Adenocarcinoma In Situ De Cervix
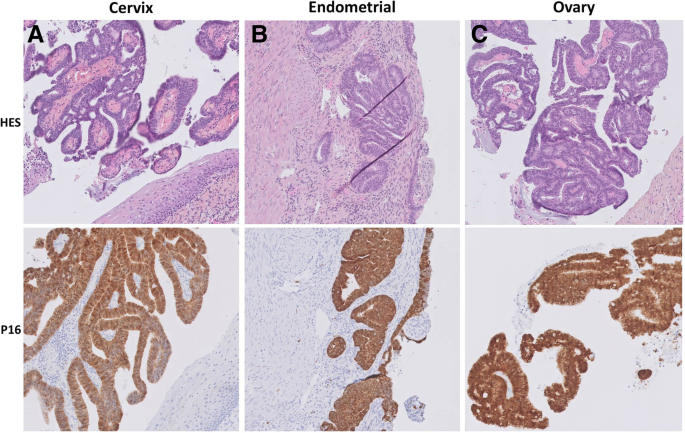
Hpv Dna Integration Site As Proof Of The Origin Of Ovarian Metastasis From Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Three Case Reports Bmc Cancer Full Text
Cervical Cancer Uterine Cancer Cervix Uterus Png 600x600px Cervical Cancer Breast Cancer Cancer Carcinoma Carcinoma In
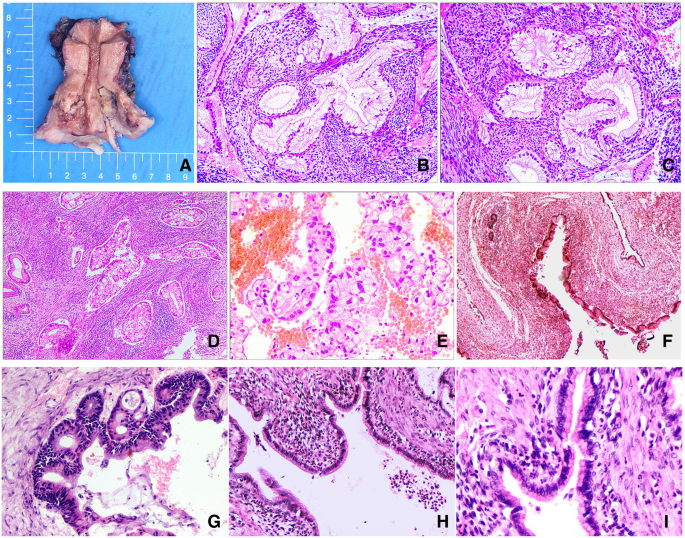
Primary Endocervical Gastric Type Adenocarcinoma A Clinicopathologic And Immunohistochemical Analysis Of 23 Cases Diagnostic Pathology Full Text

Cervical Cancer Amboss
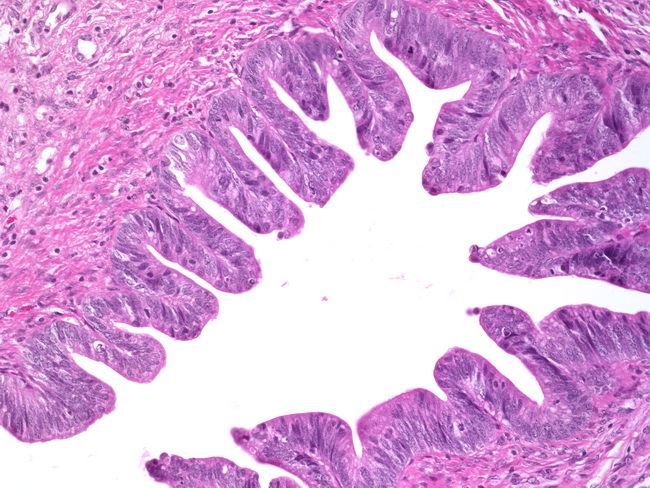
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images

Vaginal Carcinoma After Cervical Dysplasia International Journal Of Gynecologic Cancer
Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ;.

Adenocarcinoma in situ de cervix. The aim of this study was to ascertain whether cold knife conization alone for cervical adenocarcinoma in situ is safe Methods One hundred consecutive patients with a histologically proven adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix were studied from 1970 to 1992 Results. Adenocarcinoma of the cervix rarer (5%) and can have several subtypes which include 11, clear cell carcinoma of the cervix endometroid carcinoma of the cervix ~7% of adenocarcinomas 21 mucinous carcinoma of the cervix adenoma malignum ~3% of adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix is a rare condition and is considered a precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma The standard treatment for cervical AIS is hysterectomy, which is a more aggressive treatment than that used for squamous intraepithelial lesions.
Adenocarcinoma is usually high up in the cervix, like mine was, so your cervix looks normal during a pelvic exam, and pap smears miss it a lot of the time We have to be our own advocates sometimes I wish you ladies all the best!!!. High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL) of cervix (R);. METHODS Sixtyone women with adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix treated between April 1984 and December 1993 were identified Medical records and histologic material were reviewed Mixed lesions with both adenocarcinoma in situ and squamous cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) were included RESULTS The mean age of the patients was 359 years.
Materials and Methods Patients with histologically proven adenocarcinoma insitu (AIS) or invasive endocervical adenocarcinoma (EAC) over a 17yearperiod () were identified The TPPT immediately preceding the histological diagnosis of AIS/ECA was designated as index Pap (IP). For the cytology see Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (cytology) Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, also adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine endocervix, is preinvasive change of the uterine endocervix It is closely tied to HPV infection If the context is clear, it may be referred to as adenocarcinoma in situ, abbreviated AIS. Cytologic evidence of malignancy of cervix without histologic confirmation (R);.
After squamous cell cancers, Adenocarcinomas of Cervix are the second most common type of tumors, affecting the cervix This differentiation is based on the appearance of cells, when observed under a microscope Screening with Pap smear helps in early detection of precancers and cancers. The stage of a cervical cancer is the most important factor in choosing treatment But other factors can also affect your treatment options, including the exact location of the cancer within the cervix, the type of cancer (squamous cell or adenocarcinoma), your age and overall health, and whether you want to have children. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix is a premalignant glandular condition AIS is the only known precursor to cervical adenocarcinoma and, in many cases, invasive disease can be prevented with appropriate management.
Abstract Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix iscausedbyinfectionwithhighriskhumanpapillomavirusand is the recognized precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix Because most AIS lesions are caused by HPV 16/18 infection, prophylactic HPV vaccination is an important step towardpreventionofAIS,potentiallyreducingtheincidenceof invasive adenocarcinoma. La incidencia del adenocarcinomade cérvix está aumentando, así como el de suslesiones precursoras, es decir, el adenocarcinoma in situ El incremento se considera potencialmente atribuible al aumento dela infección por el virus del papiloma humano tipo18(12). The initial Pap smear that led to the patient's referral was abnormal in 39 (98%) Initial cervical biopsies showed adenocarcinoma in situ and/or glandular dysplasia in 28 (70%), squamous dysplasia in 2 (5%), chronic inflammation in 2 (5%), and no pathologic changes in 2 (5%) patients.
Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma of the cervix is a malignant neoplasm that involves the glandular epithelium of the cervix There are several types of adenocarcinoma, most of which have similar aetiology and risk factors to squamous cell carcinoma. El adenocarcinoma in situ cervical es una entidad que no se puede diagnosticar exclusivamente por biopsia (dirigida o legrado endocervical), si no que es preciso confirmarla mediante conización cervical El tratamiento más adecuado para este tipo de paciente es la histerectomía total Los factores predictivos más importantes para el desarrollo de. Carcinoma of the cervix is a malignancy arising from the cervix It is the third most common gynecologic malignancy (after endometrial and ovarian) Epidemiology It typically presents in younger women with an average age of onset at around 45 y.
Cervical intraepithelial glandular neoplasia;. Carcinoma in situ of cervix uteri Includes cervical adenocarcinoma in situ cervical intraepithelial glandular neoplasia cervical intraepithelial neoplasia III CIN III severe dysplasia of cervix uteri. Las células columnares tienen el núcleo en su base, en el adenocarcinoma in Situ, comenzamos a observar qué los núcleos se ubican en diferentes posiciones a lo largo del cilindro, de igual manera se afilan las bases de la célula y al observarla al microscopio vemos que parecen querer desprenderse del conjunto, a este fenómeno le llamamos en el argot de la Citologia "emplumamiento" o.
The term carcinoma in situ is a term used to define and describe a cancer that is only present in the cells where it started and has not spread to any nearby tissues Carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of a cancer, and is, at this stage, considered "noninvasive" With regard to staging, carcinoma in situ is considered stage 0 cancer. Adenocarcinoma in situ of cervix is increasingly managed by local excision rather than hysterectomy and this study will ascertain if conservative management by excision alone is adequate. Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) arises in the glandular epithelium of the uterine cervix and is the recognized precursor to invasive adenocarcinoma 1 • The incidence rate of AIS is much lower compared with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 2.
Fourteen cases of adenocarcinoma in situ (ACIS) of the cervix in patients 30 to 52 years old were studied In its pure form (four cases), ACIS was discovered cytologically, but when associated with a squamous abnormality (ten cases), it was found histologically Two different types of ACIS were distinguished both histologically and cytologically The first type, which was similar to the common form reported in the medical literature, predominated in 12 cases, and consisted of cells with. The precursor lesion is dysplasia cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or adenocarcinoma in situ, which can subsequently become invasive cancer This process can be quite slow Longitudinal studies have shown that in patients with untreated in situ cervical cancer, 30% to 70% will develop invasive carcinoma over a period of 10 to 12 years. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix is caused by infection with highrisk human papillomavirus and is the recognized precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
Most cases of cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and adenocarcinoma are of the usual or endocervical type However, intestinal types of AIS and adenocarcinoma exist With an intestinaltype adenocarcinoma in the cervix, the question may arise as to whether one is dealing with a primary cervical neoplasm or direct or secondary spread from an intestinal adenocarcinoma. D069 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of cervix, unspecified The code D069 is valid during the fiscal year 21 from October 01, through September 30, 21 for the submission of HIPAAcovered transactions The ICD10CM code D069 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like adenocarcinoma in situ of cervix, carcinoma in situ of uterine cervix, carcinoma in situ of uterus, carcinoma of cervix stage 0, cervical. Objective This study aimed to review literature if therapeutic strategies in adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix could lead to a more conservative approach Methods A review of the literature was conducted using a Medline search for articles published between 1966 and 13 Results Thirtyfive studies showed that after a radical cone, 165% residual disease in the recone or uterus was found.
The stage of a cervical cancer is the most important factor in choosing treatment But other factors can also affect your treatment options, including the exact location of the cancer within the cervix, the type of cancer (squamous cell or adenocarcinoma), your age and overall health, and whether you want to have children. One hundred consecutive patients with a histologically proven adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix were studied from 1970 to 1992 Results Ninetytwo women presented with abnormal smears, and of these 56% contained abnormal glandular cells. Although invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix constitutes 5–15% of all cervical cancers, the in situ counterpart is underrepresented in the published series of percursor lesions of cervical cancer Moreover, no cases are known to have been published in which in situ adenocarcinoma preceded invasive cancer Partly, this can be explained by the fact that in situ adenocarcinoma is an underdiagnosed lesion.
Although invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix constitutes 5–15% of all cervical cancers, the in situ counterpart is underrepresented in the published series of percursor lesions of cervical cancer Moreover, no cases are known to have been published in which in situ adenocarcinoma preceded invasive cancer Partly, this can be explained by the fact that in situ adenocarcinoma is an underdiagnosed lesion. Morphology of adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine cervix A study of 14 cases Morphology of adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine cervix A study of 14 cases Gloor, E;. Moderate cervical dysplasia (N871);.
Adenocarcinoma in situ is also known as noninvasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation (Figure 13) Patients are typically old (mean age 65–70 years, age range 40–87 years) and predominantly male Hematuria is seen in almost all patients. “Adenocarcinoma in situ”, or AIS, is a really confusing term It’s a kind of abnormal cell growth in the cervix The most common kind of abnormal cell growth in the cervix happens in the squamous cells, which are a specialized kind of skin cell mostly found on the outside of the cervix, the part you can touch with your finger. Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ occurs in the glandular tissue of the cervix and is the condition which leads to invasive adenocarcinoma 1 The average age of women who are diagnosed with cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) is 369 2 Sadly, in most areas with wellestablished cervical screening programs, there has been no obvious reduction in deaths due to adenocarcinoma, despite substantial decreases in deaths due to squamous cell cancer of the cervix 3 One reason for this concerns the.
Se han establecido recomendaciones por consenso para el tratamiento de las mujeres con neoplasia intraepitelial cervical o adenocarcinoma in situ Con el tratamiento adecuado, el control tumoral del carcinoma de cuello uterino in situ se debería acercar a 100 % Se necesita una biopsia dirigida mediante colposcopia realizada por un experto o. Moderate cervical dysplasia (N871);. Epidemiology Cervical adenocarcinoma is less common than squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) of the cervix, accounting for ~125% of all cervical cancer Their proportionate prevalence is thought to be increasing and this is thought to be due to being less readily detected by exfoliative cytology obtained with the Papanicolaou test 23 Pathology.
The term carcinoma in situ is a term used to define and describe a cancer that is only present in the cells where it started and has not spread to any nearby tissues Carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of a cancer, and is, at this stage, considered "noninvasive" With regard to staging, carcinoma in situ is considered stage 0 cancer. High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL) of cervix (R);. Adenocarcinoma In Situ (AIS) of Cervix is a smallsized, localized, premalignant adenocarcinoma, observed in the uterine cervix, which is the lower portion of the womb AIS of Cervix only affects women It may be described as an epithelial lesion and carries a very highrisk for invasive carcinoma, if left untreated.
Cytologic evidence of malignancy of cervix without histologic confirmation (R);. Ruzicka, J Fourteen cases of adenocarcinoma in situ (ACIS) of the cervix in patients 30 to 52 years old were studied In its pure form (four cases), ACIS was discovered cytologically, but when associated. Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a general term for an early stage cancer Cervical carcinoma in situ is also referred to as stage 0 cervical cancer It’s noninvasive, which means the cancerous cells are.
Background Adenocarcinoma in situ of cervix is increasingly managed by local excision rather than hysterectomy and this study will ascertain if conservative management by excision alone is adequate Aims To evaluate the long‐term outcomes of conservative management of adenocarcinoma in situ of cervix, particularly in relation to excisional margin status. Se han establecido recomendaciones por consenso para el tratamiento de las mujeres con neoplasia intraepitelial cervical o adenocarcinoma in situ Con el tratamiento adecuado, el control tumoral del carcinoma de cuello uterino in situ se debería acercar a 100 % Se necesita una biopsia dirigida mediante colposcopia realizada por un experto o. Cervical intraepithelial glandular neoplasia;.
Adenocarcinoma (AC) and adenocarcinoma in situ (ACIS) of the uterine cervix are rare diseases with an incidence of 12 per 100 000 women per year for AC (http//wwwoncolinenl). Melanoma in situ of cervix (D035);. El adenocarcinoma in situ cervical es una entidad que no se puede diagnosticar exclusivamente por biopsia (dirigida o legrado endocervical), si no que es preciso confirmarla mediante conización cervical El tratamiento más adecuado para este tipo de paciente es la histerectomía total.
Next, we performed a cone biopsy No papillary lesions of VGA were observed in the resected cervix on cone biopsy, and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) that appeared to correspond to the basal part of VGA was observed (Fig 3) She worried about the recurrence of cervical adenocarcinoma and requested a hysterectomy. Objetivo Considerar las indicaciones del tratamiento conservador en el adenocarcinoma in situ cervical (AIS) Material y métodos Mediante la serie conjunta del Institut Universitari Dexeus y Hospital MaternoInfantil de la Vall d'Hebron se valoran retrospectivamente () una serie de 51 adenocarcinomas cervicales (incluyendo 11 AIS). Hi, Mica1978 “Adenocarcinoma in situ”, or AIS, is a really confusing term It’s a kind of abnormal cell growth in the cervix The most common kind of abnormal cell growth in the cervix happens in the squamous cells, which are a specialized kind of skin cell mostly found on the outside of the cervix, the part you can touch with your finger.
Catalogage à la source Bibliothèque de l’OMS WHO guidelines for treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2–3 and adenocarcinoma in situ cryotherapy, large loop excision of the transformation zone, and cold knife conization. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the cervix is a premalignant precursor to cervical adenocarcinoma The usual interval between clinically detectable AIS and early invasion appears to be at least five years, suggesting ample opportunity for screening and intervention 1,2. Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ;.
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II CIN II (N871);. Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Primary Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix Version UterineCervix 4100 Protocol Posting Date August 18 Includes pTNM requirements from the 8th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual and 15 FIGO Cancer Report For accreditation purposes, this protocol should be used for the following procedures AND tumor types. Most cases of cervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and adenocarcinoma are of the usual or endocervical type However, intestinal types of AIS and adenocarcinoma exist.
Objetivo Considerar las indicaciones del tratamiento conservador en el adenocarcinoma in situ cervical (AIS) Material y métodos Mediante la serie conjunta del Institut Universitari Dexeus y Hospital MaternoInfantil de la Vall d'Hebron se valoran retrospectivamente () una serie de 51 adenocarcinomas cervicales (incluyendo 11 AIS). Adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix arise from the endocervical columnar cells and account for about 14% of cervical carcinomas 7 Over the past few decades, the percentage of adenocarcinomas has increased because, compared with squamouscell carcinomas, they are more difficult to detect at a preinvasive stage 8. Metastases to ovaries, upper abdomen, distant organs.
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix is a premalignant glandular condition Adenocarcinoma in situ is the only known precursor to cervical adenocarcinoma, and appropriate management can prevent the occurrence of invasive disease in many cases 1 The usual interval between clinically detectable adenocarcinoma in situ and early invasion appears to be at least five years, suggesting ample opportunity for screening and intervention 2,3. Adenocarcinoma is usually high up in the cervix, like mine was, so your cervix looks normal during a pelvic exam, and pap smears miss it a lot of the time We have to be our own advocates sometimes I wish you ladies all the best!!!. The precursor lesion is dysplasia cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or adenocarcinoma in situ, which can subsequently become invasive cancer This process can be quite slow Longitudinal studies have shown that in patients with untreated in situ cervical cancer, 30% to 70% will develop invasive carcinoma over a period of 10 to 12 years.
Cervical adenocarcinoma in situ is a unique diagnosis whose management needs to be differentiated from the management of the more prevalent squamous cell dysplasia. Objective We evaluated the impact of conization margin status on outcomes of patients diagnosed with cervical adenocarcinoma in situ Study design A retrospective chart review identified patients at a University hospital from with adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) on conization Results Seventyfour patients were included. Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancerThis controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (ie cervical, skin, breast) Some authors do not classify them as cancer, however, recognizing that they can potentially become cancer.
Melanoma in situ of cervix (D035);. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II CIN II (N871);.
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Pdf Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Update And Management

Adenocarcinoma And Adenocarcinoma In Situ Eurocytology
新網頁1

Casos Mayo De 12 Sil De Alto Grado Y Adenocarcinoma In Situ De Cuello Uterino Sociedad Argentina De Citologia

Cervical Cancer Treatment Pdq Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf
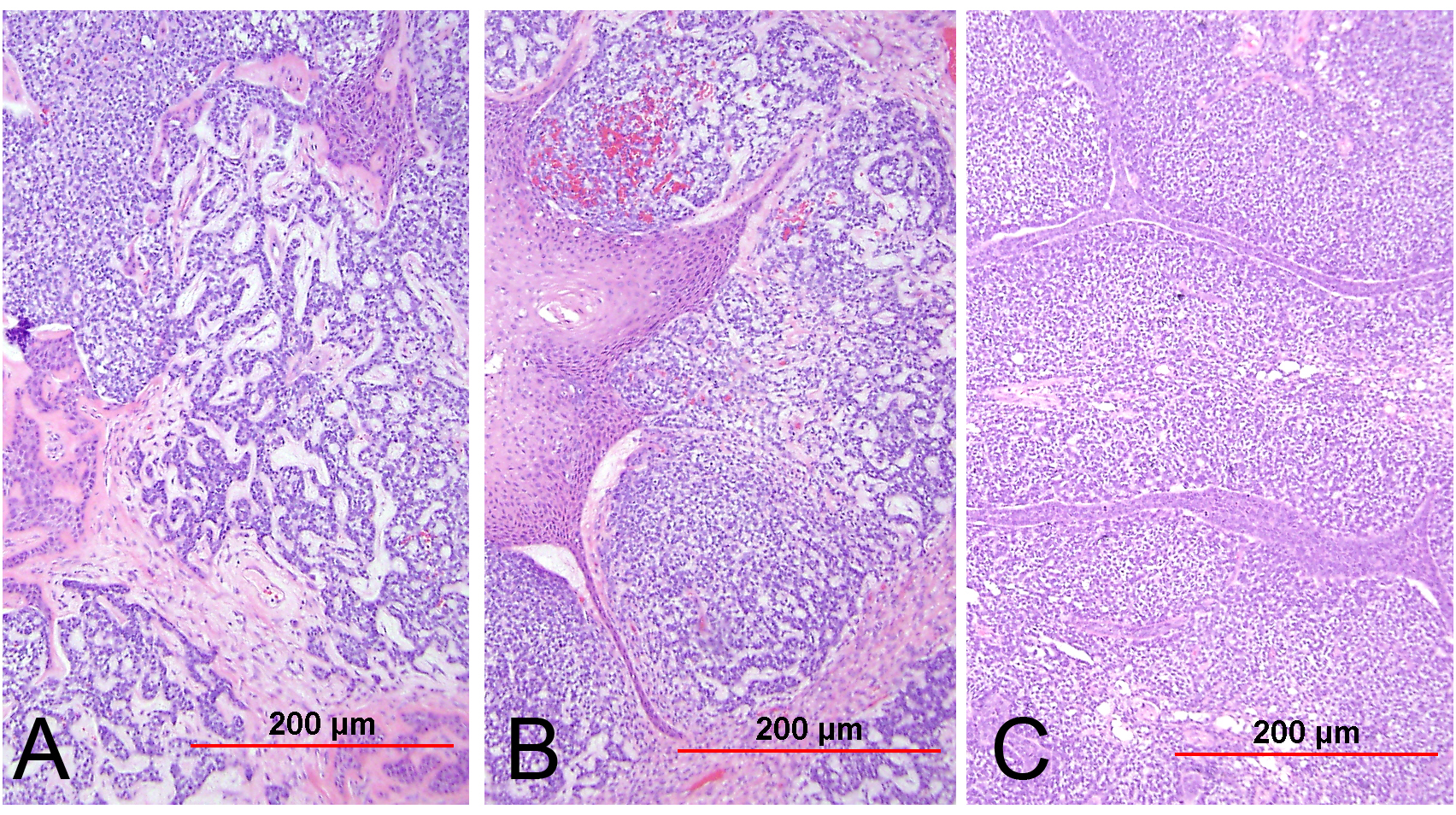
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
Cervix Image Atlas Micro Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Sunnybrook Hospital

Vaginal Carcinoma After Cervical Dysplasia International Journal Of Gynecologic Cancer

Distinguishing Primary Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma From Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix Utility Of P16

Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma Actas Dermo Sifiliograficas English Edition
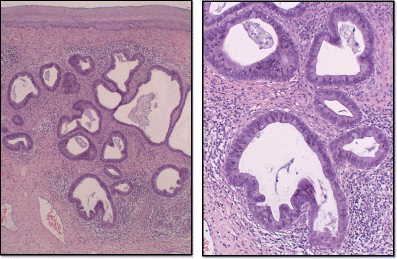
Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Update And Management Springerlink
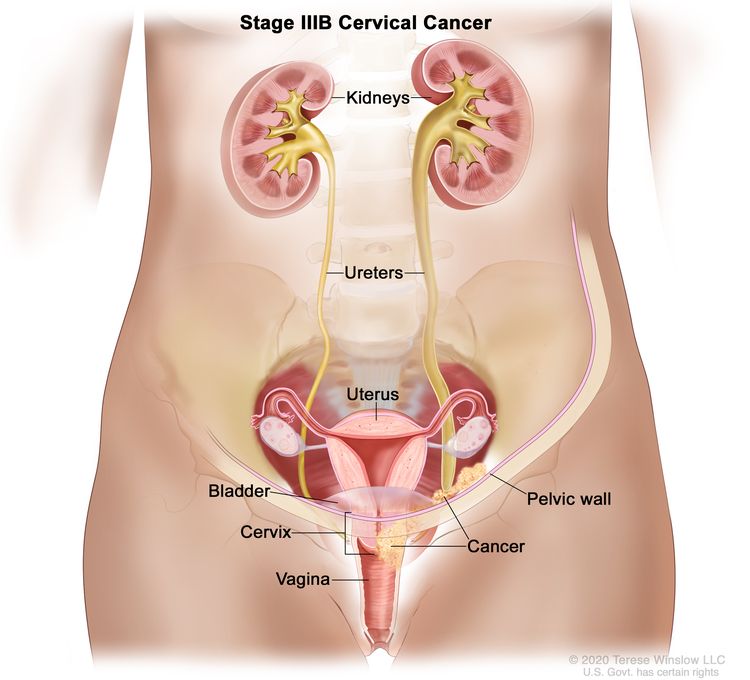
Cervical Cancer Pictures Of Cervical Cancer Stages Symptoms Diagnosis Cleveland H University Hospitals
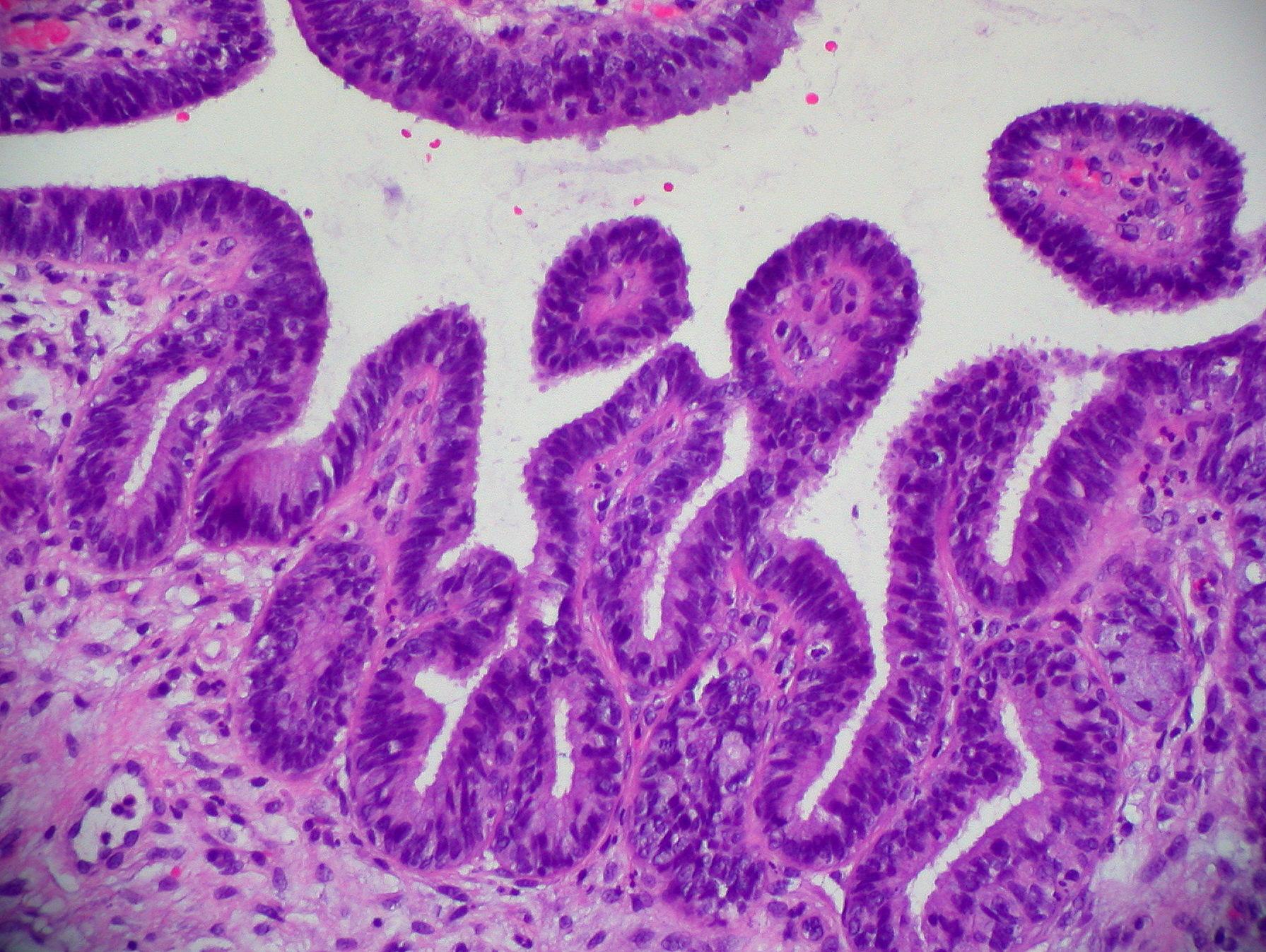
File Cervix Adenocarcinoma In Situ Jpg Wikimedia Commons

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais Of The Cervix Mypathologyreport Ca

Cervical Cancer Wikiwand
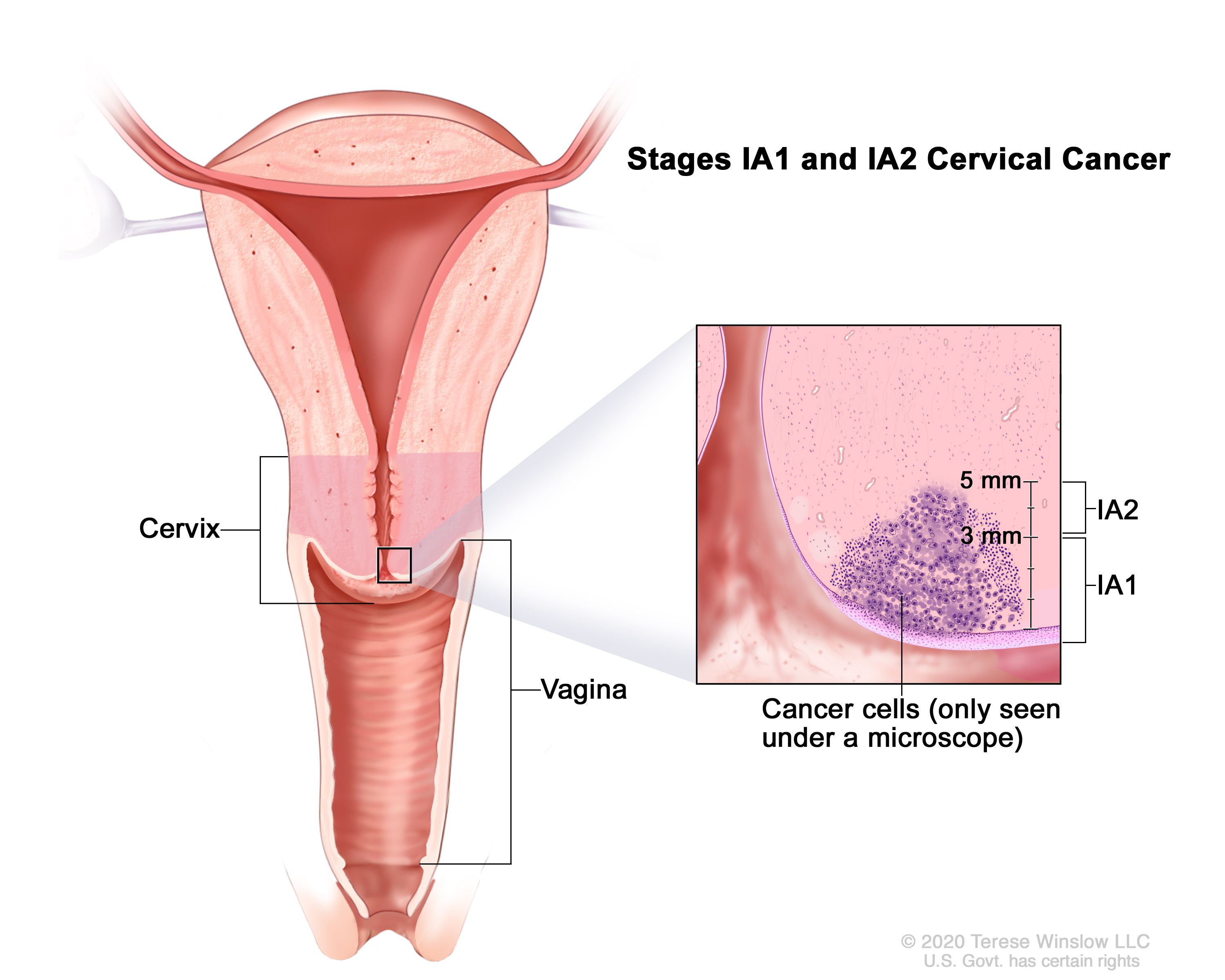
Cervical Cancer Treatment Pdq Health Professional Version National Cancer Institute
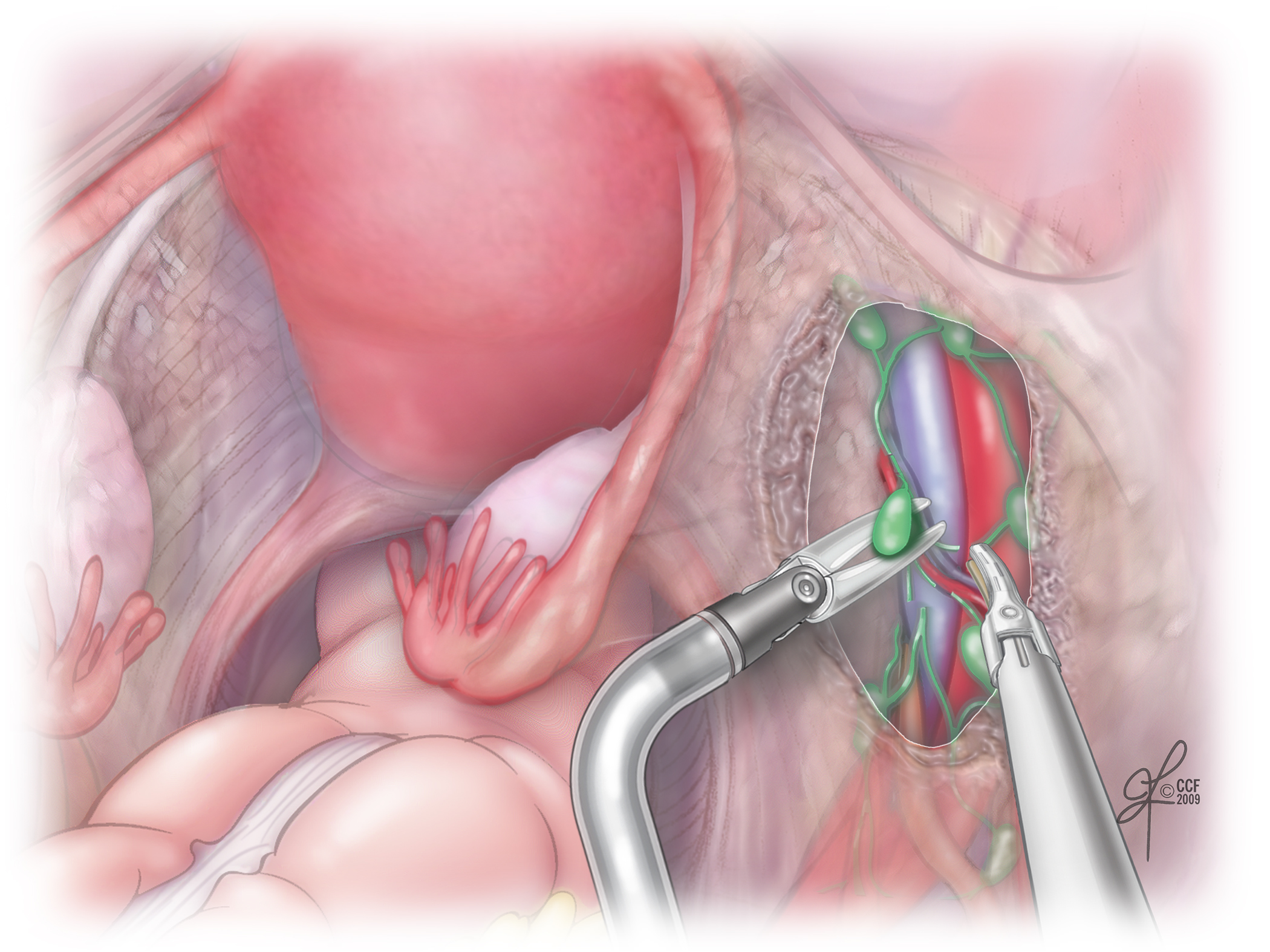
Endometrial Ovarian And Cervical Cancer

新網頁1

Adenocarcinoma And Adenocarcinoma In Situ Eurocytology

Clinical Presentation Stages And Treatment Of Cervical Cancer Eurocytology
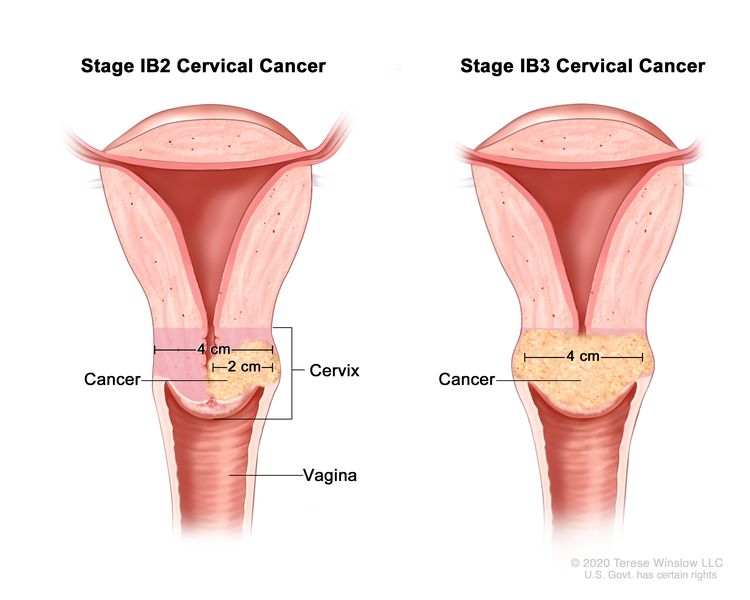
Cervical Cancer Treatment Pdq Health Professional Version National Cancer Institute
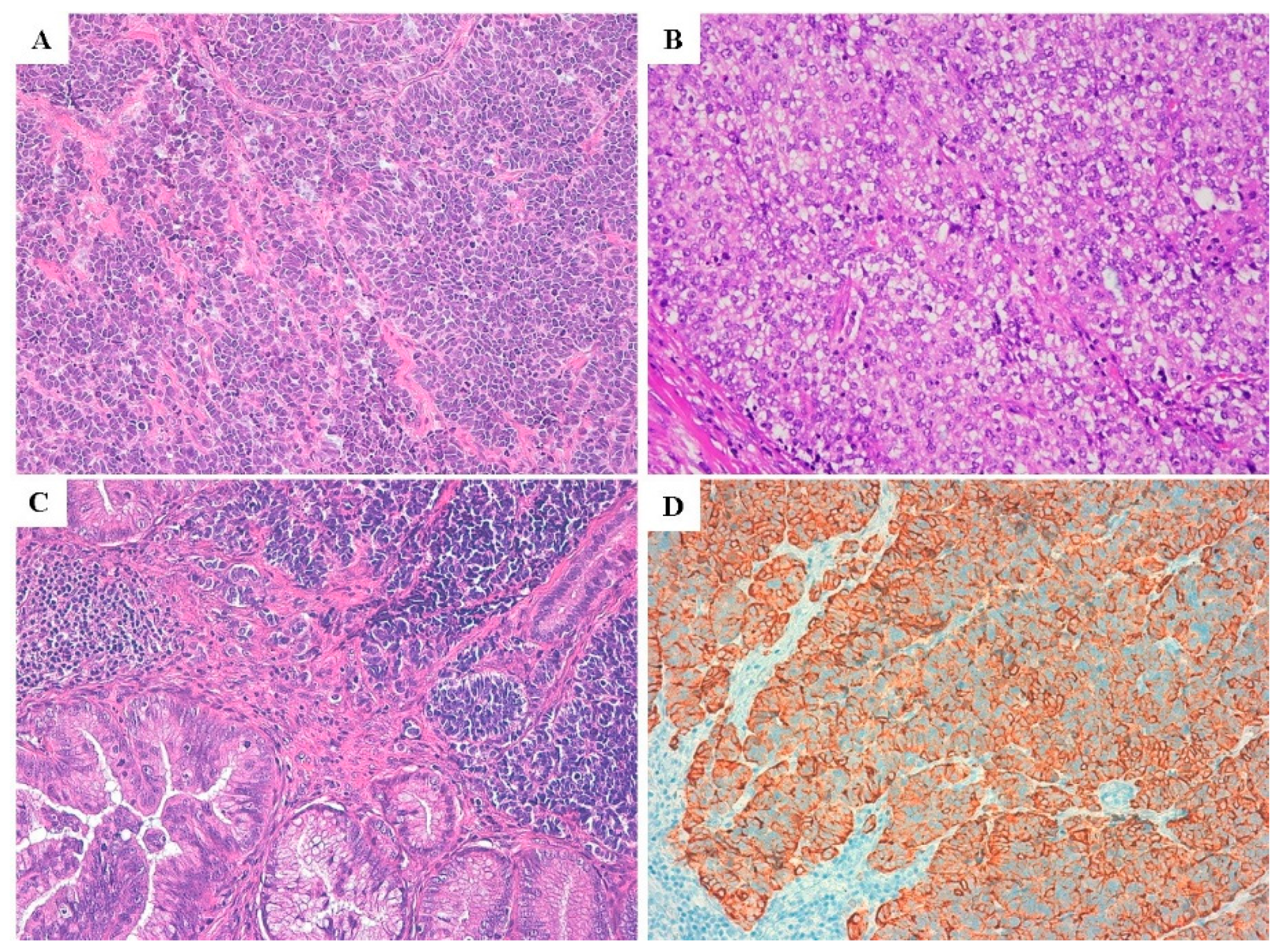
Cancers Free Full Text Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Of The Uterine Cervix A Clinicopathologic And Immunohistochemical Study With Focus On Novel Markers Sst2 Sst5 Html

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ What Every Woman Must Know
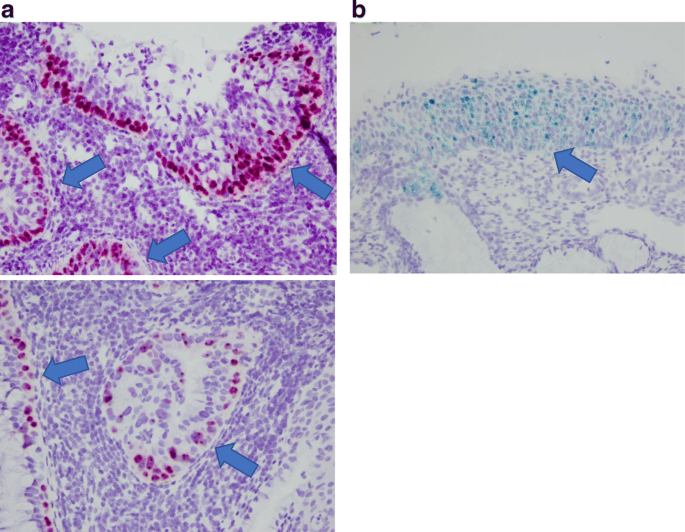
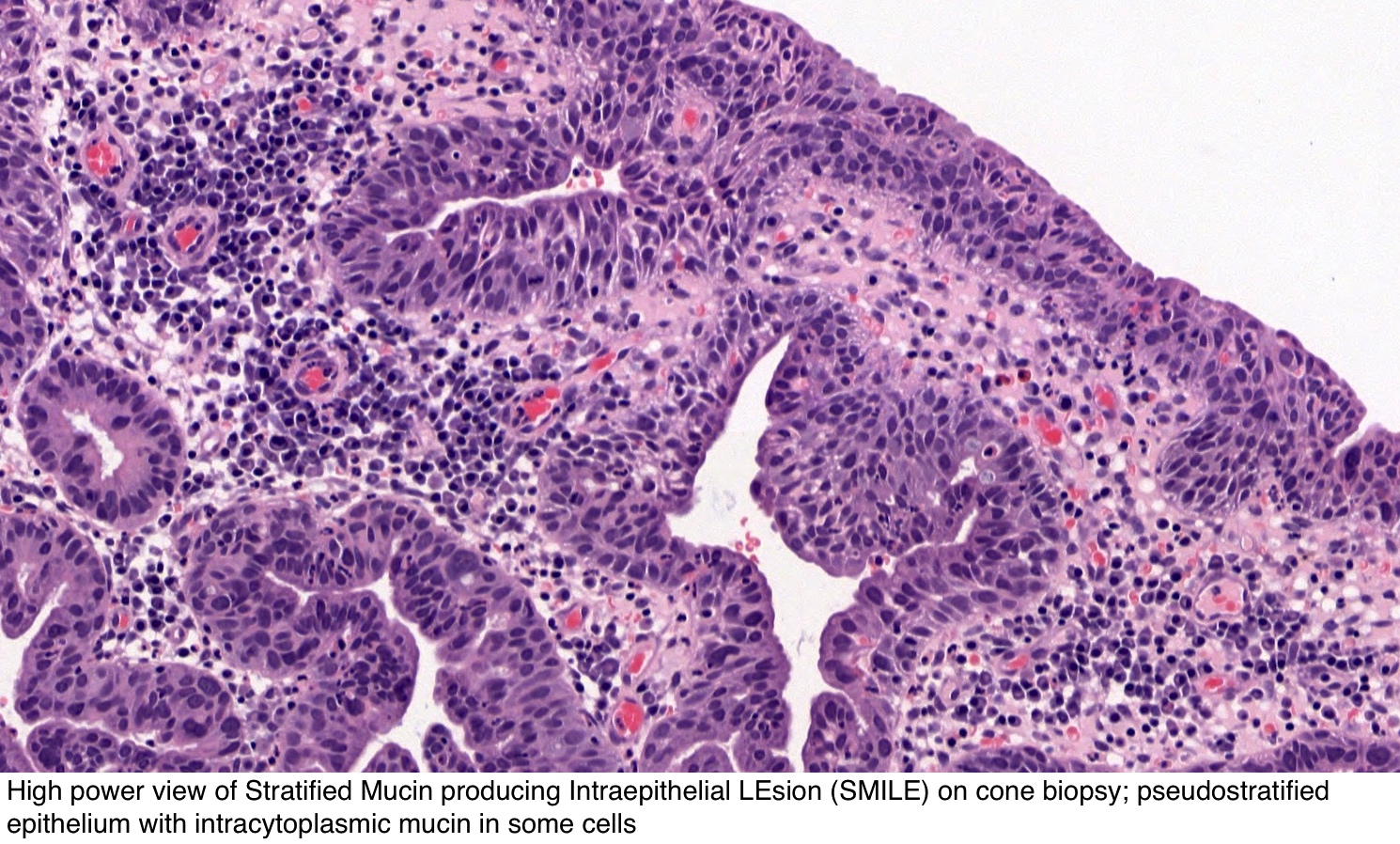
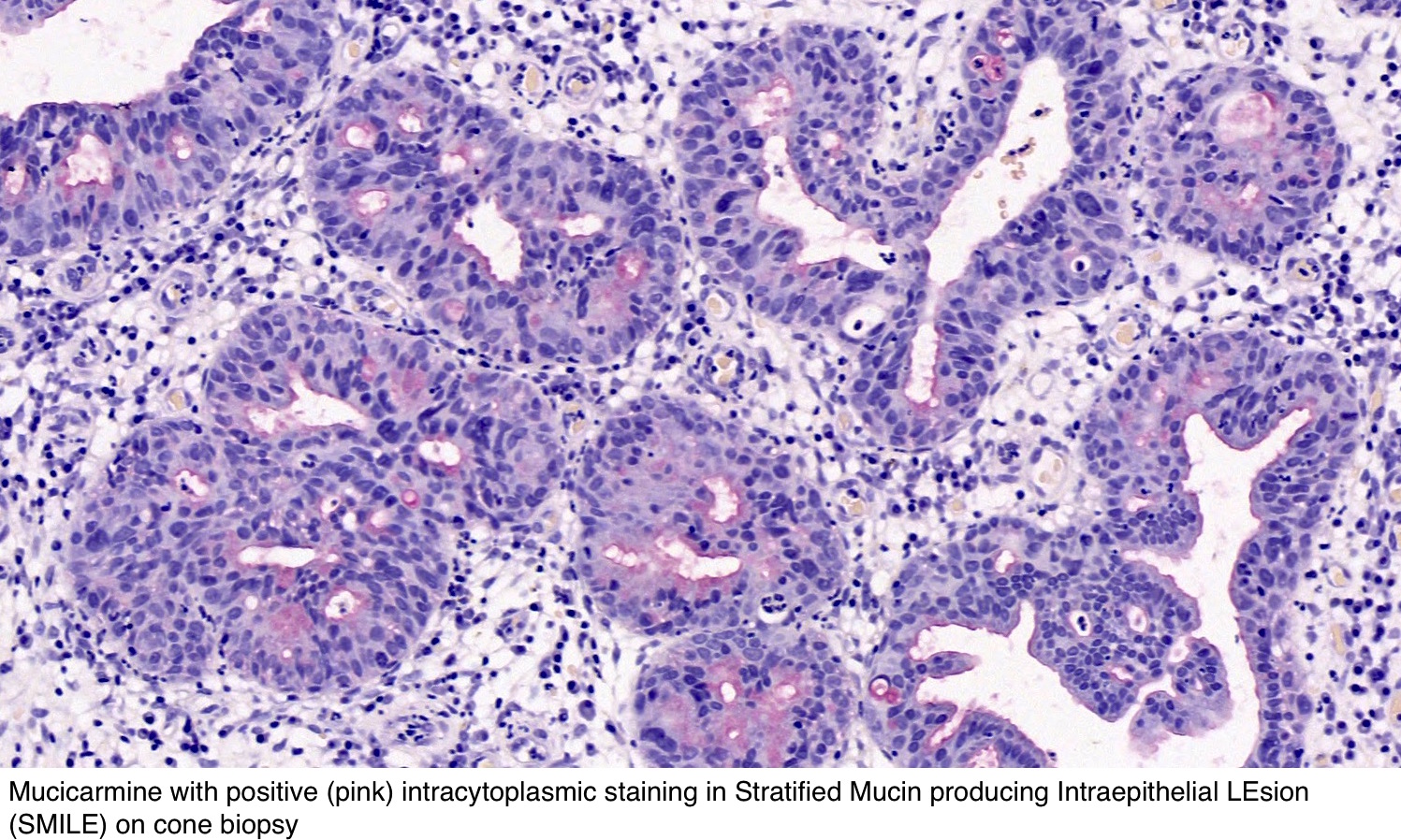
Detection Of Hpv Rna Molecules In Stratified Mucin Producing Intraepithelial Lesion Smile With Concurrent Cervical Intraepithelial Lesion A Case Report Virology Journal Full Text

Predictive Significance Of The Alterations Of P16ink4a P14arf P53 And Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen Expression In The Progression Of Cervical Cancer Clinical Cancer Research
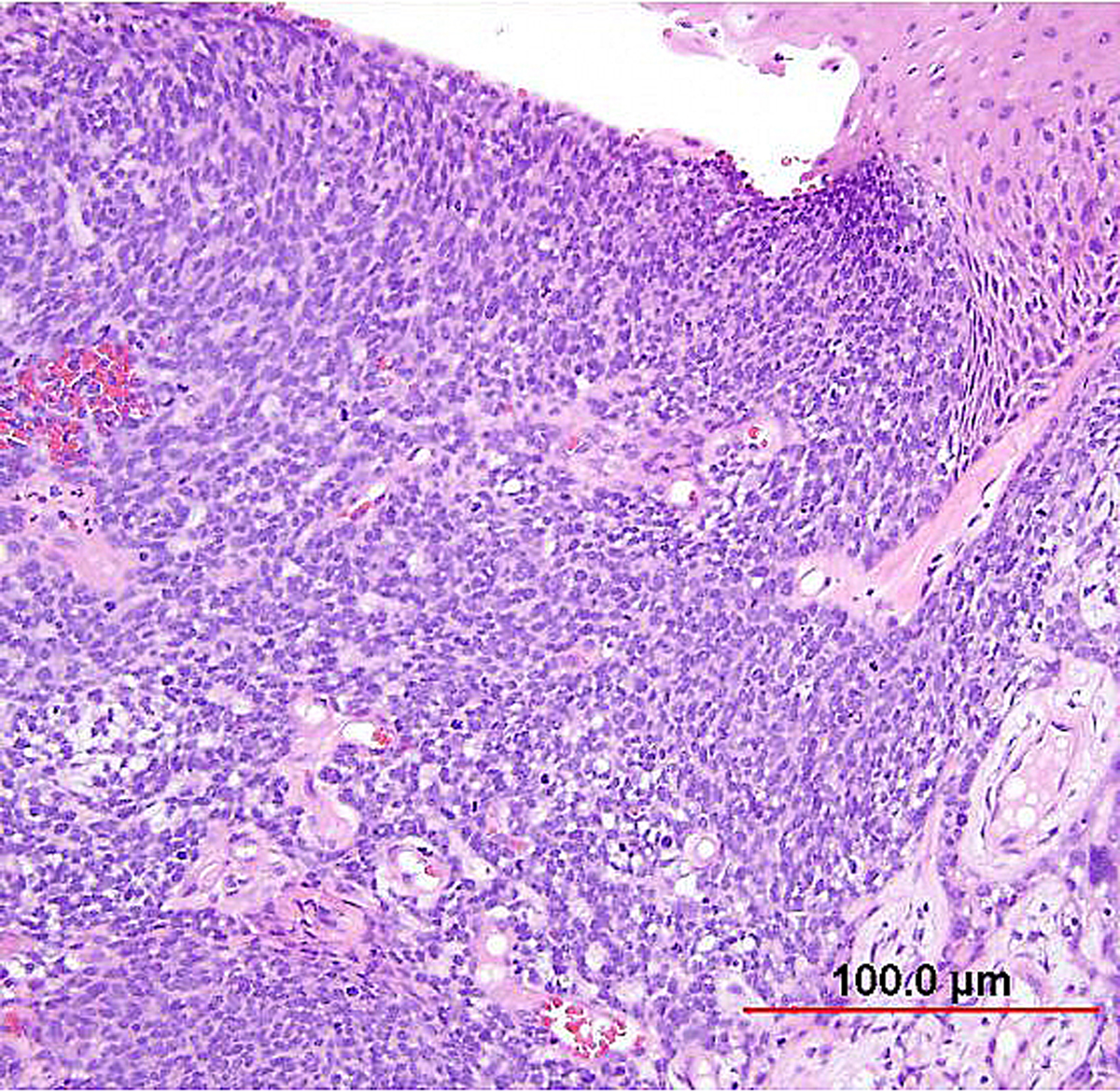
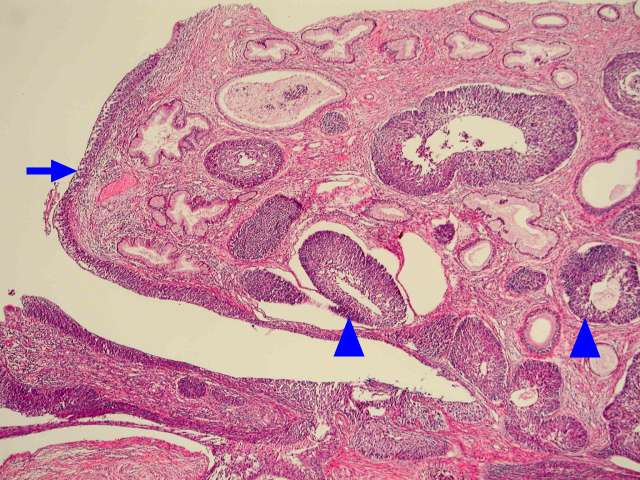
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm
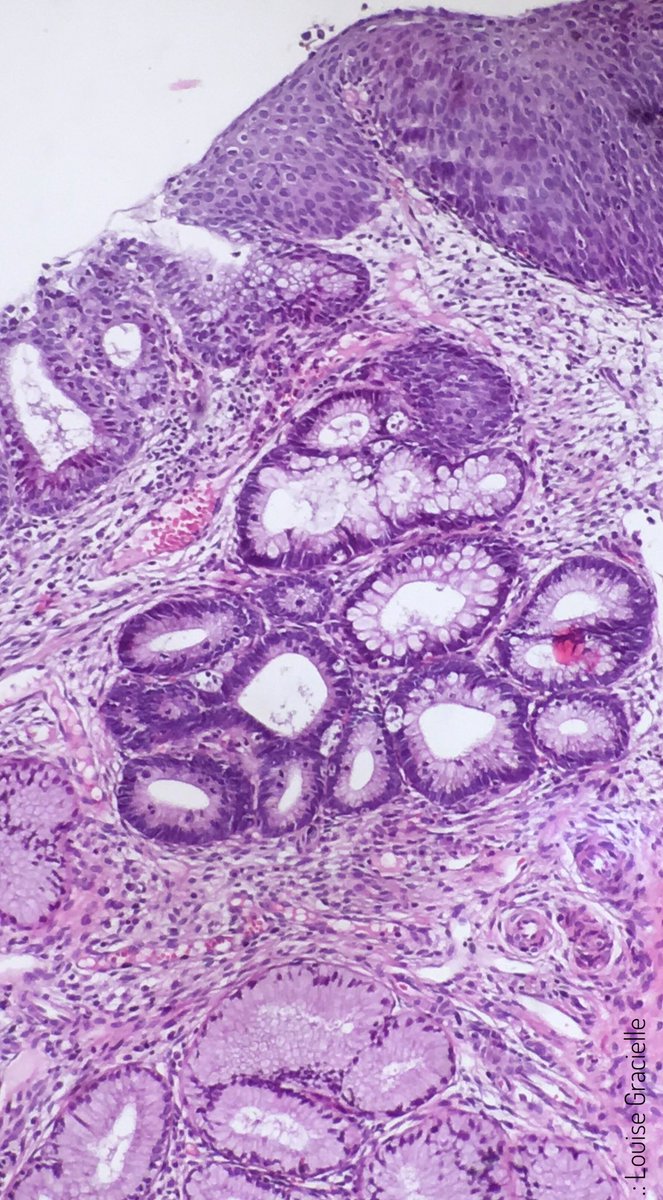
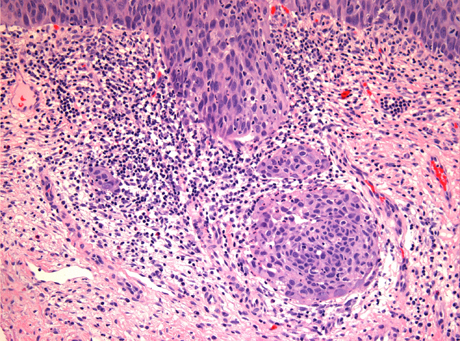
Louise Gracielle Md Nice Example Of Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Associated With High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Notice The Intestinalization Of The Epithelium Atypia Apoptotic Bodies And Mitotic Figures Gynpath Gyn

Carcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
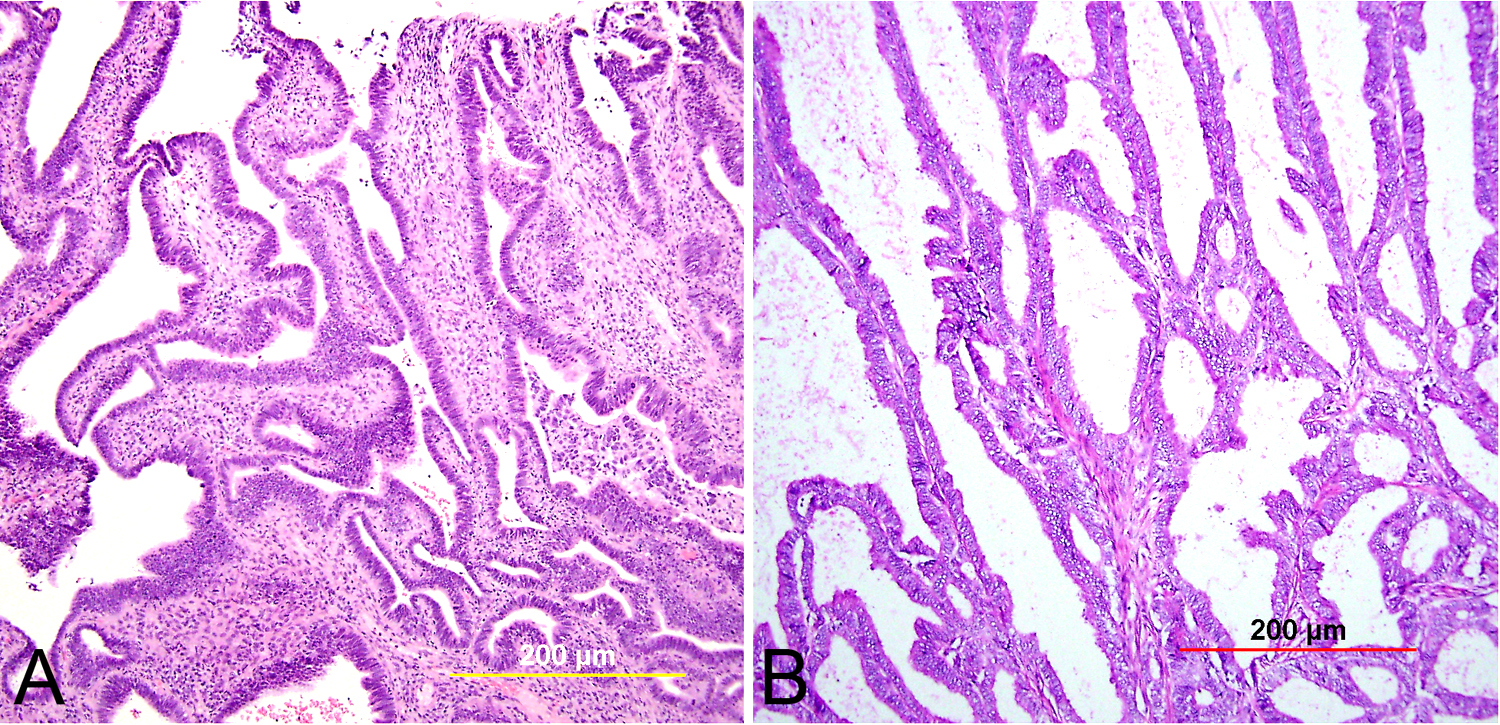
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Carcinoma Epidermoide De Cuello Uterino Con Extension Superficial A Endometrio

Citologia Del Adenocarcinoma Eurocytology
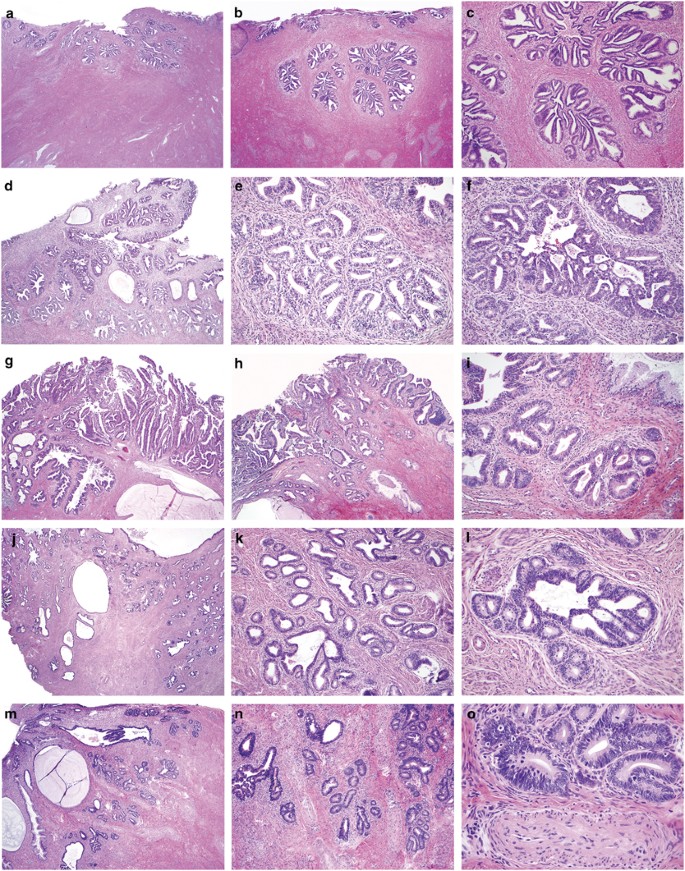
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Selected Diagnostic Challenges Modern Pathology

Citologia Del Adenocarcinoma Eurocytology

Squamous Cell Carcinoma Bowen S Disease In Situ In Three Cats
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
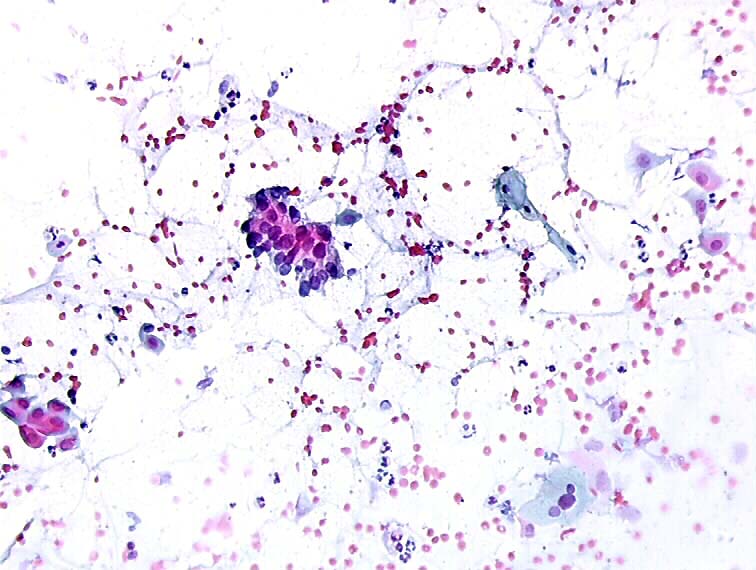
Cytopathology Of The Uterine Cervix Digital Atlas

Pdf Intestinal Type In Situ Adenocarcinoma Of The Cervix As A Precursor Of Cervical Signet Ring Cell Adenocarcino Ma Adenocarcinom Cervical In Situ De Tip Intestinal P Recursor Al Adenocarcinomului Cervical Cu

Vaginal Carcinoma After Cervical Dysplasia International Journal Of Gynecologic Cancer
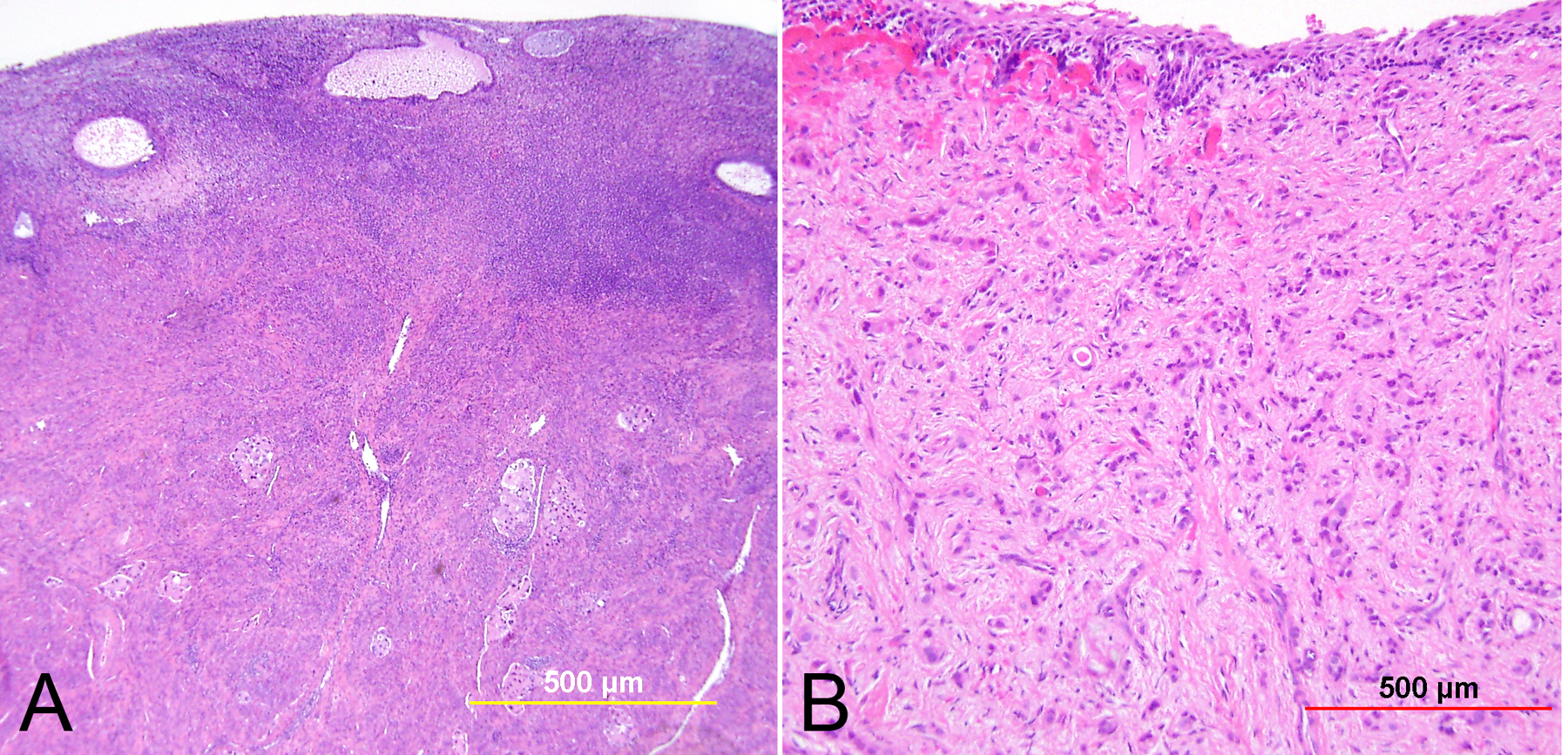
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Immunohistochemical Expression Of The Tumor Suppressor Protein P16 Ink4a In Cervical Adenocarcinoma

Role Of Immunohistochemistry In Gynec Oncopathology Including Specific Diagnostic Scenarios With Associated Treatment Implications Rekhi B Indian J Pathol Microbiol

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Anatomia Patologica Histologia Hematologia

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
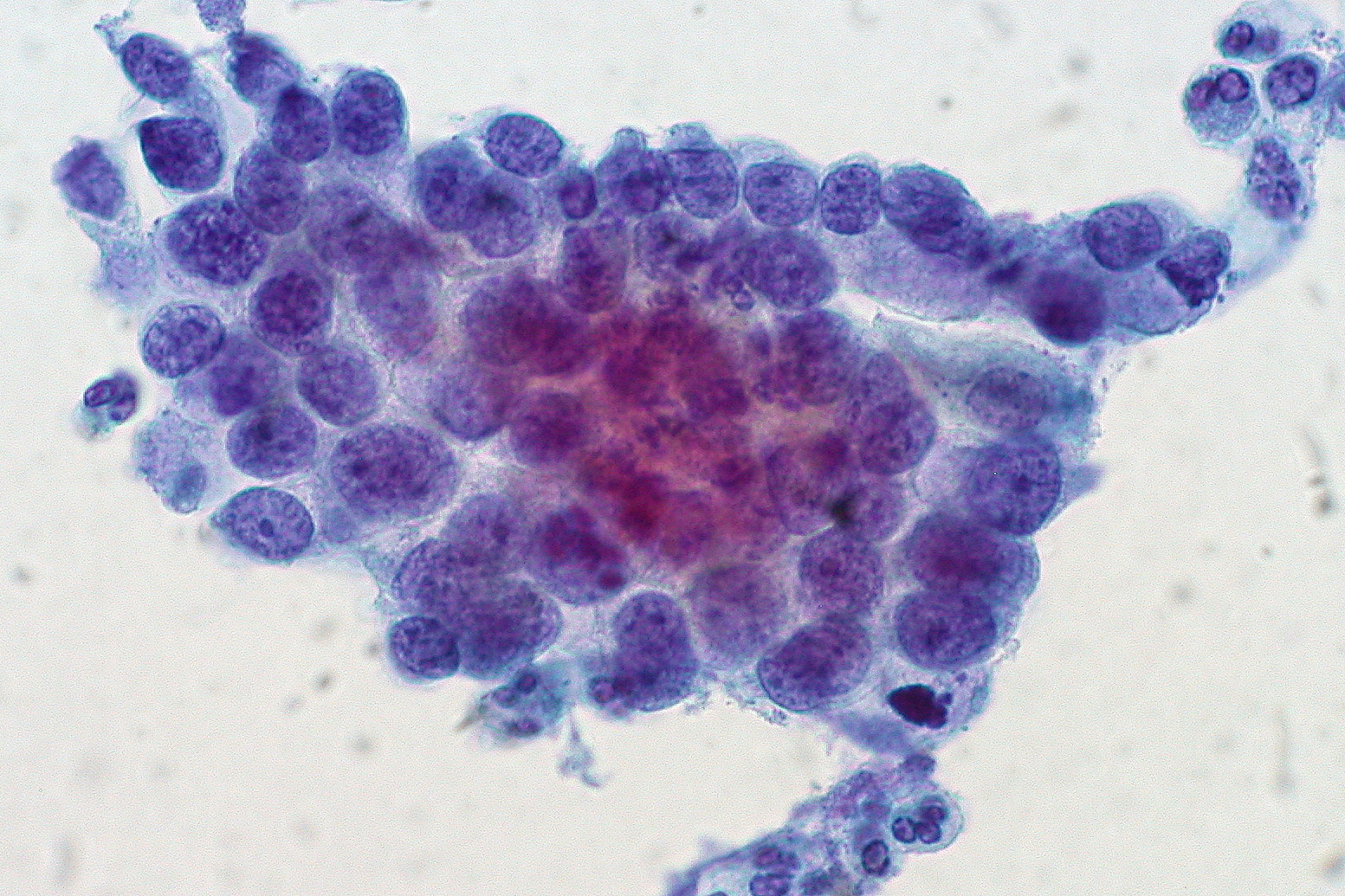
File Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Cervix Jpg Wikimedia Commons

What Is Cervical Cancer Types Of Cervical Cancer
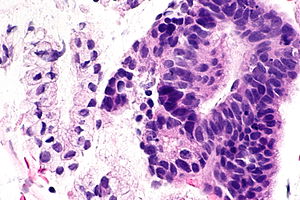
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Libre Pathology
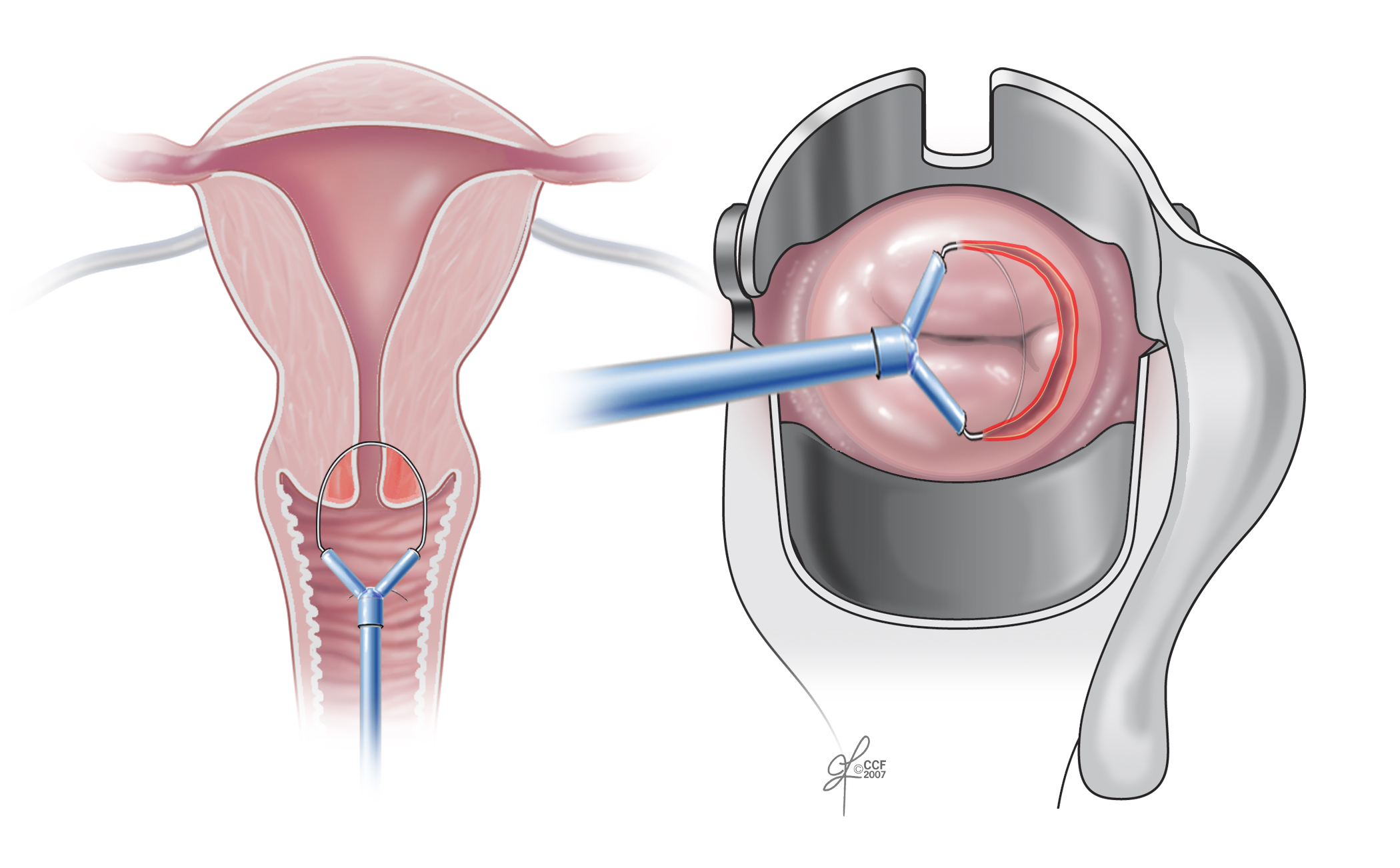
Endometrial Ovarian And Cervical Cancer

Pathology Of Cancers Of The Female Genital Tract Prat 18 International Journal Of Gynecology Amp Obstetrics Wiley Online Library

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais Of The Cervix Mypathologyreport Ca
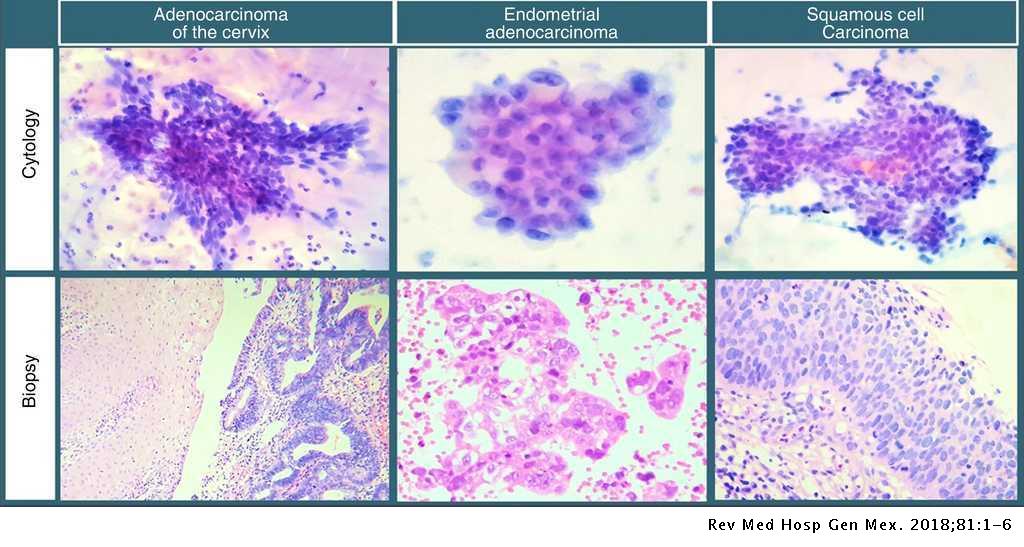
Cytological Diagnosis Of Cervical Adenocarcinoma And Cytohistological Agreement At General Hospital Of Mexico Dr Eduardo Liceaga Revista Medica Del Hospital General De Mexico
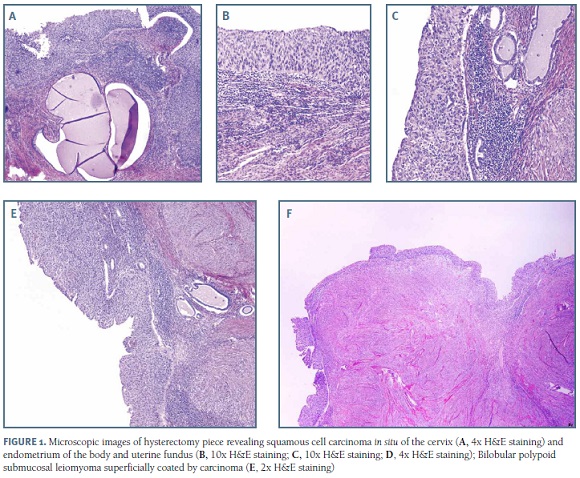
Carcinoma In Situ Do Colo Do Utero Com Extensao Superficial Ao Endometrio

Cytopathology Of The Uterine Cervix Digital Atlas
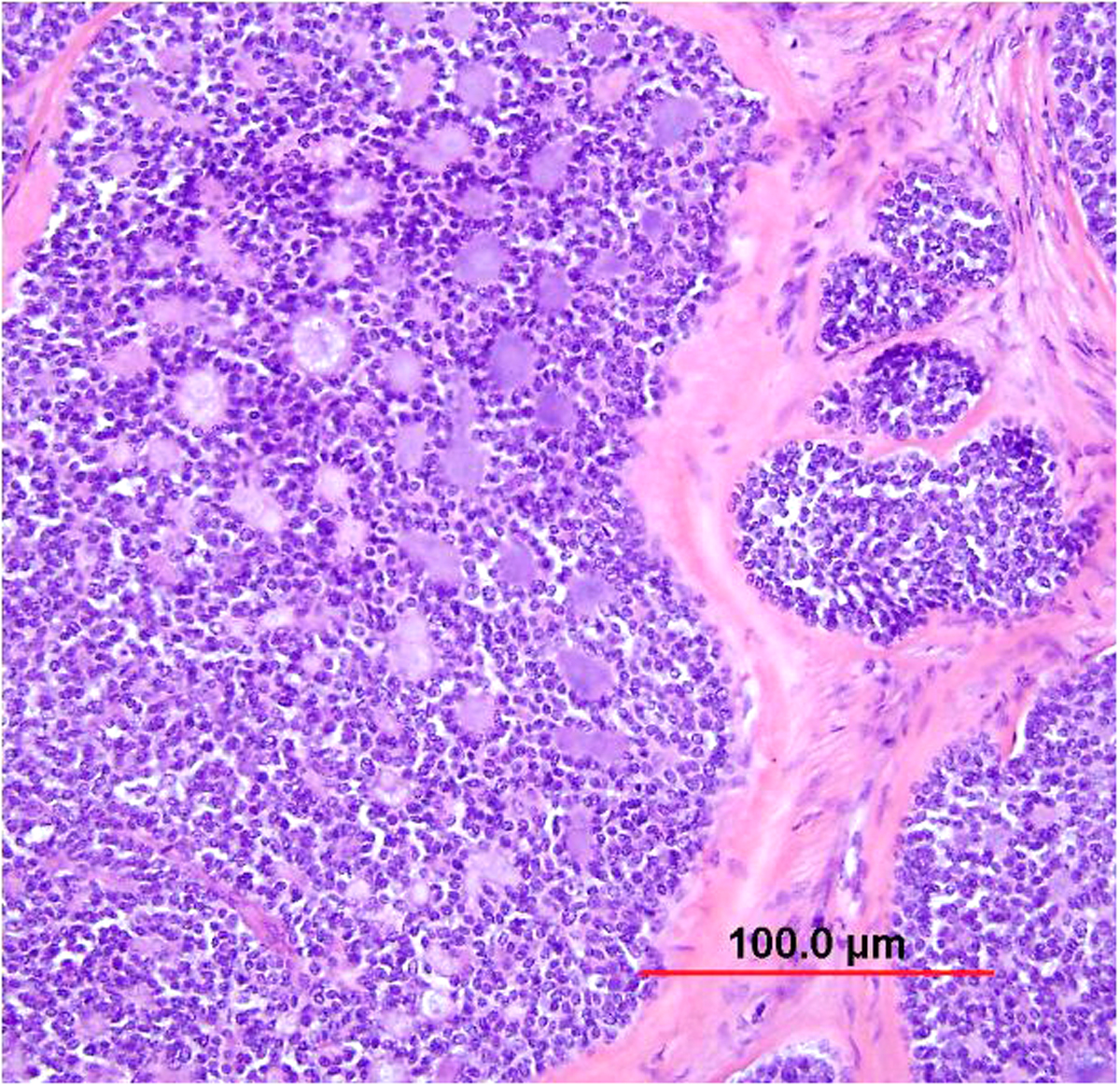
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm
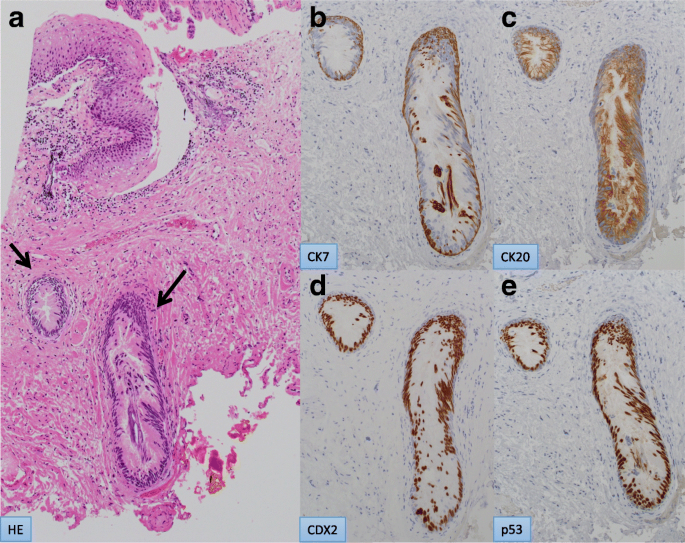
Anal Gland Adenocarcinoma In Situ With Pagetoid Spread A Case Report Surgical Case Reports Full Text
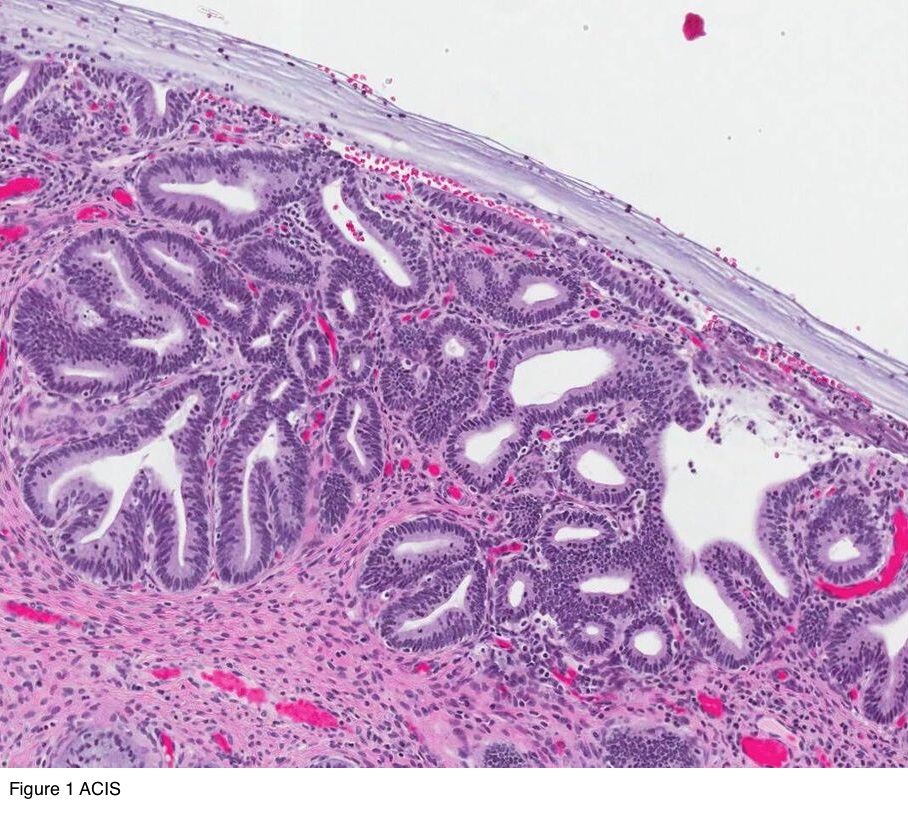
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Adenocarcinoma Wikipedia
Pathology Outlines Hpv Related Adenocarcinoma Usual Type And Variants
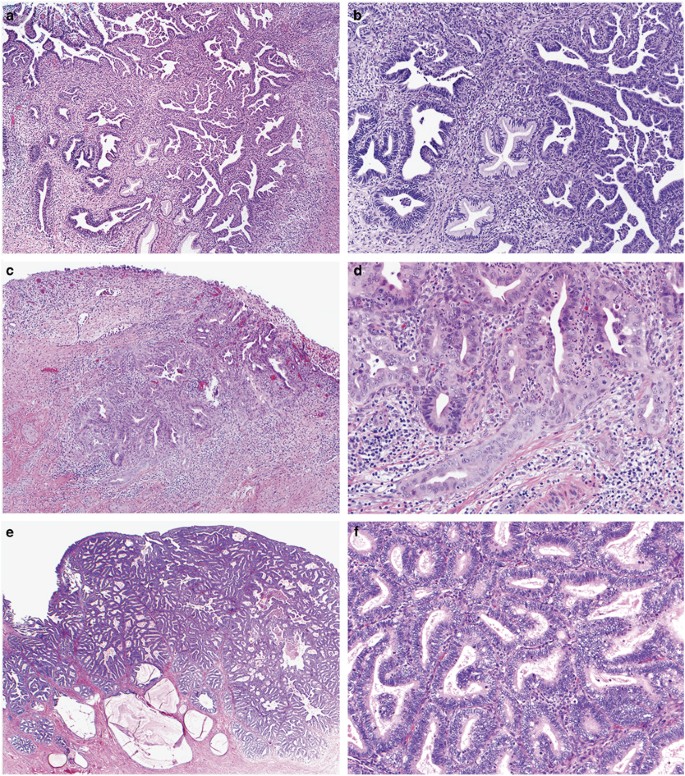
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Selected Diagnostic Challenges Modern Pathology
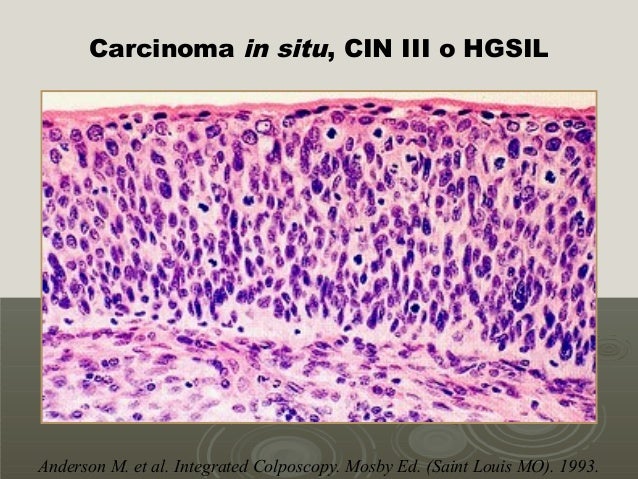
Carcinogenesis Cervical Y Hpv Curso Aconcagua 11

The Diagnostic Value Of Detection Of High Risk Hpv In Differentiating Primary Bladder Cancer Versus Uterine Cervical Cancer Involving Bladder A Case Report Sciencedirect
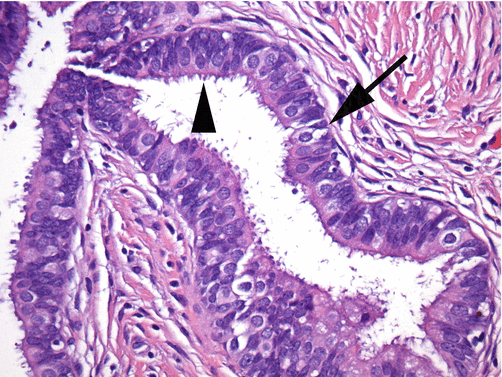
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Cervical Glandular Intraepithelial Neoplasia And Adenocarcinoma Of The Usual Type Springerlink

Pathology Of Cancers Of The Female Genital Tract Prat 18 International Journal Of Gynecology Amp Obstetrics Wiley Online Library
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Mdtd9phybc1zm
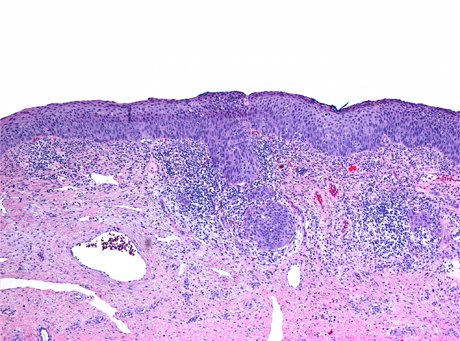
Cervix Image Atlas Micro Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Sunnybrook Hospital
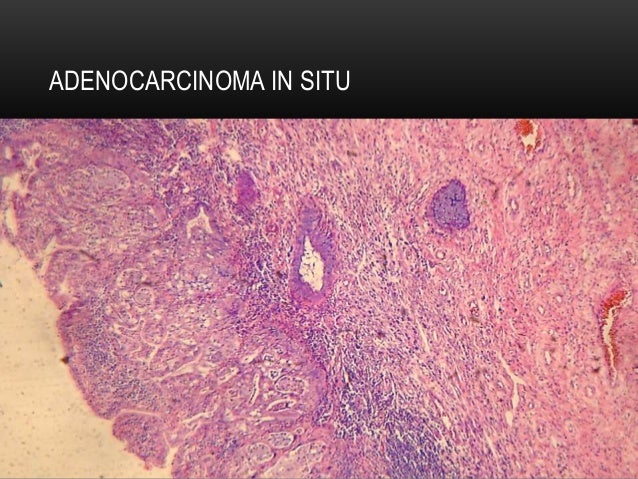
Carcinoma Invasor Del Cuello Uterino

Cervical Cancer Awareness Week Cervical Cancer With Metastasis
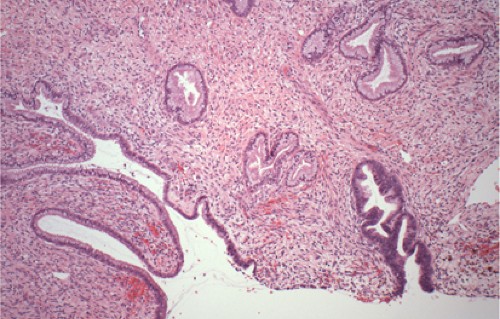
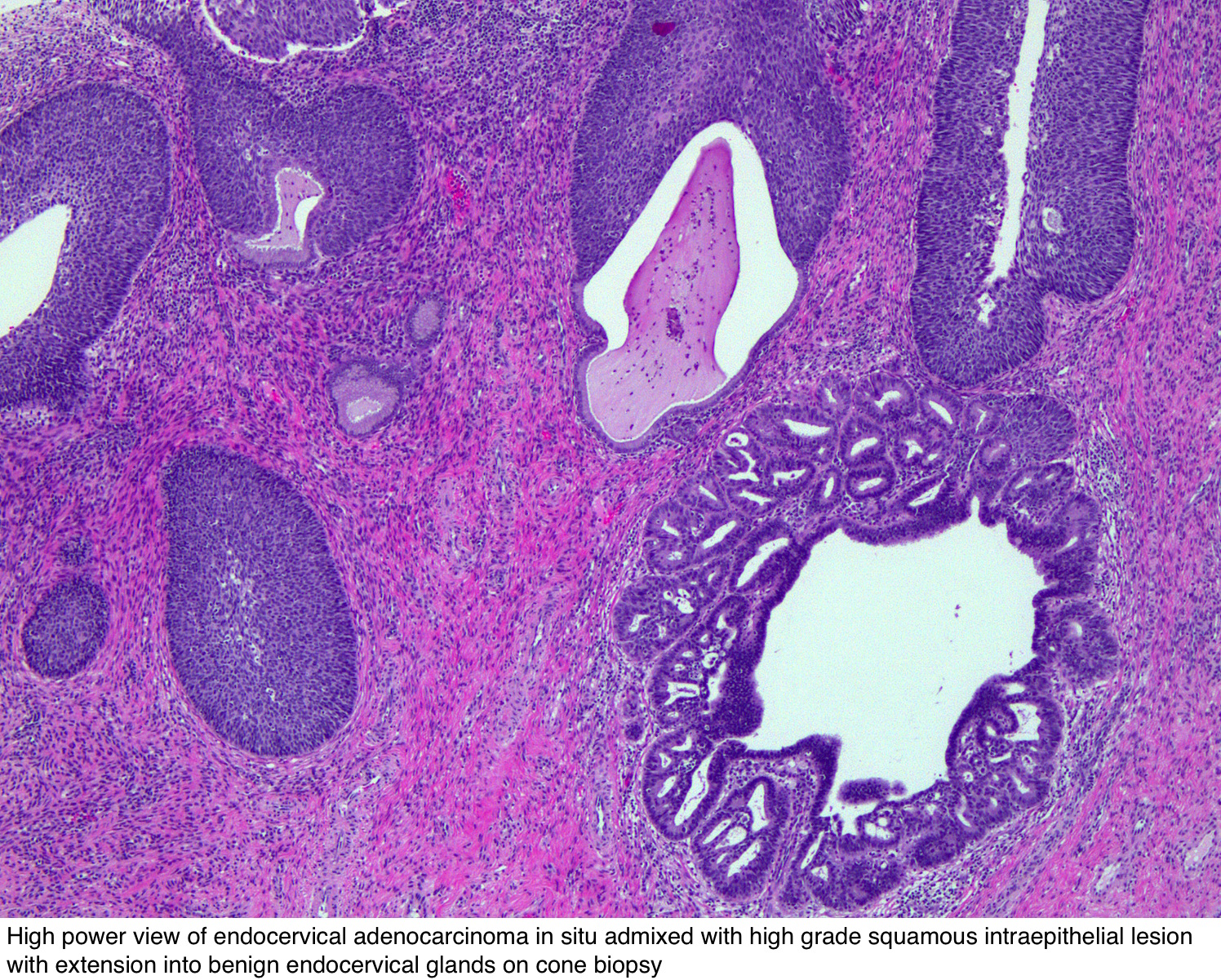
Practical Issues Related To Uterine Pathology In Situ And Invasive Cervical Glandular Lesions And Their Benign Mimics Emphasis On Cytology Histology Correlation And Interpretive Pitfalls Modern Pathology

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Cervix

Pathology Of Cancers Of The Female Genital Tract Prat 18 International Journal Of Gynecology Amp Obstetrics Wiley Online Library

Pdf Intestinal Type In Situ Adenocarcinoma Of The Cervix As A Precursor Of Cervical Signet Ring Cell Adenocarcino Ma Adenocarcinom Cervical In Situ De Tip Intestinal P Recursor Al Adenocarcinomului Cervical Cu

Figure 5 From Glandular Lesions Of The Uterine Cervix Case 2 Semantic Scholar

Nccn Guidelines Insights Cervical Cancer Version 1 In Journal Of The National Comprehensive Cancer Network Volume 18 Issue 6

Small Cell Carcinoma Wikipedia
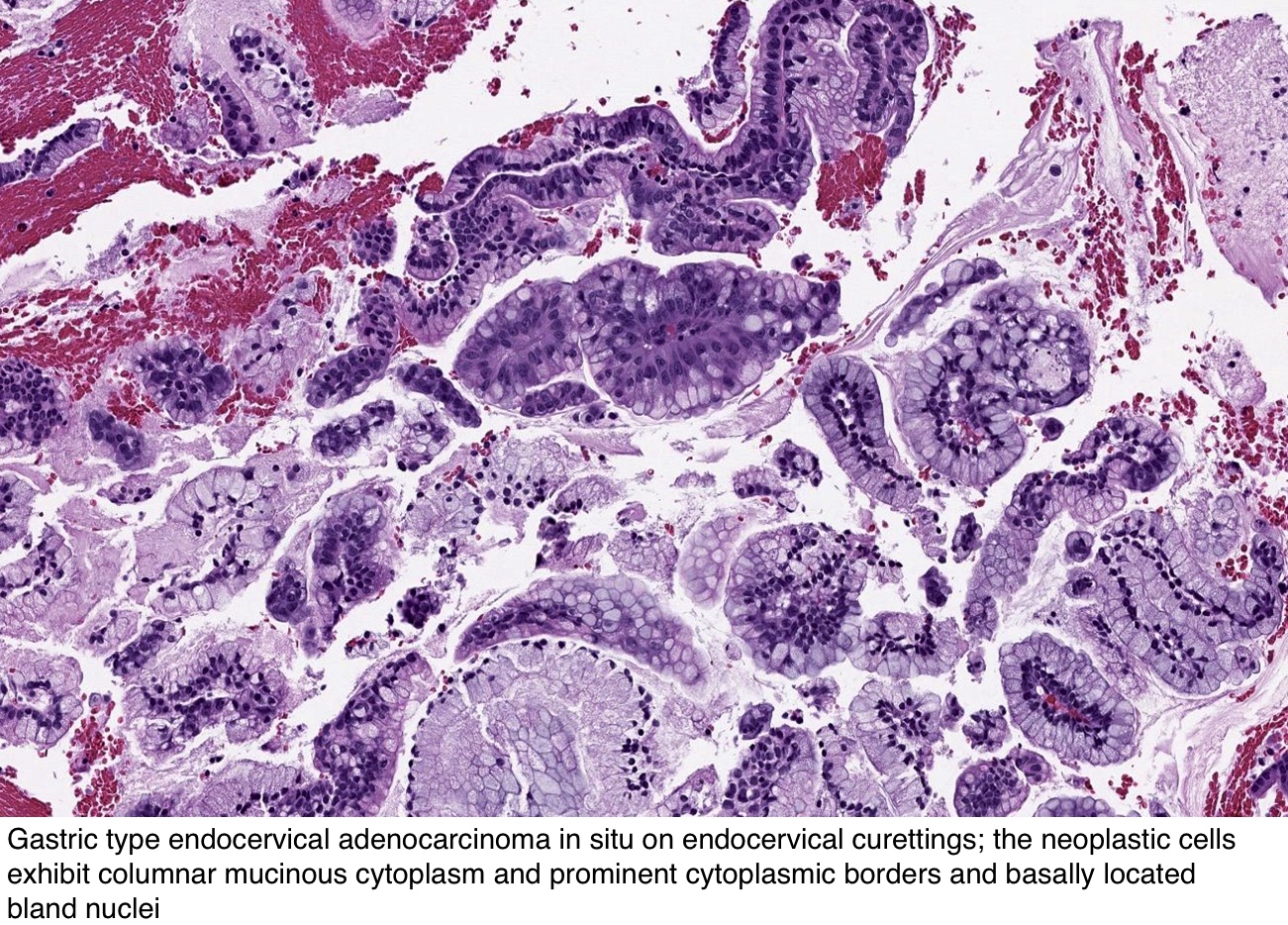
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Carcinoma In Situ Of The Uterine Cervix H E Magnification X400 Download Scientific Diagram
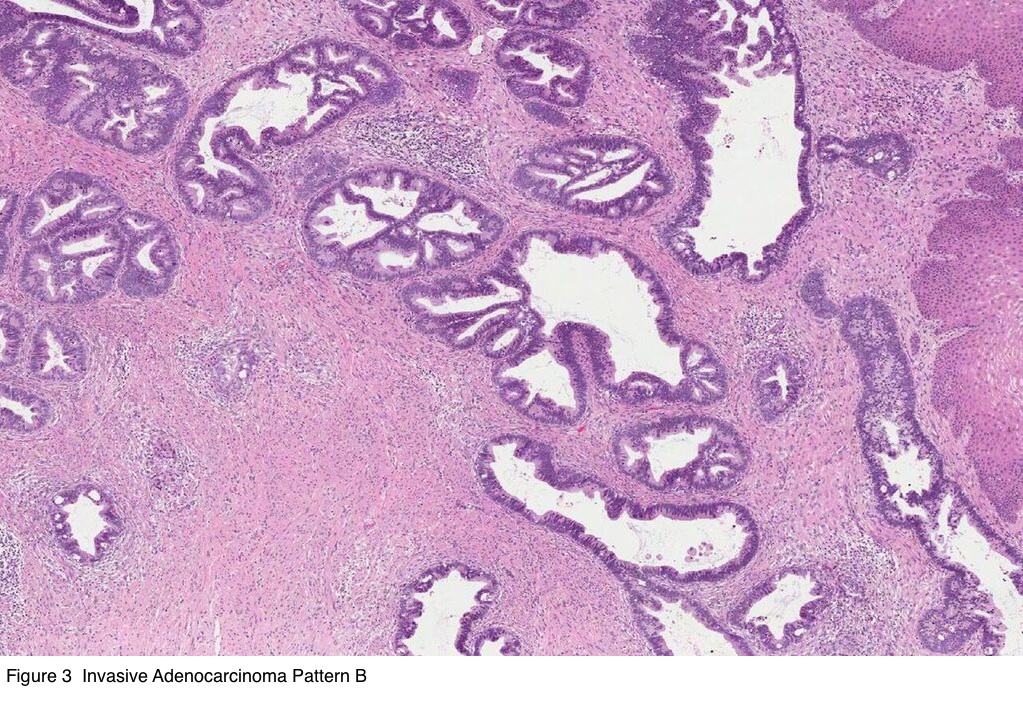
Pathology Outlines Hpv Related Adenocarcinoma Usual Type And Variants
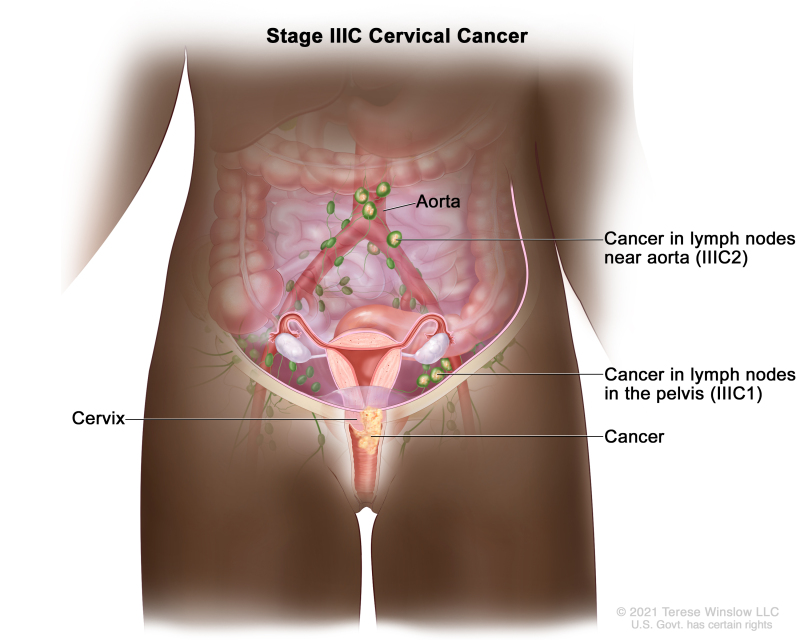
Cervical Cancer Treatment Pdq Pdq Cancer Information Summaries Ncbi Bookshelf

Bowen S Disease Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
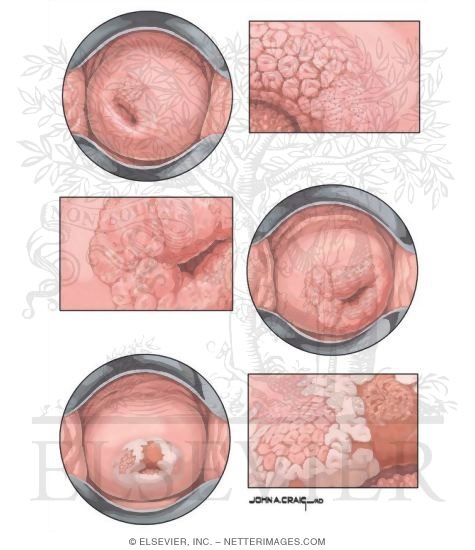
Welcome To Netter Images

Prevencion Cancer Cervix Bolivia

Carcinoma In Situ Wikipedia

Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ With Glandular Extension Of The Uterine Download Scientific Diagram

Breast Carcinoma In Situ Lobular Ductal Lcis Dcis Teachmesurgery

Carcinoma Intracelular In Situ Cancer De Utero Youtube
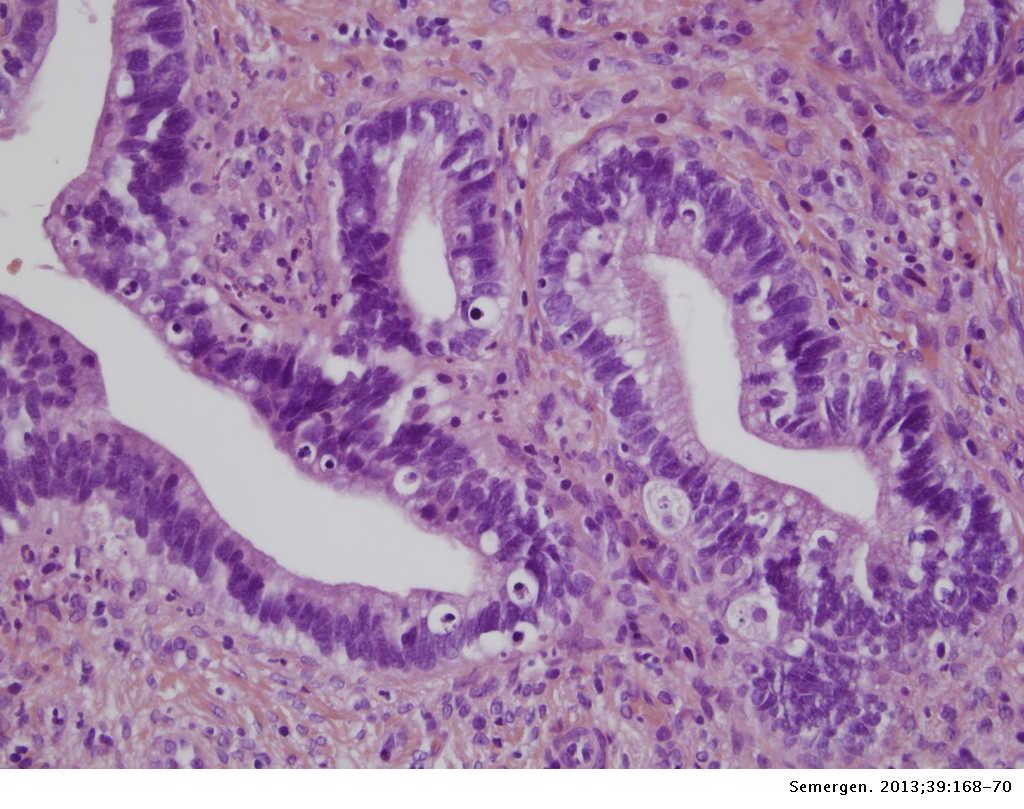
El Adenocarcinoma De Cervix Como Causa Infrecuente De Sangrado Vaginal En La Mujer Joven Medicina De Familia Semergen
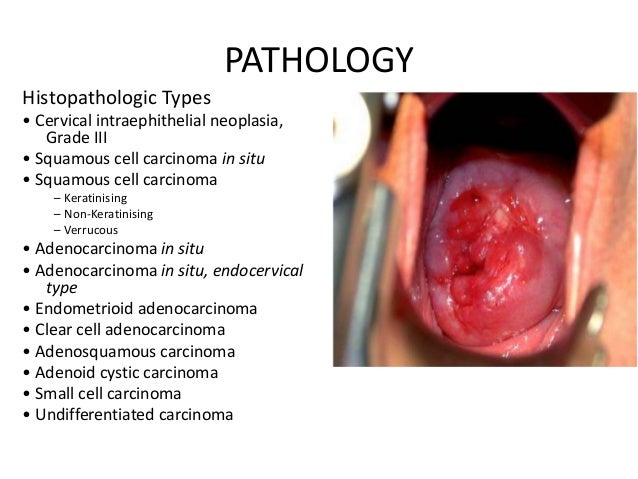
Cervical Cancer
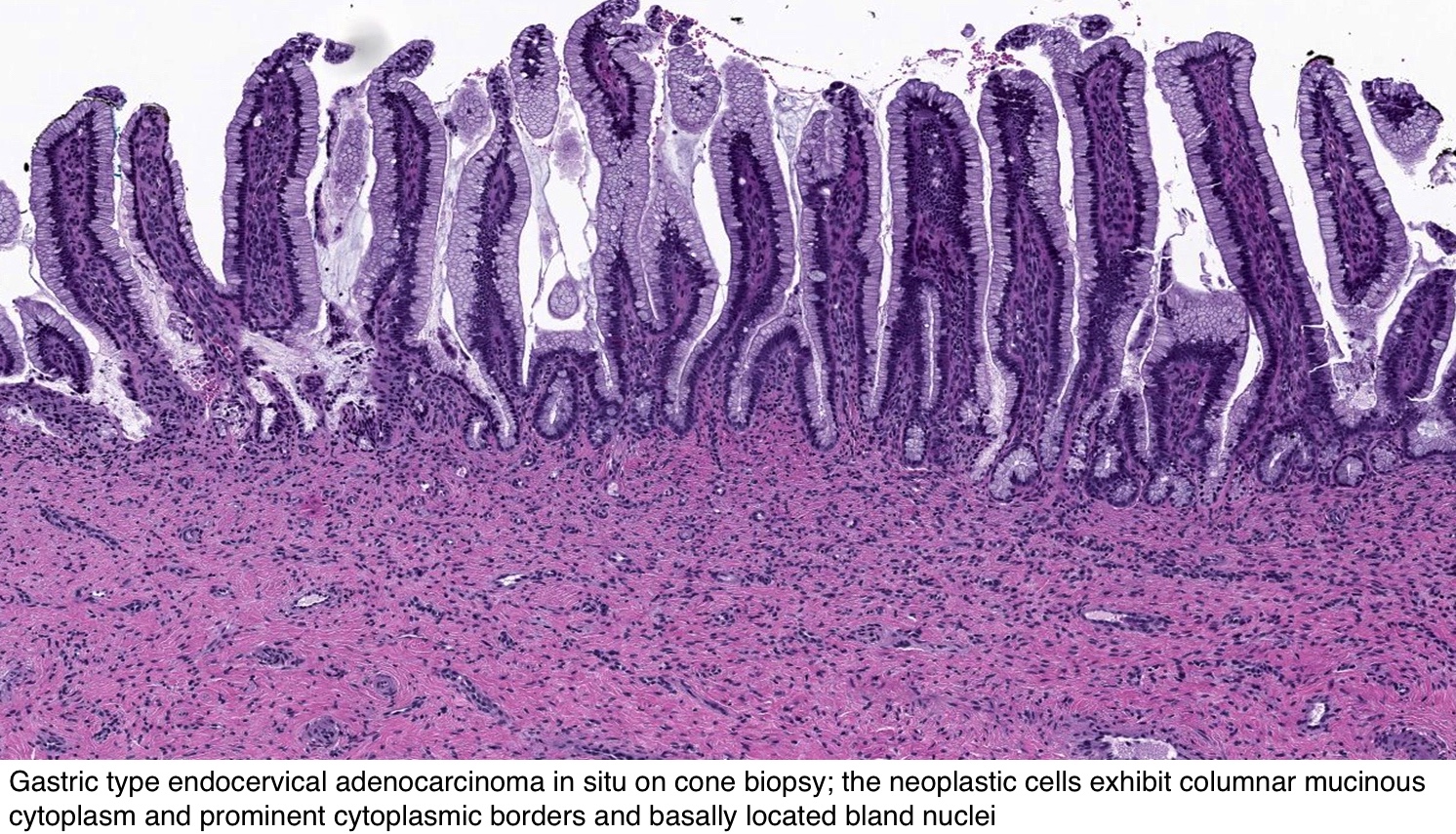
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

Cervical Adenocarcinoma Integration Of Hpv Status Pattern Of Invasion Morphology And Molecular Markers Into Classification Park Histopathology Wiley Online Library

Louise Gracielle Md Nice Example Of Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Associated With High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Notice The Intestinalization Of The Epithelium Atypia Apoptotic Bodies And Mitotic Figures Gynpath Gyn



