Fdg Pet Scan
Cureus F 18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Ct Effectively Identifying Source Of Infection In A Patient With Multiple Dialysis Arteriovenous Fistula Access Points
Impact Of Intravenous Insulin On 18f Fdg Pet In Diabetic Cancer Patients Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Accuracy Of Positron Emission Tomography Ecr Journal
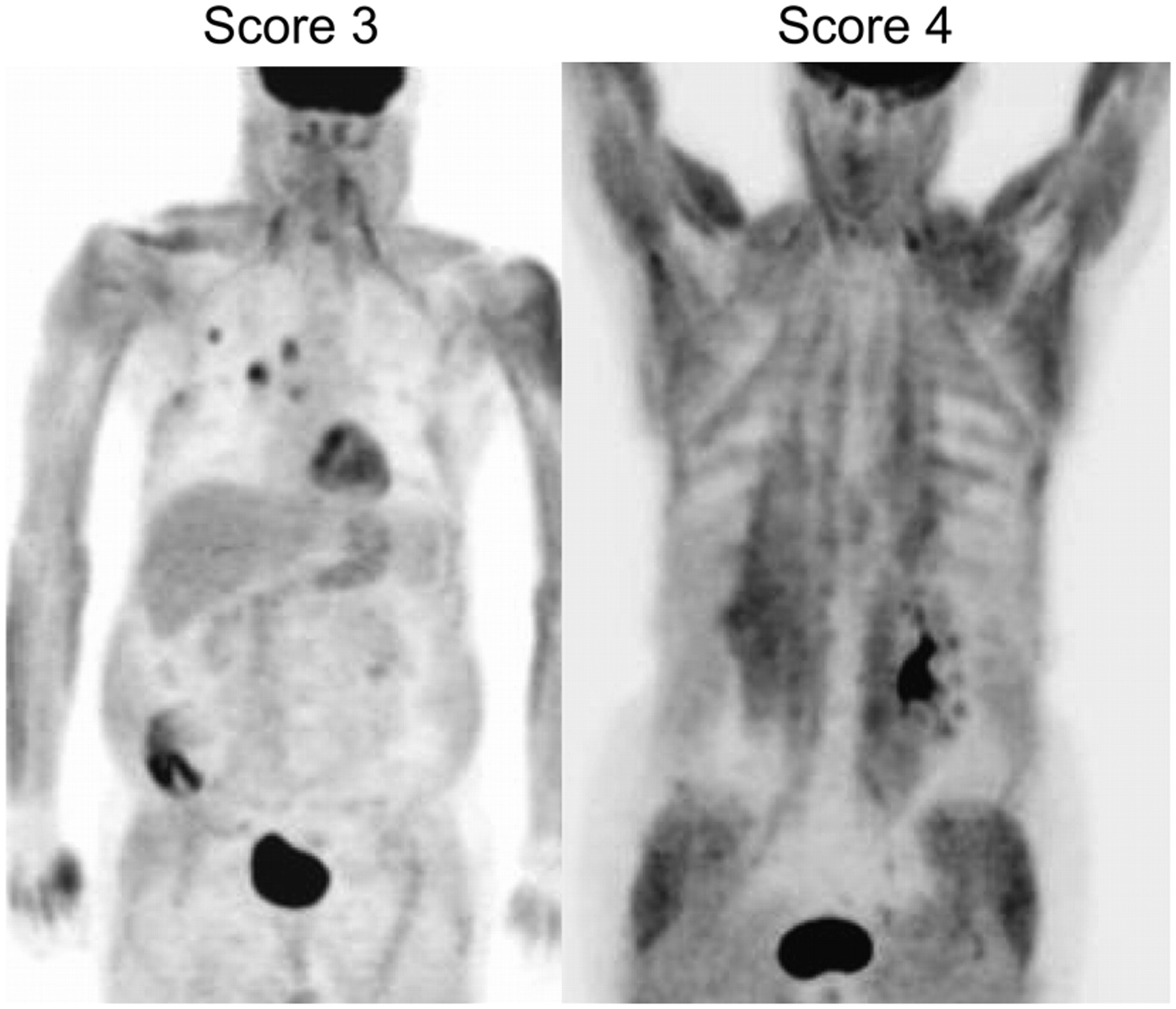
Prognostic Value Of Bone Marrow Fdg Uptake Pattern Of Pet Ct In Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
Molecules Free Full Text Positron Emission Tomography Pet Radiopharmaceuticals In Multiple Myeloma Html

Fever Of Unknown Origin The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Sciencedirect
The scan is carried out 60 minutes postinjection of FDG;.
Fdg pet scan. Type of scans FDG PET/CT;. PET scan drug ‘FDG’ to be made locally January , 21 by TSM Web Desk No Comments A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed under the “Aluth Husma” (new breath) project for the purpose of locally manufacturing fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), the radioactive drug required to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The radioactive substance most commonly used in PET scanning is a simple sugar (like glucose) called FDG, which stands for “fluorodeoxyglucose” It is injected into the bloodstream and accumulates in the body where it gives off energy in the form of gamma rays.
Background Positron emission tomography (PET) is a noninvasive imaging modality used in the diagnosis and staging of breast cancer However, several factors can affect fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake by a tumor To clarify the parameters that most affect FDG accumulation in tumors, the relationship between standardized uptake values (SUVs) and clinicopathological factors and immunohistopathological analysis was investigated in breast cancer. FDG PET scans involve a specialized sugar that shows up on PET scans This sugar injected into your body And since most tumors will take up more of it, it allows the tumor to show up on the PET scan Besides helping to diagnose cancer, FDG PET scans can also tell you if your cancer consumes a lot of sugar (ie if it’s “glucose avid” or not). Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging is a metabolic imaging technique using a radioactive tracer, 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose ( 18 FFDG), to identify the presence and severity of disease, namely cancers Most malignant tissues have increased 18 FFDG uptake associated with an increased rate of glycolysis and of glucose transport.
There are two types of PET scans One is used primarily for cardiac exams—this one is referred to as Myocardial Perfusion PET (also called Adenosine or Rubidium PET) The other PET exam is used to study such things as tumors, brain disorders, or infection;. This procedure uses fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) molecules in detecting active malignant lesions like colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, and multiple myeloma It can also be relied upon in monitoring response to therapy of a malignant disease. 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality for cancer imaging, assisting diagnosis, staging of patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, restaging following therapy and surveillance.
The radioactive substance most commonly used in PET scanning is a simple sugar (like glucose) called FDG, which stands for “fluorodeoxyglucose” It is injected into the bloodstream and accumulates in the body where it gives off energy in the form of gamma rays. A PET scan is an imaging exam that’s used to diagnose diseases or issues by looking at how the body is functioning It uses a special dye with radioactive tracers to help the machine capture. 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) has become an important modality in the evaluation of lymph nodes in oncology patients, including the central role FDG PET/CT plays in managing patients with lymphoma and the ability for FDG PET to detect nodal metastases in subcentimeter nodes which may be overlooked on CT or magnetic resonance (MR).
PETCT Diet Plan Before Your Exam If your PETCT scan is for cancer Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 24 hours Do not eat for six hours This includes tube feeding Do not chew gum You may drink only water If your PETCT scan is for a sarcoid heart scan, infection or inflammation Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 48 hours Do not eat. The short halflife of FDG creates for a shorter scan time, leaving room for increased patient use and increased financial outcome to the institution (Muhammad, Tzannon, Makrilia, 10) Hilner et al, concluded that from 80% of the PET centers in the US, PET played an integral part in 365% of treatment decisions (Hilner, Siegal & Liu, 08). PET can be used to diagnose different conditions depending on the type of radiotracer used The most common tracer, known as fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), is used in 90 percent of PET scans, the procedure of which is commonly referred to as FDGPET When injected into the bloodstream, FDG is taken up by glucose transporter molecules in cells.
PET scans were assessed visually and rated positive for BMI if at least 1 site of focal BM FDG uptake was seen, with an intensity exceeding that in the normal liver (a criterion that is often used in several types of lymphoma 16, ) and not attributable to any other cause (eg, benign osseous or cartilaginous lesions) BMI by PET was characterized as unifocal (a single BM PET lesion), bifocal (2 BM PET lesions), multifocal (3 or more BM PET lesions), or focal with diffuse uptake. An FDG PET scan is one of the most powerful tools we have to detect and monitor disease Most often used in conjunction with CT or MRI, it helps radiologists distinguish between healthy tissue and diseased tissue so that cancer can be accurately diagnosed, correctly staged, and appropriately treated. FDGPET can reveal abnormal metabolic activity in arterial walls that is considered a surrogate for local inflammation In this study, FDGPET imaging was performed at baseline, before the.
Abstract Background Positron emission tomography (PET) is a noninvasive imaging modality used in the diagnosis and staging of breast cancer However, several factors can affect fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake by a tumor. This brings the total dose of FDGPET/CT to a range of ~8 mSv up to 30 mSv, depending on the type of study performed as well as the anatomical region and number of body parts imaged, although several recent studies have reported a typical average dose of ~14 mSv for skull basetothigh FDGPET/CT examinations 28. If a patient's tumor does not have somatostatin receptor type 2 or not enough of them, then the FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) would be recommended I hope this information helps guide the discussion with your oncologist, Trixie Have they talked about receptors with you?.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Ga68 Dotatate PET PET with Ga68 dotatate is a newer SRS test that uses a radioactive tracer called Ga68 dotatate to FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) FDGPET can find fastgrowing neuroendocrine cancer MIBG scan An MIBG. In the studies, the diagnostic performance of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection varied with the type of cancer, size of cancer, and other clinical conditions False negative and false positive scans were observed Negative Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection PET scans do not exclude the diagnosis of cancer. Sometimes, your doctor may refer to a PETCT scan as a PET scan or PET imaging A PETCT scan is a way to create pictures of organs and tissues inside the body A small amount of a radioactive sugar substance is injected into the patient’s body This sugar substance is taken up by cells that use the most energy.
This PET image shows an area of reduced blood flow from one of the arteries that feeds the heart This information may help doctors decide whether to suggest bypass surgery or angioplasty to restore that blood flow A PET scan is an effective way to examine the chemical activity in parts of your body. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan. It is a nuclear medicine imaging test in which a mildly radioactive substance is injected into your body and is used to diagnose a variety of diseases The radioactive substance most commonly used in PET scanning is a simple sugar (like glucose) called FDG, which stands for “fluorodeoxyglucose” It is injected into your bloodstream and accumulates in your body where it gives off energy.
A PETCT scan is an imaging procedure that’s used to See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan radiation therapy See how treatment is working. 18FFDGPET/CT Imaging in Leukemia Abstract Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT) is a noninvasive radionuclidebased whole body Keywords PET/CT IN ACUTE LEUKEMIA Role of PET/CT is not been evaluated thoroughly in diagnosis of acute leukemia However, it is PET/CT IN. This procedure uses fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) molecules in detecting active malignant lesions like colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, and multiple myeloma It can also be relied upon in monitoring response to therapy of a malignant disease.
PET scan drug ‘FDG’ to be made locally January , 21 by TSM Web Desk No Comments A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed under the “Aluth Husma” (new breath) project for the purpose of locally manufacturing fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), the radioactive drug required to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. PET scanning with the tracer 18FFDG, is widely used in clinical oncology FDG is a glucose analog that is taken up by glucoseusing cells and phosphorylated by hexokinase (whose mitochondrial form is significantly elevated in rapidly growing malignant tumours). PET scan drug ‘FDG’ to be made locally January , 21 by TSM Web Desk No Comments A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed under the “Aluth Husma” (new breath) project for the purpose of locally manufacturing fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), the radioactive drug required to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
A PET scan or a combined CTPET scan enables your doctor to better diagnose illness and assess your condition Cancer Cancer cells show up as bright spots on PET scans because they have a higher metabolic rate than do normal cells PET scans may be useful in Detecting cancer;. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan. The short halflife of FDG creates for a shorter scan time, leaving room for increased patient use and increased financial outcome to the institution (Muhammad, Tzannon, Makrilia, 10) Hilner et al, concluded that from 80% of the PET centers in the US, PET played an integral part in 365% of treatment decisions (Hilner, Siegal & Liu, 08).
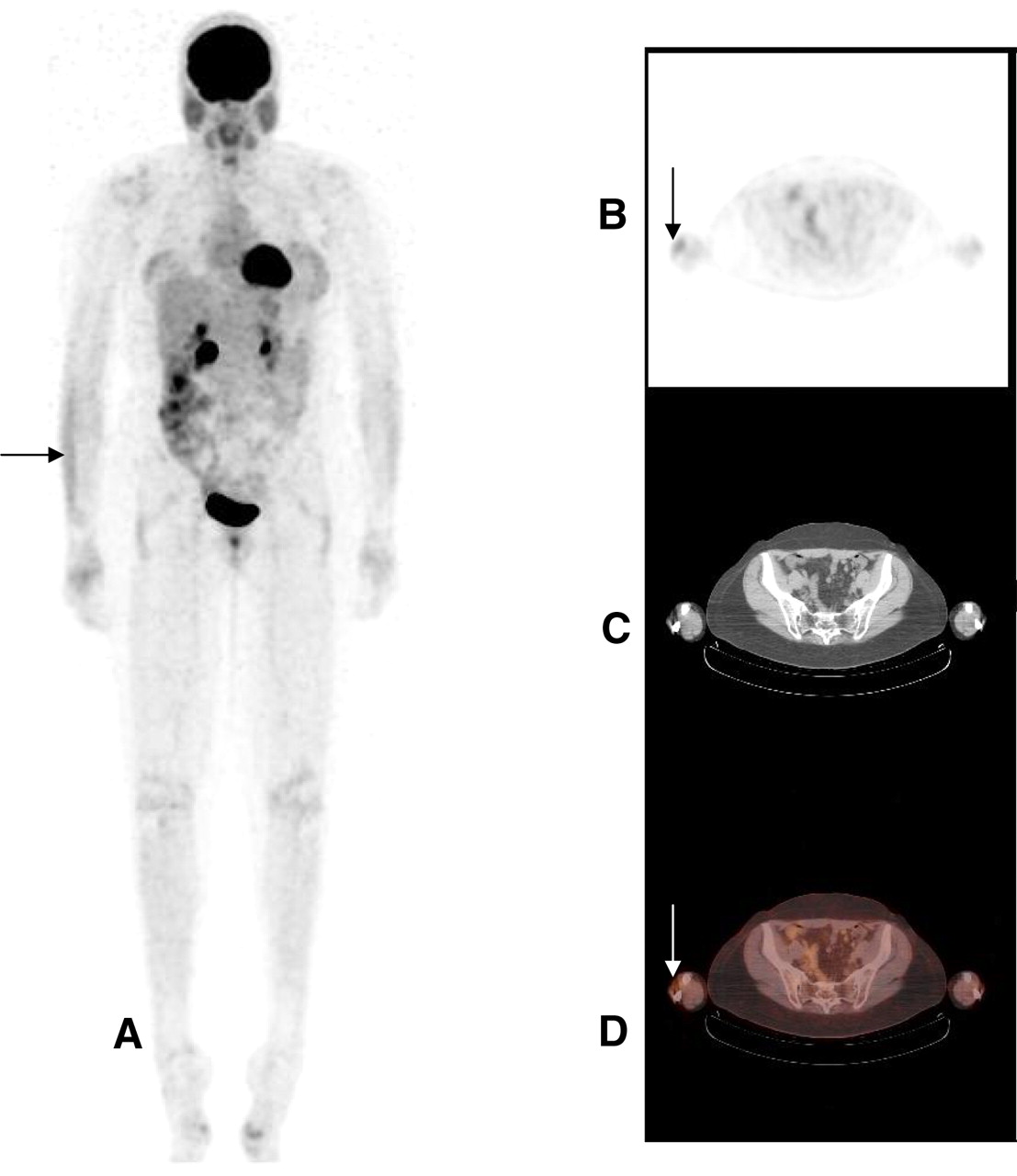
If a patient's tumor does not have somatostatin receptor type 2 or not enough of them, then the FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) would be recommended I hope this information helps guide the discussion with your oncologist, Trixie. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan. A, PET maximum intensity projection image shows a fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–avid mass (arrow) with a maximum standardized uptake value of 49 in the right lung Increased accumulation of FDG in the right paratracheal, right hilar lymph nodes (arrowheads), and bone marrow are also noted.
In the case of imaging of malignant melanoma, PET imaging can differentiate between benign cysts and metastatic tumors in the liver (and other sites) PET requires a small injection of radioactive material (eg FDG – radioactive glucose) that is preferentially absorbed by malignant tumors. PET scanning with the tracer 18FFDG, is widely used in clinical oncologyFDG is a glucose analog that is taken up by glucoseusing cells and phosphorylated by hexokinase (whose mitochondrial form is significantly elevated in rapidly growing malignant tumours) Metabolic trapping of the radioactive glucose molecule allows the PET scan to be utilized The concentrations of imaged FDG tracer. FDG PET is a biomarker for neuronal degeneration in dementia , in addition to being an oncologic imaging biomarker 5–9 Studies have shown that the appropriate use of FDG PET for evaluating patients with dementia can add valuable information to the clinical workup without adding to the overall costs of evaluation and management The purpose of this article is to review the value of FDG PET as a tool to diagnose neurodegeneration and its applicability in differentiating among various.
Revealing whether your cancer has spread. PET scan drug ‘FDG’ to be made locally January , 21 by TSM Web Desk No Comments A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed under the “Aluth Husma” (new breath) project for the purpose of locally manufacturing fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), the radioactive drug required to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. However, PET scan can allow for detailed visualization of the brain structures, to diagnose and measure the severity of brain disorders, including dementia There are a number of specialized PET scans, such as Hypometabolism brain PET scan, a measure of FDG PET pattern in dementia, PET scan frontotemporal dementia, and more.
A morning blood glucose level below 175 mg/dL is a safe range for your PET/CT FDG scan appointment • In the morning after your practice run, you may return to your normal routines of eating and taking medicine until the evening before your scan On the Day of Your Scan • Fast overnight for 12 hours before your scan. The uptake of 18FFDG by tissues is a marker for the tissue uptake of glucose, which in turn is closely correlated with certain types of tissue metabolism After 18FFDG is injected into a patient, a PET scanner can form twodimensional or threedimensional images of the distribution of 18FFDG within the body Since its development in 1976, 18FFDG had a profound influence on research in the neurosciences The subsequent discovery in 1980 that 18FFDG accumulates in tumors underpins the evoluti. A FDGPET scan is a medical imaging procedure It involves an injection of radioactive tracer liquid inside the body that congregates at tumors and other sites where the cells divide more quickly than usual The acronym FDGPET scan stands for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET), where the FDG is the radioactive liquid and the PET is the scanning machinery.
Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection is a positron emitting radiopharmaceutical that is used for diagnostic purposes in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. However, it can also be used to study the heart—this exam is referred to as FDG PET. Type of scans FDG PET/CT;.
The short halflife of FDG creates for a shorter scan time, leaving room for increased patient use and increased financial outcome to the institution (Muhammad, Tzannon, Makrilia, 10) Hilner et al, concluded that from 80% of the PET centers in the US, PET played an integral part in 365% of treatment decisions (Hilner, Siegal & Liu, 08). F18FDG PET/CT scan of an 18yearold woman diagnosed with Takayasu arteritis and an agematched control patient F18FDG uptake is present in the right and left common carotid arteries and aortic arch (arrows) Note the F18FDG uptake in vertebrae and pelvic bones (arrowheads), compared with the control. PET scan findings can be false positive Positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PETCT) scans with 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and PET–magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have become standard practice in staging and restaging of colorectal cancer patients by providing important information about the primary cancer as well as metastases.
PET scan drug ‘FDG’ to be made locally January , 21 by TSM Web Desk No Comments A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed under the “Aluth Husma” (new breath) project for the purpose of locally manufacturing fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), the radioactive drug required to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. PET scan images can provide important information about many disorders that affect the heart, lung, brain, bones, liver etc and will help the doctor plan appropriate treatment for you PET images are different than those from more conventional radiological studies such as CT scan, Ultrasound, or MRI. If a patient's tumor does not have somatostatin receptor type 2 or not enough of them, then the FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) would be recommended I hope this information helps guide the discussion with your oncologist, Trixie.
In cases of fusion imaging such as PETCT, the whole body CT scan is conducted first, followed by the wholebody PET scan and subsequently the two sets of images are coregistered. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan. PET imaging with 18FFDG takes advantage of the fact that the brain is normally a rapid user of glucose Standard 18FFDG PET of the brain measures regional glucose use and can be used in neuropathological diagnosis Examples Brain pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease greatly decrease brain metabolism of both glucose and oxygen in tandem Therefore 18FFDG PET of the brain may also be used to successfully differentiate Alzheimer's disease from other dementing processes, and also to make.
PET stands for positron emission tomography CT stands for computed tomography FDG stands for 2Deoxy218FfluoroDGlucose This exam uses Fluorine18 FDG, a radioactive tracer that acts like glucose in the body The tracer helps us see how much energy your cells are using We measure this with a FDG PET/CT scan A PET/CT camera takes 2 types of pictures. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging is a metabolic imaging technique using a radioactive tracer, 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose ( 18 FFDG), to identify the presence and severity of disease, namely cancers Most malignant tissues have increased 18 FFDG uptake associated with an increased rate of glycolysis and of glucose transport. 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality for cancer imaging, assisting diagnosis, staging of patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, restaging following therapy and surveillance Interpretation requires integration of the metabolic and anatomic findings provided by the PET and CT components which transcend the knowledge base isolated in the worlds of nuclear medicine and radiology, respectively.
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test that uses a special dye with radioactive tracers The tracers are either swallowed, inhaled, or injected into your arm They help your. To conclude, FDG PET/CT is useful in diagnosis and followup of patients with bone marrow malignancy 18 FFDG PET/CT may be useful for guiding the site of BM aspiration in cases with localized bone marrow involvement It has an important role in diagnosing extramedullary disease in de novo or relapsed AML patients. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan.

Osteoblastic Bone Flare On F18 Fdg Pet In Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Nsclc Patients Receiving Bevacizumab In Addition To Standard Chemotherapy Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

A Prechemoradiotherapy 18 F Fdg Pet Scan Arrow Indicates Focal Download Scientific Diagram
Understanding Your Fdg Pet Scan

Normal F 18 Fdg Pet Ct Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Delayed 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In The Assessment Of Residual Tumors After Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Cancer Radiology
What Is Pet Imaging Imaging Technology News
Pet Ct Appropriate Application In Lymphoma Wang Chinese Clinical Oncology

Novel Strategy For A Cocktail 18f Fluoride And 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Evaluation Of Malignancy Results Of The Pilot Phase Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Imaging The Inflammatory Activity Of Sarcoidosis European Respiratory Society

Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Cardiac Viability Perth Envision
18f Fdg Pet Ct For Detection Of Extramedullary Acute Myeloid Leukemia Haematologica
Artifacts And Normal Variants In Fdg Pet Radiology Key

Prospective Evaluation Of Physiologic Uptake Detected With True Whole Body 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Healthy Subjects Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology

Common Causes Of False Positive F18 Fdg Pet Ct Scans In Oncology
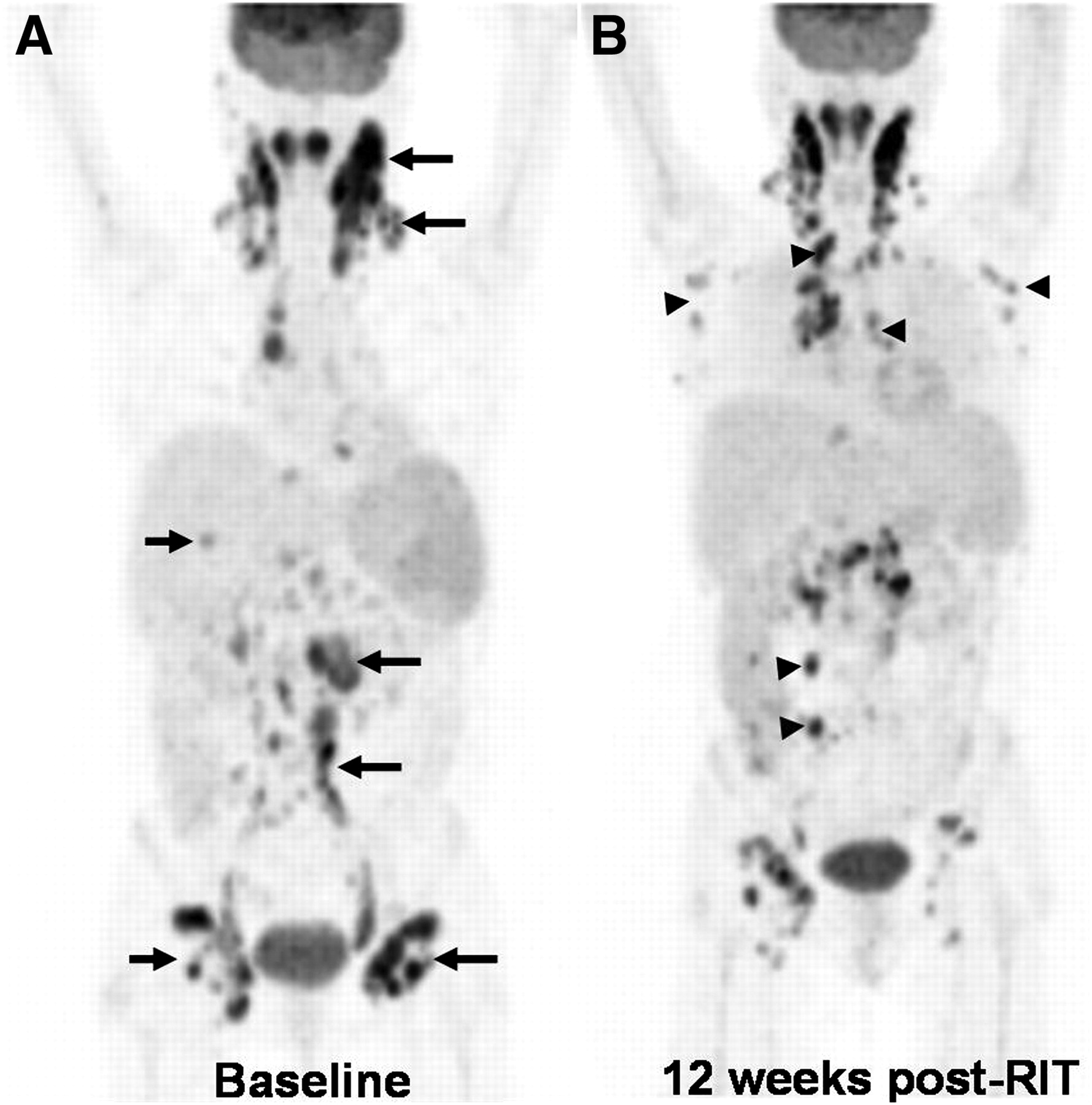
18f Fdg Pet Ct For Monitoring The Response Of Lymphoma To Radioimmunotherapy Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
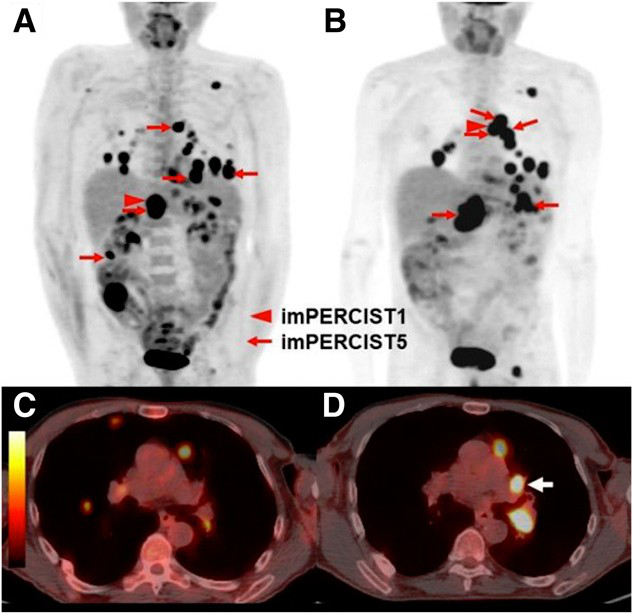
Fdg Pet Ct Aids In Melanoma Treatment Assessment

18 F Fdg Pet Imaging Evaluation On Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease And Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model Treated With Sorafenib
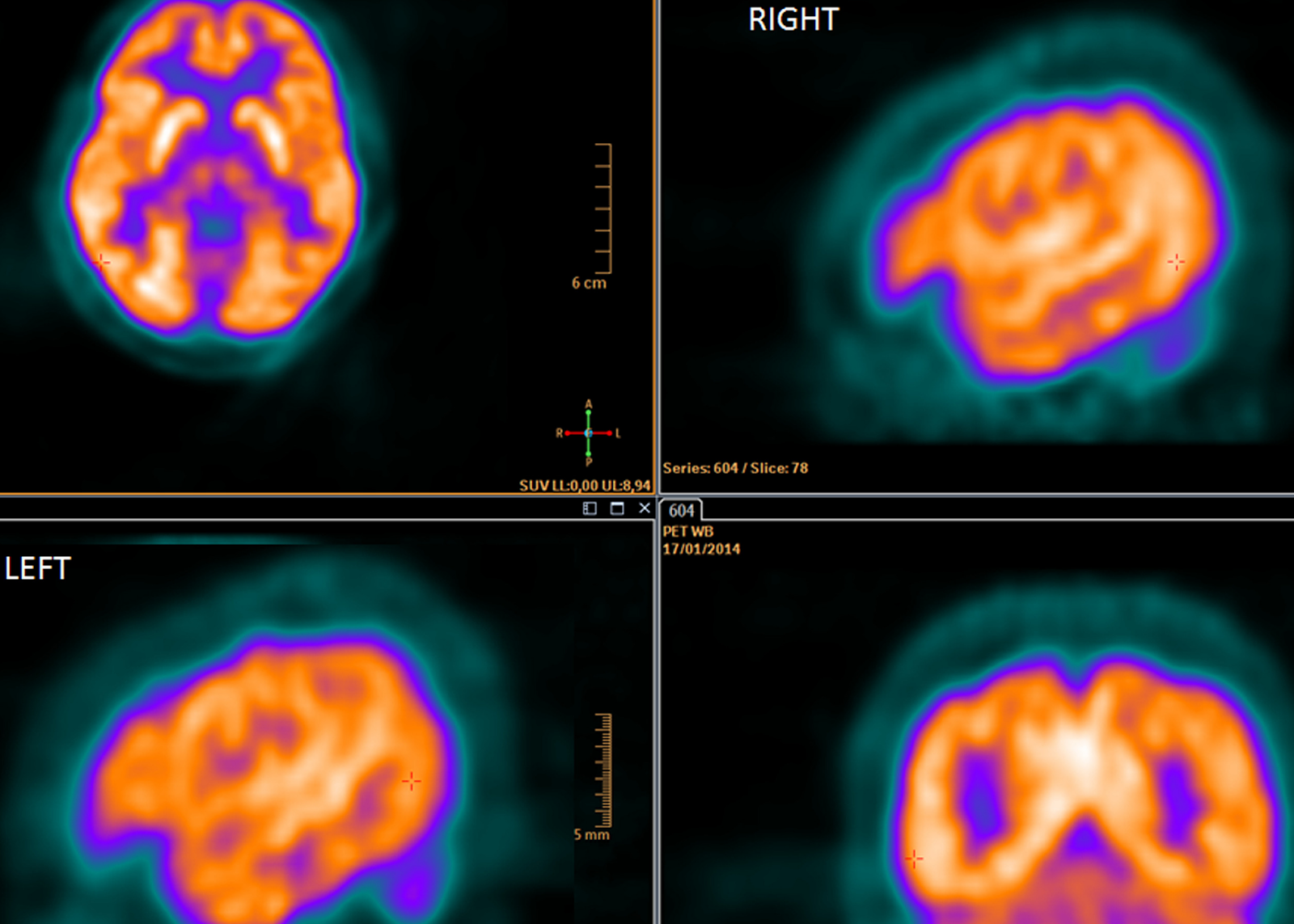
Fdg Pet Ct In Clinical Decision Making Science 2 0
Sequential 18 F Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography 18 F Fdg Pet Scan Findings In Patients With Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis During The Course Of Treatment A Prospective Observational Study Springerlink
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery
18f Fdg Pet Ct Can Be Used To Detect Non Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors

Positron Emission Tomography Wikipedia
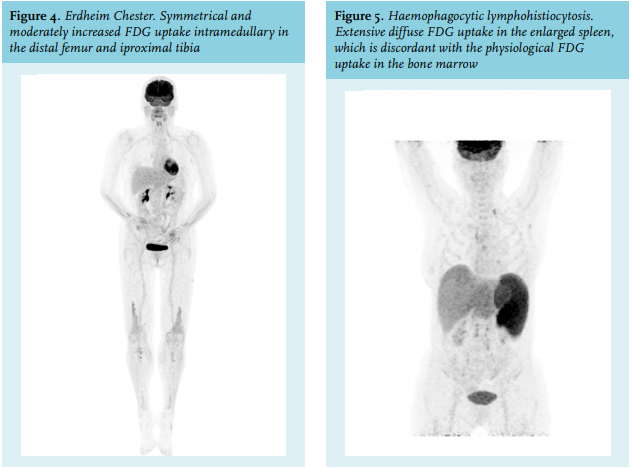
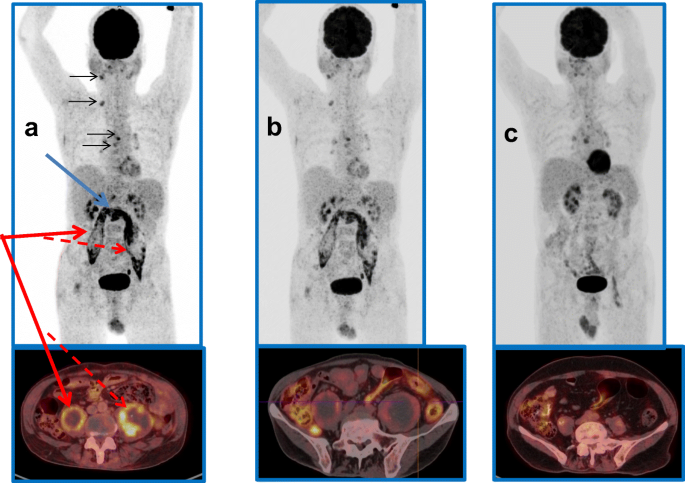
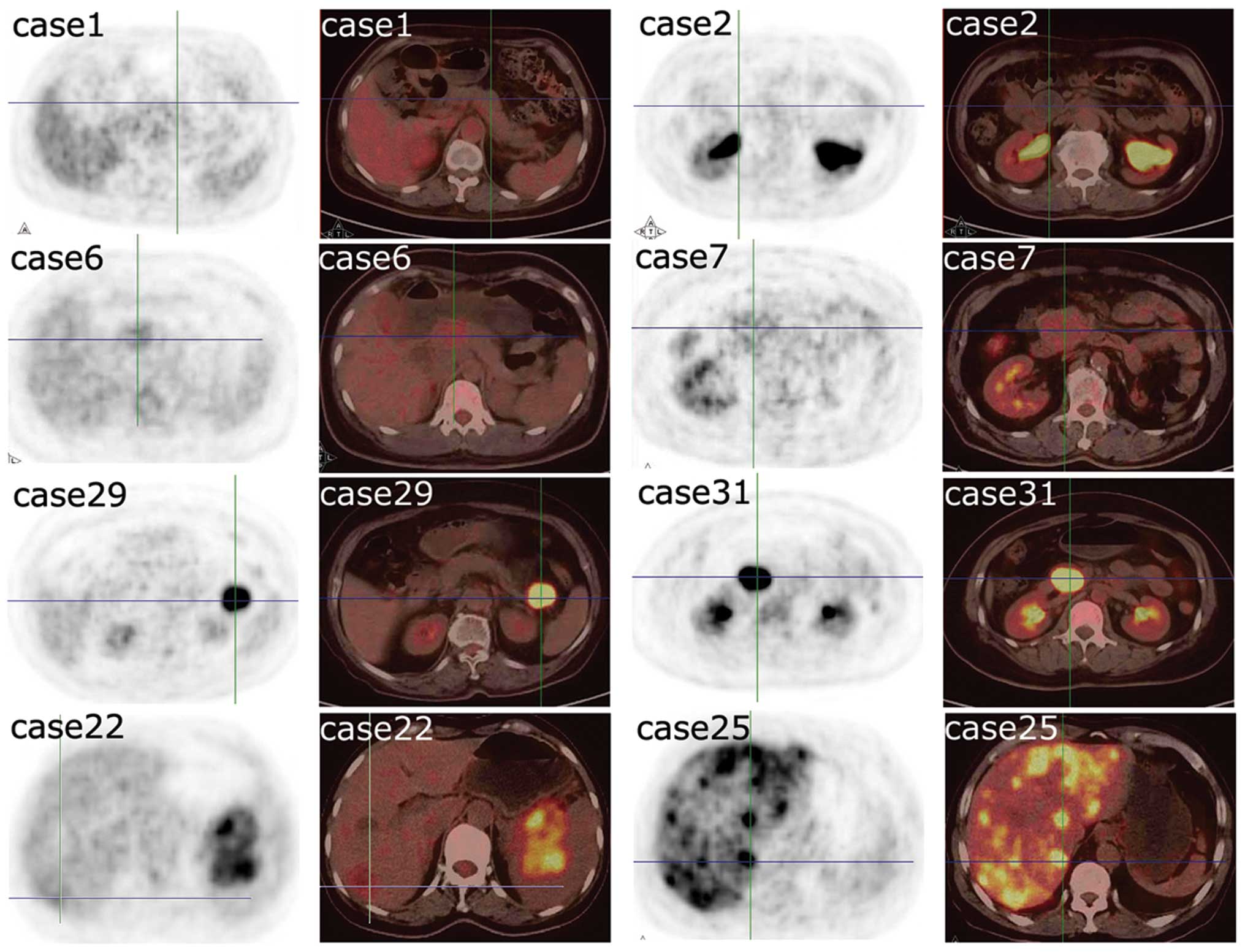
Article The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Scans To Evaluate Bone Marrow In Haemato Oncological Conditions Full Text September 19 Njm

Fdg Pet Predicts Outcomes In Paediatric Osteosarcoma Physics World

False Positive Fdg Pet Ct Resulting From Fibrous Dysplasia Of The Bone In The Work Up Of A Patient With Bladder Cancer Case Report And Review Of The Literature Iranian Journal Of Radiology

Earlier Diagnosis And Treatment Assessment Of Tuberculosis Achieved With Pet Ct Eurekalert Science News
Q Tbn And9gcthayych Dtuqhebme8rpvwg9jzkpnhxzla3dm2b1939llhmq Usqp Cau

Cardiovascular Medicine A Ring Of Fire Around The Heart Pericarditis Detected By Fdg Pet Ct

Fdg Pet Shows Tumor Dna Levels In Blood Are Linked To Nsclc Aggressiveness

Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Fdg Pet Scan Youtube

Fdg Pet Ct Normal Variants Artefacts And Pitfalls In Hepatobiliary And Pancreatic Malignancies Radiology Key

Fdg Pet Ct Scan Assessment Of Response 12 Weeks Post Radical Radiotherapy In Oropharynx Head And Neck Cancer The Impact Of P16 Status Radiotherapy And Oncology

Case Of The Quarter July 12
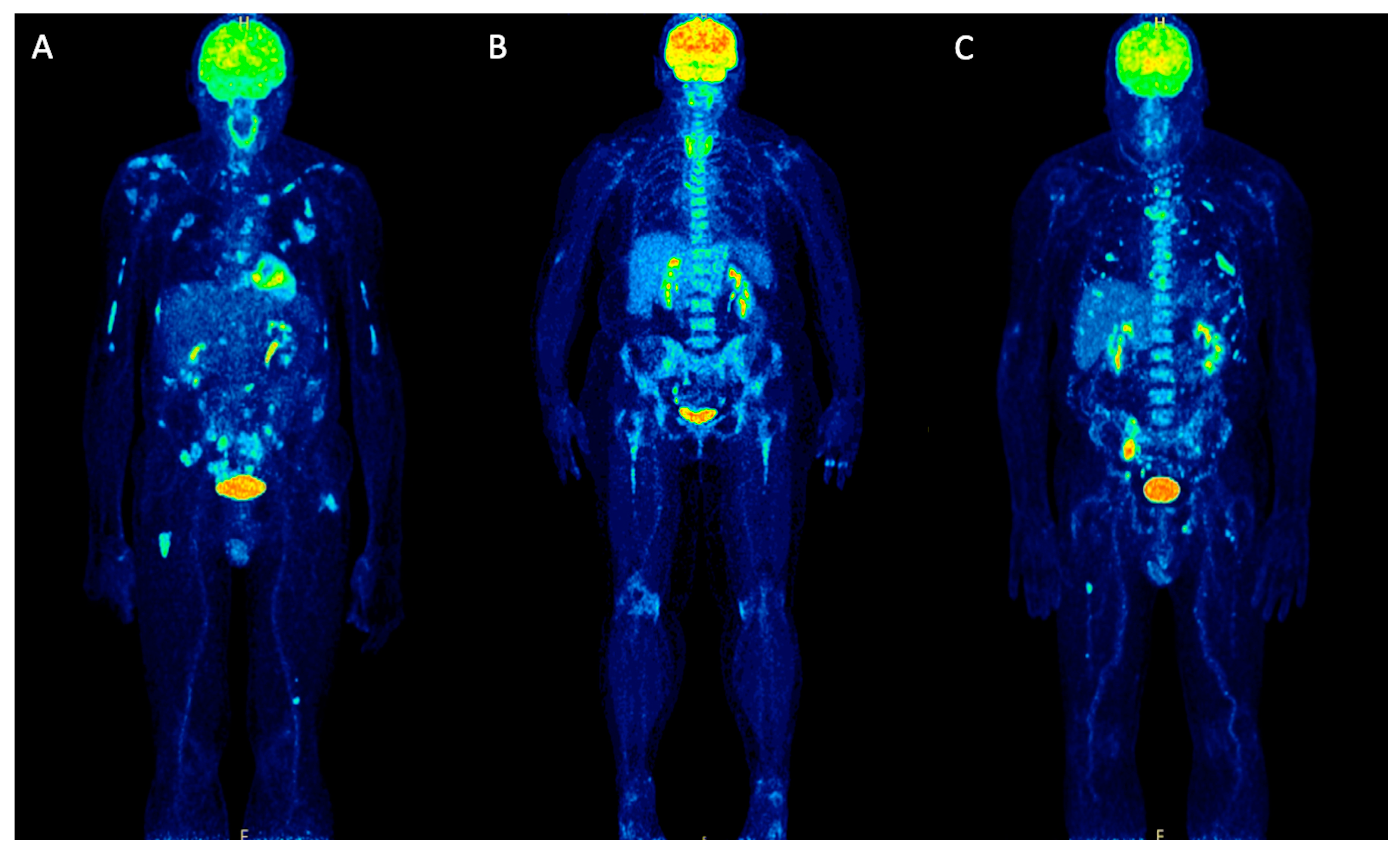
Plos One Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Patients Without Known Primary Malignancy With Skeletal Lesions Suspicious For Cancer Metastasis

The Evolving Role Of Fdg Pet Ct In The Diagnosis Staging And Treatment Of Breast Cancer Semantic Scholar

Pet Imaging In Gastric Carcinoma Intechopen

Rational Use Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma A Systematic Review Sciencedirect

Clinical Utility Of Pet Scanning In Breast Cancer Oncology Cme

Abnormal Brain Metabolism On Fdg Pet Ct Is A Common Early Finding In Autoimmune Encephalitis Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation
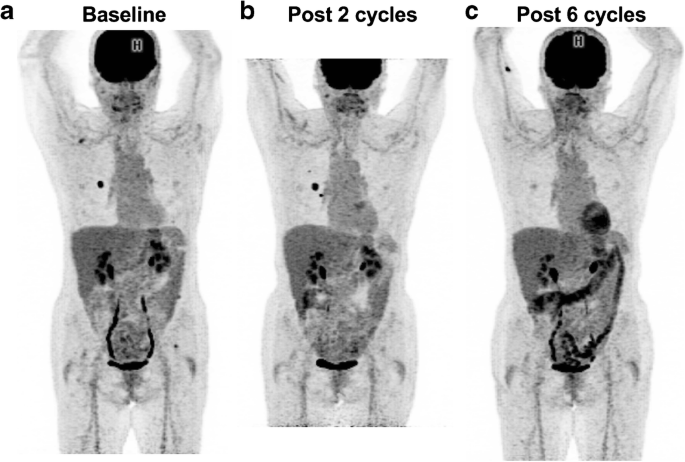
Fdg Pet Ct For Assessing Tumour Response To Immunotherapy Springerlink
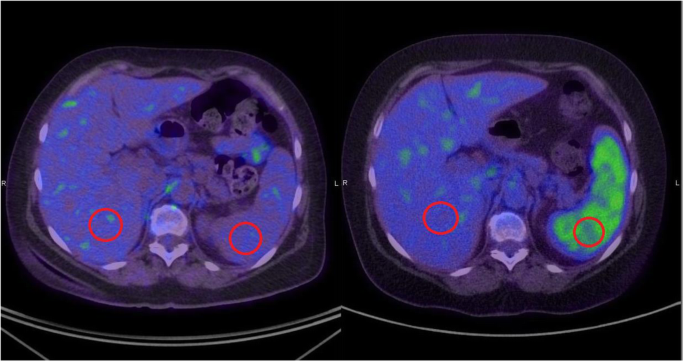
18 F Fdg Pet Ct Based Spleen To Liver Ratio Associates With Clinical Outcome To Ipilimumab In Patients With Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Imaging Full Text

Comparison Of 18f Naf Pet Ct And 18f Fdg Pet Ct For Detection Of Skull Base Invasion And Osseous Metastases In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Novel Strategy For A Cocktail 18f Fluoride And 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Evaluation Of Malignancy Results Of The Pilot Phase Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Coronal 18 F Fdg Pet Scan Shows Normal Physiologic 18 F Fdg Uptake In Download Scientific Diagram

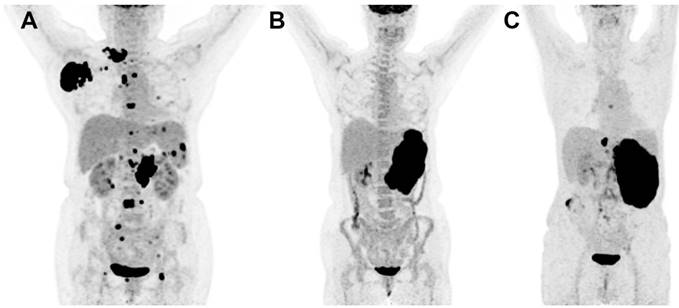
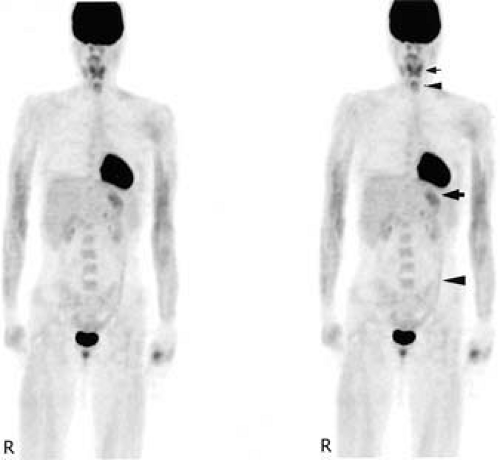
Fdg Pet Scan Images Of A Patient With Metastatic Melanoma Before A Download Scientific Diagram

Metabolic Characterization Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer With Baseline Fdg Pet Ct Relationship With Pathologic Response After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Receptor Status And Tumor Grade Clinical Breast Cancer
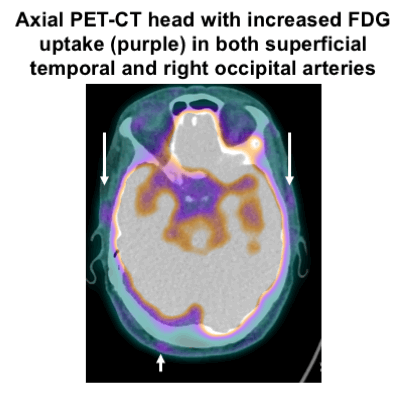
Prevalence And Distribution Of Vascular Fdg Uptake On Positron Emission Tomography Pet Ct In Patients Suspected Of Having Giant Cell Arteritis Interim Results From The Giant Cell Arteritis And Pet Scan Gaps
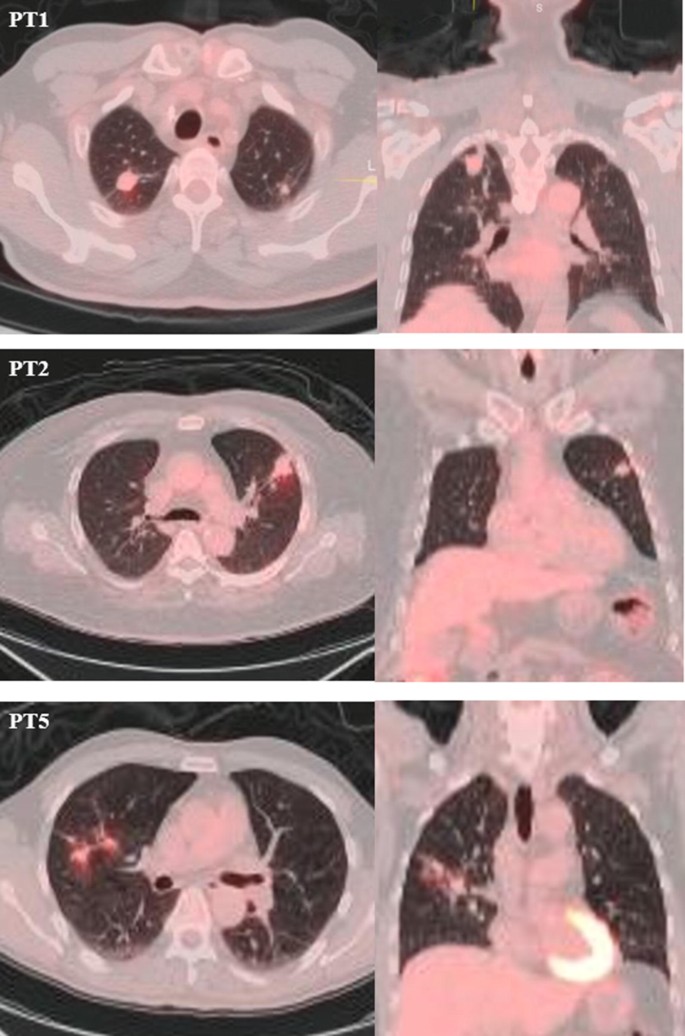
Fdg Pet Ct Activity Leads To The Diagnosis Of Unsuspected Tb A Retrospective Study Bmc Research Notes Full Text
Q Tbn And9gctl4i6z5fzghcdvnea1hyysxoib3b0yxekob3w Yqbn6ndk6wdi Usqp Cau
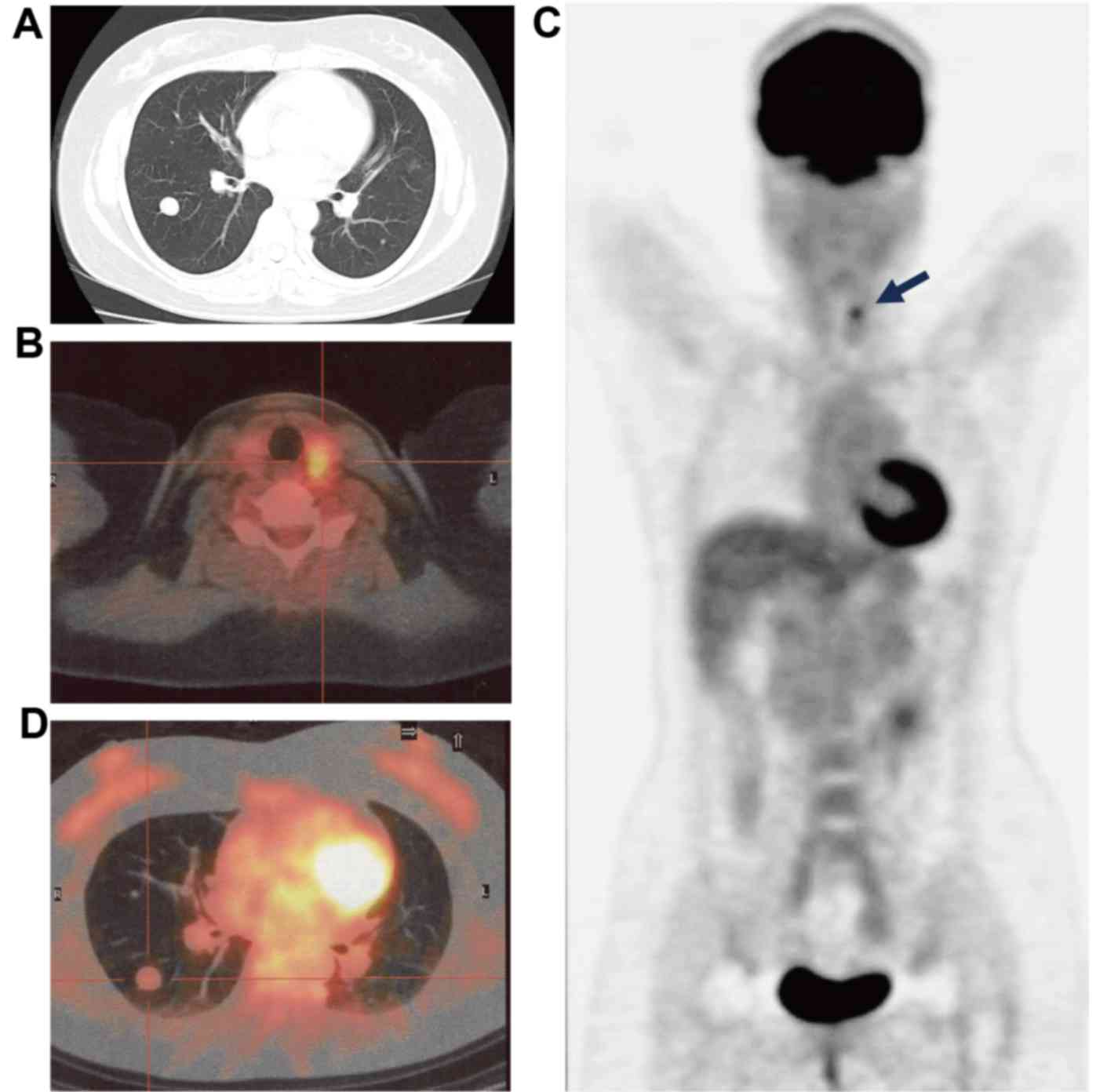
Benign Metastasizing Leiomyoma And 18 Fdg Pet Ct A Case Report And Literature Review

Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery
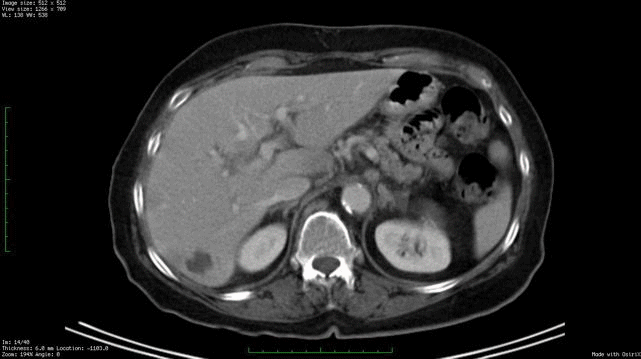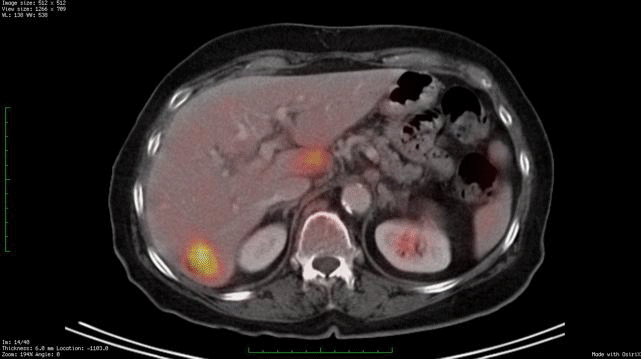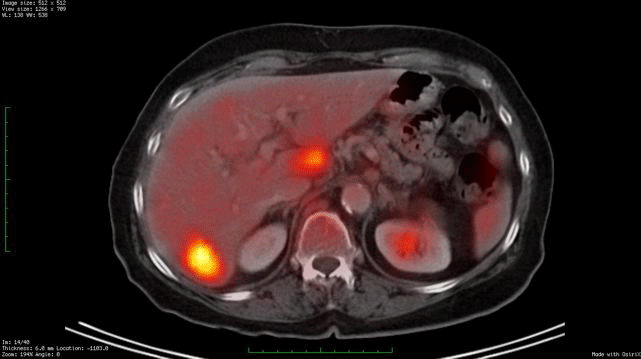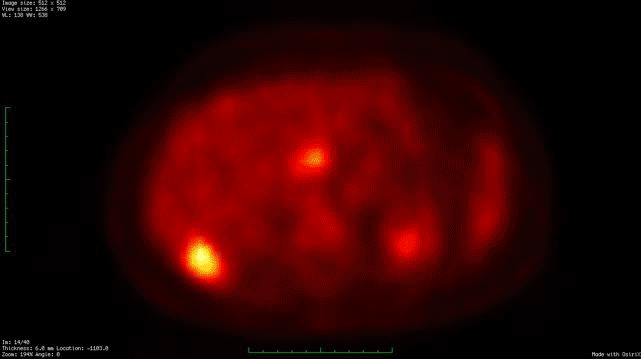
Whole Body Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Cancer New York Eye Cancer Center
Q Tbn And9gcqmb6cff 1xe18vnoqntqqyxunenn9eqvxbrmcvtaueevkxq2ay Usqp Cau
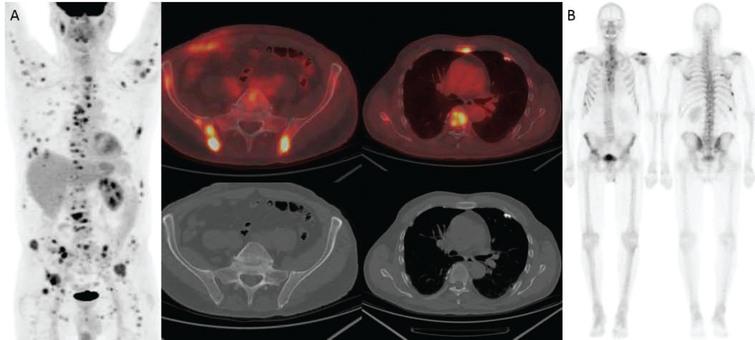
Utility Of Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma With Osseous Metastases Comparison With Ct And 99mtc Mdp Bone Scan In A Prospective Clinical Trial Ios Press

Accuracy Of Positron Emission Tomography Ecr Journal
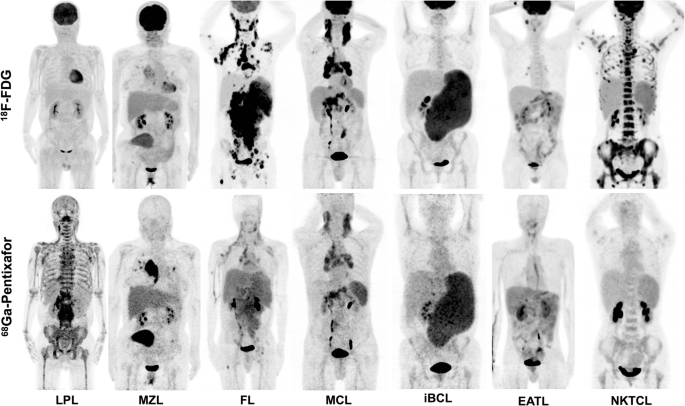
Preliminary Evidence Of Imaging Of Chemokine Receptor 4 Targeted Pet Ct With 68 Ga Pentixafor In Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Comparison To 18 F Fdg Ejnmmi Research Full Text

18f Fdg Pet Scan Over Time A Diffuse Thoracic Lymph Node Metastases Download Scientific Diagram
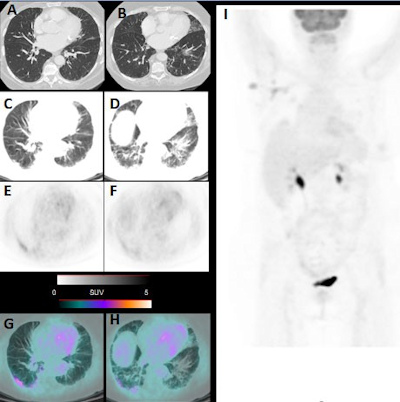
Incidental Covid 19 Findings Seen On Routine Fdg Pet Ct

Fdg Pet The Jagust Lab
Repeatability Of Brown Adipose Tissue Measurements On Fdg Pet Ct Following A Simple Cooling Procedure For Bat Activation

Figure 2 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scanning Identifying Lead Endocarditis And Gastro Intestinal Polyps Radcliffecardiology
Q Tbn And9gcqshimruwwzfcgghj6wznqjpsl27i4nz3ip3e7jl2txut8ccvnd Usqp Cau
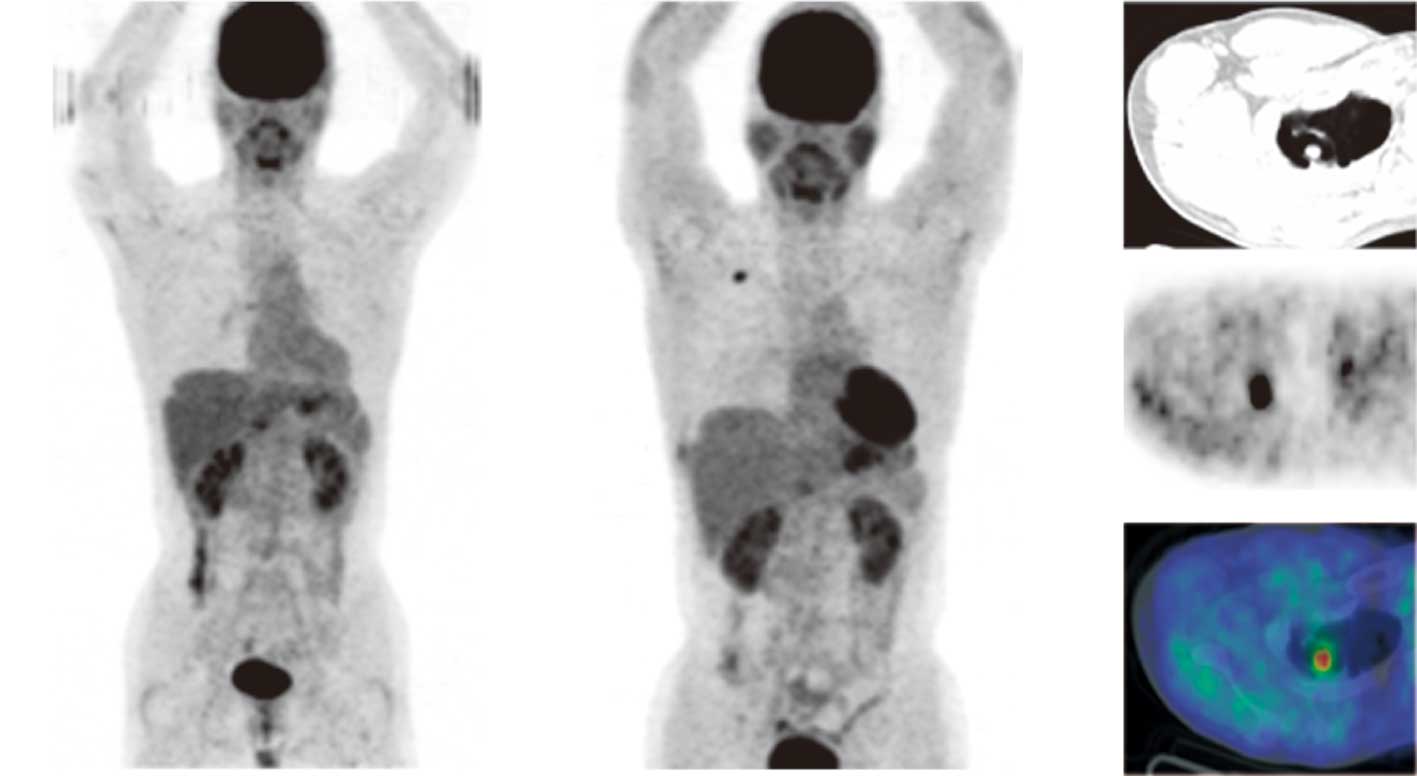
A Case Of Primary Lung Cancer Lesion Demonstrated By F 18 Fdg Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography Pet Ct One Year After The Detection Of Metastatic Brain Tumor

Pet Imaging In Gastric Carcinoma Intechopen
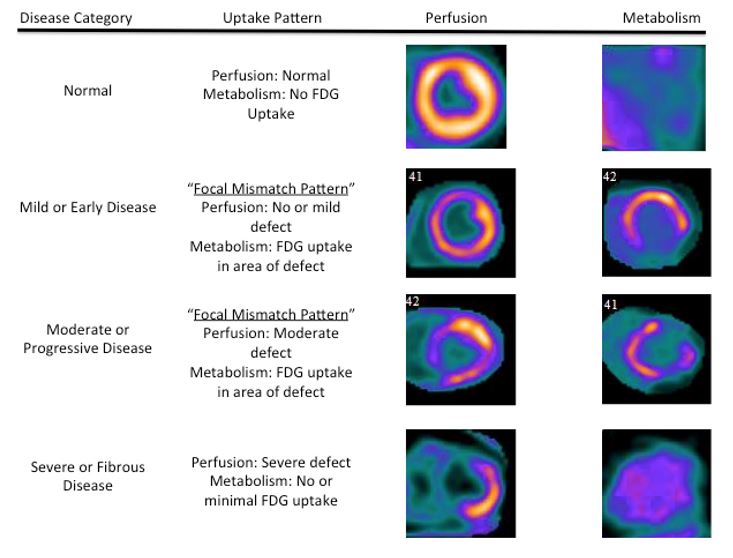
Fdg Pet Is A Superior Tool In The Diagnosis And Management Of Cardiac Sarcoidosis American College Of Cardiology
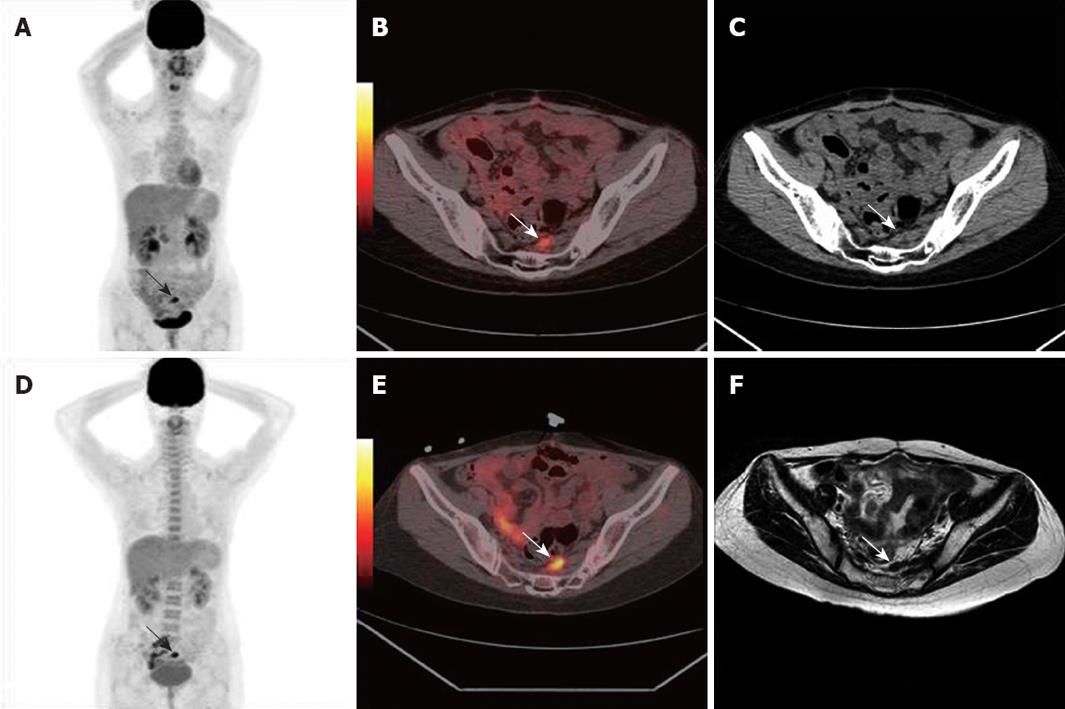
Clinical Value Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Assessing Suspicious Relapse After Rectal Cancer Resection

18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of Colorectal Cancer A Pictorial Review Postgraduate Medical Journal
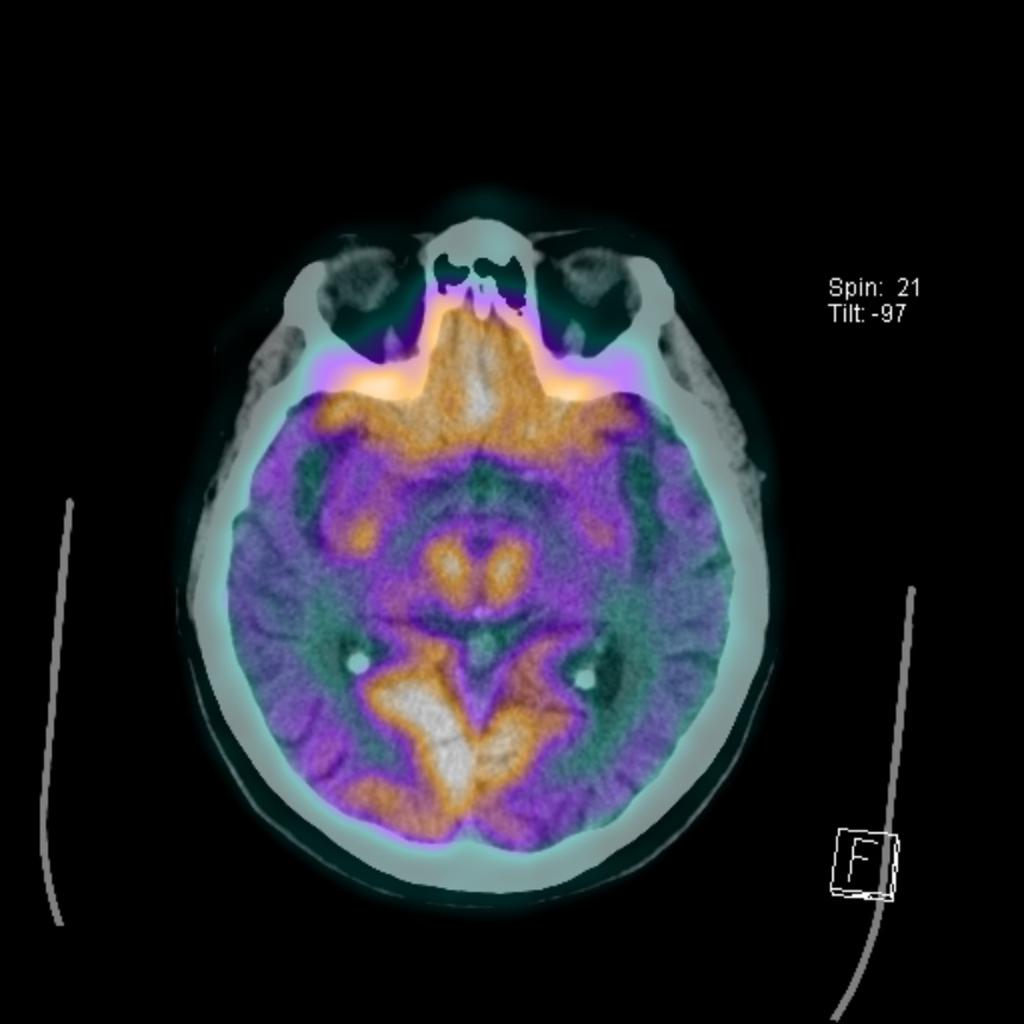
Alzheimer Disease Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

18f Fdg Pet Ct Normal Variants Artefacts And Pitfalls In Lymphoma Radiology Key
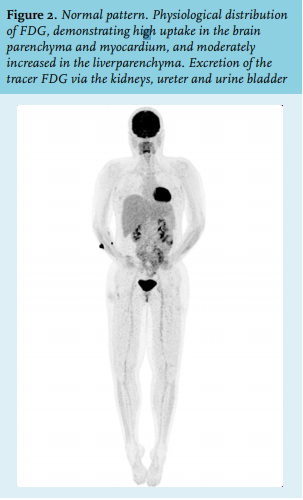
Article The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Scans To Evaluate Bone Marrow In Haemato Oncological Conditions Full Text September 19 Njm

Fdg Pet Scan Cedars Sinai

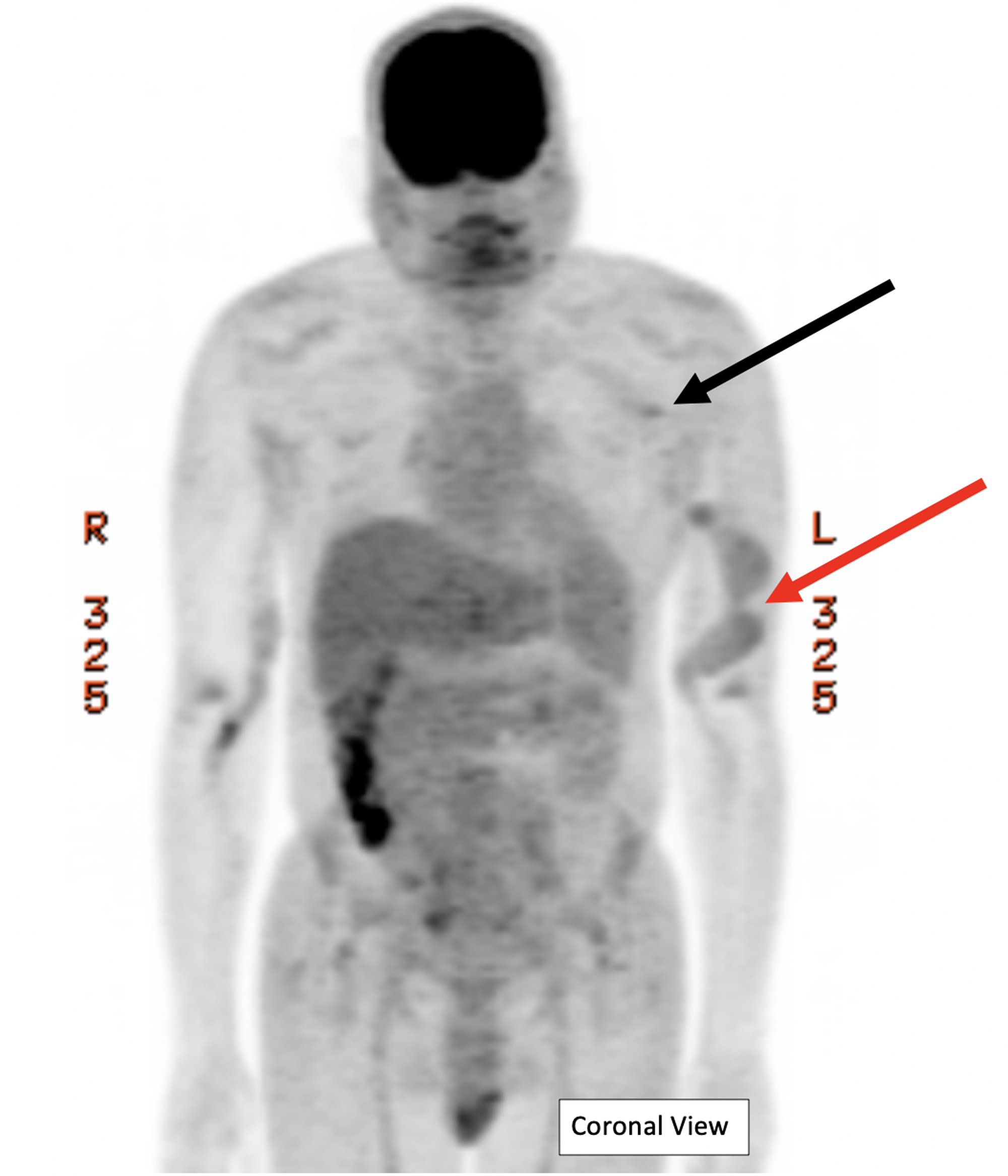
18 F Fdg Pet Scan And Ct Scan Coronal View Of The 18 F Fdg Pet In Download Scientific Diagram
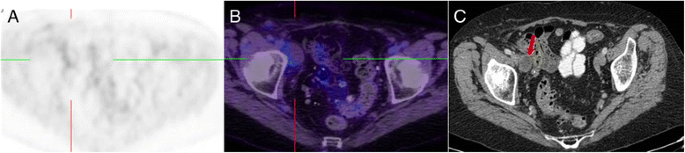
How We Read Oncologic Fdg Pet Ct Cancer Imaging Full Text

Inguinal And Scrotal Extramammary Paget S Disease 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging

Pet Imaging In Hematology Ask Hematologist Understand Hematology

Common Causes Of False Positive F18 Fdg Pet Ct Scans In Oncology

Fdg Pet Ct Has Limits In Esophageal Cancer Follow Up
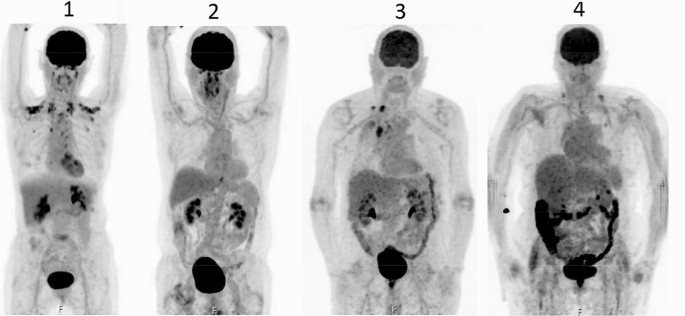
Discontinuation Of Metformin To Prevent Metformin Induced High Colonic Fdg Uptake Is 48 H Sufficient Springerlink

Fdg Pet Imaging Reliable In Identifying Abnormalities In Parkinson Disease Neurology Advisor

Towards More Accurate 18f Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography 18f Fdg Pet Imaging In Active And Latent Tuberculosis International Journal Of Infectious Diseases
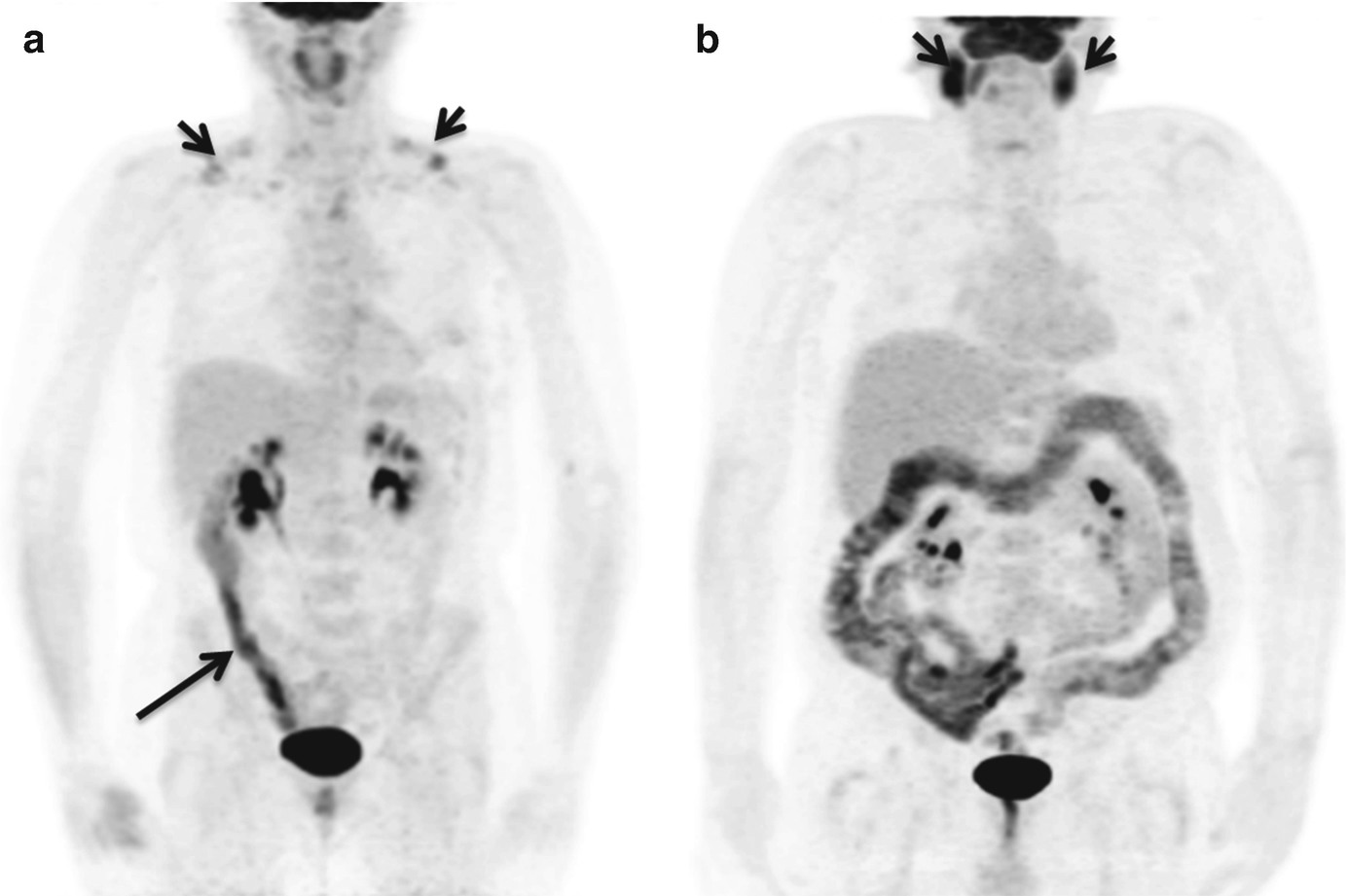
Role Of Fdg Pet Ct In Colorectal Cancer Springerlink

Acute Saddle Pulmonary Embolism On 18f Fdg Pet Ct Diagnosis By Functional Imaging Singh 19 Respirology Case Reports Wiley Online Library
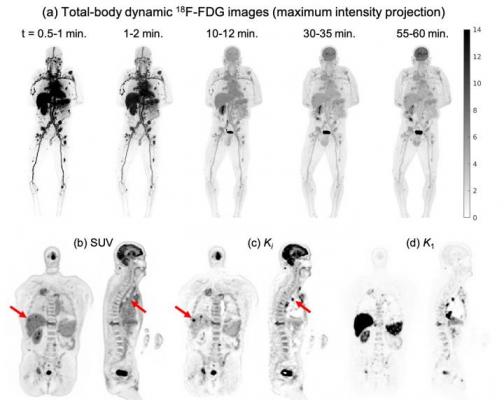
Total Body Dynamic Pet Successfully Detects Metastatic Cancer Imaging Technology News
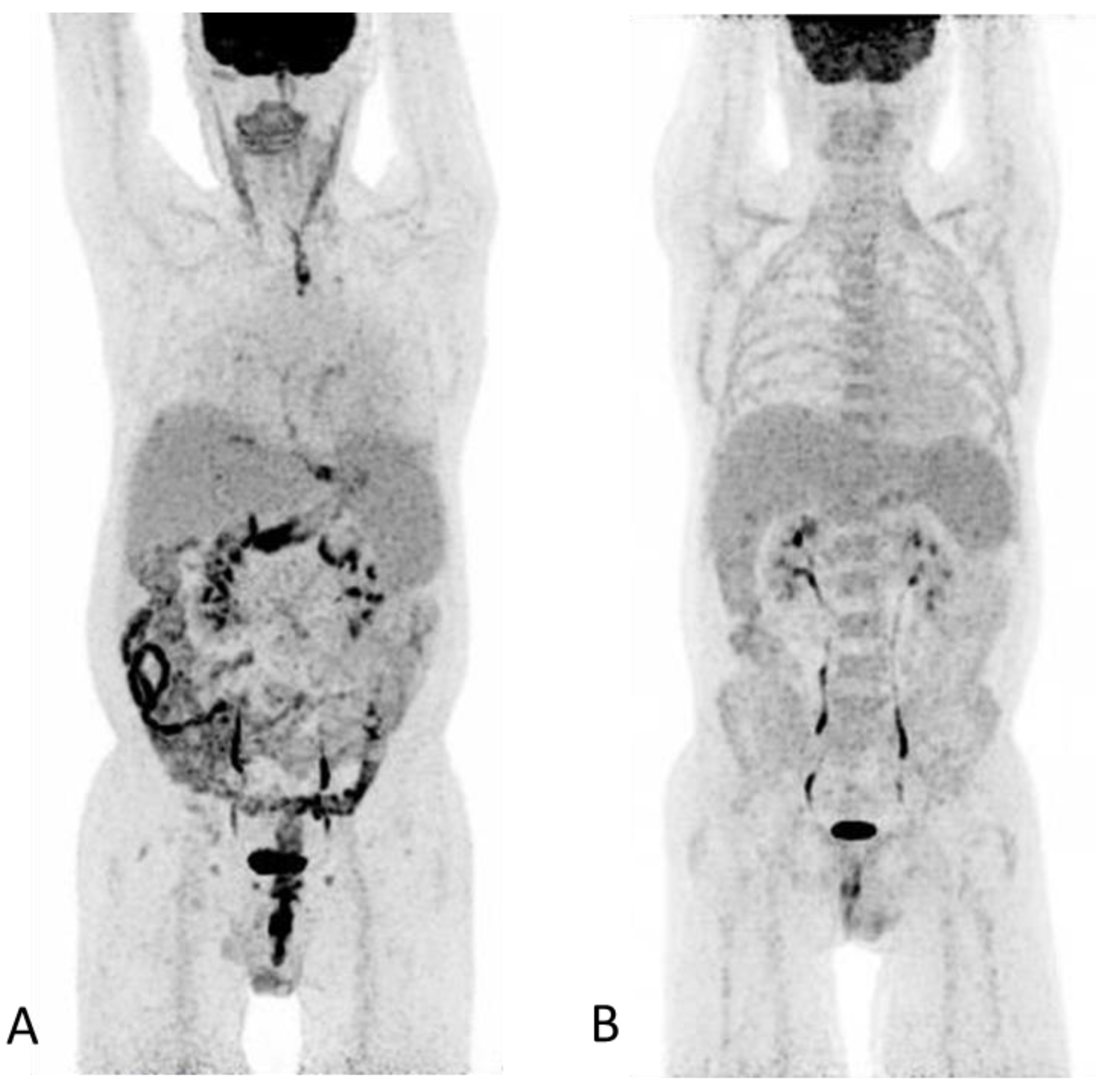
Diagnostics Free Full Text 18 F Fdg Pet Ct In Extensive Graft Versus Host Disease Of The Gastrointestinal Tract Following Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation

Molecular Imaging Radlink
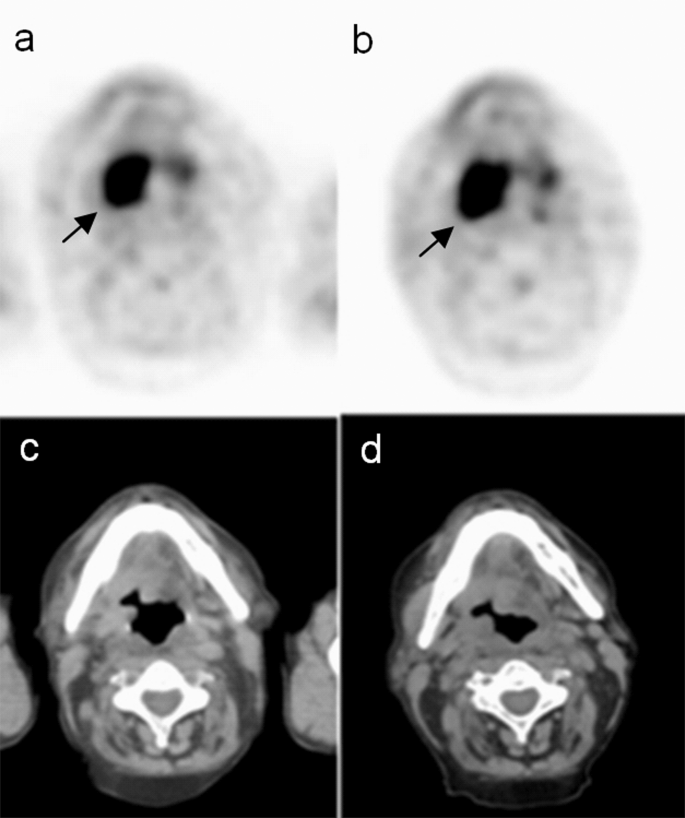
Sequential Delayed 18 F Fdg Pet Ct Examinations In The Pharynx Scientific Reports
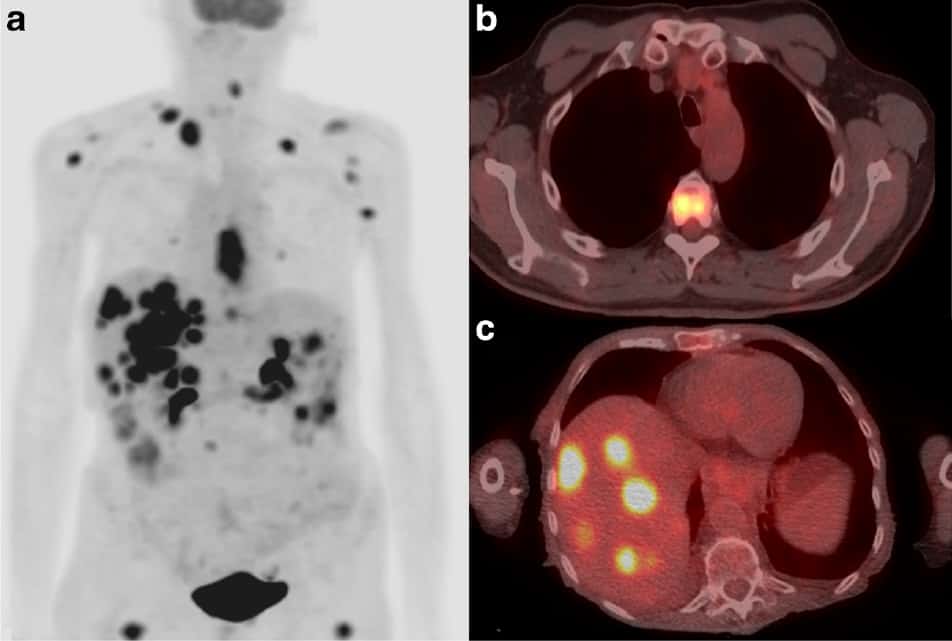
Fdg Pet Ct Provides Valuable Oesophageal Cancer Updates Physics World
Cureus Positron Emission Tomography With Fluorodeoxyglucose Incidental Detection Of Colon Cancer In A Patient S Follow Up For Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma During The Covid 19 Pandemic A Case Report
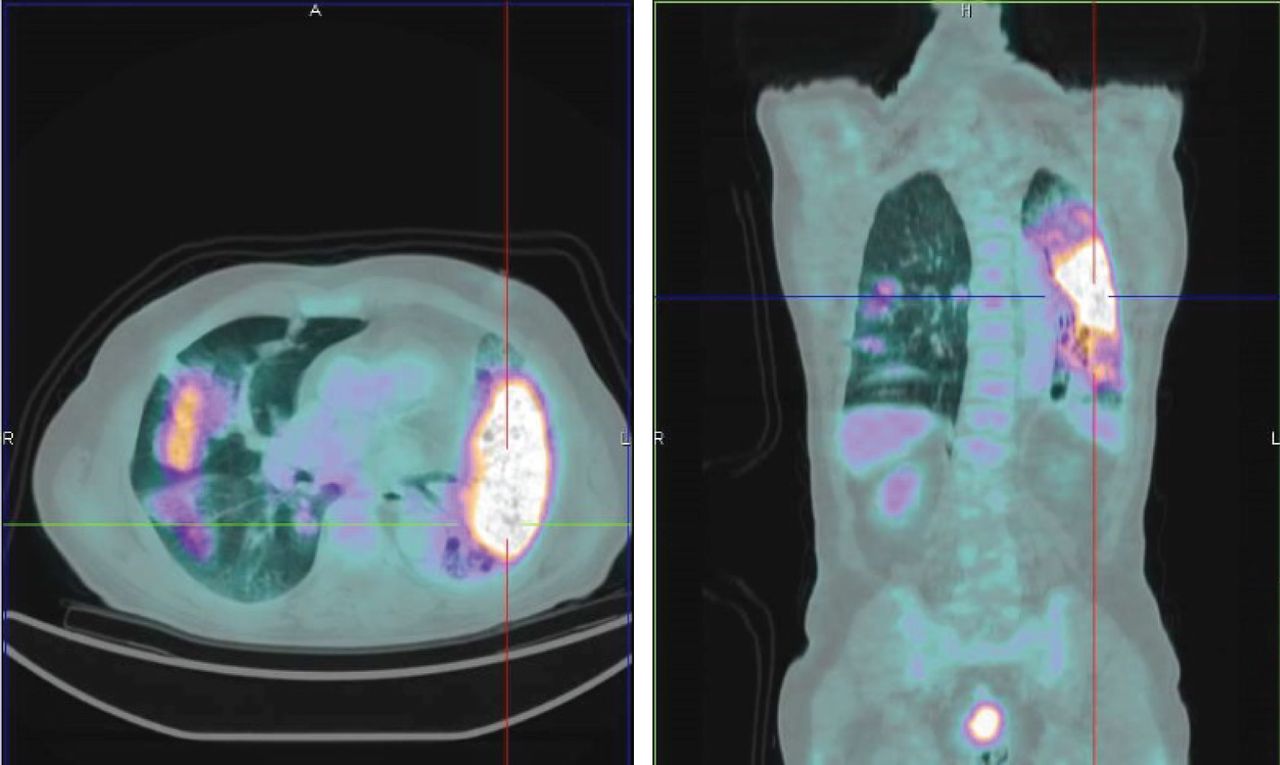
Pet Ct In Nononcological Lung Diseases Current Applications And Future Perspectives European Respiratory Society

Scar Sarcoidosis A Rare Entity Found By 18f Fdg Pet Ct Sciencedirect
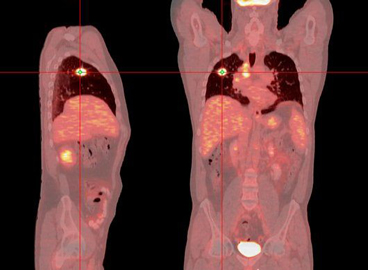
Positron Emission Tomography Scan Pet Scan Lhsc

Fdg Pet For Cardiac Sarcoid American College Of Cardiology

Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Of Gynecologic Malignancies Glowm
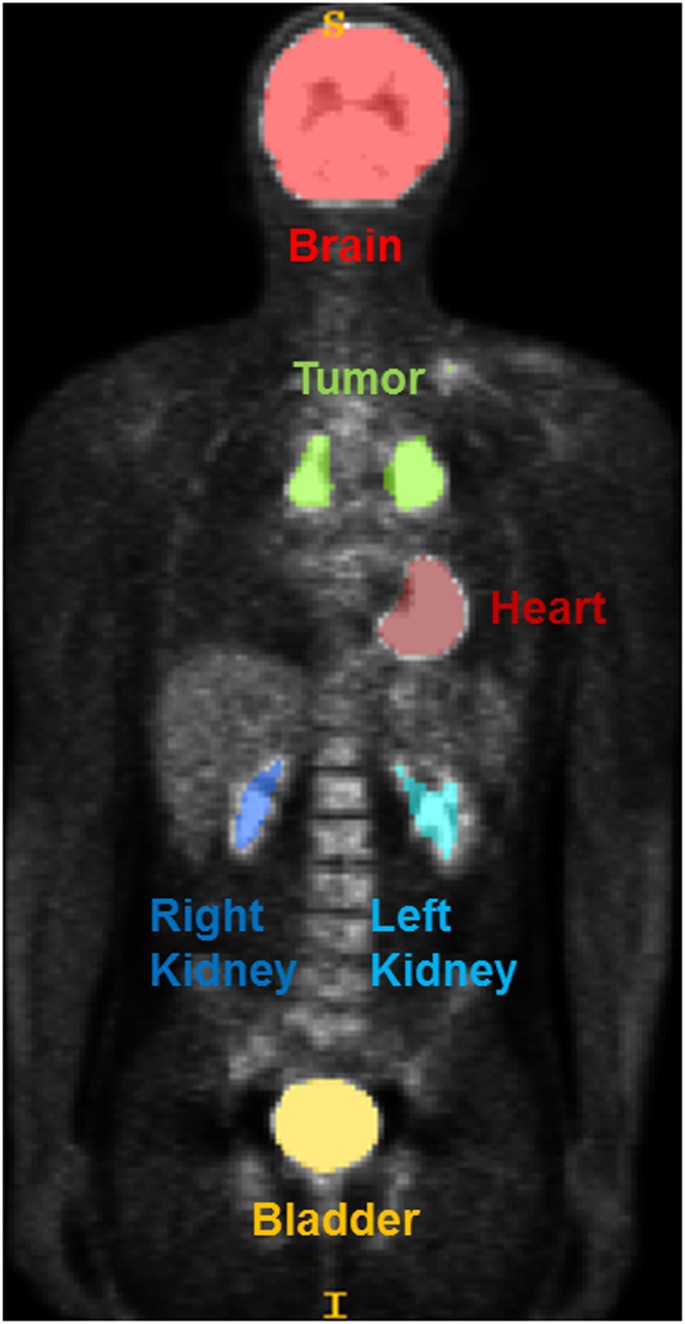
Radiomics Features Differentiate Between Normal And Tumoral High Fdg Uptake Scientific Reports
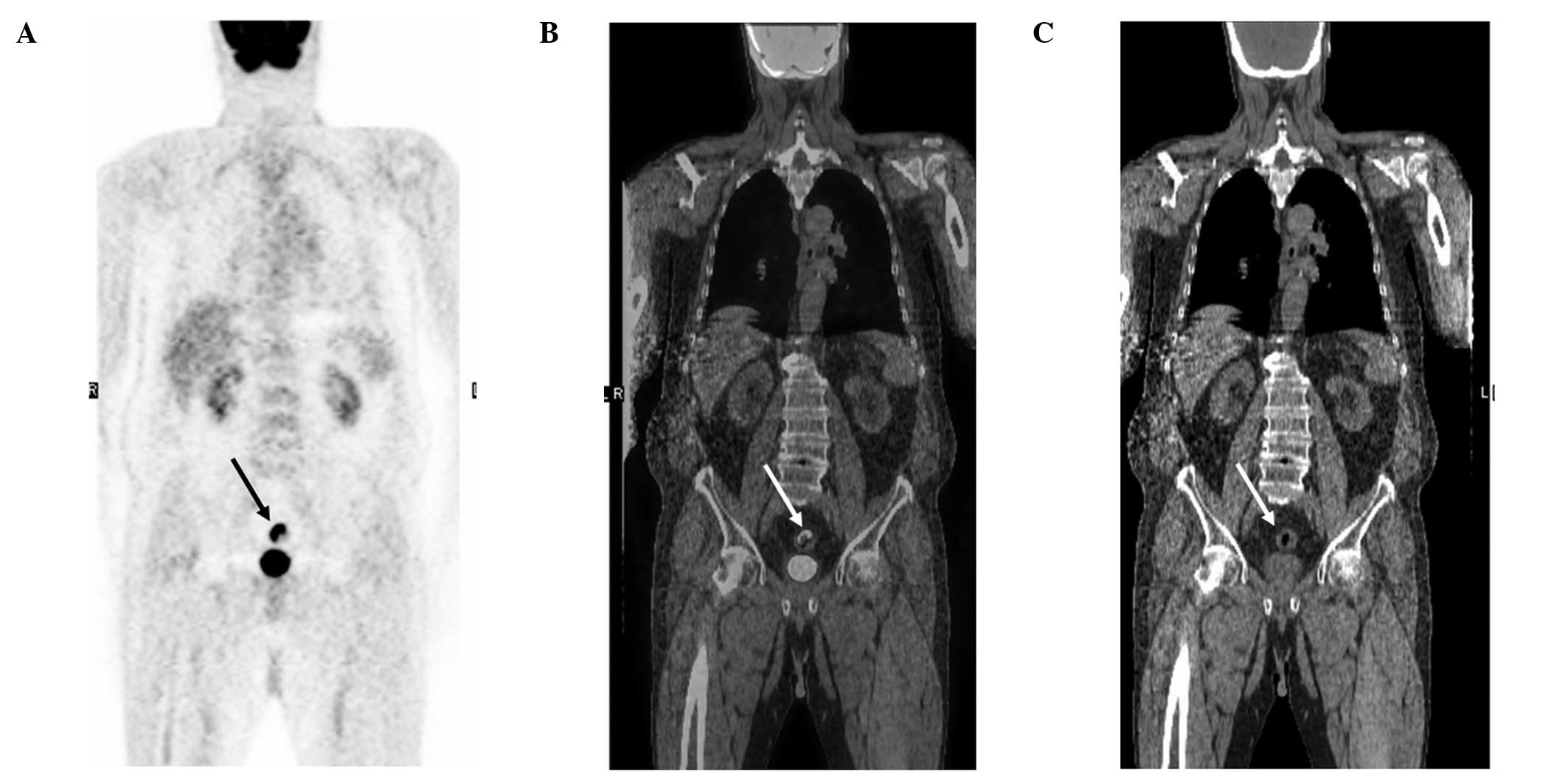
Correlation Between Incidental Fdg Pet Ct Colorectal Observations And Endoscopic And Histopathological Results

Pet Scans And Alzheimer S Bluegrass Regional Imaging
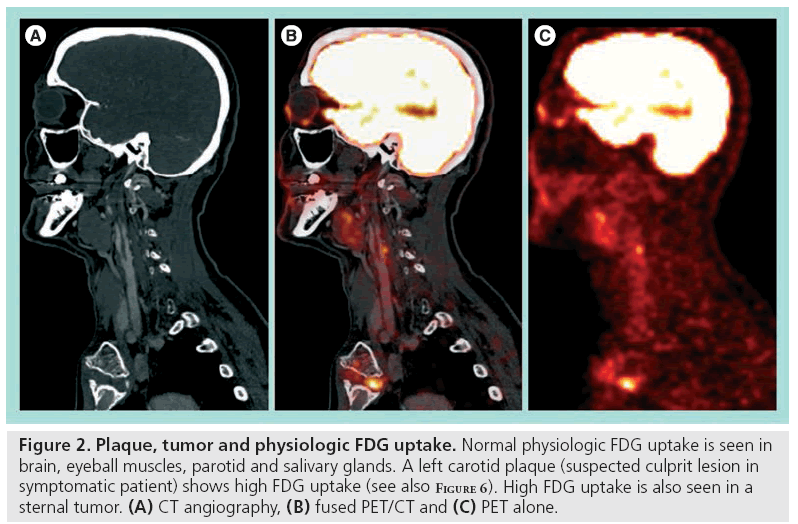
Carotid Plaque Imaging With Fdg Pet And Ultrasound



