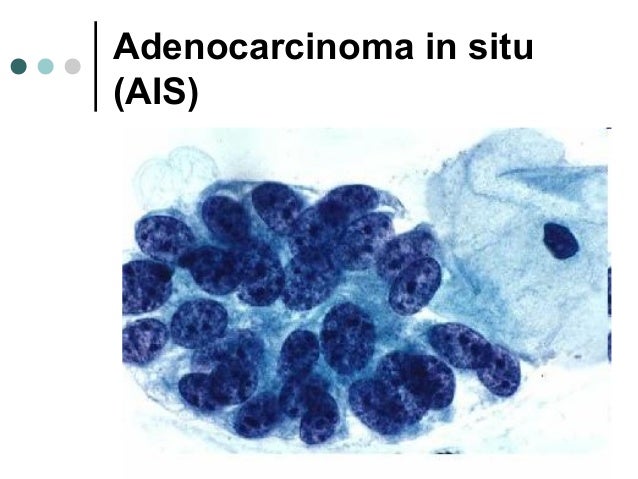
Cervix Bethesda System Abdul Quddus
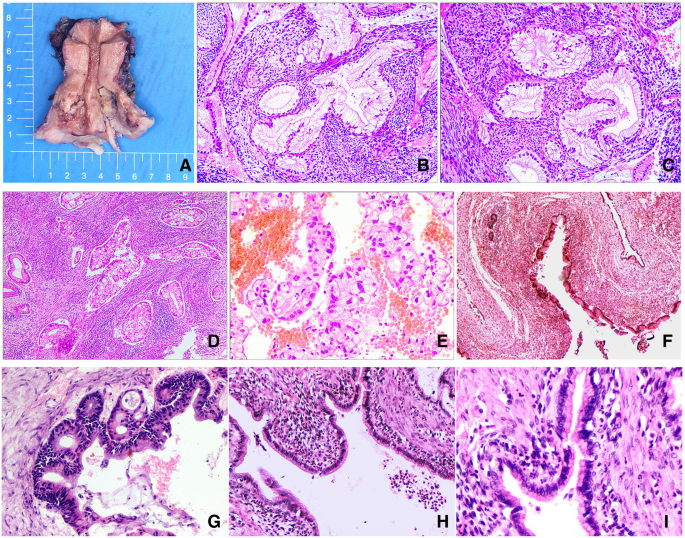
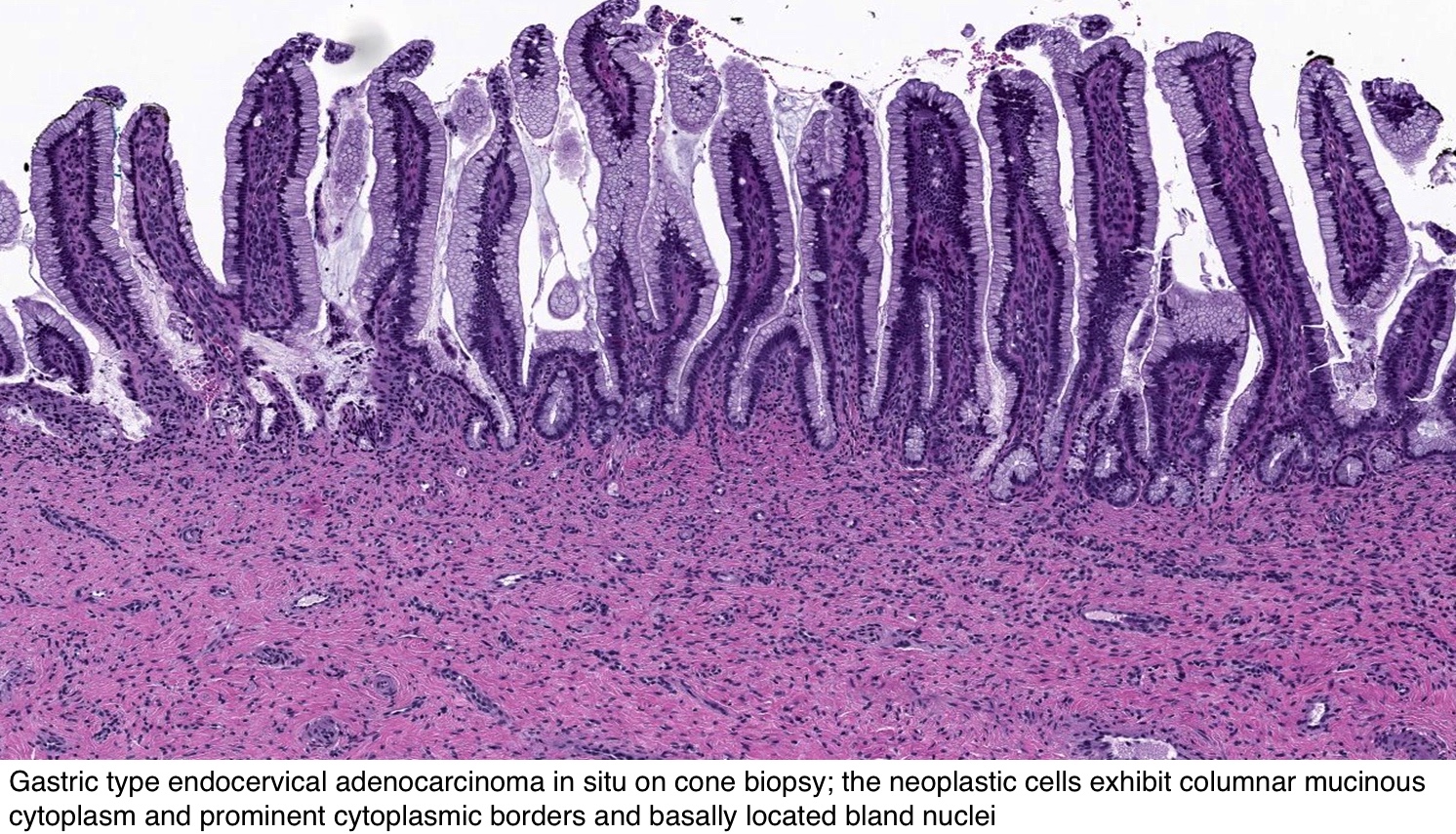
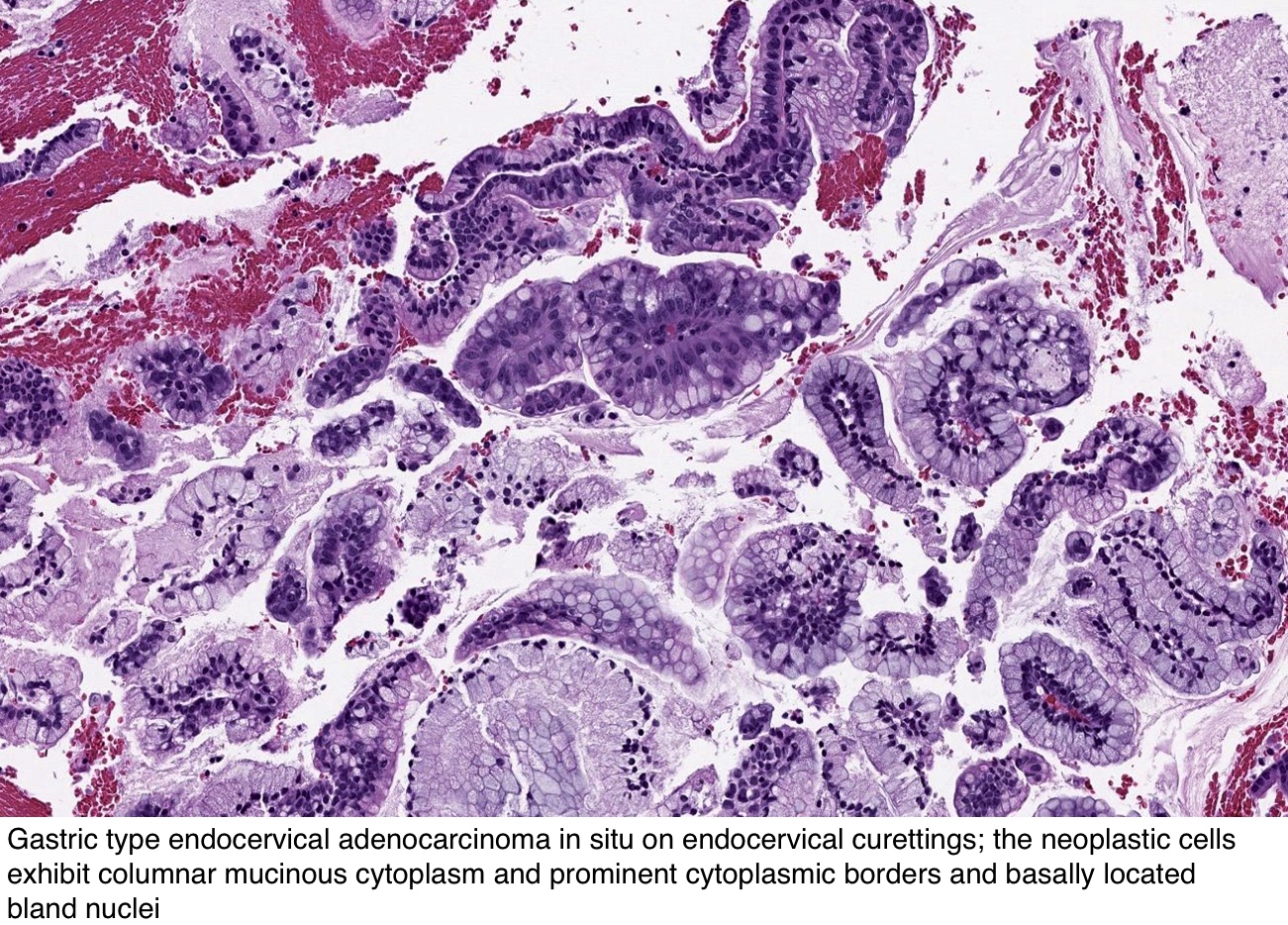
Primary Endocervical Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma A Clinicopathologic And Immunohistochemical Analysis Of 23 Cases Diagnostic Pathology Full Text
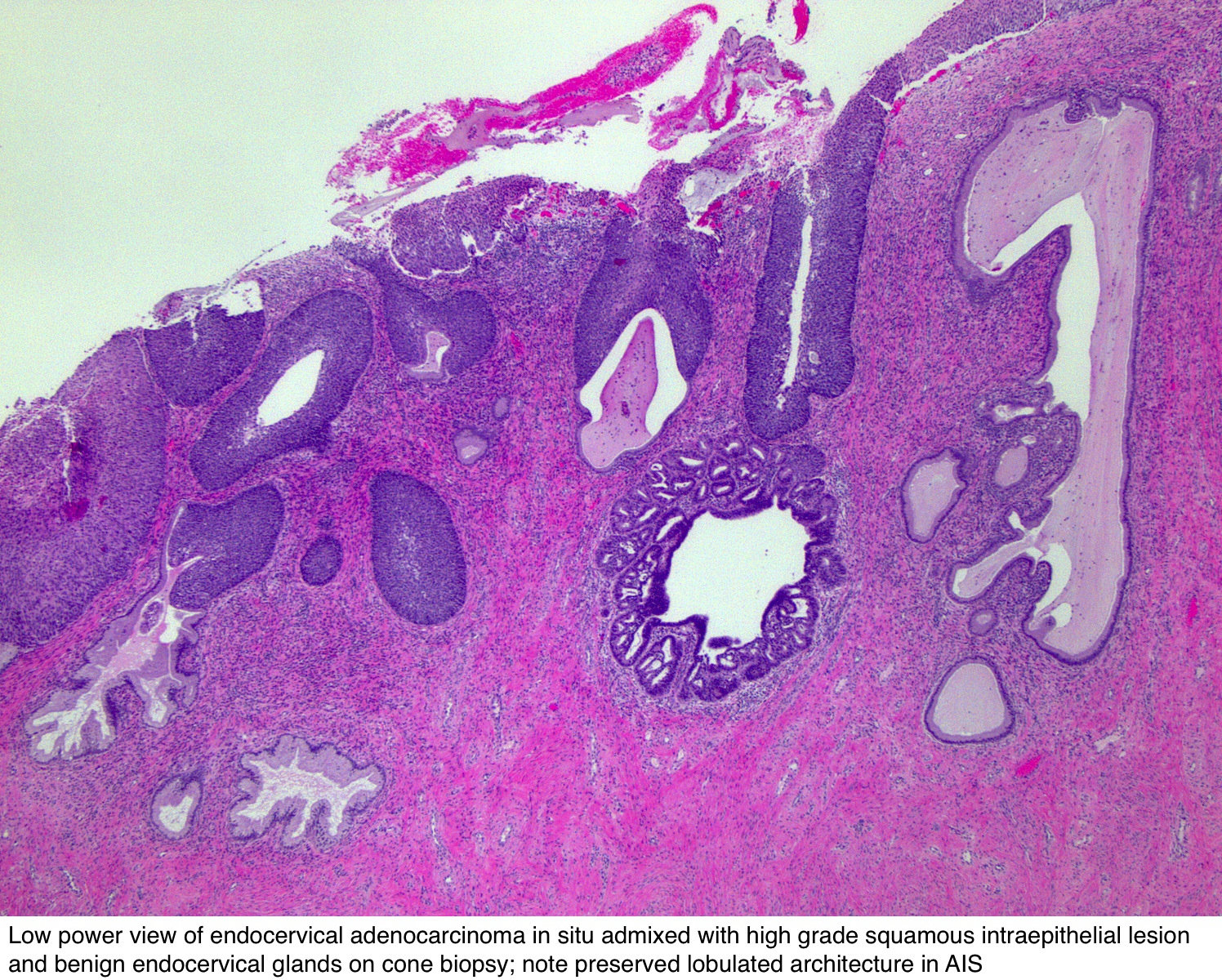
Colposcopy is less sensitive in detecting AIS and occult adenocarcinoma than CIN3;.
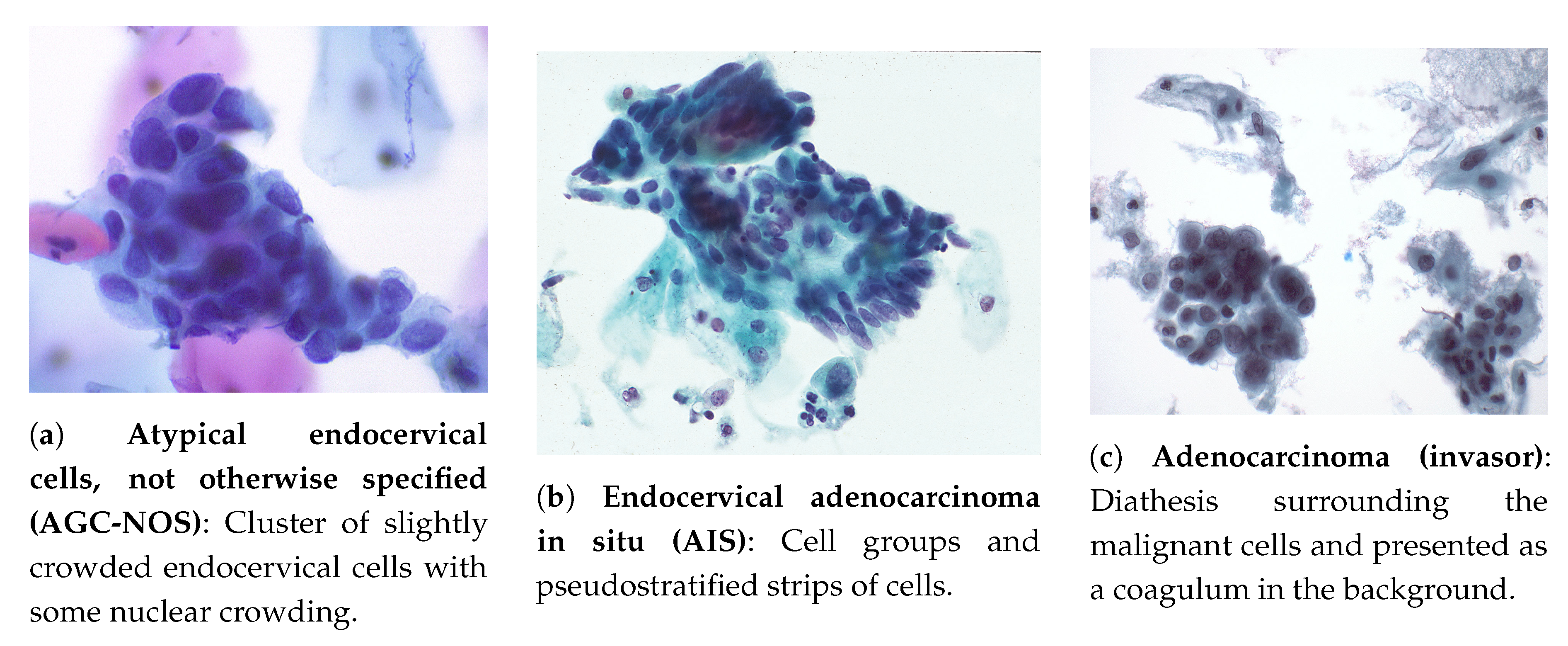
Adenocarcinoma in situ cytology. Urachus adeno carcinoma bladder;. No stromal invasion) Squamous carcinoma in situ with questionable stromal invasion () The Bethesda Cytology Reporting System This descriptive system is comprised of two groups, low grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Abstract GastricType Adenocarcinoma (GAS) is a rare and aggressive subtype of endocervical adenocarcinoma Accumulated evidence suggests that a subset of atypical Lobular Endocervical Glandular Hyperplasia (LEGH) and Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma in Situ (GAIS) may be associated with and represent precursors of GAS GAIS is rare and not yet well characterised.
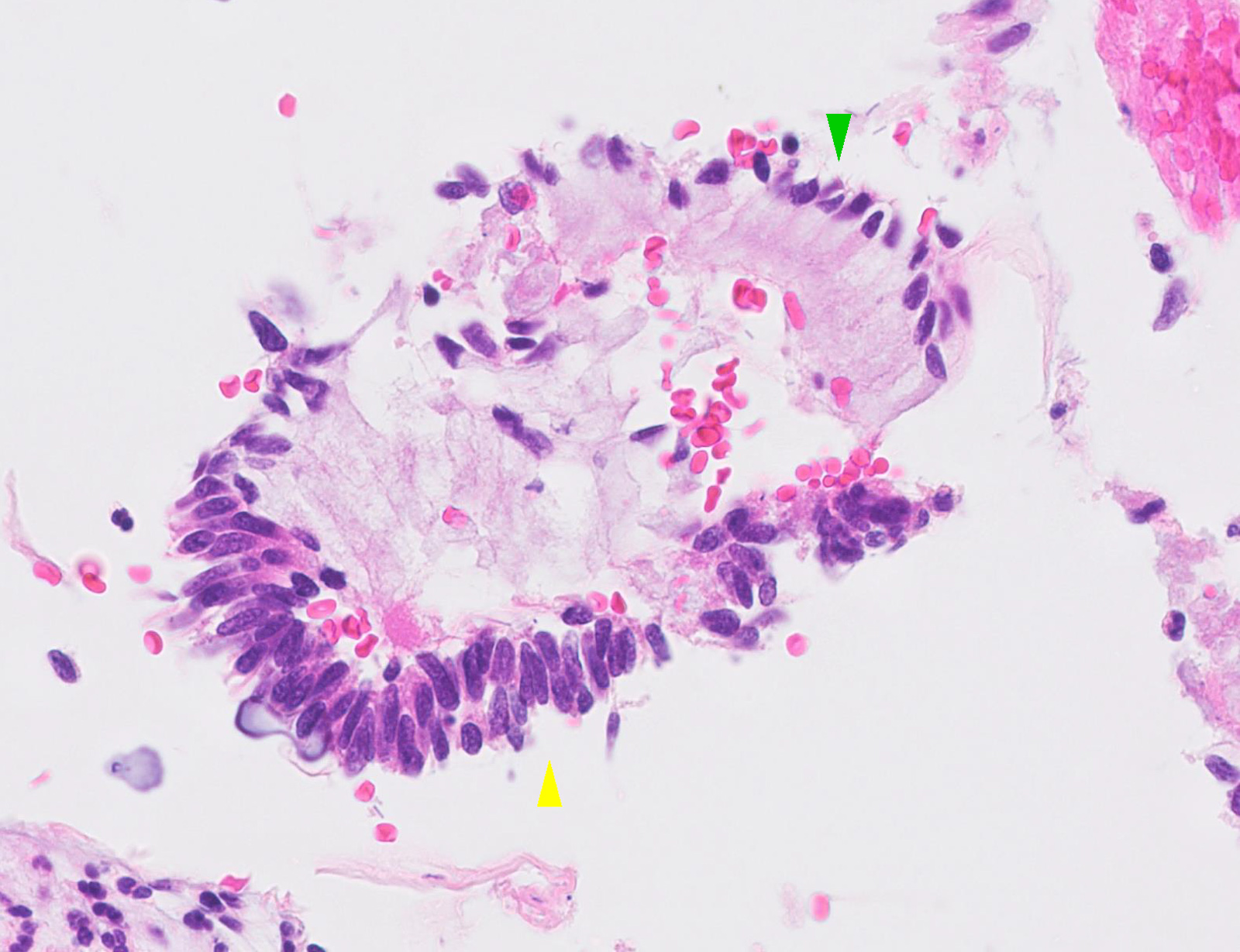
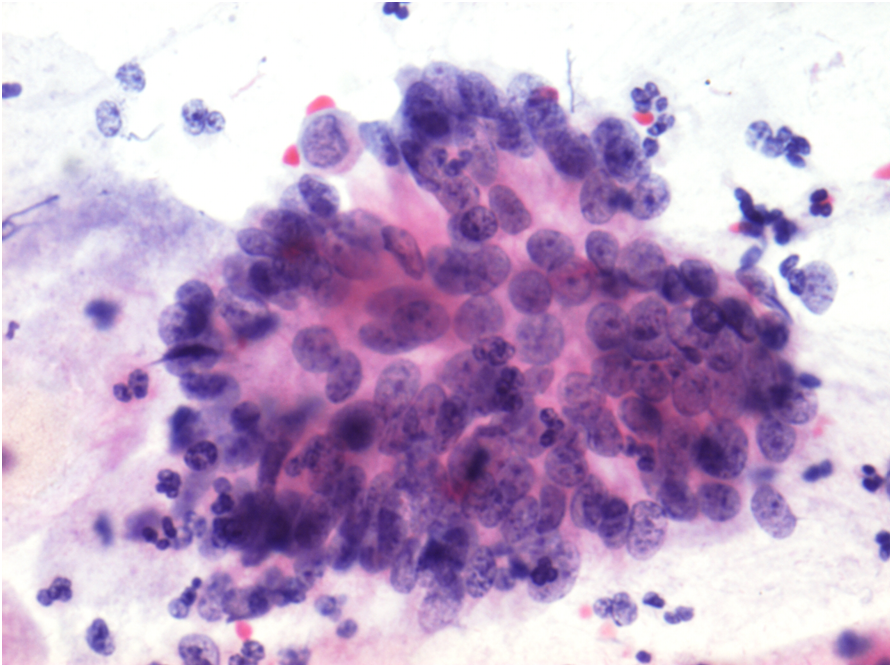
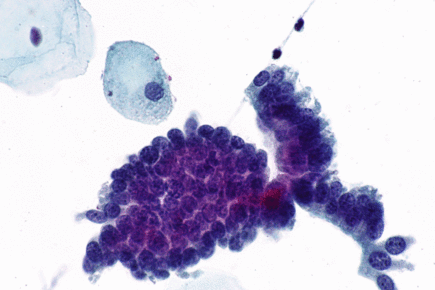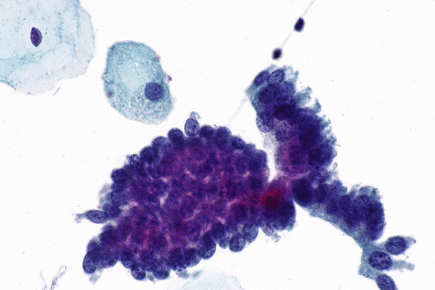
In this biopsy‐proven adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) with minimal abnormal material available on review, the review diagnosis was possible AIS A poorly preserved cellular aggregate is seen with crowding, hyperchromasia, and a poorly formed rosette in the superior portion of the aggregate Papanicolaou stain, original magnification ×400 Figure 3. Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) arises in the glandular epithelium of the uterine cervix and is the recognized precursor to invasive adenocarcinoma 1 • The incidence rate of AIS is much lower compared with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 2. And peripheral lesions Cytology can usually make the therapeutically vital distinction between small cell and nonsmall cell carcinomas There is greater difficulty in reliably distinguishing adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma, particularly when poorly differentiated The distinction.
Glandular abnormalities of the cervix remain a difficult clinical problem It is a challenge for the clinician to manage and follow this unusual cytologic finding properly This article highlights the definitions of glandular abnormalities, reviews current published guidelines for clinical management, and discusses the underlying rates of neoplasia associated with these cytology reports. Intraoperative bile cytology of the dysplasiacarcinoma in situ sequence of gallbladder carcinoma Vinod Arora T he incidence of gallbladder carcinoma varies in different parts of the world It is the most common gastrointestinal malignancy diagnosed in Northern Indian women (approximately 57/100,000 women in Delhi and Bhopal) 1 The. In situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (AIS)—previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a noninvasive growth pattern This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung If completely removed by surgery, the prognosis is excellent with up to 100% 5year survival Although the entity of.
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix is caused by infection with highrisk human papillomavirus and is the recognized precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix Because most AIS lesions are caused by HPV 16/18 infection, prophylactic HPV vaccination is an important step toward prevention of AIS, potentially reducing the incidence of invasive adenocarcinoma. The standard treatment for cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) is hysterectomy, which is a more aggressive treatment than that used for squamous intraepithelial lesions Several previous studies have primarily demonstrated that the loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is as safe and effective as cold knife cone (CKC) biopsy when AIS is unexpectedly found in a loop excision. Clinical Workshop Management Of Abnormal Cervical Cytology And Histology Workshop Title Management of Atypical Glandular Cell Cytology (AGC) and Histologic Adenocarcinoma in Situ (AIS) Presenter.
Mitchell H, Hocking J, Saville M Cervical cytology screening history of women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix a casecontrol study Acta Cytol 04;. A comparison of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy and white light cystoscopy for the detection of carcinoma in situ in patients with bladder cancer a phase III, multicenter study J Urol. Background Adenocarcinoma in situ a precursor lesion to invasive adenocarcinoma rarely produces clinical symptoms or findings on colposcopic examination, making early diagnosis difficultAlthough cytology is usually studied in patients with cervical lesions, a differential diagnosis of adenocarcinoma in situ from glandular atypia benign lesions, and invasive adenocarcinoma is also difficult.
Search term Advanced Search Citation Search Search. However, the relative proportion of glandular neoplasia has increased from 5% to 25% of all cervical cancer diagnoses in the United States during the past few decades 1 Adenocarcinoma in situ is the precursor of invasive cervical adenocarcinoma and early management will often prevent the occurrence of invasive adenocarcinoma 2 There is an interval of at least 5 years between clinically detectable AIS and invasive disease for most cases, suggesting ample opportunity for screening and. This careful large study established that cytological prediction of adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix is a very meaningful finding, with a false positive rate of only 2% ie 1 of 47 patients having adequate investigation;.
In situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (AIS)—previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinomaIt tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a noninvasive growth pattern This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution (lepidic growth) and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung. Now I have to wait until February for a scope and cytology test to see if the treatments were effective I'm hoping and praying that they work I did ask the nurse why I would pass blood after the first installation but none of the other ones and she suggested that it was probably from the insertion of the catheter and not the BCG. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix is a premalignant precursor to cervical adenocarcinoma The usual interval between clinically detectable AIS and early invasion appears to be at least five years, suggesting ample opportunity for screening and intervention 1,2.
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) TURBT proceedure indicates Invasive HighGrade Papillary Carcinoma;. Morphologic expressions of urothelial carcinoma in situ a detailed evaluation of its histologic patterns with emphasis on carcinoma in situ with microinvasion Am J Surg Pathol 01 Mar;25(3) Epstein JI Diagnosis and classification of flat, papillary, and invasive urothelial carcinoma the WHO/ISUP consensus. Adenocarcinoma is often invasive when detected by cytology.
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma should not be used in the reporting of small biopsies and cytology Tumours with a noninvasive pattern are referred to by their pattern, eg lepidic growth, not as AIS Lung, Right Upper Lobe, Core Biopsy INVASIVE ADENOCARCINOMA, NONMUCINOUS. Adenocarcinoma in situ (CGIN) summary AIS is a known precursor of the commonest type of cervical adenocarcinoma (endocervical type) AIS is far less common than CIN3;. Mitchell H, Hocking J, Saville M Cervical cytology screening history of women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix a casecontrol study Acta Cytol 04;.
Cervical cytology screening history of women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix a casecontrol study Mitchell H(1), Hocking J, Saville M Author information (1)Victorian Cervical Cytology Registry, Macfarlane Burnet Institute for Medical Research and Public Health, and Victorian Cytology Service, Melbourne, Australia. Adenocarcinoma in situ demonstrates several histological patterns papillary, glandular, cribriform, and flat Adenocarcinoma in situ can be pure or coexist with urothelial CIS or noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma In some cases, in situ adenocarcinoma is seen in association with invasive adenocarcinoma. A comparison of hexaminolevulinate fluorescence cystoscopy and white light cystoscopy for the detection of carcinoma in situ in patients with bladder cancer a phase III, multicenter study J Urol.
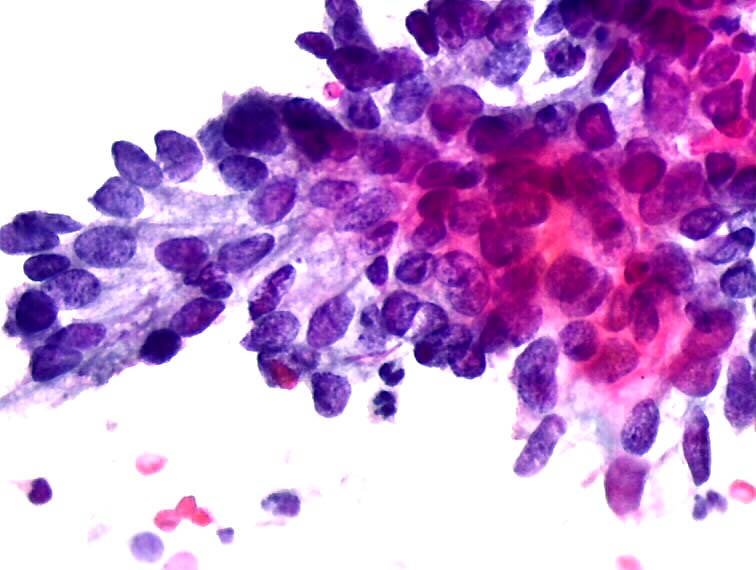
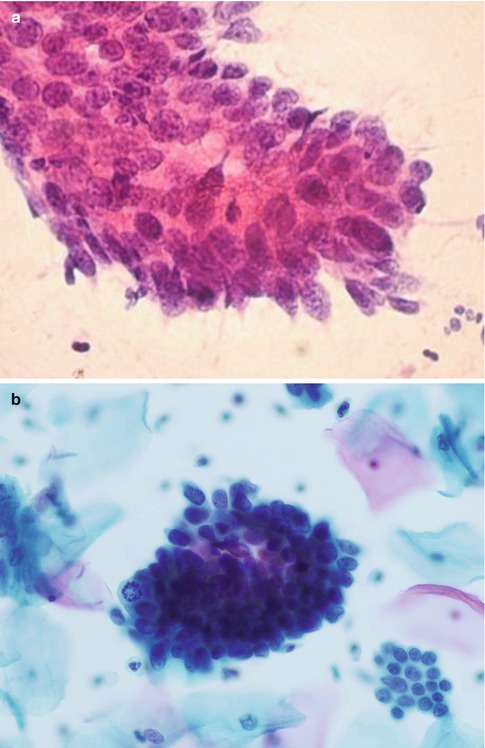
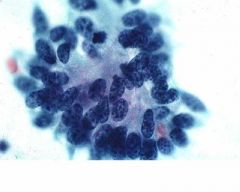
El adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) Basándose en los hallazgos citológicos, es difícil distinguir entre adenocarcinoma in situ y el adenocarcinoma invasivo bien diferenciado En AIS el epitelio endocervical normal y anormal pueden encontrarse asociados en el mismo frotis y usualmente éste es limpio. Carcinoma in situ of the pancreas with fibrosis area around the carcinoma A case report Mori, (EUSFNA), considering pancreatic cancer, mass forming pancreatitis, and a neuroendocrine tumor Cytology showed small atypical cells suspicious for neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas, therefore pancreaticoduodenectomy was performed. Cytological pictures of endocervical polymorphic adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) (a) The tissue fragments of typical endocervical AIS Dense clusters of darkly stained AIS cells in.
Adenocarcinoma in situ Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS)* represents a precancerous condition that can progress to cervical adenocarcinoma Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ occurs in the glandular tissue of the cervix and is the condition which leads to invasive adenocarcinoma 1 The average age of women who are diagnosed with cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) is 369 2. Adenocarcinoma in situ 1/2 Las muestras cervicales de un foco de AIS son frecuentemente muy celulares y contienen numerosas sábanas de células glandulares Esta apariencia en si misma es sospechosa de neoplasia glandular, a menos que la muestra haya sido tomada con un cepillo endocervical. While cytology is useful in detecting high‐grade tumours and carcinoma in situ, low‐grade tumours are often missed 24, 25 Cytology from a bladder washing has been shown to be better than that from voided urine in the detection of bladder cancer Therefore, bladder‐wash cytology, like the UroVysion assay, was used in the present analysis although there are no published studies documenting the sensitivity and specificity of the latter test with bladder washings.
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma should not be used in the reporting of small biopsies and cytology Tumours with a noninvasive pattern are referred to by their pattern, eg lepidic growth, not as AIS Lung, Right Upper Lobe, Core Biopsy INVASIVE ADENOCARCINOMA, NONMUCINOUS. • Carcinoma in situ, NOS (8010) and a specific carcinoma in situ or • Adenocarcinoma in situ, NOS (8140) and a specific adenocarcinoma in situ or Rule H10 Code the histology documented by the physician when there is no pathology/cytology specimen or the pathology/cytology report is not available. Neoplasm of the vaginal vault may occur up to 12 years after a hysterectomy for carcinomainsitu (Rutledge 1967) and most authorities therefore state that vault cytology must be continued for life (Rutledge 1967;Hall 1970;Boyes et al 1970;Kanbour et al 1974 Gallup & Morley 1974 Kolstad & Klem 1976 Lee & Symonds 1976Payne & Mookgaoker 1981;Stuart el al 1981).
It is a common type of lung cancer and its incidence is increasing, particularly in women Adenocarcinoma is the one cell type of primary lung tumor that occurs more often in nonsmokers and in smokers who have quit Most adenocarcinomas arise in the periphery of the lung Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is considered as a variant of adenocarcinoma. Rate of cervical cancer, severe intraepithelial neoplasia, and adenocarcinoma in situ in primary HPV DNA screening with cytology triage randomised study within organised screening programme Anttila A(1), KotaniemiTalonen L, Leinonen M, Hakama M, Laurila P, Tarkkanen J, Malila N, Nieminen P. Retrospective analysis of women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma in situ and their management between 1992 and 10 retrieved from the Victorian Cervical Cytology Registry, Australia Failure of conservative treatment is defined by histologically proven adenocarcinoma in situ or adenocarcinoma at follow‐up after negative excisional margins.
Report says high grade in situ urothelial carcinoma;. Rate of cervical cancer, severe intraepithelial neoplasia, and adenocarcinoma in situ in primary HPV DNA screening with cytology triage randomised study within organised screening programme Bmj , 340 , c1804. Gadducci A, Guerrieri ME, Cosio S Adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix Pathologic features, treatment options, clinical outcome and prognostic variables.
The patients with negative ECCs above the cone regardless of margin status had residual disease in 58% of treated specimens Conclusion Women with adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine cervix had residual disease in 31% of cases with negative margins in cone biopsies and/or with negative ECCs and in 56% of cases with positive endocervical margins. Rate of cervical cancer, severe intraepithelial neoplasia, and adenocarcinoma in situ in primary HPV DNA screening with cytology triage randomised study within organised screening programme Bmj , 340 , c1804. The main factors contributing to screening or diagnostic errors in the detection or diagnosis of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix in Papanicolaou smears were minimal, poorly preserv.
Distinguishing between urothelial carcinoma in situ (CIS) and reactive cellular atypia in bladder specimens can prove challenging 1, 2, requiring careful correlation with clinical and cytologic features 3, 4Though recent studies have shown the overexpression of cytokeratin (CK), p53 and even alphamethylacylCoA racemase (AMACR) in CIS 5,6,7, few studies have evaluated each marker. Cytopathologists and histopathologists are involved in the diagnosis of endocervical adenocarcinoma (EAC) and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) The main objective of cytology is screening for and identifying squamous intraepithelial lesions (SILs). For the cytology see Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (cytology) Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, also adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine endocervix, is preinvasive change of the uterine endocervix It is closely tied to HPV infection If the context is clear, it may be referred to as adenocarcinoma in situ, abbreviated AIS.
Cervical cytology screening history of women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix a casecontrol study Mitchell H(1), Hocking J, Saville M Author information (1)Victorian Cervical Cytology Registry, Macfarlane Burnet Institute for Medical Research and Public Health, and Victorian Cytology Service, Melbourne, Australia. Nour Sneige, Gary Tse, Puay Hoon Tan, Fernando Schmitt, Gary Tse, Puay Hoon Tan, Fernando Schmitt, Cytology of Epithelial Proliferative Lesions and HighGrade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ, Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Breast, /, (102), (13). Cytology is less likely to detect AIS than CIN3;.
Adenocarcinoma can arise from the endocervix, endometrium and extrauterine sites AGC AGC, formerly AGUS, is an acronym for atypical glandular cells of undetermined significance Renamed AGC to avoid confusion with ASCUS The management of AGC is colposcopy with or without an endometrial biopsy Thyroid nodules. The other 46 patients having in situ (28) or invasive (18) carcinomas. Squamous carcinoma in situ (;.
Search term Advanced Search Citation Search Search. They are often arranged in thick groups Keratinization is rare or absent. Postive Urine Cytology, No Carcinoma from TURBT.
Flow chart of 74 pathologicallyconfirmed adenocarcinoma in situ cases before and after a cytological review The left column shows the distribution of the initial cytological diagnoses, and the. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ is the precancer that can become invasive squamous cell carcinoma (a type of nonsmall cell lung cancer) Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is the precancer that can become adenocarcinoma (another type of nonsmall cell lung cancer) If either of these is present in a biopsy, it may mean that there is invasive. Most cases of CIS are diagnosed by pancreatic juice cytology, and the motives for such tests are promoted by secondary changes, such as retention cysts, main pancreatic duct stenosis, and.
For detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization, these values were 600%, 840%, 938. Gadducci A, Guerrieri ME, Cosio S Adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix Pathologic features, treatment options, clinical outcome and prognostic variables. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix is a premalignant precursor to cervical adenocarcinoma The usual interval between clinically detectable AIS and early invasion appears to be at least five years, suggesting ample opportunity for screening and intervention 1,2.
The entity of adenosquamous carcinoma in situ described by Steiner and Friedell 155 closely resembles squamous cell carcinoma in situ Intermixed with the dysplastic squamous cells, however, are cells with vacuolated or basophilic cytoplasm Mucicarmine and periodic acidSchiff (PAS) stains reveal mucin production in these cells. Adenocarcinoma In Situ (AIS) of Cervix is a smallsized, localized, premalignant adenocarcinoma, observed in the uterine cervix, which is the lower portion of the womb AIS of Cervix only affects women It may be described as an epithelial lesion and carries a very highrisk for invasive carcinoma, if left untreated. The cells of moderately or poorly differentiated tumors show larger nuclei with coarse and granular chromatin texture and cyanophilic cytoplasm (with Papanicolaou stains);.
Adeno carcinoma in bladder (urachus cancer) Hematuria and Atypical Urothelial Cells from Ureter and Bladder Washings;. Adenocarcinoma in situ 30 mm in size, atypical type II pneumocytes, purely lepidic type, non invasive (Diagn Interv Imaging 16;) Adenoid cystic carcinoma cribriform architecture and pseudocysts, PAS positive. Seventyfive highgrade urothelial carcinomas (HGUCs), 10 lowgrade urothelial carcinomas, and five other conditions were enrolled Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for HGUC detection by urinary cytology were 280%, 1000%, 1000%, and 316%, respectively;.
For the cytology see Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (cytology) Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, also adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine endocervix, is preinvasive change of the uterine endocervixIt is closely tied to HPV infection If the context is clear, it may be referred to as adenocarcinoma in situ, abbreviated AIS. A comparison of cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of urothelial carcinoma J Urol, 164 (00), pp Article Download PDF View Record in Scopus Google Scholar.

Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Wikipedia

Cytologic Features Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ In Fine Needle Aspiration Of The Breast Mirror The Histopathologic Growth Pattern Heterogeneity And Grading Sauer 05 Cancer Cytopathology Wiley Online Library
Www Nature Com Articles Modpathol Pdf Origin Ppub
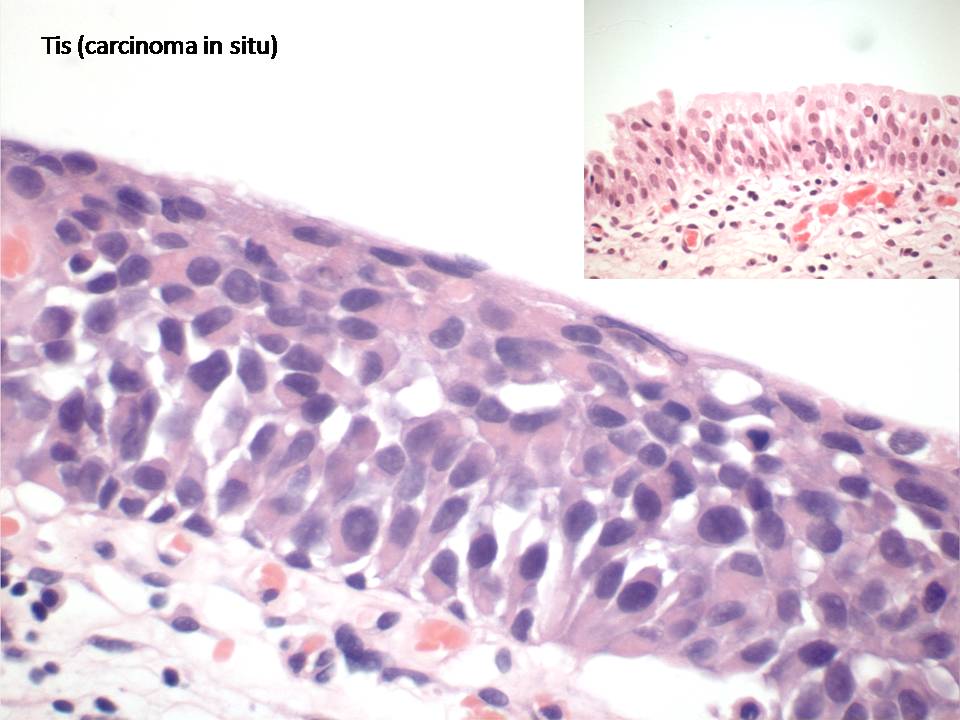
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

J C Prolla Cytology Uterine Cervix Adenocarcinoma In Situ Endocervix

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Cervix
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
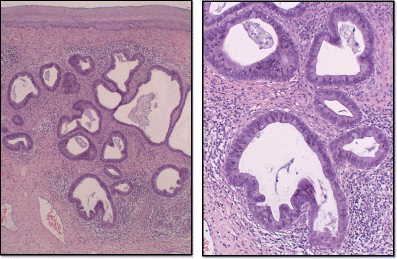
Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Update And Management Springerlink
3
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Carcinoma Wikipedia
Histopathology And Cytopathology Of The Uterine Cervix Digital Atlas Glossary
3
Cervical Cancer Rates Higher In Poorer Areas Science News Naked Scientists

Can True Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast And Their Mimickers Be Accurately Classified By Cytology Michael 02 Cancer Cytopathology Wiley Online Library

Tubal Metaplasia Can Closely Mimic Adenocarcinoma In Situ However On Download Scientific Diagram
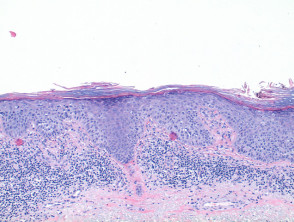
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Pathology Dermnet Nz

23 Cytology 2 Vaginal Smear Cytology Carcinoma In Situ Pathology Core Pictures
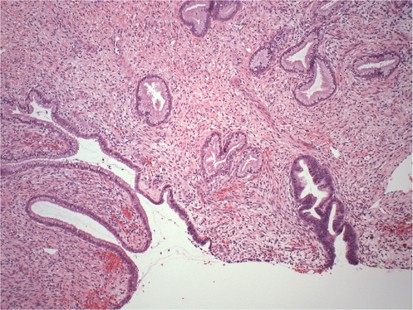
Practical Issues Related To Uterine Pathology In Situ And Invasive Cervical Glandular Lesions And Their Benign Mimics Emphasis On Cytology Histology Correlation And Interpretive Pitfalls Modern Pathology
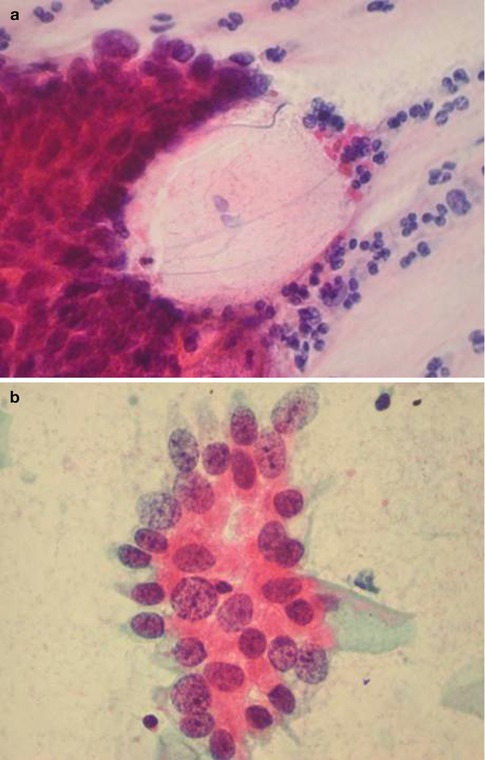
Cytology Of Glandular Lesions Basicmedical Key

Severe Squamous Dysplasia Or Carcinoma In Situ Causing Laryngeal Leukoplakia Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
Http Www Jpatholtm Org Upload Pdf Kjp 45 1 79 Pdf

Figure 2 From Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Uterine Cervix Cytological And Histopathological Features Of Two Cases Semantic Scholar

J C Prolla Cytopathology Urine Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ
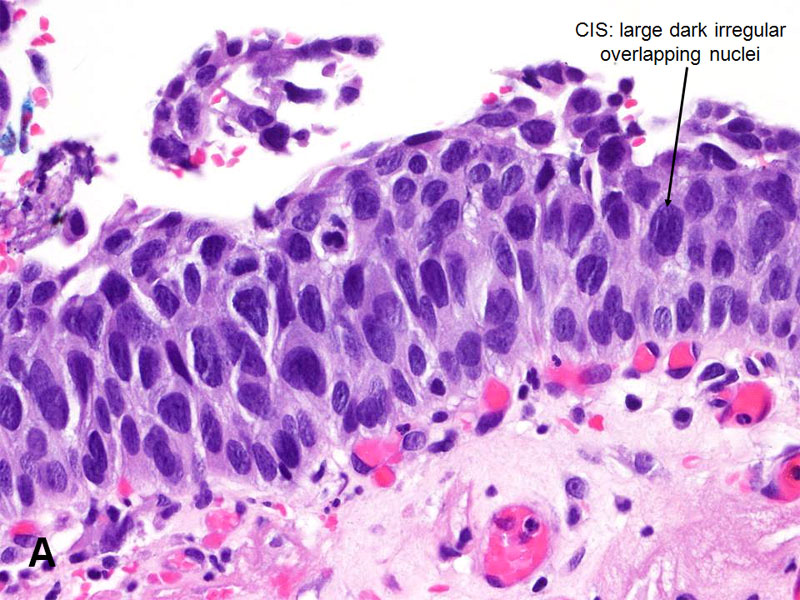
Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ American Urological Association

Cervical Cancer Incidence After Normal Cytological Sample In Routine Screening Using Surepath Thinprep And Conventional Cytology Population Based Study The Bmj
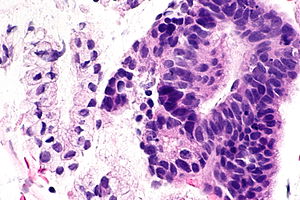
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Libre Pathology

J C Prolla Cytology Uterine Cervix Adenocarcinoma In Situ Endocervix
Adenocarcinoma Wikipedia

Pap Smear Cytology Blog Site
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Springerlink
Q Tbn And9gcs0mpzcrzmzuevemuk3bild Ckhdve8b Fwneejlq55jhc6uyxo Usqp Cau

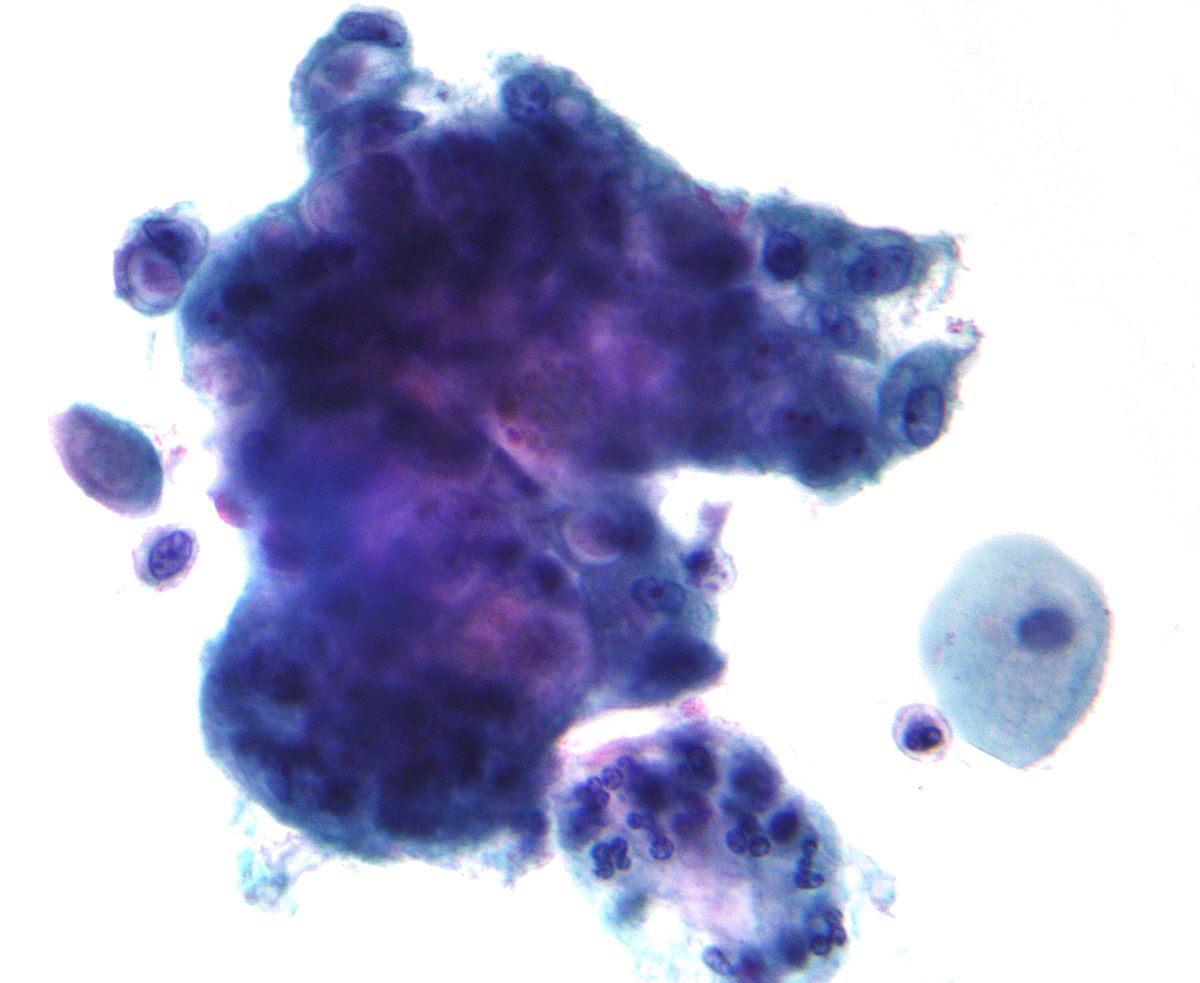
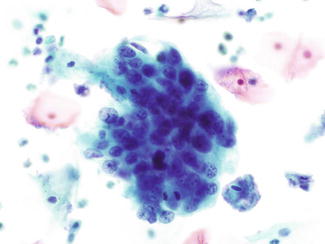
Lara Pijuan Md Phd Dr David Wilbur Talking About Glandular Lesions In Cytopathcoursehmar Nice Pictures Of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ In Cytology As A Example T Co Remyqwcsea
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Secondary Prevention Of Cervical Cancer
Glandular Abnormalities Of The Cervix Eurocytology
Adenocarcinoma And Related Tumors Of The Uterine Cervix Basicmedical Key

Figure 1 From Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Uterine Cervix Cytological And Histopathological Features Of Two Cases Semantic Scholar
Ijms Free Full Text A Review Of Computational Methods For Cervical Cells Segmentation And Abnormality Classification Html

Bladder Cancer Cancer Therapy Advisor
Cytology Of Glandular Lesions Basicmedical Key

Cytology Of Endocervical Glandular Neoplasia Obgyn Key

Cytologic Features Of Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia Alh And Lobular Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www Britishcytology Org Uk Resources Glandular Lesions Conventional And Liquid Based Gynaecological Prep Nayar Wilbur Russell Pdf
Www Mathewsopenaccess Com Scholarly Articles The Cytomorphological Spectrum Of Papillary Lesions In The Breast Pdf
Quiz Pap Test 2 Libre Pathology
Cytopathology Gyn Flashcards Cram Com
Academic Oup Com Ajcp Article Pdf 122 1 44 Ajcpath122 0044 Pdf

The New Iaslc Ats Ers Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification From A Clinical Perspective Current Concepts And Future Prospects Zugazagoitia Journal Of Thoracic Disease
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Springerlink
Academic Oup Com Ajcp Article Pdf 122 1 44 Ajcpath122 0044 Pdf
Acsjournals Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdfdirect 10 1002 Cncr 735
Www Nature Com Articles Modpathol Pdf Origin Ppub

Adenocarcinoma And Adenocarcinoma In Situ Eurocytology

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais Of The Cervix Mypathologyreport Ca

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Adenocarcinoma Of Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma An Overview
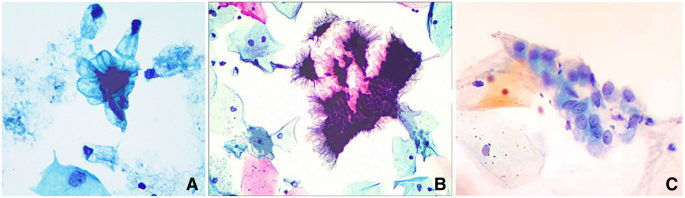
Primary Endocervical Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma A Clinicopathologic And Immunohistochemical Analysis Of 23 Cases Diagnostic Pathology Full Text

Secondary Prevention Of Cervical Cancer

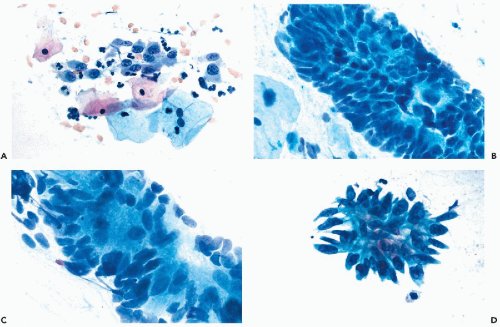
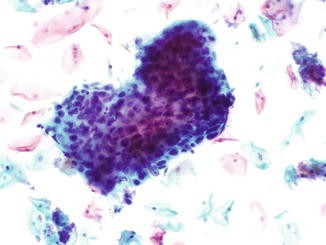
Typical Cytological Features Of Adenocarcinoma In Situ A Download Scientific Diagram
3
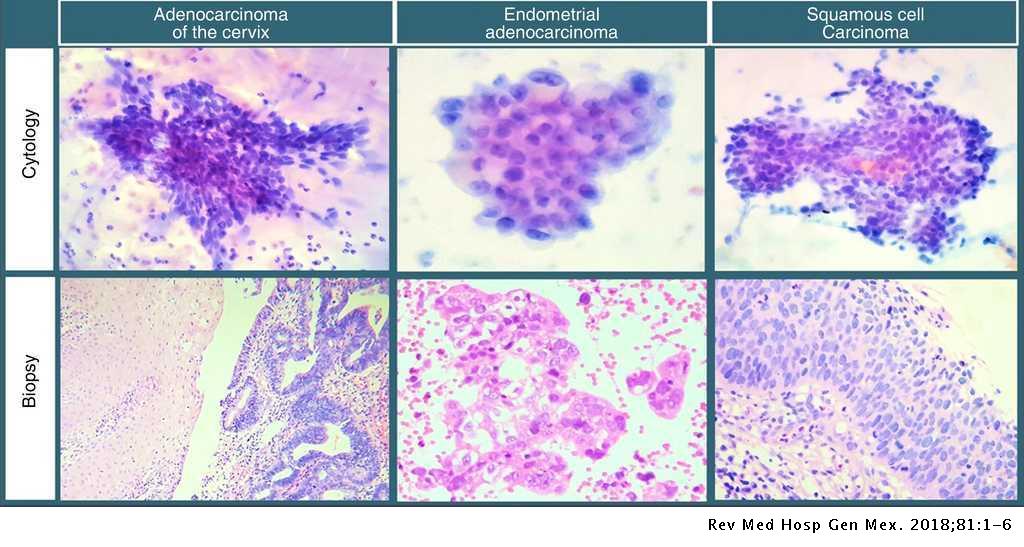
Cytological Diagnosis Of Cervical Adenocarcinoma And Cytohistological Agreement At General Hospital Of Mexico Dr Eduardo Liceaga Revista Medica Del Hospital General De Mexico
Academic Oup Com Ajcp Article Pdf 122 1 44 Ajcpath122 0044 Pdf

Adenocarcinoma And Adenocarcinoma In Situ Eurocytology
Www Karger Com Article Pdf

The Changing Incidence Of Carcinoma In Situ Of The Bladder Worldwide Intechopen

Oncocytologic Investigation And Interpretation
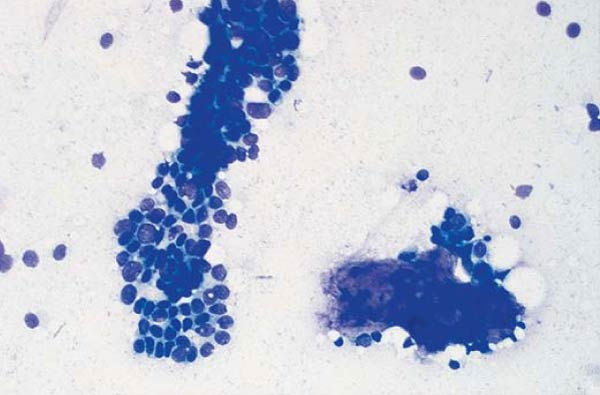
Women S Health And Education Center Whec Pathology Of Breast Cancer
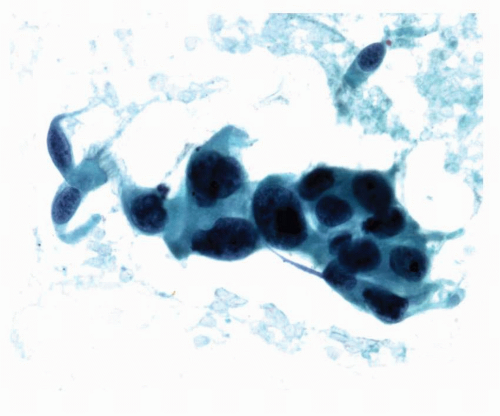
Large Cell Carcinoma Oncohema Key

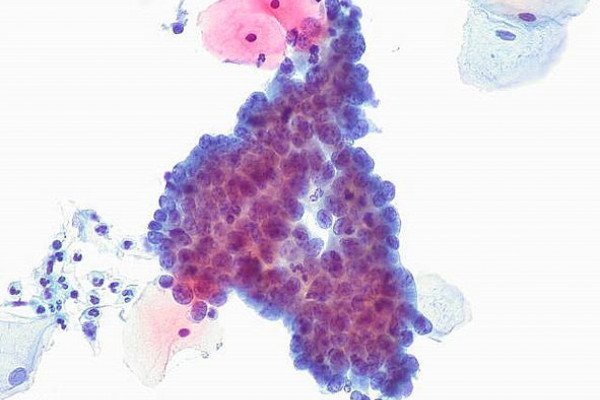
Pdf Cytological Variations And Typical Diagnostic Features Of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ A Retrospective Study Of 74 Cases

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
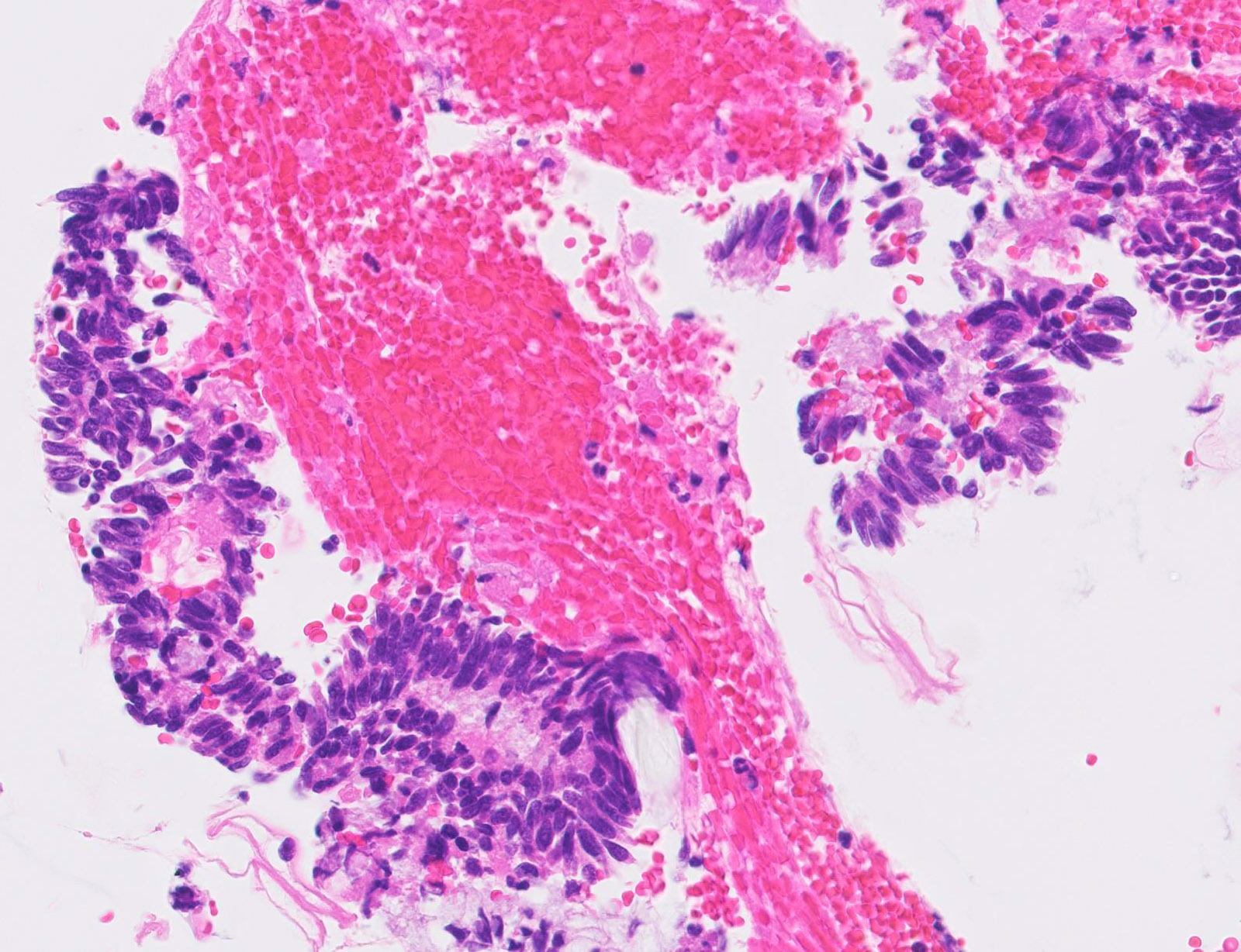
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

The Pivotal Role Of Pathology In The Management Of Lung Cancer Davidson Journal Of Thoracic Disease
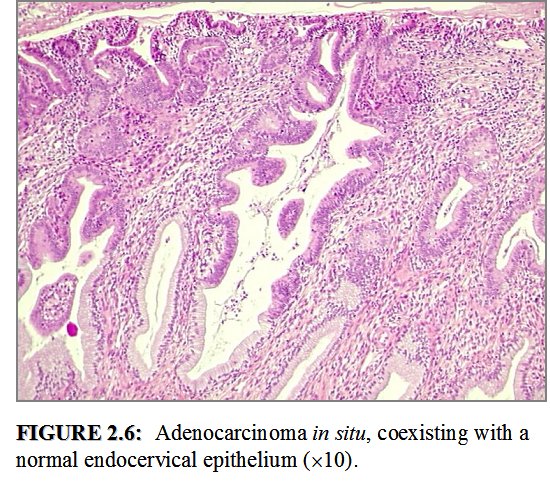
Colposcopy And Treatment Of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia A Beginners Manual
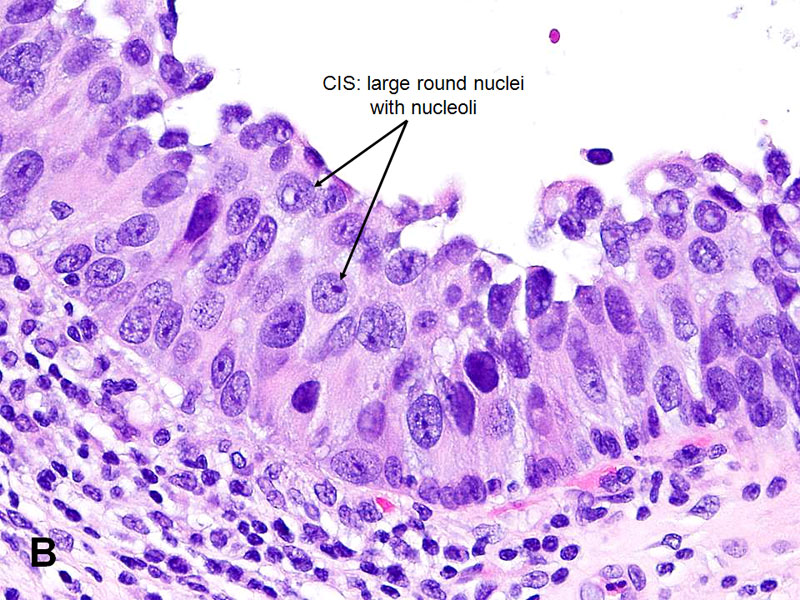
Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ American Urological Association
Cytopathology Glowm
Cytopathology Basicmedical Key

Severe Squamous Dysplasia Or Carcinoma In Situ Causing Laryngeal Leukoplakia Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Reducing Cervical Cancer Clinical Lab Product

Adenocarcinoma And Adenocarcinoma In Situ Eurocytology
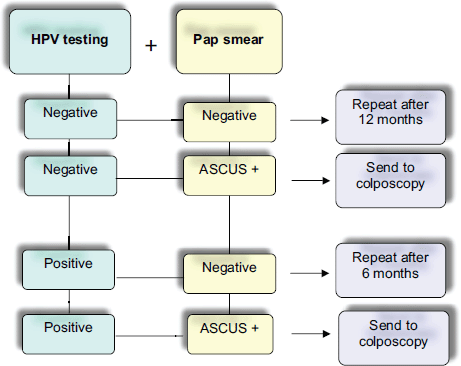
Performance Of Hpv Dna Testing In The Follow Up After Treatment Of High Grade Cervical Lesions Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais And Microinvasive Carcinoma Ecanc

8 Cytopathology Cells Ideas The Incredibles Pathology Science And Nature
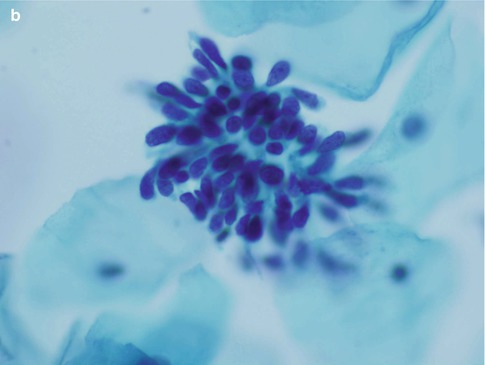
Cytology Of Glandular Lesions Basicmedical Key

8 Cytopathology Cells Ideas The Incredibles Pathology Science And Nature

Adenocarcinoma Eurocytology
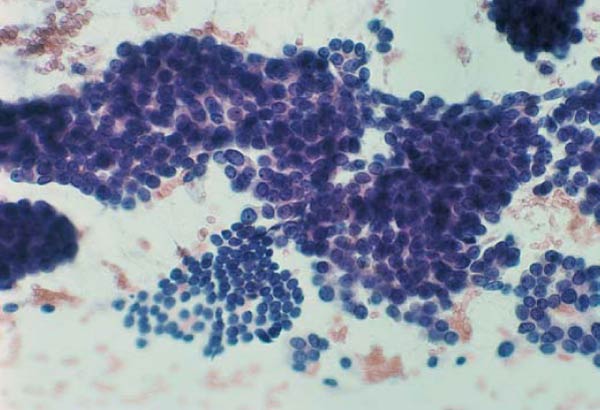
Women S Health And Education Center Whec Gynecologic Pathology And Cytopathology Pathology Of Breast Cancer

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Welcome Glandular Workshop 29 Th May Glandular Cytology In The Surepath Liquid Based Pap Test Advanced Customer Training And Education Diagnostics Ppt Download
Www Anzgog Org Au Wp Content Uploads 19 05 Paul Cohen 1 Pdf
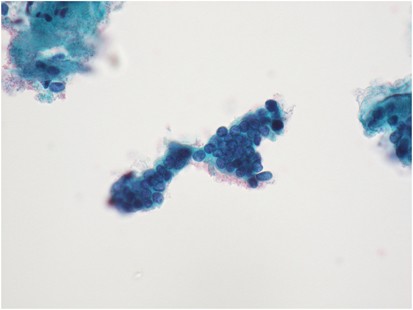
Practical Issues Related To Uterine Pathology In Situ And Invasive Cervical Glandular Lesions And Their Benign Mimics Emphasis On Cytology Histology Correlation And Interpretive Pitfalls Modern Pathology
Http Www Jpatholtm Org Upload Pdf Kjp 45 1 79 Pdf
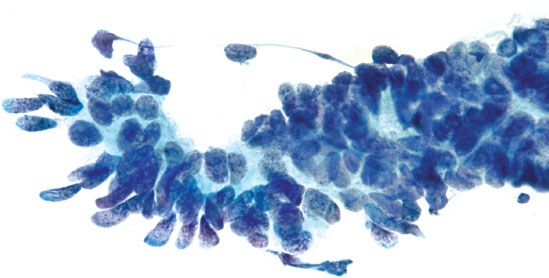
Pathology Oncohema Key
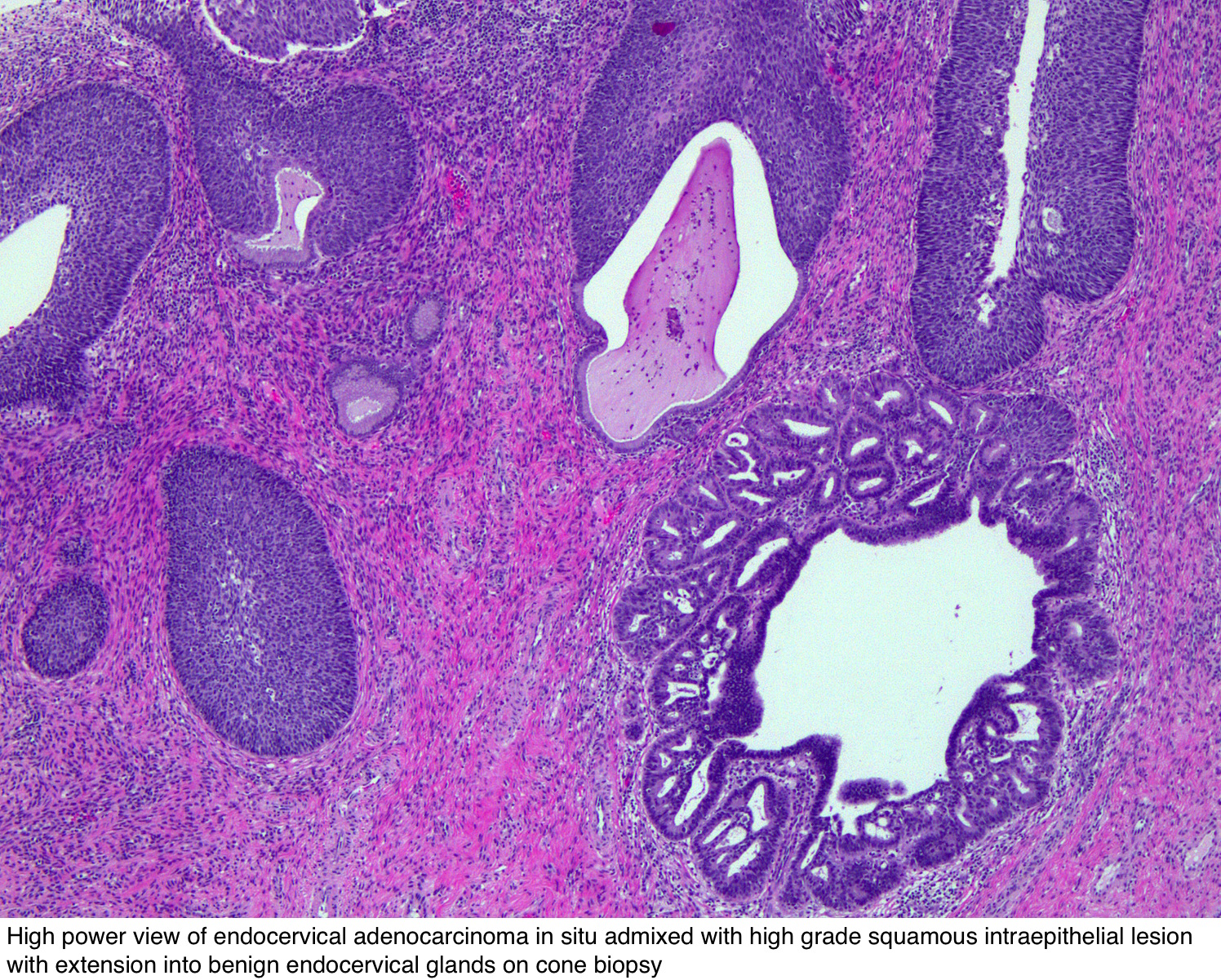
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Anatomia Patologica Histologia Hematologia

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Secondary Prevention Of Cervical Cancer

Bladder Cancer Cancer Therapy Advisor



