Ifrs 9
Www Ifrs Org Media Feature Meetings 19 June Iasb Ap30c Smes Review Pdf

A New Beginning A Regulatory Change Are You Ready For Ifrs 9 Glc Europe
Help Sap Com Doc Ff1bcaed2fbe2c3771a76 10 1 4 En Us Ifrs9 Analysis Pdf

Ifrs Webinar Series Ifrs 9 Problem Areas Youtube

Ifrs 9 Three Critical Areas Of Focus For Collections

What You Need To Know About Ifrs 9 Opus Kinetic
Financial asset impairment calculated on an expected loss basis, some easing of hedge accounting rules, and fewer categories for assets Banks and other financial institutions are most affected IFRS 9 is mandatory for financial periods beginning on or after 1 January, 18.

Ifrs 9. Under IFRS 9, subsequent to initial recognition, an entity classifies its financial assets as measured at amortized cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI) and fair value through profit or loss (FVTPL) depending on the (a) the entity’s business model for managing the assets, and (b) the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial assets. Ifrs 9 447 (ךשמה) םי יי ע ןכות ףיעסמ לחה הדעווה לש 9 רפסמ תו שרפ לש לוטיב 73 9 ) ימואל יב יפסכ חוויד לש תויו שרפל 9 ימואל יב יפסכ חוויד ןקת לש ,(ifric( 10 ) 9 ימואל יב יפסכ חוויד ןקת לש ,( 09 ). Learning Objectives This course is beneficial to preparers and users of IFRS financial statements The participants will analyse the principles in IFRS 9 Analyse financial instruments to differentiate between liabilities, equity, or a combination of both.
IFRS 9, disclose for each class of financial instrument − the amount that best represents the entity’s maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date, without taking account of any collateral held or other credit enhancements;. Under IFRS 9, the ‘Coffee C ICE future’ can be separately identified as a contractually specified component of the pricing contract, meaning that Entity A can designate the ‘Coffee C ICE futures’ component of the contract price as a hedged. Definition IFRS 9 is a financial reporting standard developed and approved by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), an independent, privatesector body that develops and approves International Financial Reporting Standards IFRS 9 concerns the accounting and reporting specifically of financial instruments.
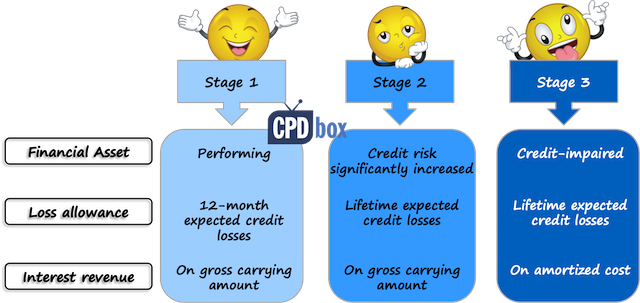
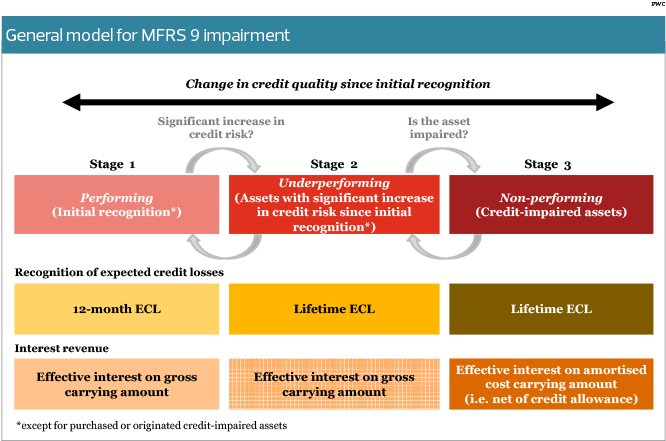
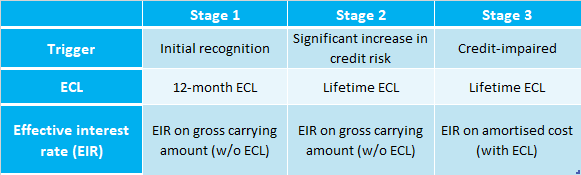
MFRS 9 / IFRS 9 Incurred Loss Model Expected Credit Loss (ECL) Model 12month ECL ECL features Forwardlooking, time element Also sensitive to economic cycle 1 Measurement of ECL reflects a probabilityweighted outcome Time value of money Best available forwardlooking information (eg oil price, purchasing power index, GDP). IFRS 9 allows an alternative of designating full or the intrinsic value of an option as a hedging instrument (IFRS 9624(a)) Time value of an option is often the only composite of a premium paid and is considered by risk managers as a cost of hedging (IFRS 9BC6387). − except for lease receivables, a narrative description of collateral held as.
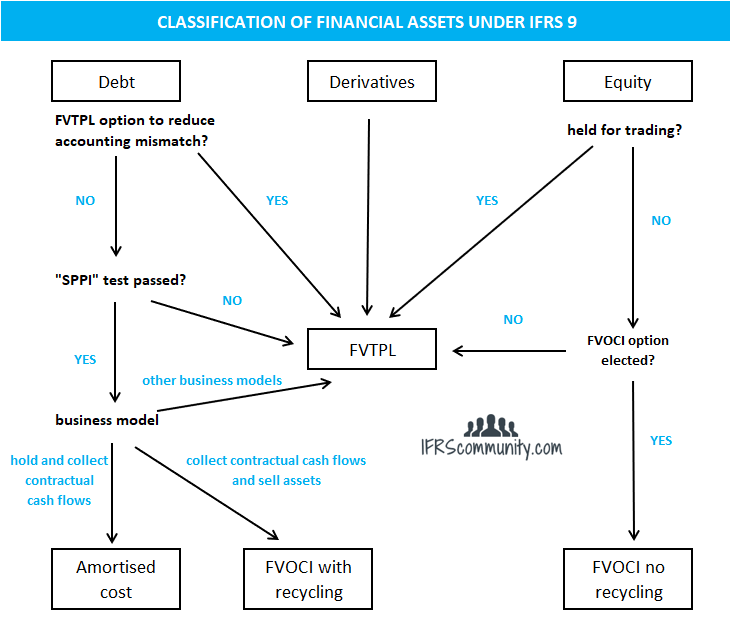
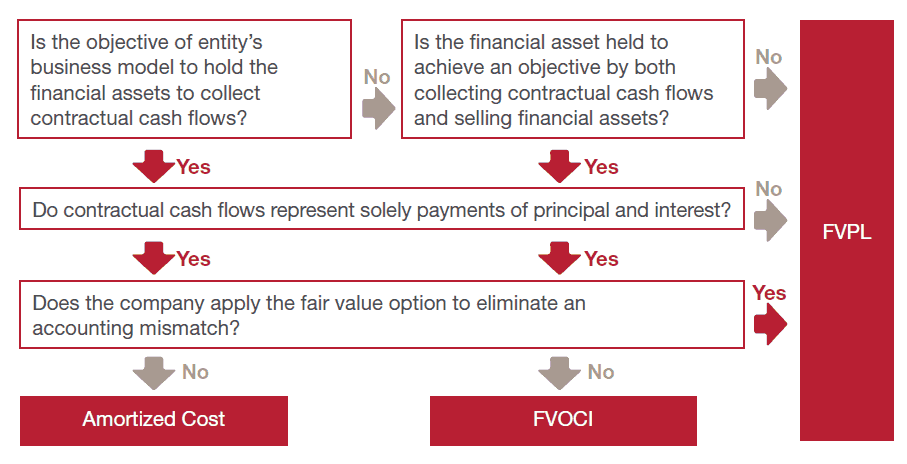
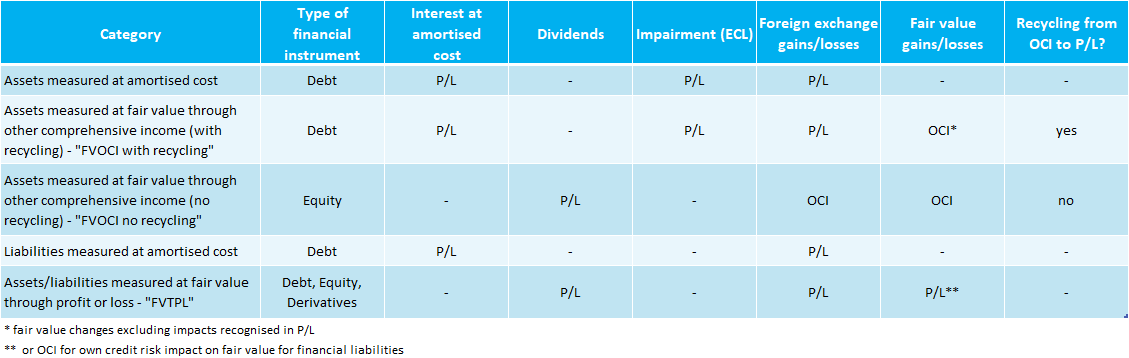
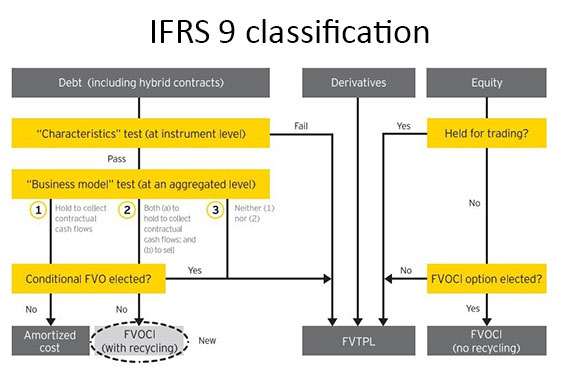
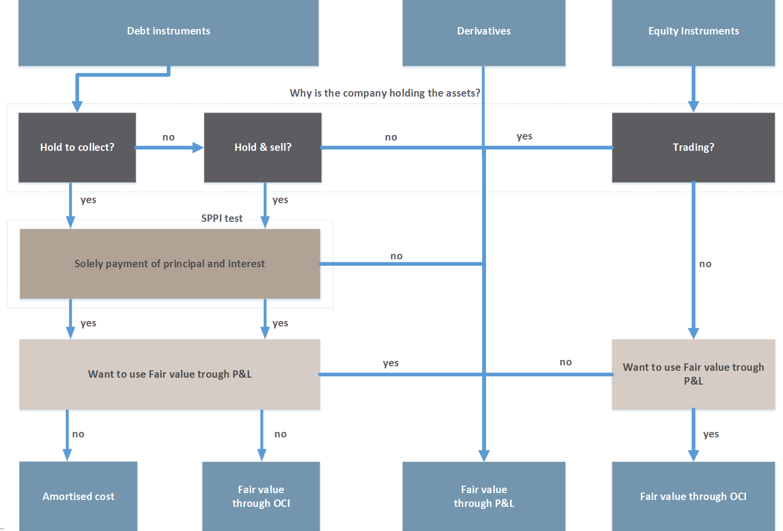
Classification of financial liabilities Summary Arguably, IFRS 9 has simplified and improved accounting for financial assets in comparison with its predecessor, IAS ® 39 There is increased emphasis on fair value accounting and reporting, which is regarded as both relevant and reliable information to those interested in financial reports. Classification of financial assets (IFRS 9) 17 21 Classification financial assets Cash flows are solely payments of principal and interest (SPPI) Business model = hold to collect Business model = hold to collect and sell Other business model Other types of cash flows Amortised cost FVOCI* FVTPL FVTPL FVTPL FVTPL *Excludes investments in equity instruments (see later slides). IFRS 9 5517 IFRS 9 Expected Credit Loss (ECL) ModelRequirements 12 month and lifetime expected loss models required Forward looking loss estimate Sensitive to economic cycle Discounting incorporated Forecasting elements Assess credit deterioration from origination Determine ‘significant deterioration’.
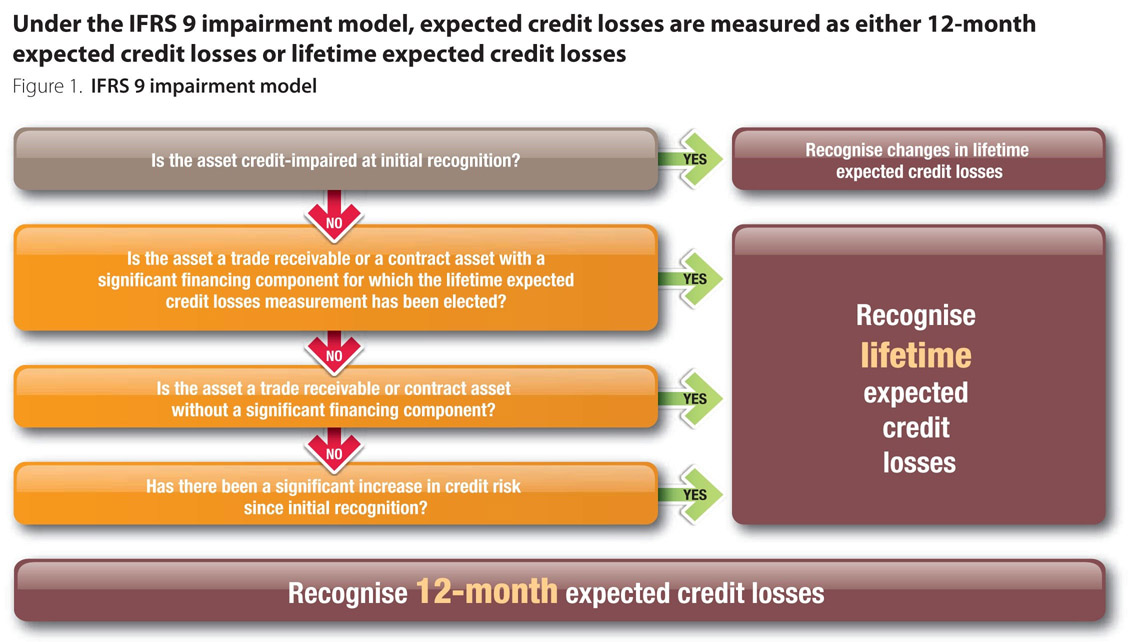
Essential IFRS 9 Impairment Solutions Get peace of mind when estimating expected credit losses, with access to default and ratings migration data, statistical models, and scorecards that assess probability of default, loss given default, and macroeconomic considerations Request More Information Insurance Companies. Resources to demystify financial instruments IFRS 9 incorporates the requirements of all three phases of the IASB’s financial instruments project classification and measurement, impairment, and hedge accounting. IFRS 9 requires that when there is a significant increase in credit risk, institutions must move an instrument from a 12month expected loss to a lifetime expected loss In making the evaluation, the institution will compare the initial credit risk of a financial instrument with its current credit risk, taking into consideration its remaining life.
Understanding the new standard is vital International Financial Reporting Standard 9 (IFRS 9) responds to criticisms that International Accounting Standard 39 (IAS 39) is too complex, is inconsistent with the way entities manage their businesses and risks, and defers the recognition of credit losses on loans and receivables until too late in the credit cycle. IFRS 9 introduce o nouă abordare privind clasificarea activelor financiare, determinată de modelul de afaceri al entității, adică modul în care o entitate își gestionează activele financiare pentru a genera fluxuri de trezorerie, și de fluxurile de trezorerie contractuale reprezentând exclusiv plăți ale principalului și ale dobânzii aferente valorii principalului datorat, eliminând categoriile de clasificare a activelor financiare prevăzute în IAS 39 Noua clasificare. IFRS 9 – Financial Instruments (Provision for Bad debtsGeneral method) Posted by Charles The Accountant March 6, March 7, Posted in Uncategorized The information below relate to Junior Company Limited trade receivables Junior Company Limited had TR carrying ng amount of $570,000as at period end Dec 17.
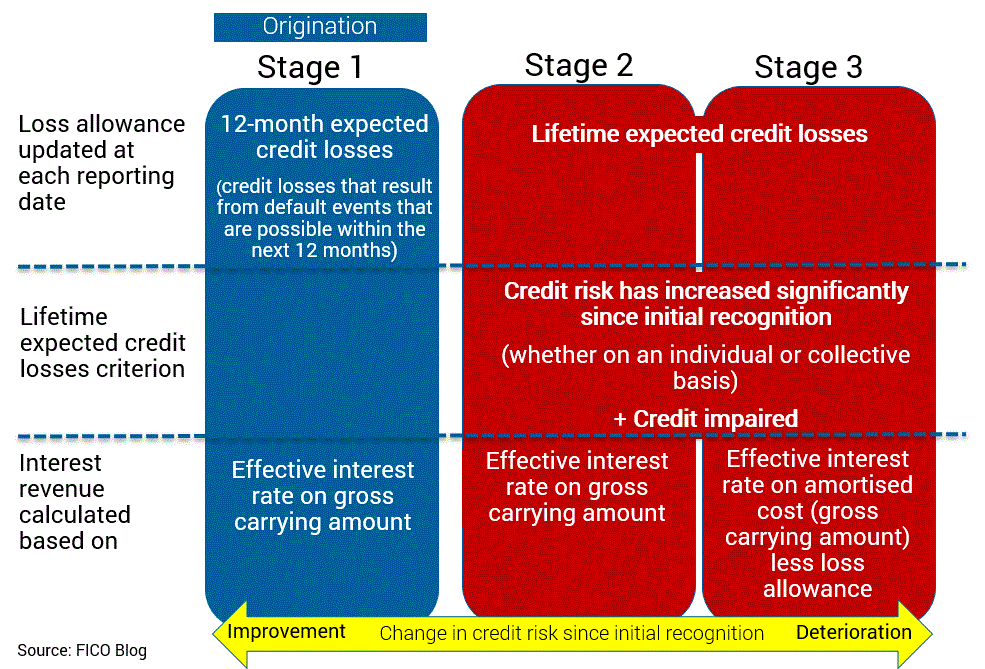
The new IFRS 9 impairment model requires impairment allowances for all exposures from the time a loan is originated, based on the deterioration of credit risk since initial recognition If the credit risk has not increased significantly (Stage 1), IFRS 9 requires allowances based on 12 month expected losses. IFRS 9 represents a new era of expected credit loss provisioning The global financial crisis (GFC) of 079 highlighted the systemic costs of delayed recognition of credit losses by banks and other lenders. In a nutshell, IFRS 9 is the new financial instrument accounting standard that includes requirements for the classification, measurement and impairment of financial assets It became effective as of 1 January 18, and is mandatory for all listed companies in South Africa.
The new IFRS 9 impairment model requires impairment allowances for all exposures from the time a loan is originated, based on the deterioration of credit risk since initial recognition If the credit risk has not increased significantly (Stage 1), IFRS 9 requires allowances based on 12 month expected losses. IFRS 9 is an International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) It addresses the accounting for financial instrumentsIt contains three main topics classification and measurement of financial instruments, impairment of financial assets and hedge accountingThe standard came into force on 1 January 18, replacing the earlier. And – Certain loan commitments and financial guarantee contracts.
IFRS 9 FlexFinance provides a comprehensive IFRS solution which includes valuation of financial instruments, calculation of impairment and hedge management;. IFRS 9 requires a more granular and dynamic approach for portfolio segmentation Firms must capture and collect historical data and other trend information required for building a forwardlooking impairment model and for tracking credit risk migration since the origination and recognition of the financial instrument. IFRS 9 will bring profound change to financial instrument accounting;.
Https//wwwcpdboxcom/This is just the short executive summary of IFRS 9 and does NOT replace the full standard you can see the full text on IFRS Foundati. International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS9) The IFRS9 standard became effective since 18 as a replacement of the previous IAS39 standard following the financial crisis of 08 The IAS39 incurred loss model was criticised for being ‘too little too late’ and the IFRS9 expected credit loss seeks to address that as it helps banks identifying and mitigating credit risk early. In determining the period of credit exposure an entity is required to consider all three factors listed in paragraph B5540 of IFRS 9 – ie the entity considers if and how its credit risk management actions affect the period of exposure.
National Professional Services Group CFOdirect Network –wwwcfodirectpwccom In depth 12 IFRS 9 establishes that management must still determine whether the contractual cash flows that could arise over the life of the instrument due to those contractual provisions meet the SPPI condition. IFRS 9 introduces new rules for financial instruments on classification and measurement, impairment (with a new expected credit loss impairment approach) and hedge accounting and is effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 18, with early application permitted. IFRS 9 is the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB) response to the financial crisis, aimed at improving the accounting and reporting of financial assets and liabilities IFRS 9 replaces IAS 39 with a unified standard The mandatory effective date for implementation is January 1, 18.
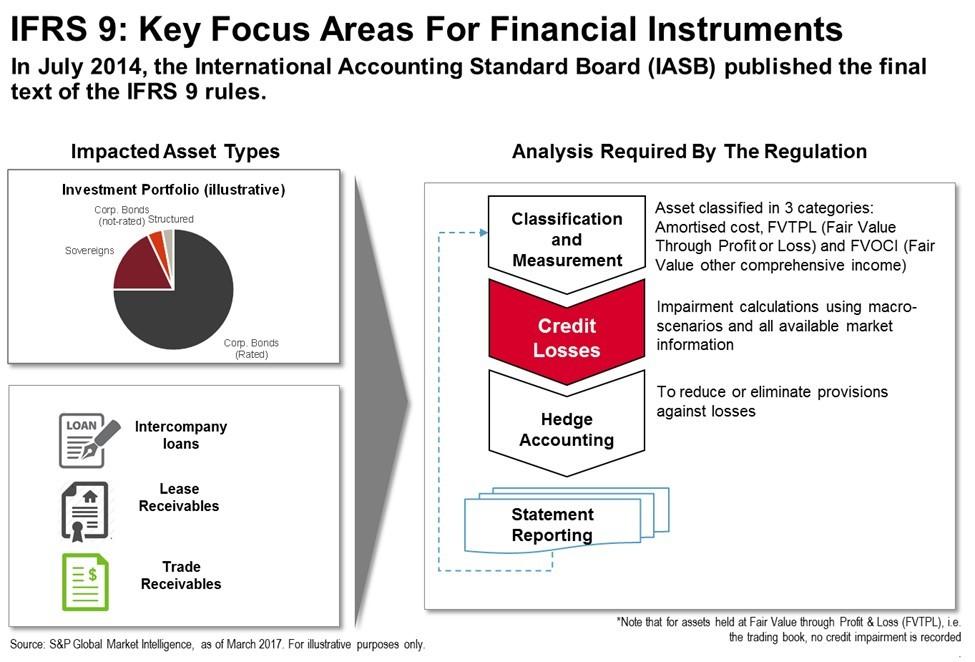
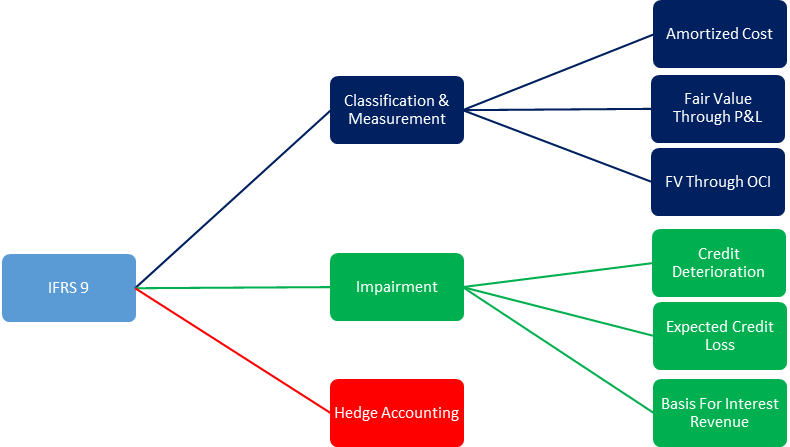
IFRS 9 (10), to address specific application questions raised by interested parties as well as to try and reduce differences with the FASB However, the FASB tentatively decided that it would not continue to pursue a classification and measurement model similar to the IASB As a consequence, the FASB’s classification and measurement. This publication discusses the new expected credit loss model as set out in IFRS 9 and also describes the new credit risk disclosures under the expected credit loss model, as set out in IFRS 7 In July 14, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued the final version of IFRS 9 Financial Instruments (IFRS 9, or the standard), bringing together the classification and measurement, impairment and hedge accounting phases of the IASB’s project to replace IAS 39 and all previous. IFRS 9 Financial Instruments 1 Objective The objective of this Standard is to establish principles for the financial reporting of financial assets and financial liabilities that will present relevant and useful information to users of financial statements for their assessment of the amounts, timing and uncertainty of an entity’s future cash flows Navigating through IFRS 9.
IFRS 9 requires financial assets to be measured at amortised cost or fair value Fair value changes will be in profit or loss or taken to OCI Fair value through OCI is a consequence of the business model for some assets but an irrevocable election at initial recognition for other assets. IFRS 9 – The Expected Credit Loss Method In Numerology, Number 9 is known as the number of Universal Love, though in the International Financial Reporting Standards, IFRS 9 ‘Financial Instruments’ was certainly not welcomed with much love After the financial crisis of 07 and 08, the accounting standard bodies were blamed for not adequately catering the impairment provisions of financial assets. In a nutshell, IFRS 9 is the new financial instrument accounting standard that includes requirements for the classification, measurement and impairment of financial assets It became effective as of 1 January 18, and is mandatory for all listed companies in South Africa Stephen explains “The most notable change is that of IFRS 9’s expected credit loss impairment requirements.
IFRS 9 is an International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) It addresses the accounting for financial instrumentsIt contains three main topics classification and measurement of financial instruments, impairment of financial assets and hedge accountingThe standard came into force on 1 January 18, replacing the earlier. IFRS 9 – the new era of expected loss provisioning The IFRS Roadmap in Vietnam was officially announced in Decision No345/QDBTC on 16 March by the Ministry of Finance (MoF), a year after introduction of the draft version Against the mandate by the MoF and economic distress caused by COVID19 outbreak, KPMG now view the application of IFRS to be more challenging than anticipated as banks in Vietnam plan forward to embrace IFRS 9. IFRS 9 is an International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) It addresses the accounting for financial instrumentsIt contains three main topics classification and measurement of financial instruments, impairment of financial assets and hedge accountingThe standard came into force on 1 January 18, replacing the earlier.
IFRS 9 is a financial reporting standard developed and approved by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), an independent, privatesector body that develops and approves International Financial Reporting Standards IFRS 9 concerns the accounting and reporting specifically of financial instruments. IFRS 9 sets out a new forward looking ‘expected loss’ impairment model which replaces the incurred loss model in IAS 39 and applies to – Financial assets measured at amortised cost;. In July 14, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued the final version of IFRS 9 Financial Instruments (IFRS 9, or the standard), bringing together the classification and measurement, impairment and hedge accounting phases of the IASB’s project to replace IAS 39 and all previous versions of IFRS 9.
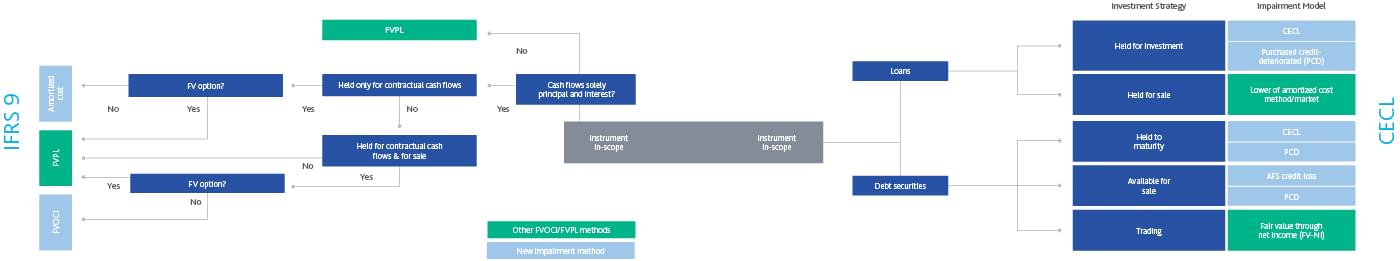
IFRS 9 EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES Acknowledgement This material is based on IFRS 9 (published by IASB) and Get ready for IFRS 9 (published by Grant Thornton) Required For Examples 1 to 7, determine the objective of the business model Example 1 An entity holds investments to collect their contractual cash flows The funding needs of the entity. – Debt investments measured at fair value through other comprehensive income;. IFRS 9 replaces the multiple classification and measurement models in the previous standard Classification is now driven by a combination of how a company manages its financial assets ("business model test") and the characteristics of their contractual cash flow ("cash flow test").
IFRS 9 introduce o nouă abordare privind clasificarea activelor financiare, determinată de modelul de afaceri al entității, adică modul în care o entitate își gestionează activele financiare pentru a genera fluxuri de trezorerie, și de fluxurile de trezorerie contractuale reprezentând exclusiv plăți ale principalului și ale dobânzii aferente valorii principalului datorat, eliminând categoriile de clasificare a activelor financiare prevăzute în IAS 39 Noua clasificare. IFRS® 9, Financial Instruments, is the result of work undertaken by the International Accounting Standards Board (the Board) in conjunction with the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the US It was last revised in October 17. IFRS 9 requires a financial asset and liabilities to be initially measured at fair value and subsequently at amortized cost or fair value depending on the classification It also introduces a new forwardlooking expected credit losses impairment requirements Initial measurement.
Consolidation with multicurrency capability The IFRS accounting logic and the standard chart of accounts are part of each delivery Learn more. Https//wwwcpdboxcom/This is just the short executive summary of IFRS 9 and does NOT replace the full standard you can see the full text on IFRS Foundati. For a December 18 yearend, an entity that has not adopted earlier versions of IFRS 9 will have a DIA of 1 January 18 In the period of initial application of IFRS 9, an entity generally provides the disclosures required by IFRS 9 (as outlined in IFRS 7) and IAS 8.
IFRS 9 and expected loss provisioning Executive Summary The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and other accounting standard setters set out principlesbased standards on how banks should recognise and provide for credit losses for financial statement reporting purposes In July 14, the IASB issued International Financial Reporting Standard 9 Financial Instruments (IFRS 9), which introduced an "expected credit loss" (ECL) framework for the recognition of impairment. A simple explanation of the basic classifications within IFRS 9 for financial assets and liabilities For free content and ACCA / CIMA courses visit https//. IFRS 9 specifies how an entity should classify and measure financial assets, financial liabilities, and some contracts to buy or sell nonfinancial items IFRS 9 requires an entity to recognise a financial asset or a financial liability in its statement of financial position when it becomes party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
IFRS 9 does NOT deal with your own (issued) equity instruments like your own shares, issued warrants, written options for equity, etc IFRS 9 DOES deal with the equity instruments of someone else, because they are financial assets from your point of view. IFRS 9 is an International Accounting Standards Board's (IASB) response to the 08 global financial crisis The objective is to improve the accounting and reporting of financial assets and liabilities post financial crisis In simple words, idea is to predict loss recognition by avoiding finanacial issues faced during global recression. IFRS9 Introduction IFRS9 In July 14, the final version of IFRS9 accounting standards was issued by International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) In the wake of financial crisis of 08 the IASB in collaboration with the Financial Accounting Standard board launched a project to address the issues of delayed recognition of losses in IAS39 accounting standards prevalent at that time.
Classification of financial assets Under IFRS 9, subsequent to initial recognition, an entity classifies its financial assets as measured at amortized cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI) and fair value through profit or loss (FVTPL) depending on the (a) the entity’s business model for managing the assets, and (b) the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial assets. IFRS 9 gives an example of a commodity purchase where initial measurement includes transaction costs (IFRS 9B6529 (a)) Subsequent accounting for amounts accumulated in OCI is set out in IFRS (b) and is very similar to accounting for cash flow hedge reserves Example Transaction related hedged items. IFRS 9 contains an option to designate, at initial recognition, a financial asset as measured at FVTPL if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces an ‘accounting mismatch’ that would otherwise arise from measuring assets or liabilities or recognising the gains and losses on them on different bases Financial assets designated at FVTPL.
IFRS 9 aims to streamline and strengthen risk measurement and reporting of financial instruments in an efficient, forwardlooking manner This new accounting standard will have farreaching impacts on accounting practices and performance results. IFRS 9 replaces the incurred loss model used in IAS 39, where impairments were only recognised when they occurred, with an expected loss model where expected losses are provided for To measure impairment IFRS 9 introduces a three stage approach to measuring impairments as follows Stage One. IFRS 9 describes requirements for subsequent measurement and accounting treatment for each category of financial instruments It presents the rules for derecognition of financial instruments, with focus on financial assets It contains the derecognition decision tree to assist in assessment of derecognition criteria.
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments 3 An entity shall apply this Standard retrospectively, in accordance with IAS 8Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors, except if it is impracticable (as defined in IAS 8) for an entity to assess a modified time value of money element Defined terms.
Ifrs Numerical Technologies

Is Valuing Equity Instruments At Cost Permissible Under Ifrs 9 Gaap Dynamics
Ifrs 9 And Collections The 31 Day Time Bomb Fico

Pdf Comparison Of Ias 39 And Ifrs 9 The Analysis Of Replacement Semantic Scholar

Ifrs 9 Summary Ifrs 9 Compliance Oracle

Analytics Ifrs 9 2 Infogram Charts Infographics Management Infographic Infographic Analytics
Cecl Vs Ifrs 9 Moody S Analytics
Q Tbn And9gcqcagbt6szrhmtck Wb2y7qss7jompg4zqqxt9 F9oxgluiat2a Usqp Cau

3 Benefits Of Ifrs 9 Hedge Accounting
Updates The Asian Banker
Classification Of Financial Assets Liabilities Ifrs 9 Ifrscommunity Com
Q Tbn And9gcrkpizu Ggsui7fijwnsmxl5dkxilrcotla1clltk9 S0lzldyi Usqp Cau
Ifrs 9 Impairment How It Impacts Your Corporation And How We Can Help S P Global Market Intelligence

Ifrs 9 New Approach To Classification And Impairment Of Financial Assets Korpus Prava Publications
Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments

Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments Reporting Solutions November 17
Help Sap Com Doc Ff1bcaed2fbe2c3771a76 10 1 4 En Us Ifrs9 Analysis Pdf

Updates The Asian Banker

Impairmentstudio For Ifrs 9
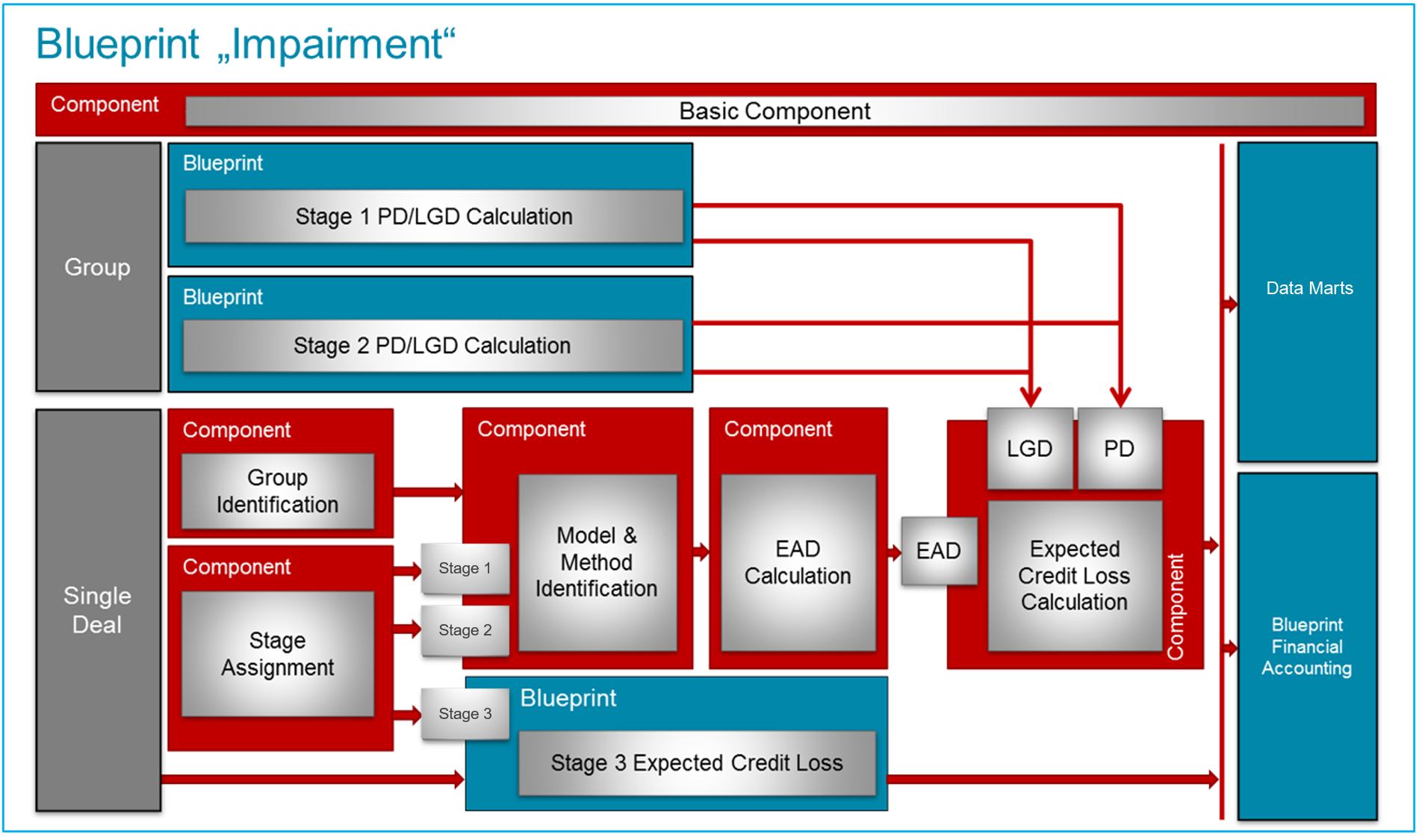
Ifrs 9 Impairment Blueprint Flexfinance Flexfinance Finance

How To Make Sense Of Transition To Ifrs 9 Expected Credit Loss Model Ey Global

Ifrs 9 The New Kid On The Block Bank Of Valletta Bov Group

Ifrs 9 Hedge Accounting A Financial Opportunity For Corporate Treasuries Refinitiv Perspectives

Ifrs 9 International Accounting Standards Board
Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments Measurement Annualreporting Info

What Tom Cruise Seems To Understand About Ifrs 9 o
Measurement Of Financial Instruments Ifrs 9 Ifrscommunity Com
Ifrs9 What Banks Shareholders Should Know Nasdaq Eufn Seeking Alpha
Ifrs 17 9 Series Asset Allocation Considerations Insurance Asset Risk

Ias 39 Is History Ifrs 9 A Mystery Expected Credit Losses Explained Kpmg Luxembourg

Challenges Of Ifrs 9 Impairment Requirement To Prepare Early For The New Impairment Approach Bankinghub
Q Tbn And9gcrjwwhk2thcsnjdoiyykaezehh5rolf8yjqyh7uvl0nvfavo1lh Usqp Cau

Ifrs 9 Impairment Practical Implications Protiviti Singapore

3 Key Benefits Of Hedge Accounting Under Ifrs 9
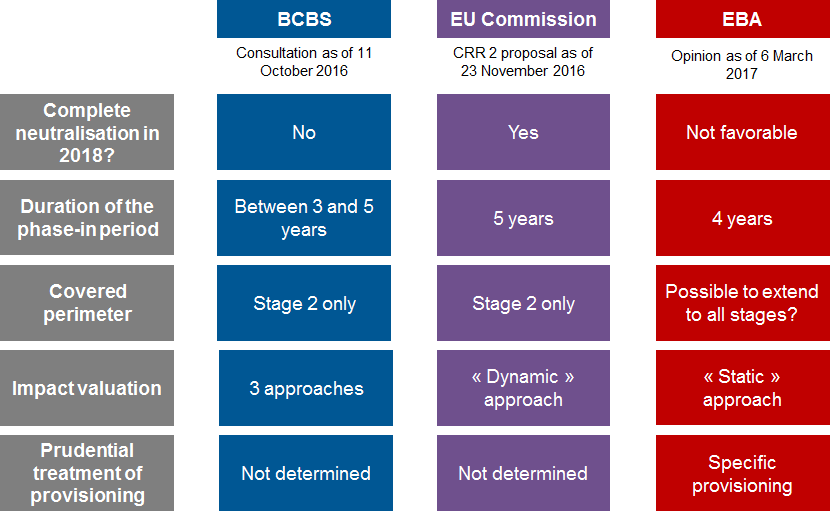
Ifrs 9 New Provisioning And The Phase In Period Of Regulatory Capital A Discretionary Approach Mazars Financial Services Blog

Ifrs 9 Hedge Accounting A Financial Opportunity For Corporate Treasuries Refinitiv Perspectives

Bankpedia

Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments Overview

Hedge Accounting Changes Under Ifrs 9 Zanders Treasury Finance Solutions
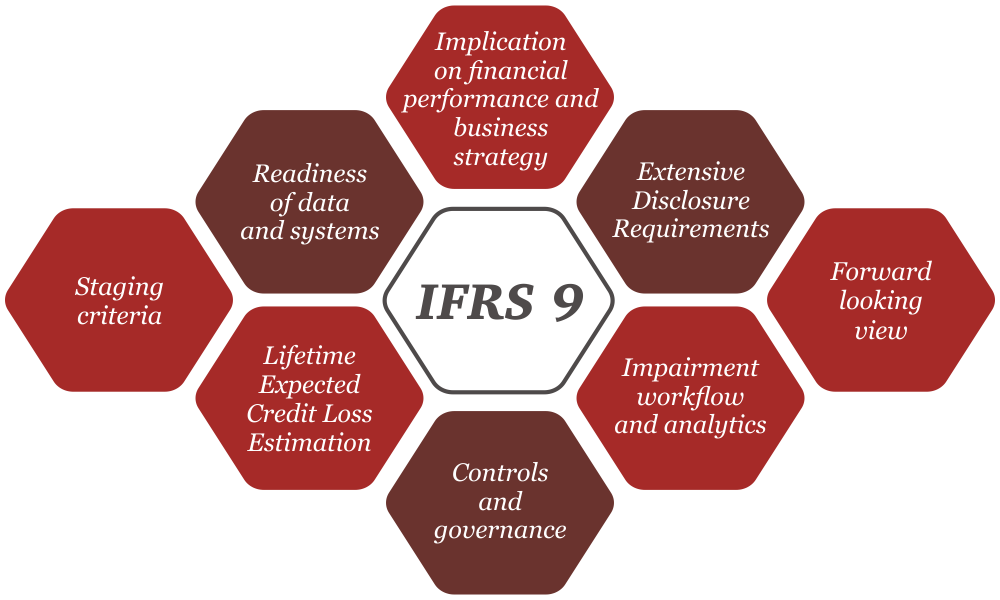
Ifrs9 New Dimension Of Decision Making Pwc Polska

Ifrs 9 Bad Debt Provisioning Nci
An Introduction To Ifrs 9 And Ifrs 17 Ifrs 17

Ifrs 9 Impairment Model Download Scientific Diagram
The Ifrs 9 Three Stage Expected Loss Model For Impairment Of Financial Download Scientific Diagram

Guide To Annual Financial Statements Ifrs 9 Illus Kpmg China

International Financial Reporting Standards 9 Ifrs 9 Solution Axiomsl

Financial Assets Under Ifrs 9 The Basis For Classification Has Changed o Australia
Http Www Toknowpress Net Isbn 978 961 6914 23 9 Papers Ml18 029 Pdf
Ifrs 9 May Make Loans More Expensive For Borrowers The Edge Markets

Validation Of Ifrs 9 Models
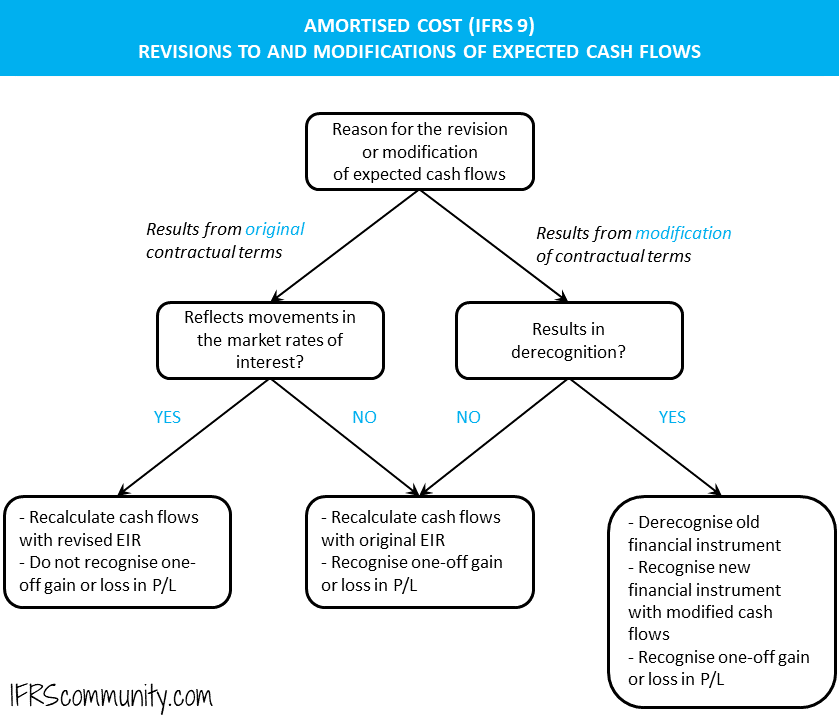
Amortised Cost And Effective Interest Rate Ifrs 9 Ifrscommunity Com
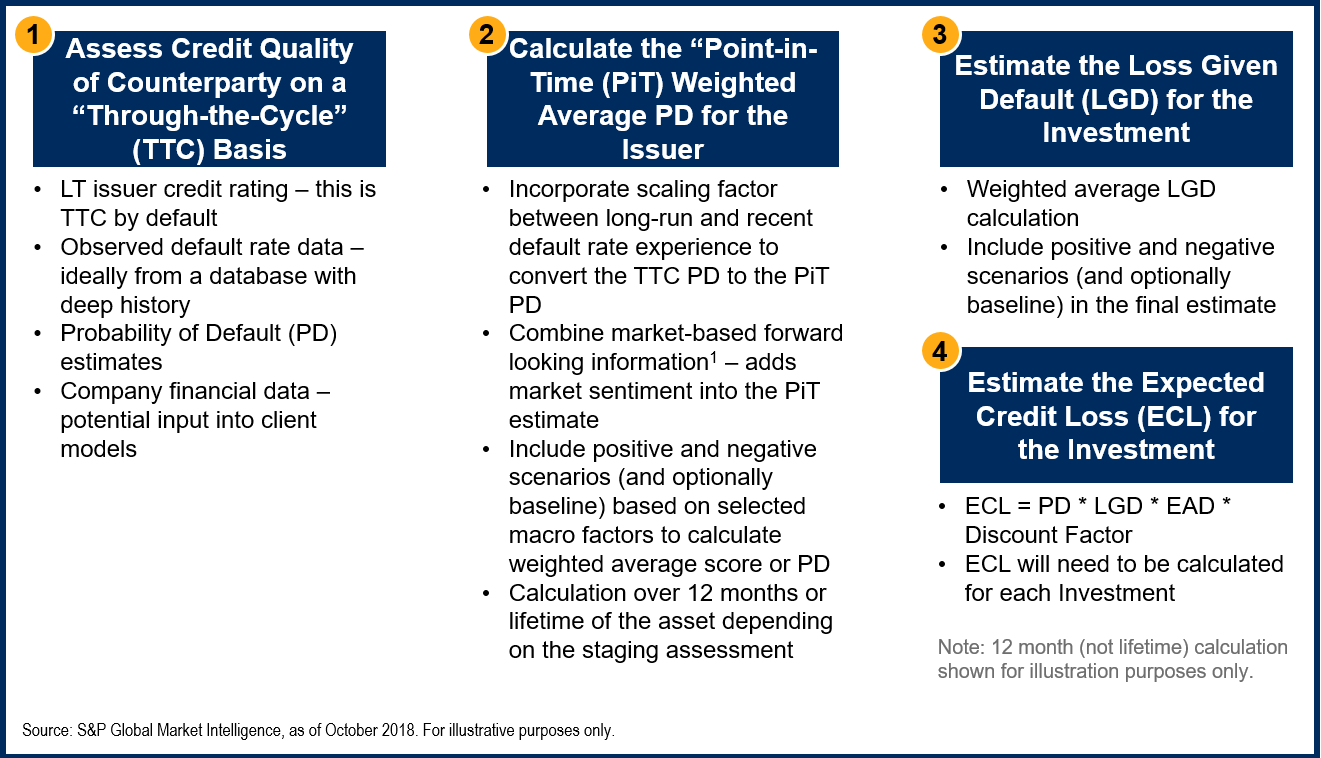
The Essential Ifrs 9 Check List For Insurers S P Global Market Intelligence
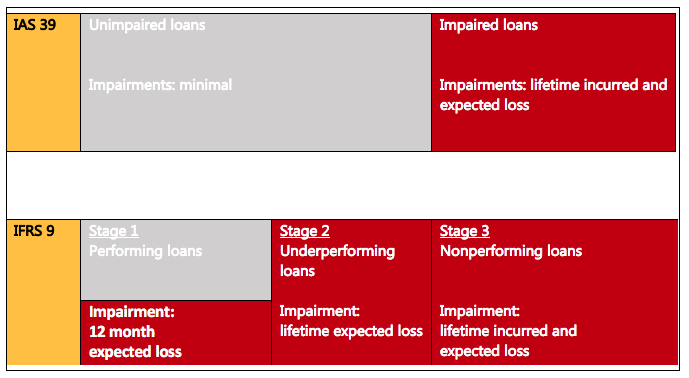
Loan Valuations In The Age Of Expected Loss Provisioning Vox Cepr Policy Portal

Ifrs 9 Credit Impairment Wikibanks
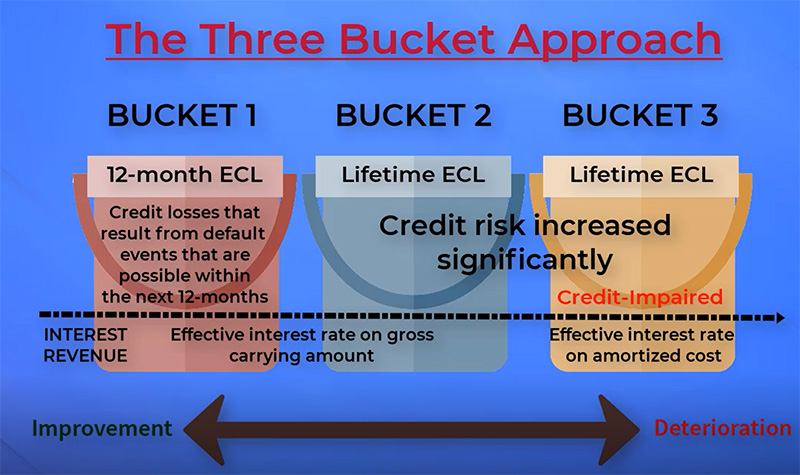
Impairments Of Financial Instruments Are Changing Under Ifrs 9 Gaap Dynamics

Ifrs 9 In Asia Pervasive Challenges To Implementation Bloomberg Professional Services
Www2 Deloitte Com Content Dam Deloitte Ng Documents Audit Financial reporting Ng Ifrs9 Implementation Pdf

Ifrs 9 Critical Aspects Cesare Schiarea etik Blog

Ifrs 9 Accounting Mini Series Hedge Accounting Under Ifrs 9 Accounts Examples
Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments
Ifrs 9 Summary Requirements Changes Deloitte Cfr

Peter Worth Do We Need A Statutory Override For Ifrs 9 Room 151

Doubts Cast On Europe S Ifrs 9 Transition Period Risk Net

Implementing Ifrs 9 Expected Loss Impairment Model Moody S Analytics
Ifrs 9 Valuation Blueprint Flexfinance Flexfinance Finance

Challenges Of Ifrs 9 Impairment Requirement To Prepare Early For The New Impairment Approach Bankinghub

Ifrs 9 Hedge Accounting A Financial Opportunity For Corporate Treasuries Refinitiv Perspectives
Interview Global Credit Data On Ifrs 9 Report Trade Finance Global

Will Ifrs 9 Pass The Pandemic Test Intheblack

Ifrs 9 Classification And Measurement Financial Asset Financial Instrument Financial Institutions

Ifrs 9 Credit Impairment Wikibanks
Impairment Of Financial Assets Ifrs 9 Ifrscommunity Com
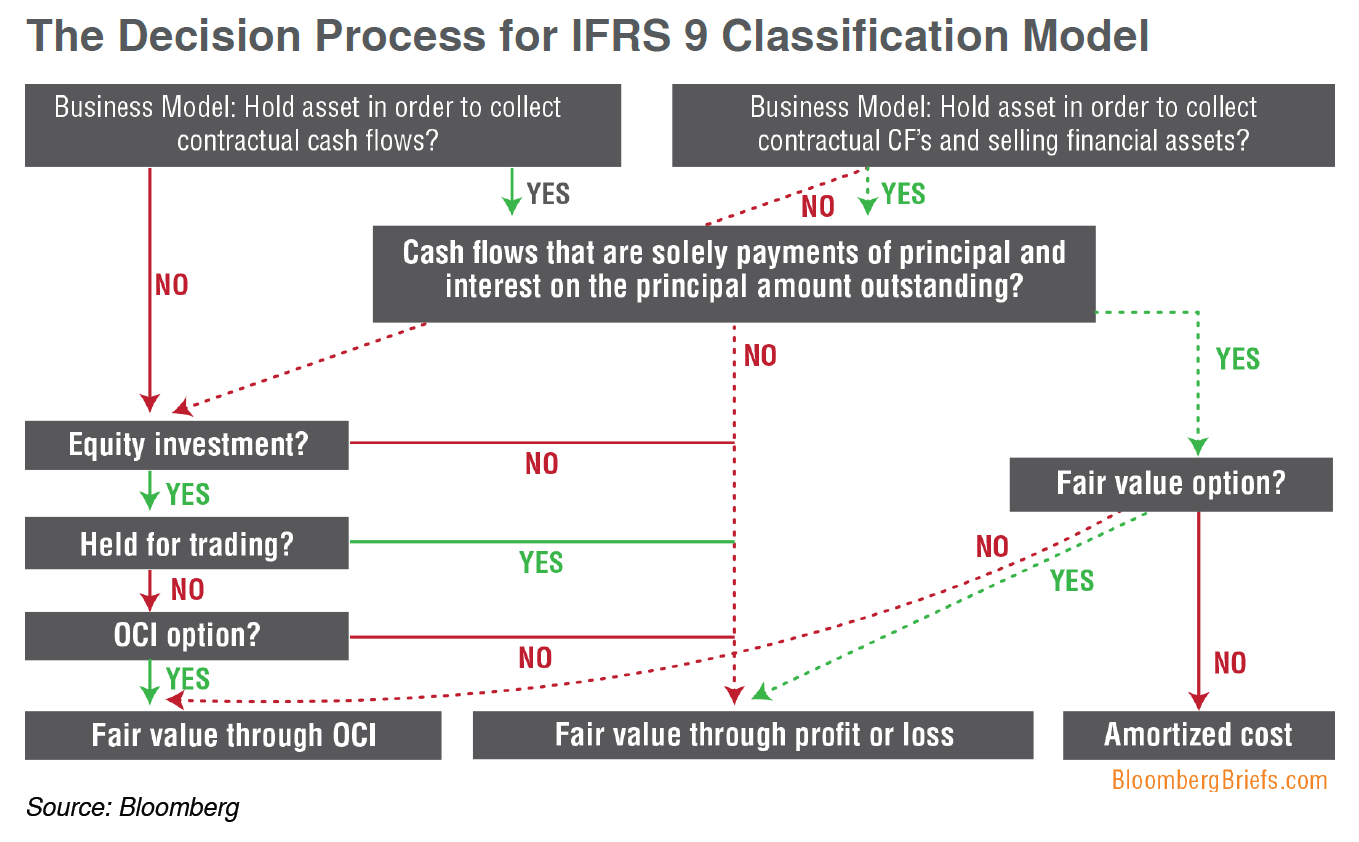
Getting Ready For Ifrs 9 Accounting Standards Bloomberg Professional Services

Ifrs 9 Will Impact Banks Provisions Moody S Analytics

Ifrs 9 Impairment Banking Survey 18 Financial Services Thought Gallery

Ifrs 9 Too Much Too Soon Or Timely And Responsive The Global Treasurer

Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments Theactuary Net Actuarial Knowledge
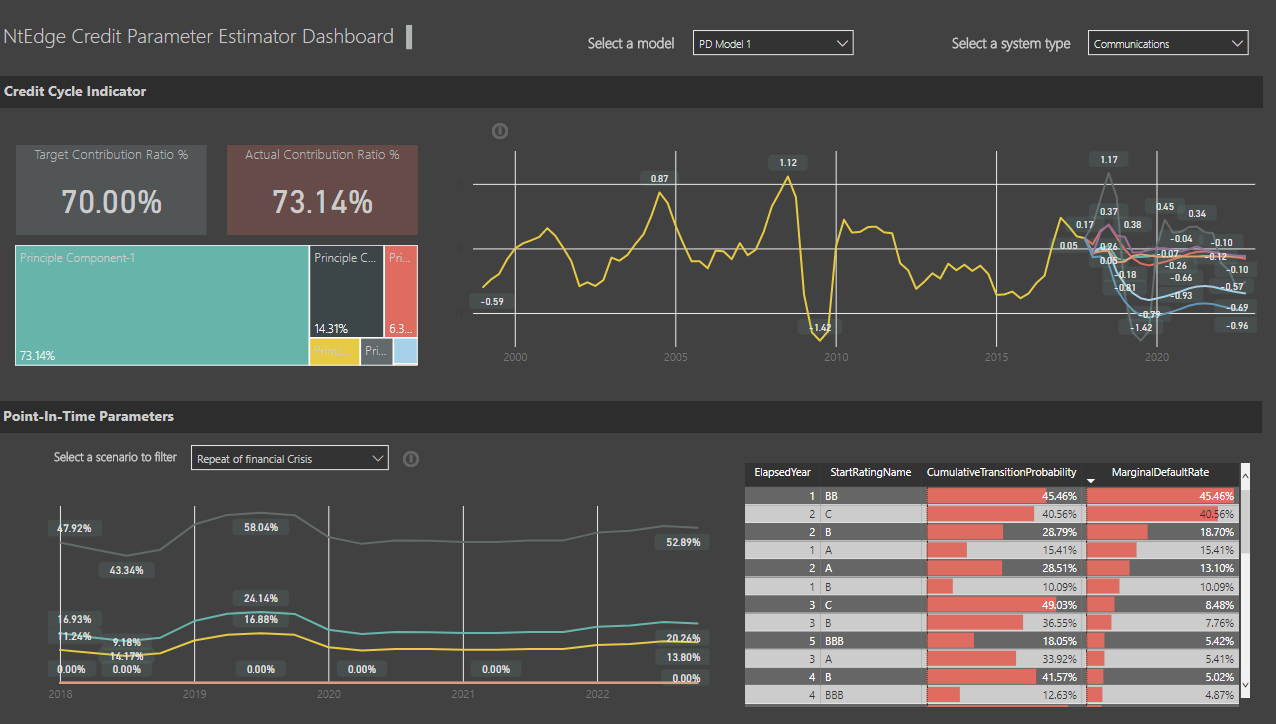
1

What Every Treasurer Must Know About Ifrs 9 The Association Of Corporate Treasurers

European Banks And The Q3 Ifrs 9 Overlay Fundamental Vs Technical Input To Accounting Ir Global
Ifrs 9 Step By Step Guide
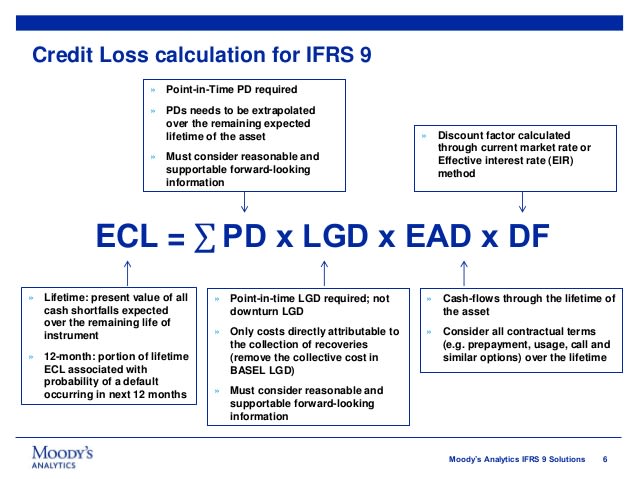
Prepare Ifrs 9 Ecl Model Using Both General And Simplified Approach By Basit
Www Ey Com Publication Vwluassets Ey Apply Ifrs 9 Fi Impairment April18 File Ey Apply Ifrs 9 Fi Impairment April18 Pdf

Increased Detail On Bank Disclosures Real Time Ifrs 9 Kpmg Global

Ifrs 9 Blog Series Tackling The Challenge Of Calculating Impairment S P Global Market Intelligence
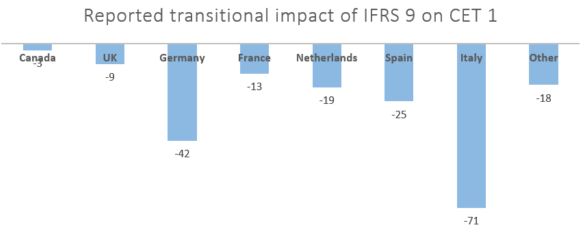
We Analysed The First Ifrs 9 Disclosures By Banks Finance And Banking Luxembourg
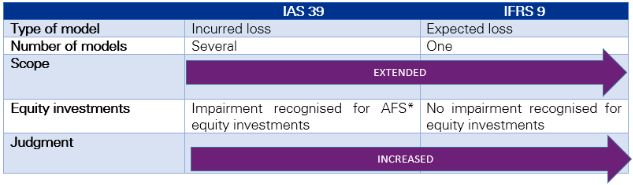
What Ifrs 9 15 And 16 Mean For The Real Estate Sector Real Estate And Construction Luxembourg

International Basel Iv Channel Impact Of Ifrs 9 On Regulatory Reporting 14th Oct 16 Youtube

1 Thee Stage Model Of Ifrs 9 Impairment Download Scientific Diagram
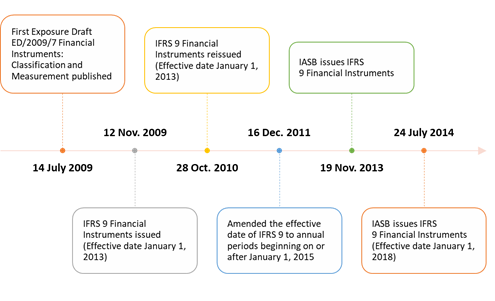
Ifrs 9 The Expected Credit Loss Method Discover N Learn
Www Ifrs Org Media Project Financial Instruments Project Summaries Ifrs 9 Project Summary July 14 Pdf
Ifrs 9 Financial Instruments Ifrs Reporting Audit Assurance Services Pwc
Ifrs 9 How Credit Data Can Help Markit Commentary

Banks Rising To The Challenges Of Ifrs 9 Kpmg Global

Ifrs9 Expected Credit Loss Ecl Models For Retail Lending

Ifrs 9 Impairment Practical Implications Protiviti Singapore

The Forward Looking Provisions Of Ifrs 9 Zanders Treasury Finance Solutions

Ifrs 9 Kantox



