Fdg Pet Ct Scan
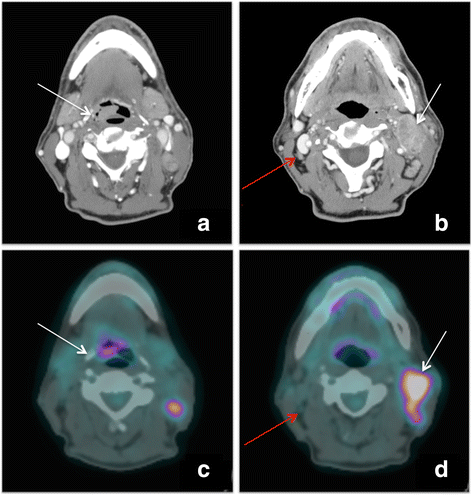
18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan Confirmed By Pathology Findings In A Singular Case Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Epiglottis European Journal Of Hybrid Imaging Full Text

Imaging The Inflammatory Activity Of Sarcoidosis European Respiratory Society
Plos One The Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct Integrated Imaging In Distinguishing Malignant From Benign Pleural Effusion
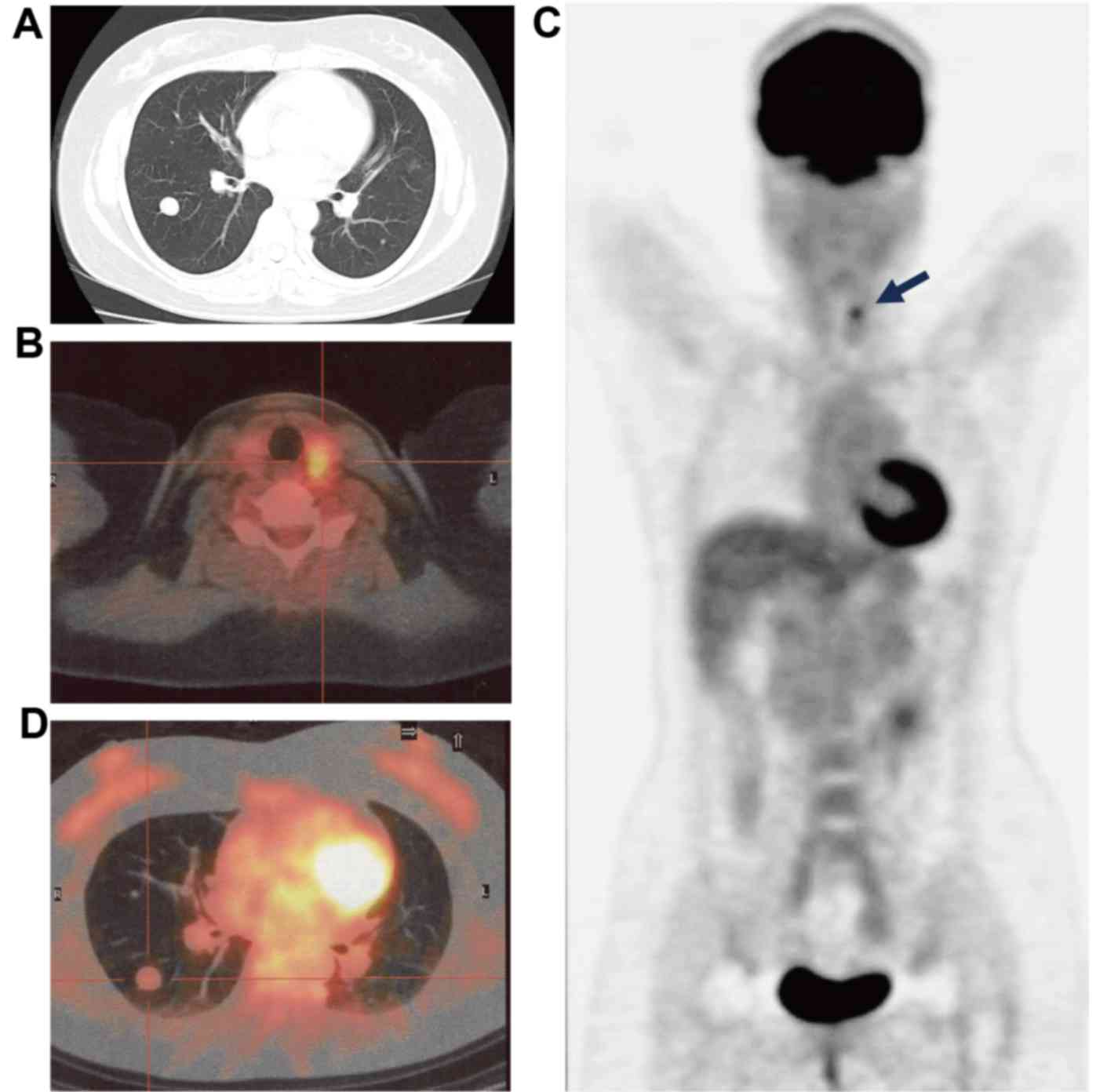
Benign Metastasizing Leiomyoma And 18 Fdg Pet Ct A Case Report And Literature Review

Effect Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Patients With Clinical Stage Ii And Iii Breast Cancer International Journal Of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics

Pet Ct Detection Of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection 18f Fdg Avid Radioiodine Negative Recurrent Thyroid Cancer Siemens Healthineers Philippines
A FDG PET/CT Scan is a diagnostic procedure which uses a small amount of a tracer (FDG) to help physicians identify abnormal from normal functioning organs and tissues FDG, when given to a patient, is absorbed by the body's cells.
Fdg pet ct scan. In follicular lymphoma (FL), detection of bone marrow (BM) involvement (BMI) by 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) improves the accuracy of staging vs BM biopsy (BMB) alone Our objective was to determine the diagnostic utility of PET for BMI FL and the prognostic value of BMI by PET (positive PET result PET ). Eightyseven patients (maletofemale ratio, 4641) diagnosed with pulmonary TB and extrapulmonary TB underwent wholebody 18 FFDG PET/CT for initial assessment and a followup scan 3 to 4 months after initiation of antitubercular therapy (ATT) Visual and semiquantitative (SUV max) analyses were used for scan assessment Treatment responses on interim scans were categorized as complete metabolic response (CMR), favorable response to therapy (FRT), stable disease (SD), and disease. Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography (PET/CT) is an imaging technique in which a small amount of radioactive sugar (18FFDG), once injected into one of your veins, provides information about the anatomy (CT) and function (PET) of your internal organs When your appointment is made we will need to know if any of the following applies to you.
A PETCT scan combines a PET scan and a CT scan PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography and is a medical imaging technique where the patient is given an injection containing a small amount of radioactive tracer prior to the scan to assess body function 18FFluorodeoxyglucose, more commonly known as 18FFDG, is the most commonly used radioactive tracer in PET. A PETCT scan will take approximately 2 hours from the time you arrive until completion Most of that time you will be relaxing in a comfortable room while the radioactive tracer accumulates in the body The PETCT scan itself will take about half an hour B During your FDG PETCT Scan – Oncology. Abstract This handout explains a positron emission tomography (PET)/CT FDG brain scan, which allows doctors to see your brain while it is working This scan is often used to check for tumors and to find the reason for memory problems Included are how to prepare for the scan, what to expect, and how to get your results.
PET sets the gold standard in the evaluation of an indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodule or mass, where PET has proven to be significantly more accurate than computed tomography (CT) For NSCLC chest CT is the standard imaging modality for assessing primary tumor size and identifying its margins. PETCT Diet Plan Before Your Exam If your PETCT scan is for cancer Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 24 hours Do not eat for six hours This includes tube feeding Do not chew gum You may drink only water If your PETCT scan is for a sarcoid heart scan, infection or inflammation Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 48 hours Do not eat. FDG PET/CT is useful in early detection of occult lesions in myeloid sarcoma which are nondetectable by conventional imaging techniques as CT or MRI It identifies extramedullary sites of involvement which facilitates biopsy and diagnosis.
FDG is an injected radionuclide (or radiopharmaceutical) that emits subatomic particles, known as positrons, as it decays FDG PET uses a positron camera (tomograph) to measure the decay of FDG The rate of FDG decay provides biochemical information on glucose metabolism in the tissue being studied. Axial fused FDG PETCT image shows extensive segmental occlusive and subocclusive pulmonary emboli (arrows), findings that would be missed with PET (b) FDG PETCT was performed for staging in a patient with Hodgkin lymphoma Axial fused FDG PETCT image of the brain shows an aneurysm of the right middle cerebral artery (long arrow). After 18F‐FDG PET/CT scan all, but one patient had a change in treatment for fever Anti‐tuberculous treatment was given in 15 patients, antibiotics in four patients and anti‐malaria treatment in one patient Discussion The present study is first study of 18F‐FDG PET/CT scan in patients of end stage renal disease on dialysis with FUO The study showed that the 18 F FDG PET/CT scan may present an opportunity to attain the diagnosis in end stage renal disease patients on dialysis with.
FDG PET/CT is a valuable imaging modality that impacts the clinical management of patients with CRC and those with anal cancer Keywords anal cancer, colorectal cancer, PET/CT, radiation therapy planning, therapy assessment Colorectal cancer (CRC) and anal cancer are major drivers of morbidity and mortality in the United States Accordingly, appropriate imaging for the diagnosis and management of these malignancies remains a topic of current investigations. Table 2 summarizes the typical ranges of techniques and dosimetry for these two categories of CT imaging for adult wholebody FDGPET/CT for a scan range from the eye to midthigh Additional helpful dosimetry can also be obtained from US Diagnostic Reference Levels and Achievable Doses for 10 Adult CT Examinations 18. The scan is carried out 60 minutes postinjection of FDG In cases of fusion imaging such as PETCT, the whole body CT scan is conducted first, followed by the wholebody PET scan and subsequently the two sets of images are coregistered.
Abstract The brain demonstrates substantial physiologic FDG avidity Malignancy involving the brain, including metastases, lymphoma, and primary gliomas, may be detected either as foci of FDG avidity greater than physiologic brain background, areas of FDG photopenia, or as lesions on the corresponding CT scan FDG PET/CT plays an important role in distinguishing recurrent malignancy from. What is a FDG PET/CT scan?. A PETCT scan combines a CT scan and a PET scan It gives detailed information about your cancer The CT scan takes a series of xrays from all around your body and puts them together to create a 3 dimensional (3D) picture The PET scan uses a mildly radioactive drug to show up areas of your body where cells are more active than normal.
Objectives Bone is the most frequent site of breast cancer metastasesConsidering many breast cancer patients are old age,bone is likely affected by degenerative or inflammatory bone diseaseRecently PET/CT has become an alternative study which could provide an accurate and efficient tool for detection of primary and metastatic fociThe purpose of this study was to compare the accuracy between PET/CT and bone scan for detecting bone metastases in breast cancer. 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality for cancer imaging, assisting diagnosis, staging of patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, restaging following therapy and surveillance Interpretation requires integration of the metabolic and anatomic findings provided by the PET and CT components which transcend the knowledge base isolated in the worlds of nuclear medicine and radiology, respectively. What is a PET/CT scan?.
Normal F18 FDG Distibution in PET/CT Imaging This radiotracer, which enters cells through glucose transporters and thus represents glycolytic rate of cells, is used to find many forms of cancers PET imaging is based on detecting coincident gamma photos from annhiliation events, thus providing higher resolution images than single photon imaging. FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) FDGPET can find fastgrowing neuroendocrine cancer cells for aggressive tumors A small amount of FDG, a type of radioactive glucose (sugar), is injected into a vein The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where the body is using glucose. What is an FDG PETCT Scan?.
FDG, PET/CT, attenuation correction 18Fflourodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) provides noninvasive metabolic and anatomic imaging The radioisotope, flouride18, has a short halflife allowing for imaging with limited patient dose Fluoride18 is used to chemically replace a hydroxyl group on glucose, and the resultant FDG is taken up into cells analogous to glucose. Fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT was performed for further evaluation The PET maximum intensity projection image (Figure, part A) depicted an FDGavid mass with a maximum standardized uptake value of 49 in the right lung Increased accumulation of FDG was noted in the right paratracheal and right hilar lymph nodes as well as in. A molecule similar to glucose Cancer cells absorb glucose at a higher rate which can be detected on PET/CT scans The radiotracer is injected into the body through intravenous access or port.
FDGPET Scan Your doctor has ordered a FDGPET scan Those abbreviations stand for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)positron emission tomography (PET) The role of this procedure is to detect metabolically active malignant lesions including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, brain cancer and multiple myeloma. F18 FDG PET /CT demonstrated intense uptake in the marginal parenchymal region of the cystic tumor in the left lobe of the liver Subsequently an extended left hepatectomy was performed The histopathological findings demonstrated biliary cystadenocarcinoma FDG / PET may thus contribute to the diagnosis of malignant cystic tumors in the liver. Following your 18FFDG PET/CT scan you can return to all normal daily activities You are advised to minimise contact with pregnant women and children (.
FDG PET scans involve a specialized sugar that shows up on PET scans This sugar injected into your body And since most tumors will take up more of it, it allows the tumor to show up on the PET scan Besides helping to diagnose cancer, FDG PET scans can also tell you if your cancer consumes a lot of sugar (ie if it’s “glucose avid” or not). PETCT Diet Plan Before Your Exam If your PETCT scan is for cancer Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 24 hours Do not eat for six hours This includes tube feeding Do not chew gum You may drink only water If your PETCT scan is for a sarcoid heart scan, infection or inflammation Follow a low carbohydrate diet for 48 hours Do not eat. Before your PETCT, you’ll get a radioactive medication with glucose called a tracer through an intravenous (IV) line in your arm This is done to show differences between healthy tissue and diseased tissue Your PETCT will use FDG as the tracer FDG is taken up by your cells and doesn’t stay in your body long.
WholeBody FDGPET/CT scans are not new to the Rheumatology world, but I guess it is to my Rheumatologist I’ve been reading about patients getting this type of scan for years now An interesting article to read from the NIH is found here. FDG stands for 2Deoxy218FfluoroDGlucose This exam uses Fluorine18 FDG, a radioactive tracer that acts like glucose in the body The tracer helps us see how much energy your cells are using We measure this with a FDG PET/CT scan A PET/CT camera takes 2 types of pictures • The PET scan shows where the tracer has collected in your body. The development of dualmodality positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) systems with nearsimultaneous acquisition capability has addressed the limited spatial resolution of PET and has improved accurate anatomical localization of sites of radiotracer uptake detected on PET.
18Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality for cancer imaging, assisting diagnosis, staging of patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, restaging following therapy and surveillance Interpretation requires integration of the metabolic and anatomic findings provided by the PET and CT components which transcend the knowledge base isolated in the worlds of nuclear medicine. FDG PET/CT plays an important role in distinguishing recurrent malignancy from benign radiation necrosis following radiation therapy of brain malignancy Benign findings resulting from seizures and infarcts must be distinguished from brain malignancy. Positron emission tomography, also called PET imaging or PET scan, is a test that images the function of cells to show differences between healthy tissue and diseased tissue It uses a small amount of a radioactive chemical which is combined with sugar.
In FDG, radioactive fluoride molecules are tagged to glucose to make a radiotracer FDG is the radiotracer most commonly used today Differences between PET, CT, and MRI scans. PATIENT PREPARATION FOR CARDIAC PET/CT FOR CARDIAC SARCOIDOSIS Optimal patient preparation is essential when using fluorine18 deoxyglucose (18FFDG) PET/CT to evaluate for CS The predilection for 18FFDG accumulation within inflamed tissues, in particular macrophages, is the pathophysiologic underpinning of 18FFDG PET/CT CS imaging It is impera. The scan is carried out 60 minutes postinjection of FDG In cases of fusion imaging such as PETCT, the whole body CT scan is conducted first, followed by the wholebody PET scan and subsequently the two sets of images are coregistered.
Positron emission tomography–computed tomography is a nuclear medicine technique which combines, in a single gantry, a positron emission tomography scanner and an xray computed tomography scanner, to acquire sequential images from both devices in the same session, which are combined into a single superposed image Thus, functional imaging obtained by PET, which depicts the spatial distribution of metabolic or biochemical activity in the body can be more precisely aligned or correlated. This handout explains a positron emission tomography (PET)/CT FDG brain scan, which allows doctors to see your brain while it is working This scan is often used to check for tumors and to find the reason for memory problems Included are how to prepare for the scan, what to expect, and how to get your results. A morning blood glucose level below 175 mg/dL is a safe range for your PET/CT FDG scan appointment • In the morning after your practice run, you may return to your normal routines of eating and taking medicine until the evening before your scan On the Day of Your Scan • Fast overnight for 12 hours before your scan.
Introduction Readers of fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scans are familiar with the typical radiotracer pattern that results from high levels of heterogeneous FDG uptake in the bowel, especially the large bowel, attributed to metforminrelated medication effect ( 1, 2 ) However, in cancer imaging with FDG PET/CT or PET/MRI, the high FDG activity throughout the bowel due to metformin can potentially confound detection and assessment of treatment response in both primary malignancy. One of the best ways of cancer detection is a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) ScanTypically, glucose speeds up the growth of cancer cells and that is why doctors inject glucose into the patient’s body when performing the PET scan. 18FFDG PET is a noninvasive diagnostic technique utilizing biochemical metabolic differences between benign and malignant tissues Integrated PET/CT combines func tional imaging and anatomic imaging and has increased diagnostic accuracy To date, few studies have reported the role of18FFDG PET/CT in the evaluation of ascites.
FDG PET/CT is useful in early detection of occult lesions in myeloid sarcoma which are nondetectable by conventional imaging techniques as CT or MRI. A retrospective study of 15,109 18FFDG PET/CT scans of 10,432 patients (5035 males and 5397 females, BMI 256 5kgm22, age years) was performed over a 7year period from January 08 to October 14 All 18FFDG PET/CT scans were performed on wholebody PET/CTscanners (Gemini TF or Gemini TF Big Bore;. The radioactive substance most commonly used in PET scanning is a simple sugar (like glucose) called FDG, which stands for “fluorodeoxyglucose” It is injected into your bloodstream and accumulates in your body where it gives off energy This energy is detected by the PET scanner creating images showing how your tissues and organs are working.
F18 FDG PET /CT demonstrated intense uptake in the marginal parenchymal region of the cystic tumor in the left lobe of the liver Subsequently an extended left hepatectomy was performed The histopathological findings demonstrated biliary cystadenocarcinoma FDG / PET may thus contribute to the diagnosis of malignant cystic tumors in the liver. Radiotracer accumulates in cancerous tumors as well in the areas of inflammation F18 fluorodeoxyglucose or FDG is the most commonlyused radiotracer;. The purpose of these guidelines is to assist physicians in recommending, performing, interpreting, and reporting the results of 18FFDG PET/CT for oncologic imaging of adult and pediatric patients PET is a tomographic scintigraphic technique in which a computergenerated image of local radioactive.
FDGPET scan (fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography scan) FDGPET can find fastgrowing neuroendocrine cancer cells for aggressive tumors A small amount of FDG, a type of radioactive glucose (sugar), is injected into a vein The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where the body is using glucose. This brings the total dose of FDGPET/CT to a range of ~8 mSv up to 30 mSv, depending on the type of study performed as well as the anatomical region and number of body parts imaged, although several recent studies have reported a typical average dose of ~14 mSv for skull basetothigh FDGPET/CT examinations 28. Conclusions The difference between bone scan and PET/CT for detection of bone metastases may be attributable to the different mechanismBone scan depends on the osteoblastic response to bone destruction by tumor cells,and FDGPET/CT detects the metabolic activity of the tumor cellsTherefore FDG PET/CT and bone scan are complementary modalities and bone scan is still important tool to detect.
By Paul T Finger, MD Whole body PET/CT technology combines positron emission tomography (PET) with computed radiographic imaging (CT) to put FUNCTION and FORM on the same diagnostic page (PET/CT) Spiral computed tomography CT is used to generate anatomic images of the entire body When suspicious areas or tumors are found, CT allows your doctor to see their Read More. A retrospective study of 15,109 18FFDG PET/CT scans of 10,432 patients (5035 males and 5397 females, BMI 256 5kgm22, age years) was performed over a 7year period from January 08 to October 14 All 18FFDG PET/CT scans were performed on wholebody PET/CTscanners (Gemini TF or Gemini TF Big Bore;. A PETCT scan is a way to create pictures of organs and tissues inside the body A small amount of a radioactive sugar substance is injected into the patient’s body This sugar substance is taken up by cells that use the most energy Because cancer tends to use energy actively, it absorbs more of the radioactive substance.
PET scan images can provide important information about many disorders that affect the heart, lung, brain, bones, liver etc and will help the doctor plan appropriate treatment for you PET images are different than those from more conventional radiological studies such as CT scan, Ultrasound, or MRI. This information will help you get ready for your positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography (CT) scan with fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) tracer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) See how the tissues and organs in your body are working Find and diagnose many disorders, such as cancer Plan. The scan is carried out 60 minutes postinjection of FDG In cases of fusion imaging such as PETCT, the whole body CT scan is conducted first, followed by the wholebody PET scan and subsequently the two sets of images are coregistered.
A PETCT scan is a nuclear medicine imaging test used commonly to detect a range of cancers, heart diseases, neurological conditions, infections and PUO (Pyrexia of Unknown Origin)Radioactive glucose is injected and then taken up by tissues, which are in fasting state in your body Activity within your body is then detected by the PET scanner which shows how tissue and organs are working. Abstract Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging is a metabolic imaging technique using a radioactive tracer, 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (18 FFDG), to identify the presence and severity of disease, namely cancers Most malignant tissues have increased 18 FFDG uptake associated with an increased rate of glycolysis and of glucose transport.
Q Tbn And9gcs3fz2n2aqkoumcnqtaawjx1fn1ip5wtfkwjfskwuwtwsfcnoew Usqp Cau
18 F Fdg Pet Ct Based Spleen To Liver Ratio Associates With Clinical Outcome To Ipilimumab In Patients With Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Imaging Full Text

Abnormal Brain Metabolism On Fdg Pet Ct Is A Common Early Finding In Autoimmune Encephalitis Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation

Prone 18f Fdg Pet Ct Changes Diagnostic And Surgical Intervention In A Breast Cancer Patient Some Considerations About Pet Ct Imaging Acquisition Protocol Clinical Imaging

Pitfalls And Artifacts In The Interpretation Of Oncologic Pet Ct Of The Chest

Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Cardiac Viability Perth Envision
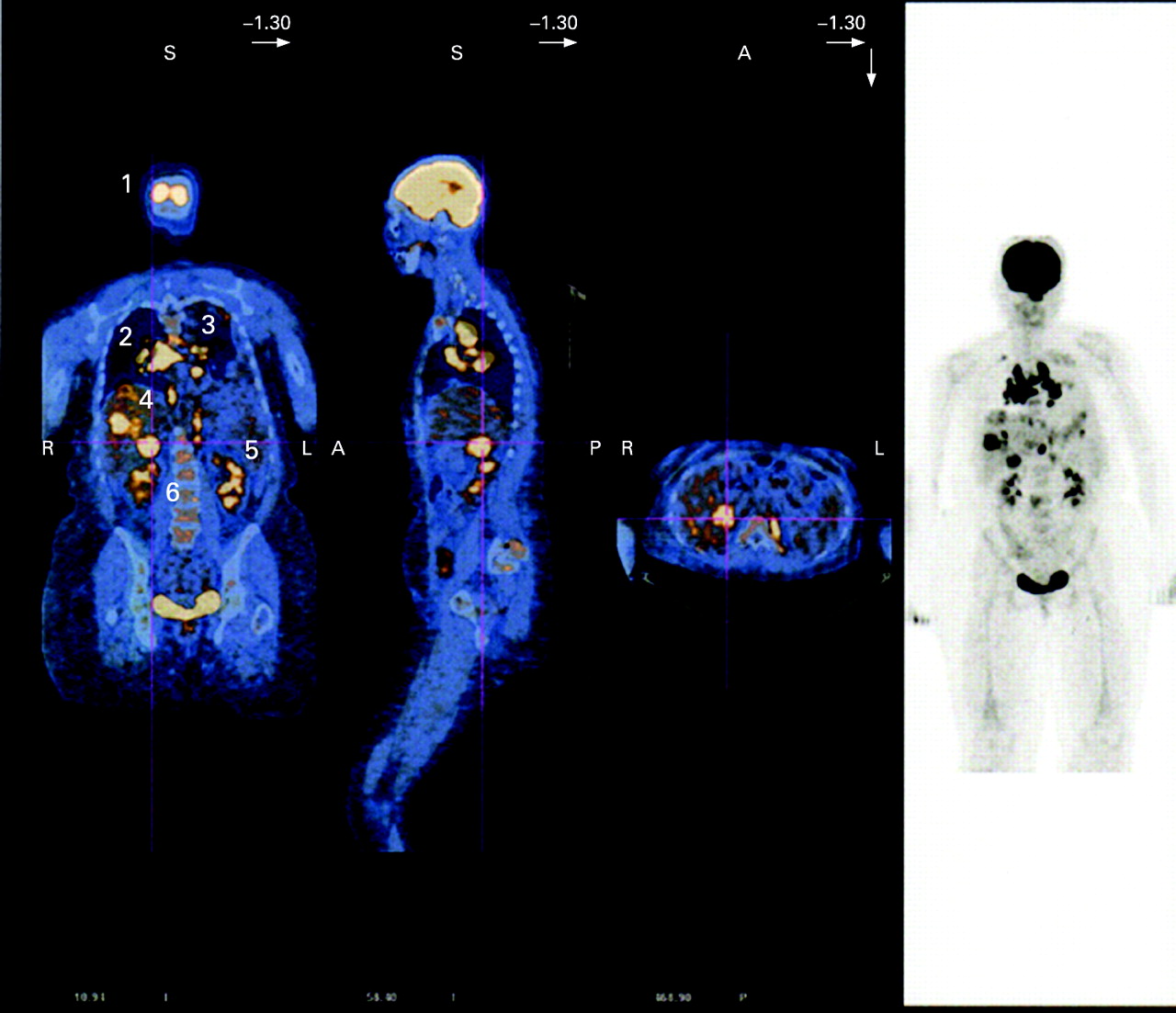
Whole Body 18 Fdg Pet Ct Imaging For Lymph Node And Metastatic Staging Of Conjunctival Melanoma British Journal Of Ophthalmology

When Should Fdg Pet Be Used In The Modern Management Of Lymphoma Barrington 14 British Journal Of Haematology Wiley Online Library

Fdg Pet Ct Scan Before A And After B Chemotherapy A Left Level 3 Download Scientific Diagram

Fdg Pet Ct Normal Variants Artefacts And Pitfalls In Hepatobiliary And Pancreatic Malignancies Radiology Key
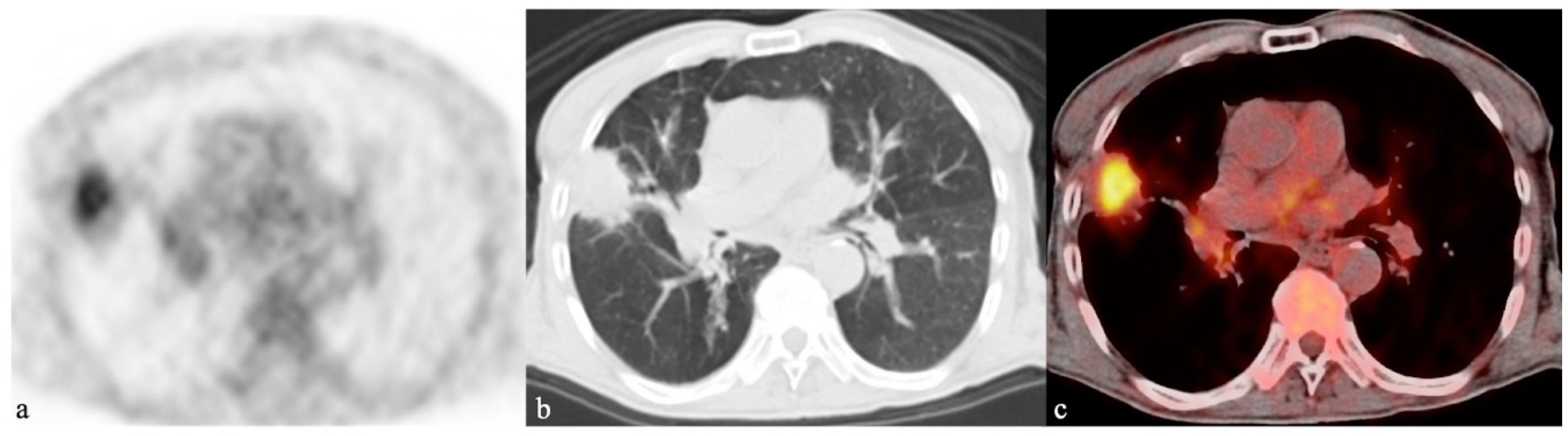
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Imaging Of Pulmonary Inflammation And Infection Html

Fdg Pet Shows Tumor Dna Levels In Blood Are Linked To Nsclc Aggressiveness Eurekalert Science News

The Value Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Early Detecting Asymptomatic Drug Induced Pneumonitis In Patients With Lymphoma Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
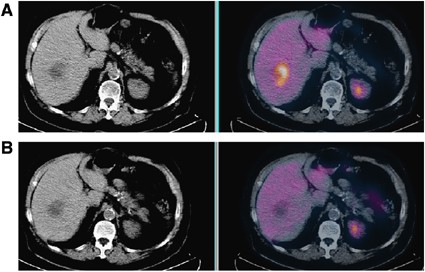
Quantitative Techniques In 18 Fdg Pet Scanning In Oncology British Journal Of Cancer

Normal F 18 Fdg Pet Ct Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

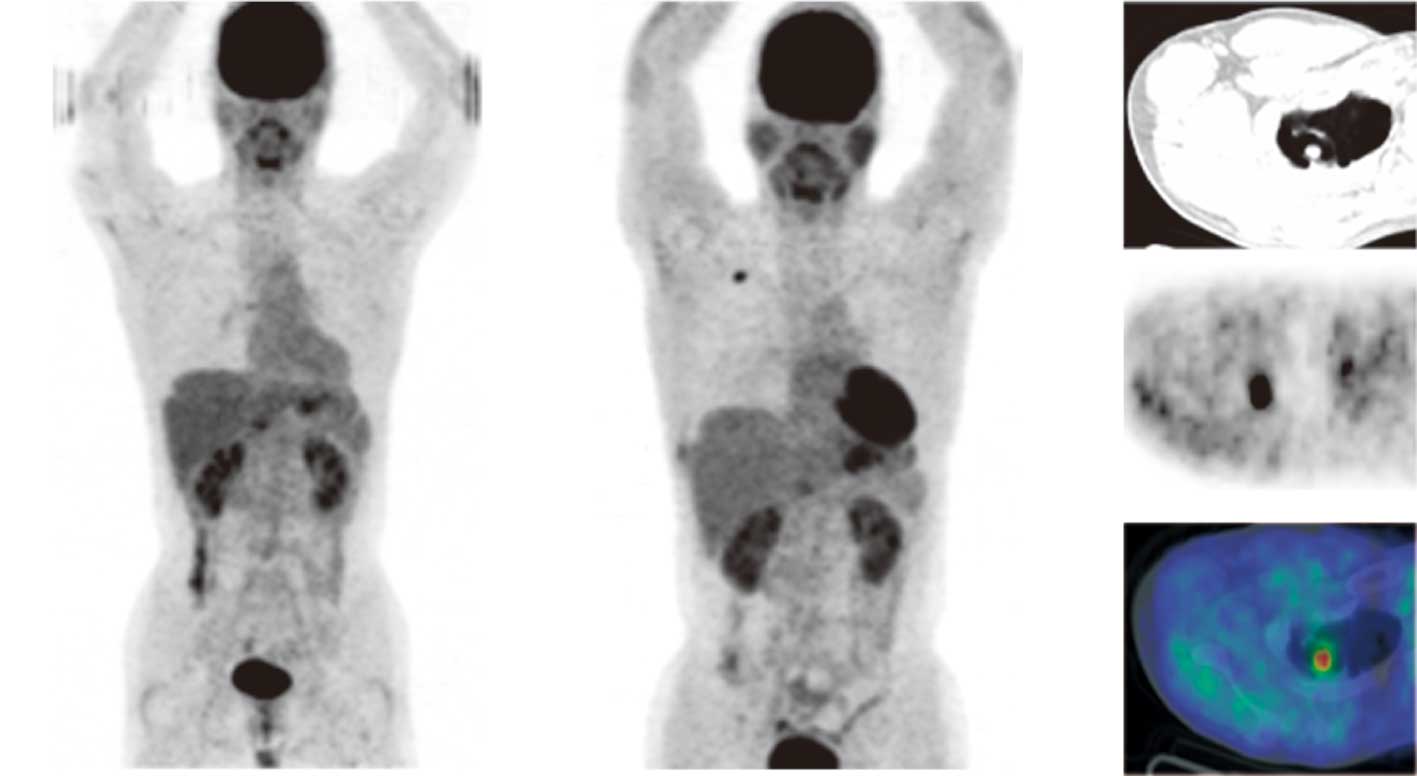
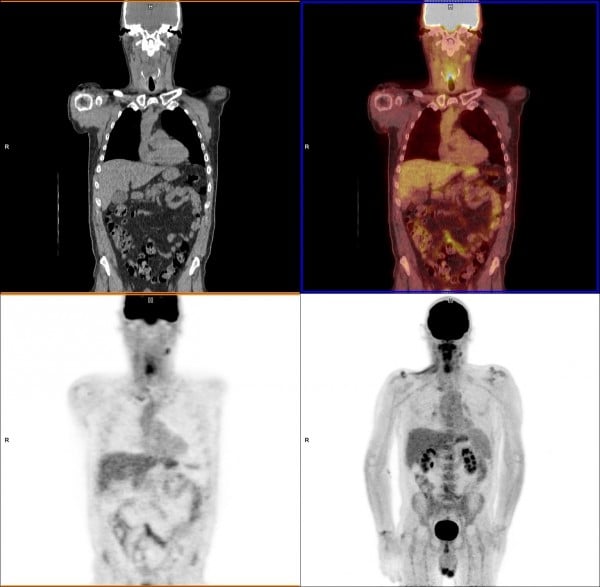
18 F Fdg Pet Ct Scan With Whole Body Images And Dedicated Download Scientific Diagram

Novel Strategy For A Cocktail 18f Fluoride And 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Evaluation Of Malignancy Results Of The Pilot Phase Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
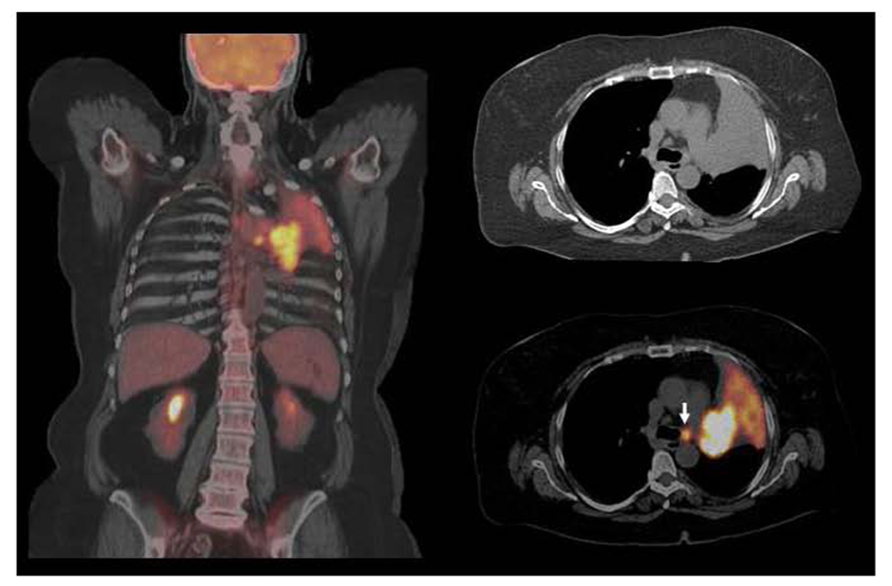
Frontiers Current Concepts In F18 Fdg Pet Ct Based Radiation Therapy Planning For Lung Cancer Oncology
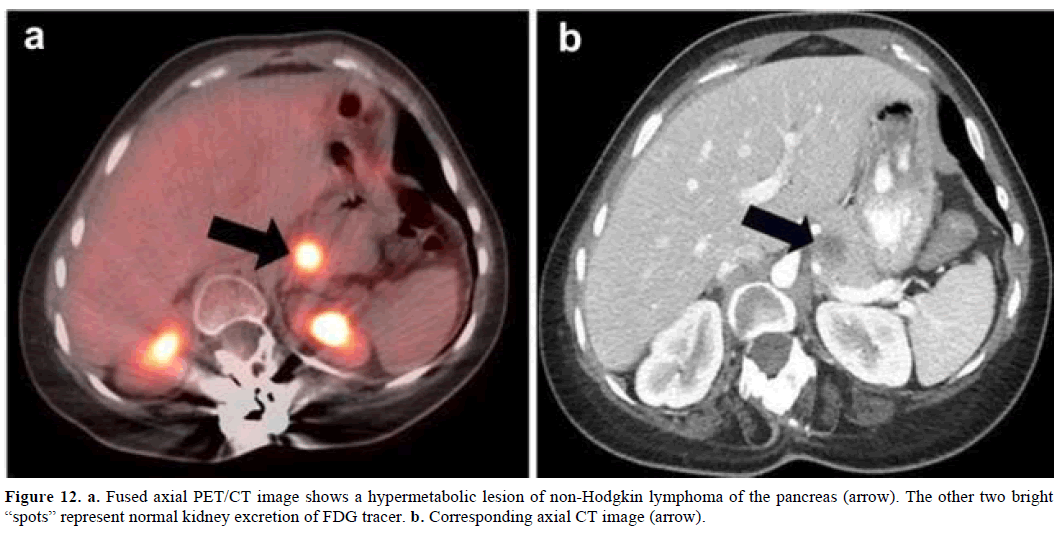
18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of The Pancreas Spectrum Of Diseases Insight Medical Publishing

Fdg Pet Ct Has Limits In Esophageal Cancer Follow Up
What Is Pet Imaging Imaging Technology News
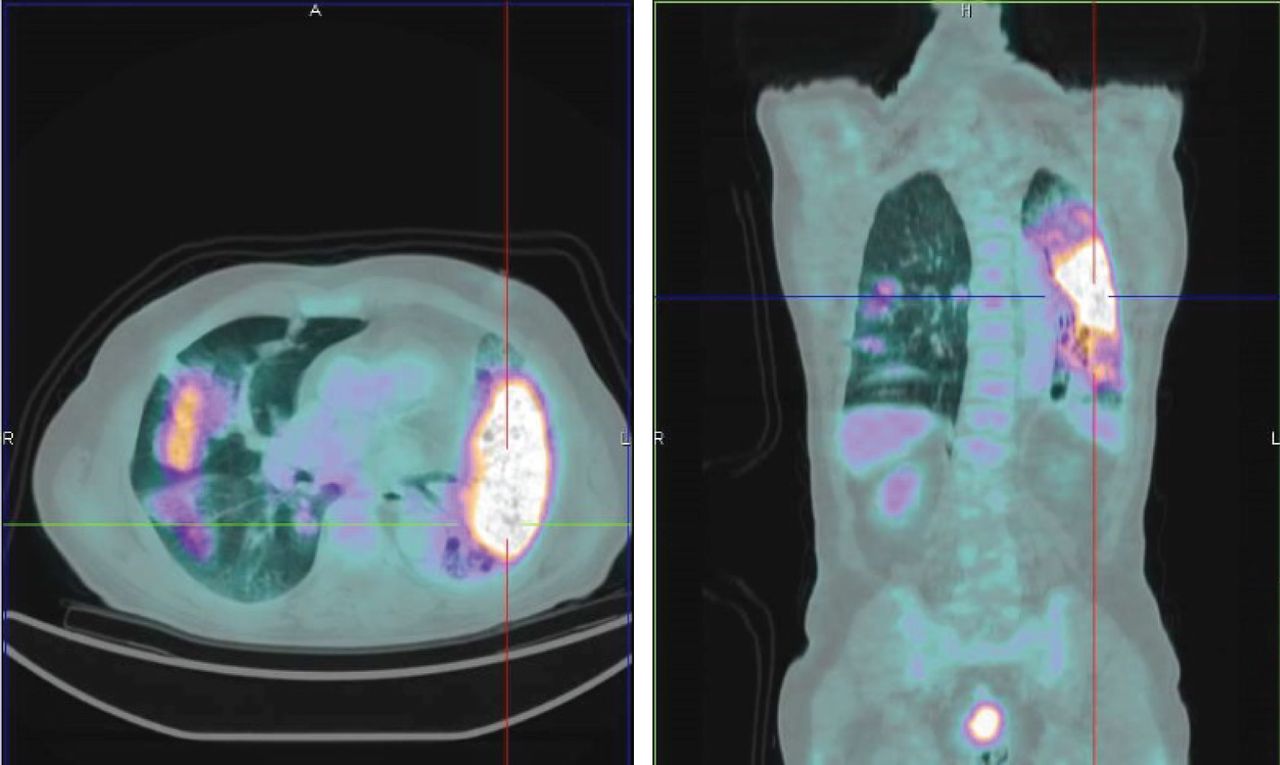
Pet Ct In Nononcological Lung Diseases Current Applications And Future Perspectives European Respiratory Society
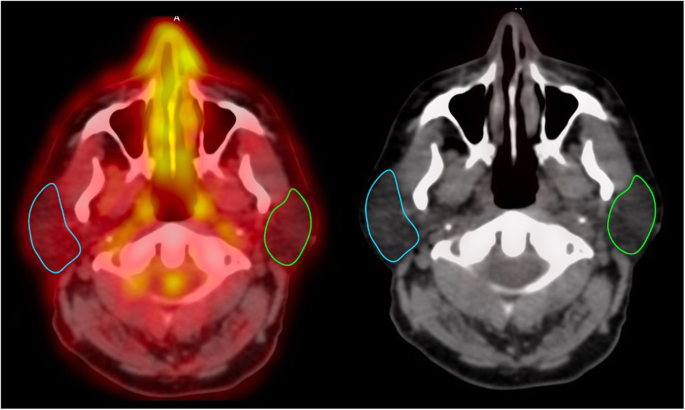
18 F Fdg Pet Ct In Radiation Therapy Induced Parotid Gland Inflammation European Journal Of Hybrid Imaging Full Text

Use Of Fdg Pet Ct Scan In The Planning Of Radiation Therapy For Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
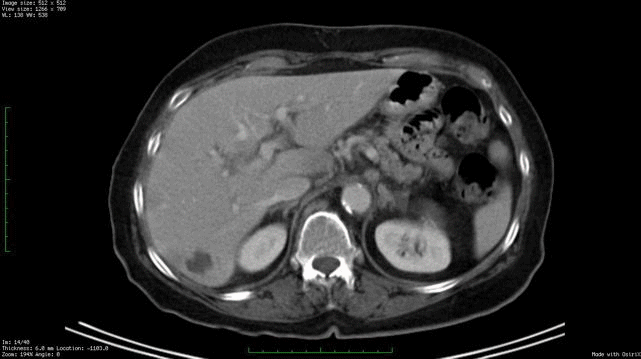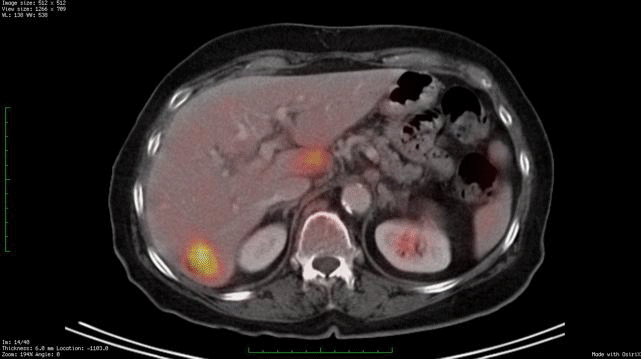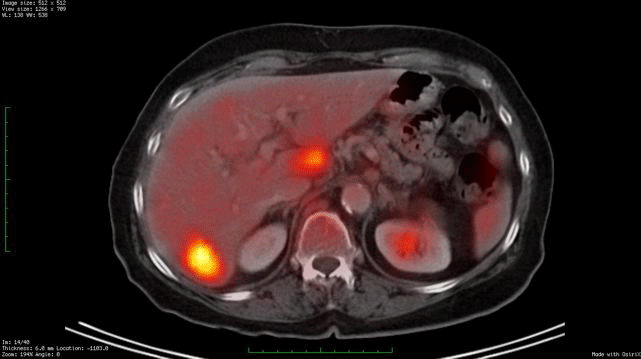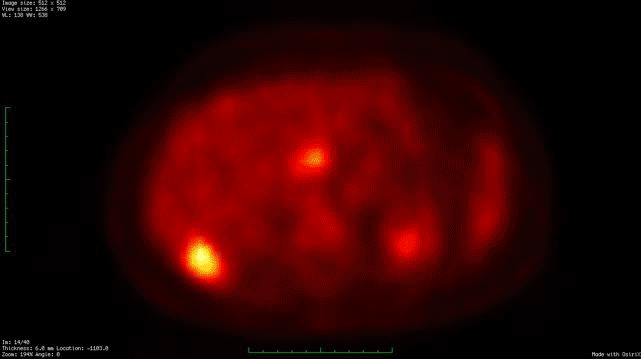
Whole Body Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Cancer New York Eye Cancer Center

The Value Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Identifying The Cause Of Fever Of Unknown Origin Fuo And Inflammation Of Unknown Origin Iuo Data From A Prospective Study Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases

Diagnostic And Clinical Impact Of Staging 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Mantle Cell Lymphoma A Two Center Experience Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma And Leukemia
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Figure 1 From The Diagnostic Contribution Of 18 F Fdg Pet Ct Scan In Cancer Of Unknown Primary Semantic Scholar
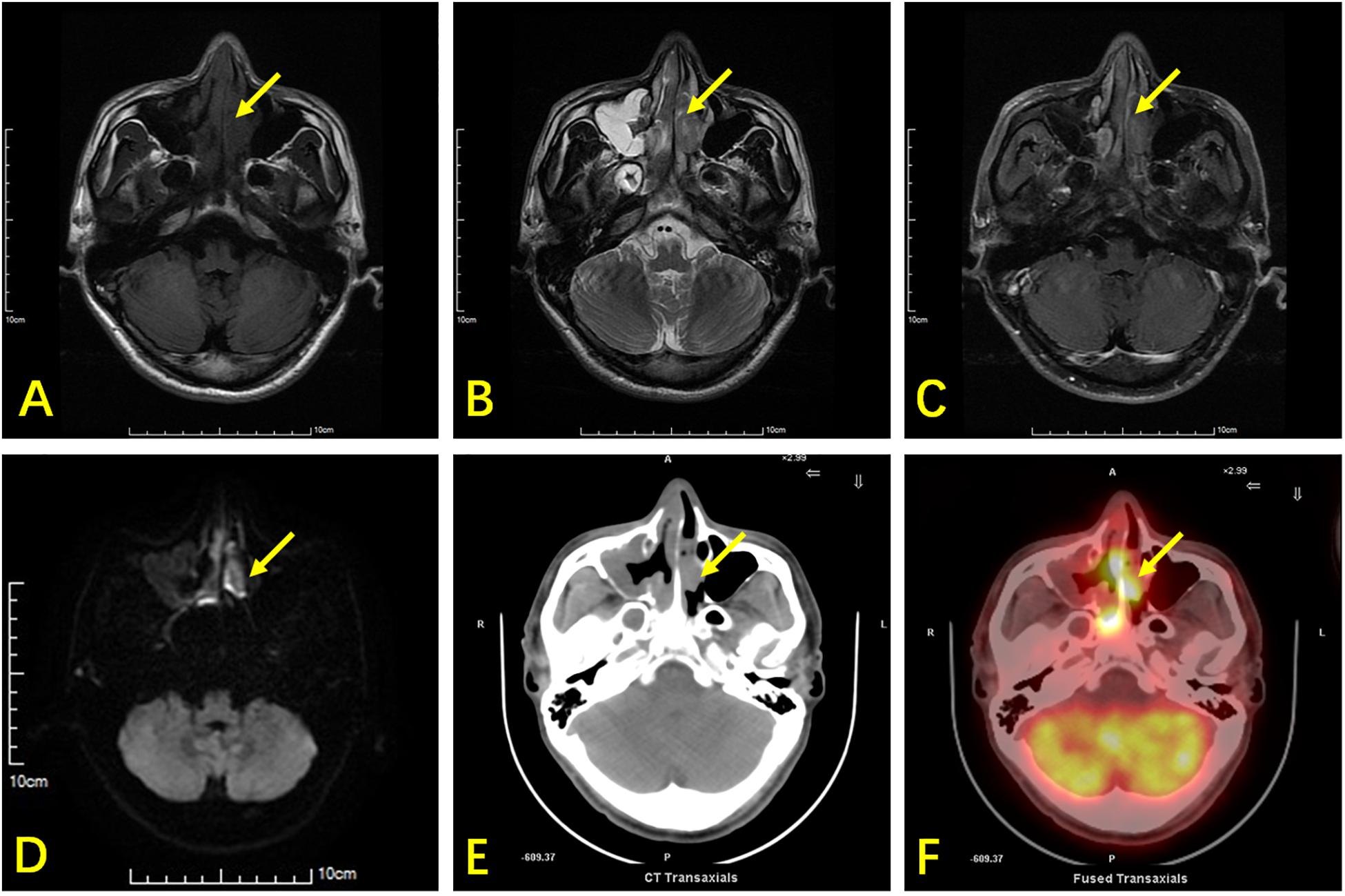
Frontiers Comparison Of Nasopharyngeal Mr 18 F Fdg Pet Ct And 18 F Fdg Pet Mr For Local Detection Of Natural Killer T Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type Oncology

The Value Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Breast Cancer Staging Bosnian Journal Of Basic Medical Sciences

Earlier Diagnosis And Treatment Assessment Of Tuberculosis Achieved With Pet Ct Eurekalert Science News
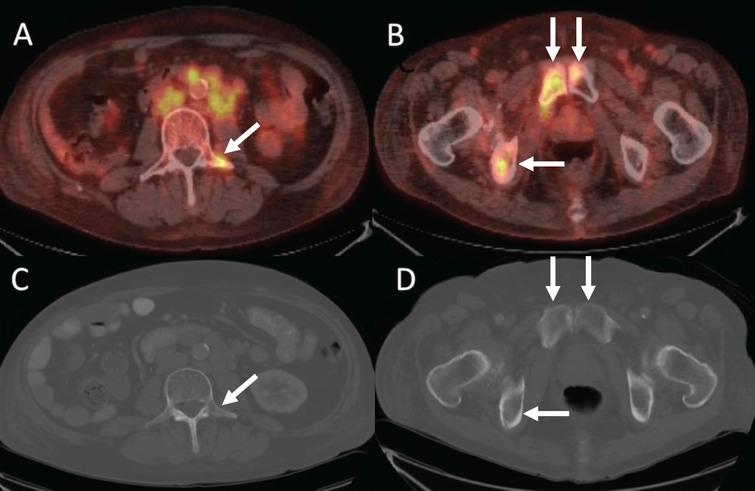
Utility Of Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma With Osseous Metastases Comparison With Ct And 99mtc Mdp Bone Scan In A Prospective Clinical Trial Ios Press

At Baseline 18 F Fdg Pet Ct Scan With Contrast A 3d Mip Image In Download Scientific Diagram
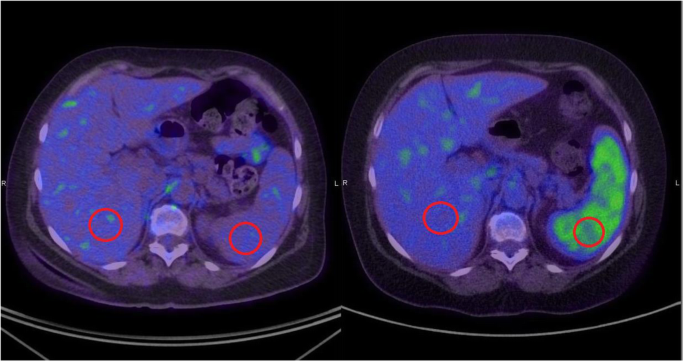
Atypical Spleen Tuberculosis In A Melanoma Patient Accidentally Detected During A 18f Fdg Pet Ct Study Case Report
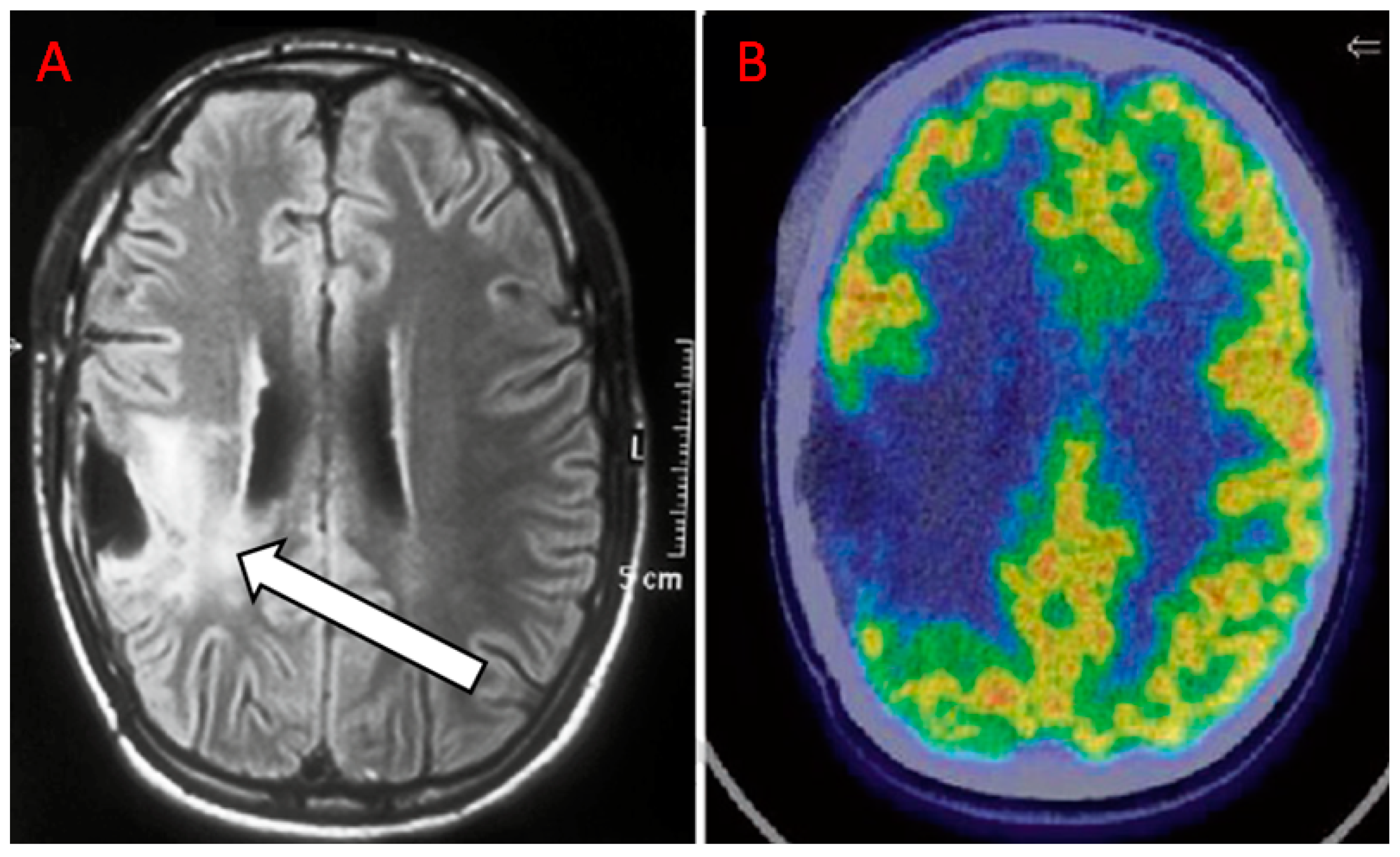
Diagnostics Free Full Text The Additional Value Of 18f Fdg Pet And Mri In Patients With Glioma A Review Of The Literature From 15 To

Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association

Non Corrected Images Guide Correct Interpretation Of Fdg Pet Ct Artifactual Fdg Uptake In Vertebra Due To Bone Cement Joshi P Lele V Shah H Indian J Nucl Med
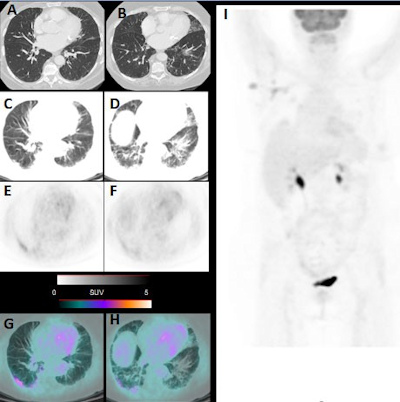
Incidental Covid 19 Findings Seen On Routine Fdg Pet Ct
Q Tbn And9gctiqg0j2igvmrudd069vz32x6fzk8q2e0wnbbu8 Ueb Rc0lk86 Usqp Cau

Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Pyrexia Of Unknown Origin Sciencedirect

Ct And Fdg Pet Ct Of The Chest A Ct Scan And B Fdg Open I

18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Oncology Annals Of Saudi Medicine

Usefulness And Pitfalls Of F 18 Fdg Pet Ct For Diagnosing Extramedullary Acute Leukemia European Journal Of Radiology
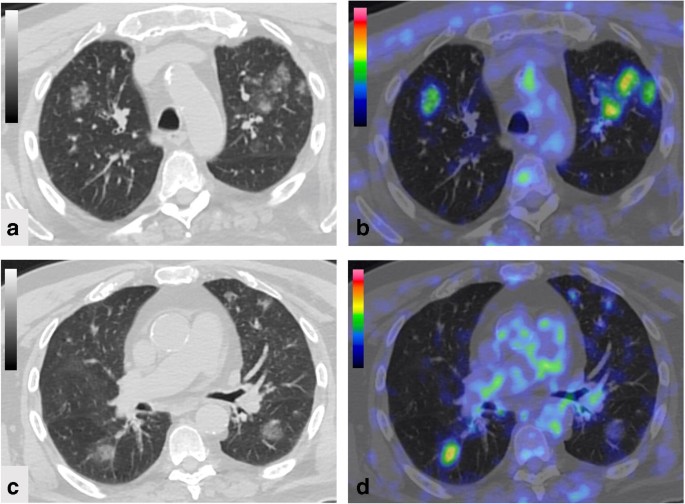
Fdg Pet Ct Imaging During The Covid 19 Emergency A Southern Italian Perspective Springerlink

Fever Of Unknown Origin The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Sciencedirect
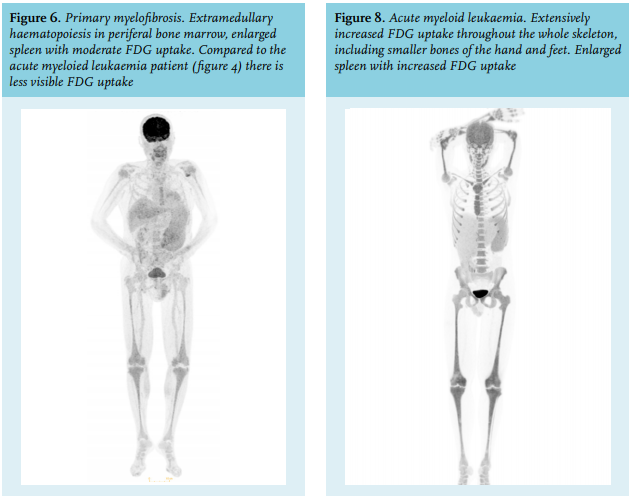
Article The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Scans To Evaluate Bone Marrow In Haemato Oncological Conditions Full Text September 19 Njm
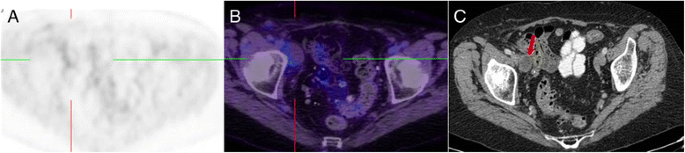
How We Read Oncologic Fdg Pet Ct Cancer Imaging Full Text
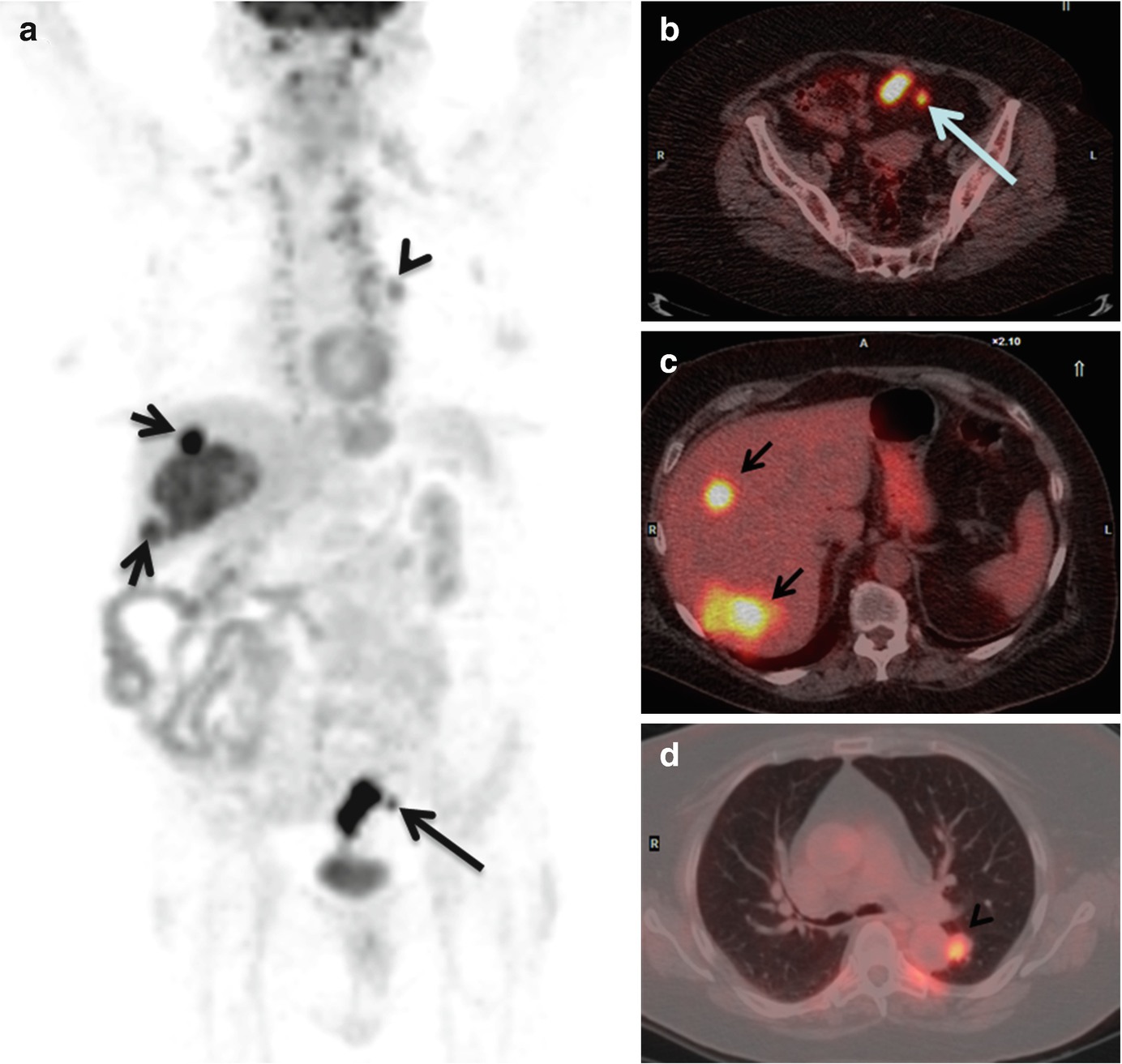
Role Of Fdg Pet Ct In Colorectal Cancer Springerlink

When Should Fdg Pet Be Used In The Modern Management Of Lymphoma Barrington 14 British Journal Of Haematology Wiley Online Library

Malignant Involvement Of The Spine Assessment By 18f Fdg Pet Ct Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Clinical Applications Of Fdg Pet And Pet Ct In Head And Neck Cancer

Diagnostic Performance Of Pet Or Pet Ct With Different Radiotracers In Patients With Suspicious Lung Cancer Or Pleural Tumours According To Published Meta Analyses
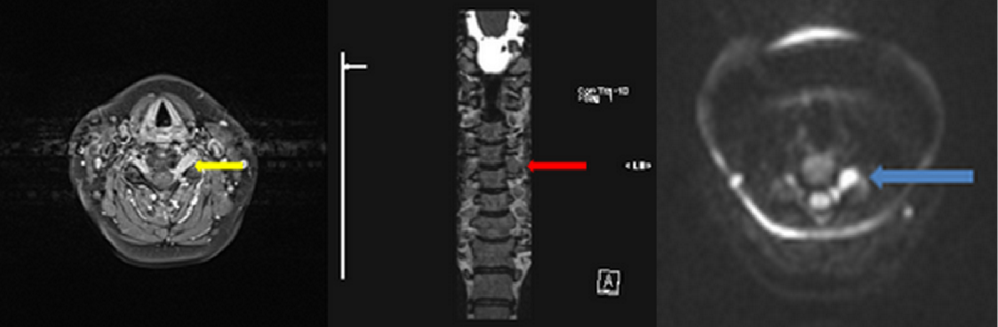
Cureus Quantitative Imaging Analysis Of Fdg Pet Ct Imaging For Detection Of Central Neurolymphomatosis In A Case Of Recurrent Diffuse B Cell Lymphoma

Whole Body Positron Emission Tomography 18 Fdg Pet Ct Open I
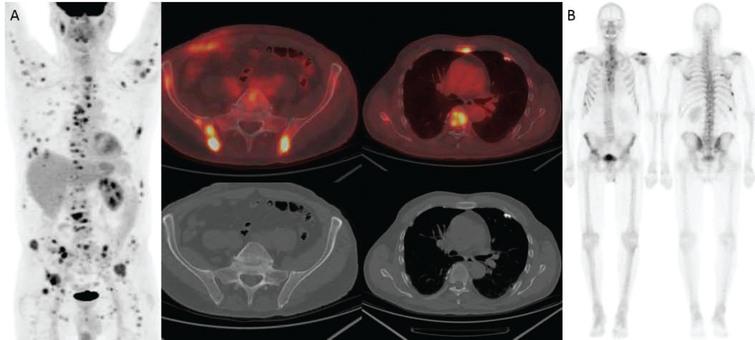
Utility Of Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma With Osseous Metastases Comparison With Ct And 99mtc Mdp Bone Scan In A Prospective Clinical Trial Ios Press

Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Granulomatous Changes Secondary To Breast Silicone Injection Clinical Radiology

Role Of 18 F Fluoro 2 Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Malignant Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors A Single Center Experience With Long Term Follow Up International Journal Of Gynecologic Cancer

Rational Use Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma A Systematic Review Sciencedirect

Clinical Utility Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In The Follow Up Of A Large Cohort Of Patients With High Risk Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Q Tbn And9gctog794rzftwzvgcjzd0fdawd 2fygzisgpiou A6pklkuaqyb5 Usqp Cau
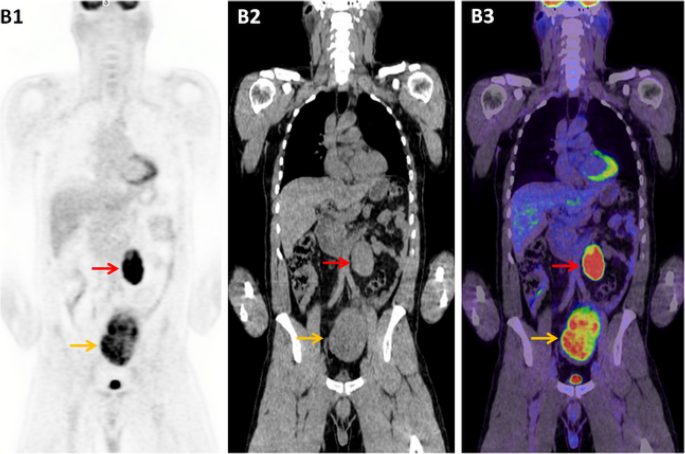
The Role Of 18 F Fdg Pet Ct In Evaluating Retroperitoneal Masses Keeping Your Eye On The Ball Cancer Imaging Full Text
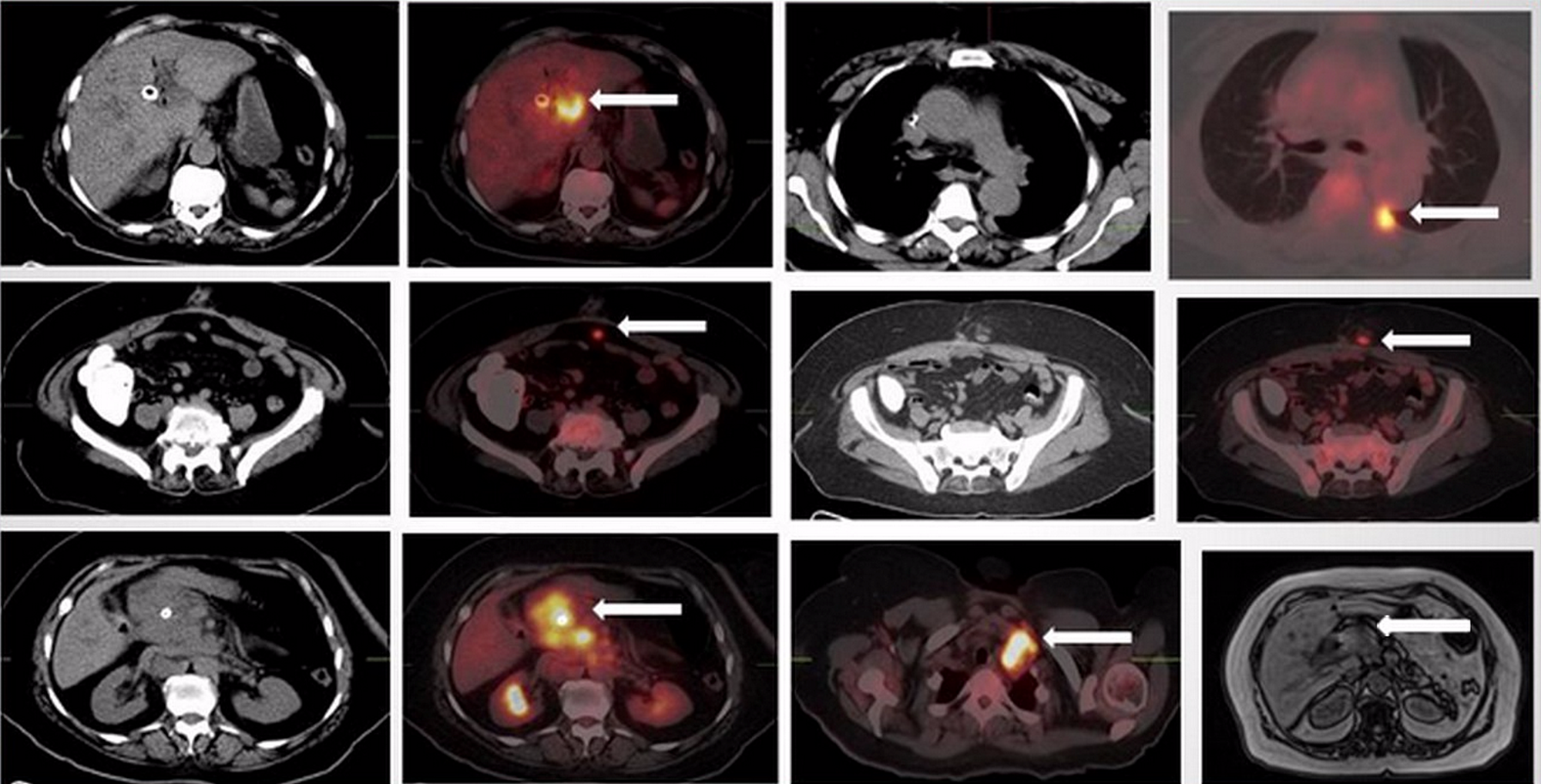
Cureus 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma A Pictorial Review

Pdf False Positive Fdg Pet Ct Scan In Vertebral Hemangioma Semantic Scholar
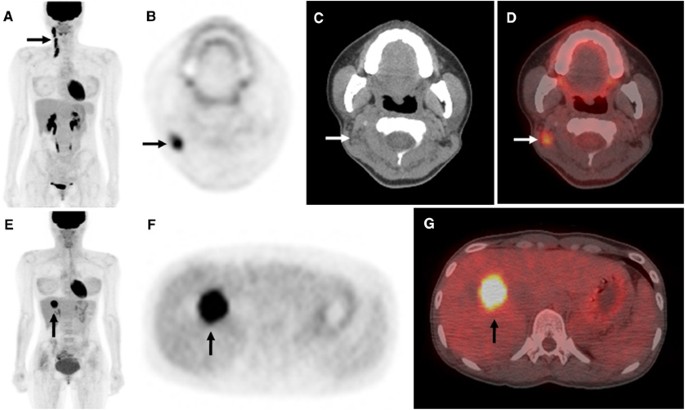
Fdg Pet Ct Helps Stage Men With Breast Cancer Too

Inclusion Of Brain In Fdg Pet Ct Scanning Techniques In Cancer Patients Does It Obviate The Need For Dedicated Brain Imaging Semantic Scholar

Accuracy Of Positron Emission Tomography Ecr Journal

Fdg Pet Ct Scan Demonstrating Bilateral Increased Fdg Activity In The Download Scientific Diagram
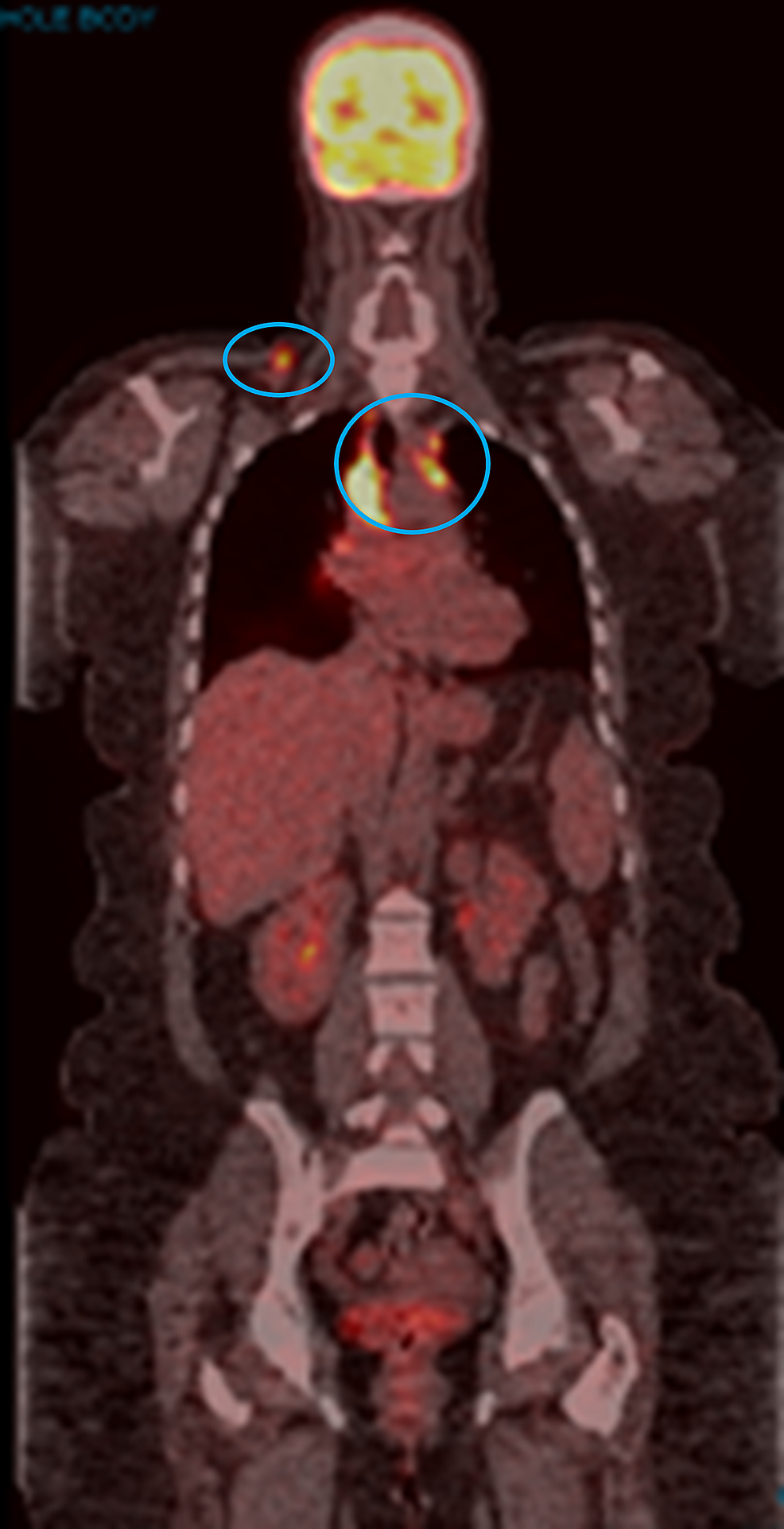
Cureus Pembrolizumab Induced Sarcoid Like Reaction Fdg Pet Scan Interpretation In The Era Of Immunotherapy
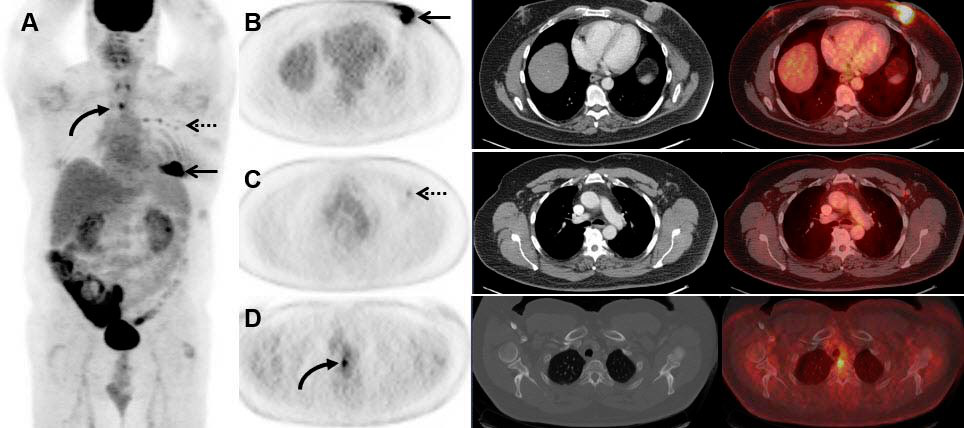
18 F Fdg Pet Ct Surveillance At 3 6 And 12 Months For Detection Of Recurrence And Second Primary Cancer In Patients With Head And Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma British Journal Of Cancer
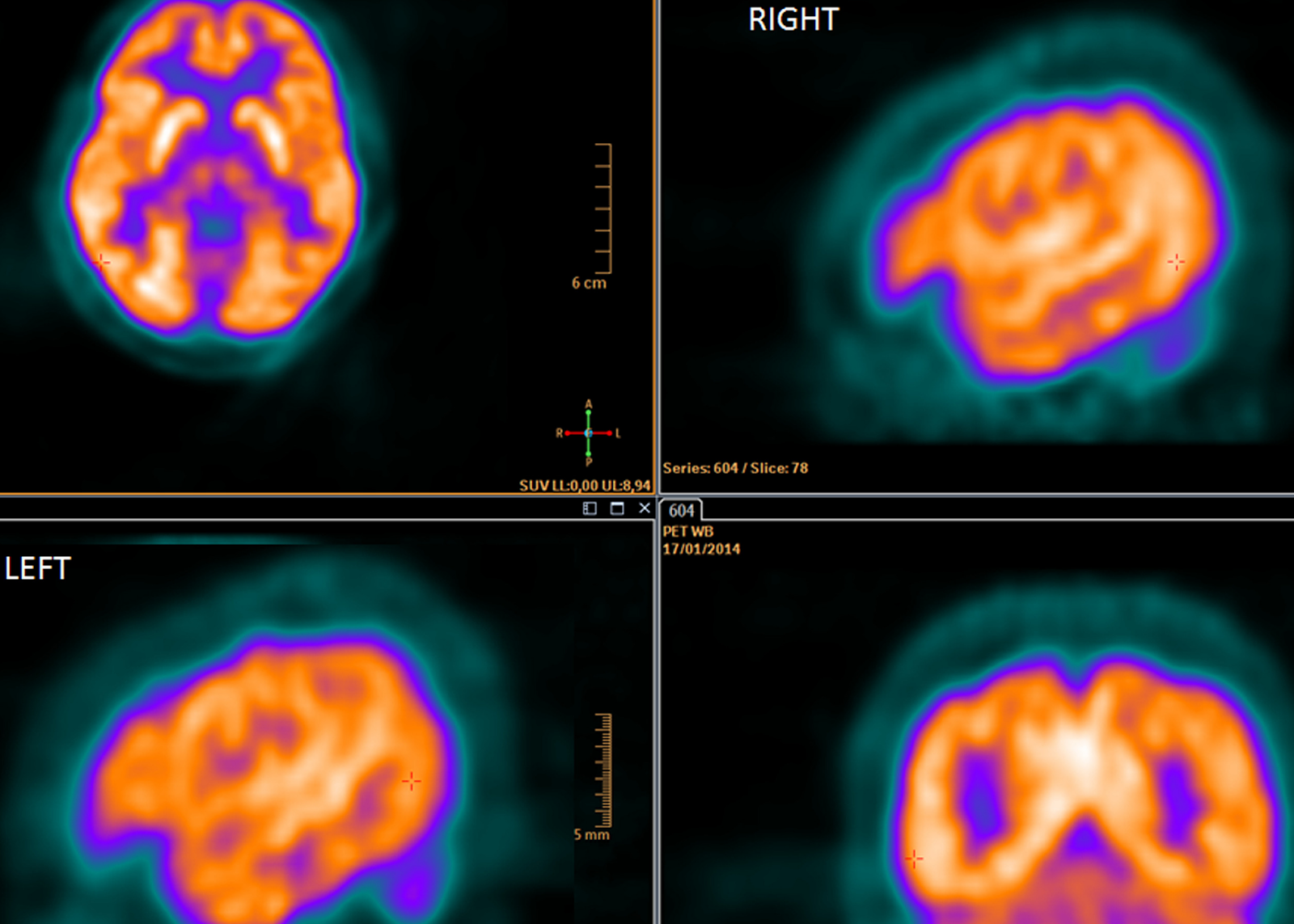
Fdg Pet Ct In Clinical Decision Making Science 2 0
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Resisting The Need To Quantify Putting Qualitative Fdg Pet Ct Tumor Response Assessment Criteria Into Daily Practice American Journal Of Neuroradiology

The Use Of Pet Ct In Rheumatology In Hong Kong Bulletin On Rheumatic Diseases Volume 17 Issue 1 17

Accuracy Of Positron Emission Tomography Ecr Journal

Total Body Pet Ct Captures Full Picture Of Systemic Inflammatory Arthritis Imaging Technology News
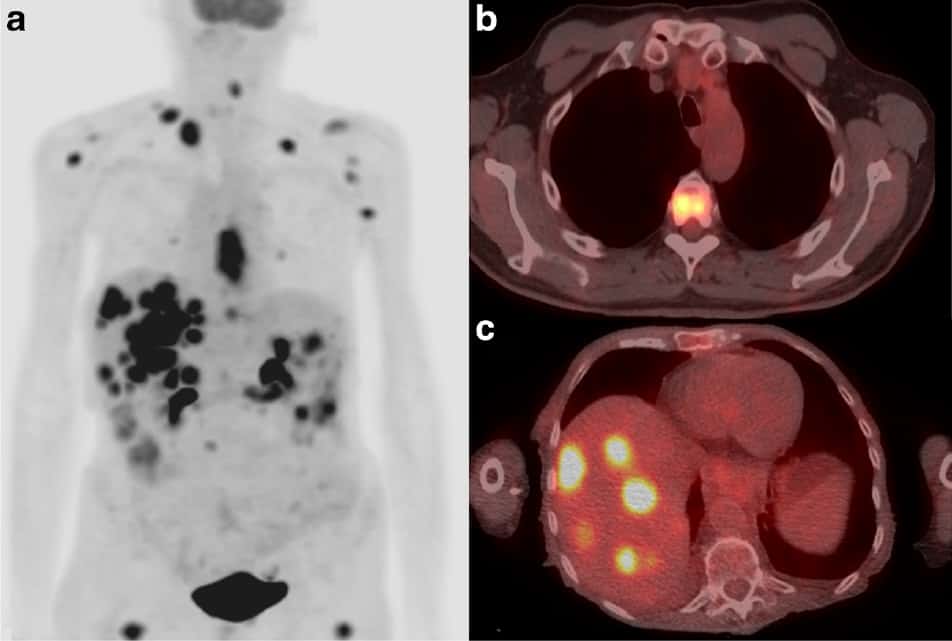
Fdg Pet Ct Provides Valuable Oesophageal Cancer Updates Physics World
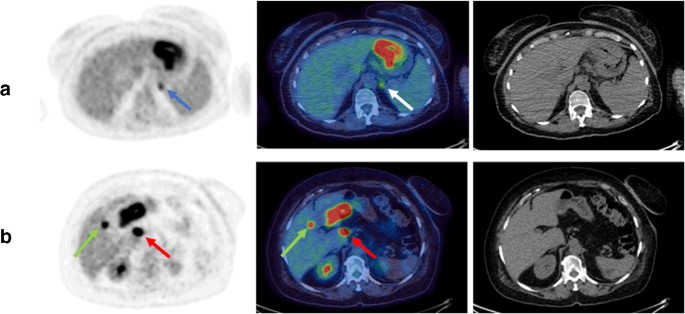
Staging Fdg Pet Ct Changes Management In Patients With Gastric Adenocarcinoma Who Are Eligible For Radical Treatment Springerlink

A Case Of Primary Lung Cancer Lesion Demonstrated By F 18 Fdg Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography Pet Ct One Year After The Detection Of Metastatic Brain Tumor
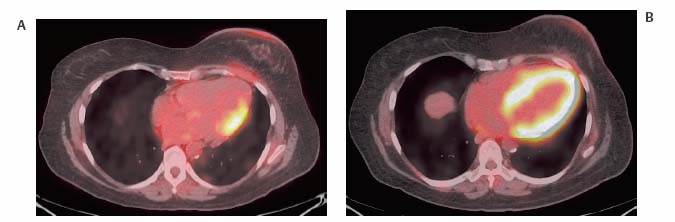
Normal Variants And Benign Findings Radiology Key

Pin On Body
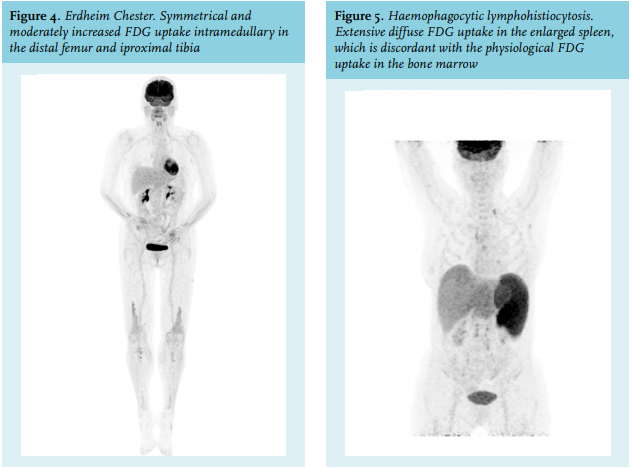
Article The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Scans To Evaluate Bone Marrow In Haemato Oncological Conditions Full Text September 19 Njm
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Fdg Pet Ct Provides Added Valuein Routine Multiple Imaging Scans Diagnostic Imaging

Resisting The Need To Quantify Putting Qualitative Fdg Pet Ct Tumor Response Assessment Criteria Into Daily Practice American Journal Of Neuroradiology

View Image

Ct And Fdg Pet Ct Of The Chest A Ct Scan And B Fdg Pet Ct Download Scientific Diagram

Role Of Fdg Pet Ct In The Eighth Edition Of Tnm Staging Of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Radiographics
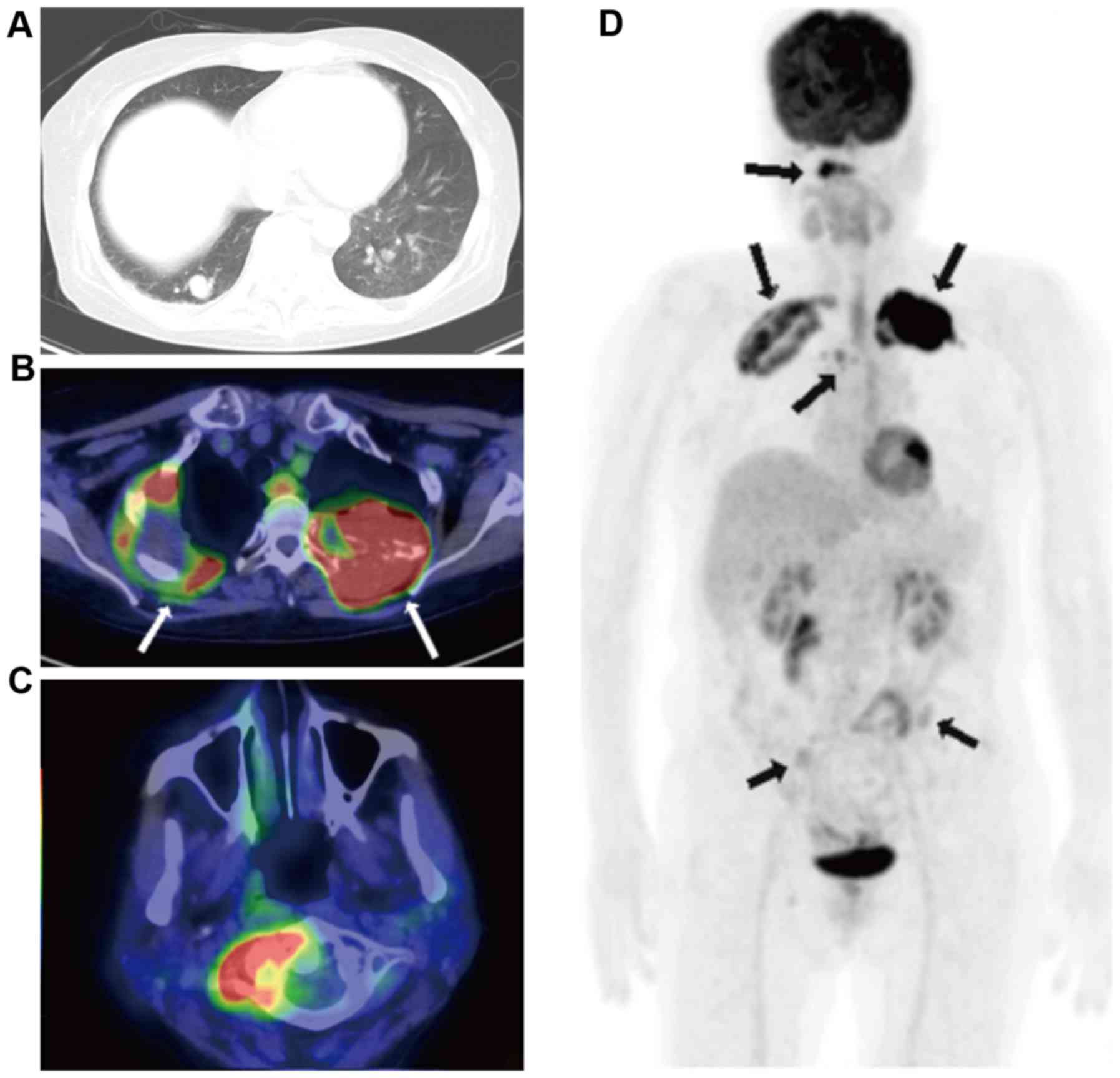
Benign Metastasizing Leiomyoma And 18 Fdg Pet Ct A Case Report And Literature Review
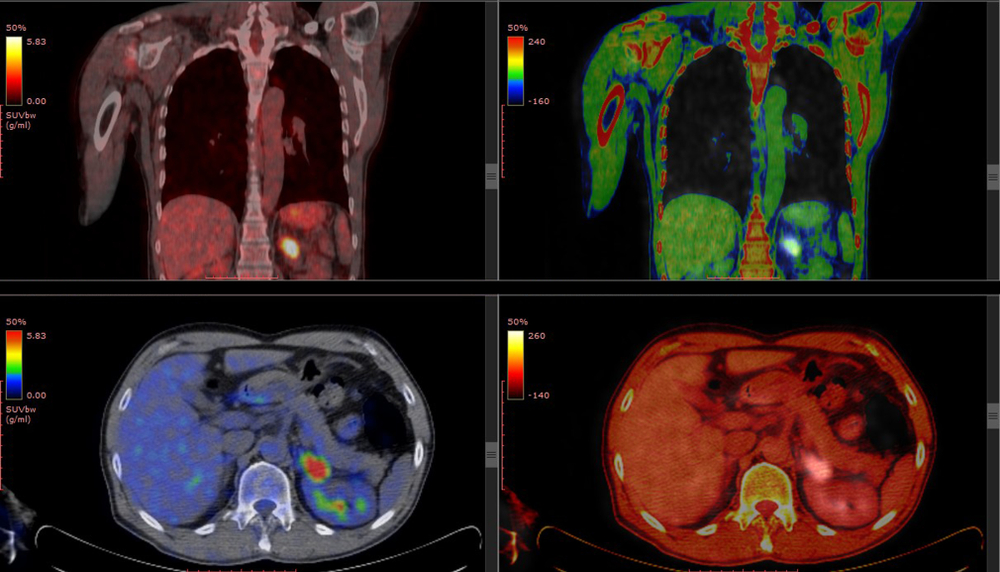
Understanding Your Fdg Pet Scan

Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of Fibrous Dysplasia Left Maximum Intensity Download Scientific Diagram
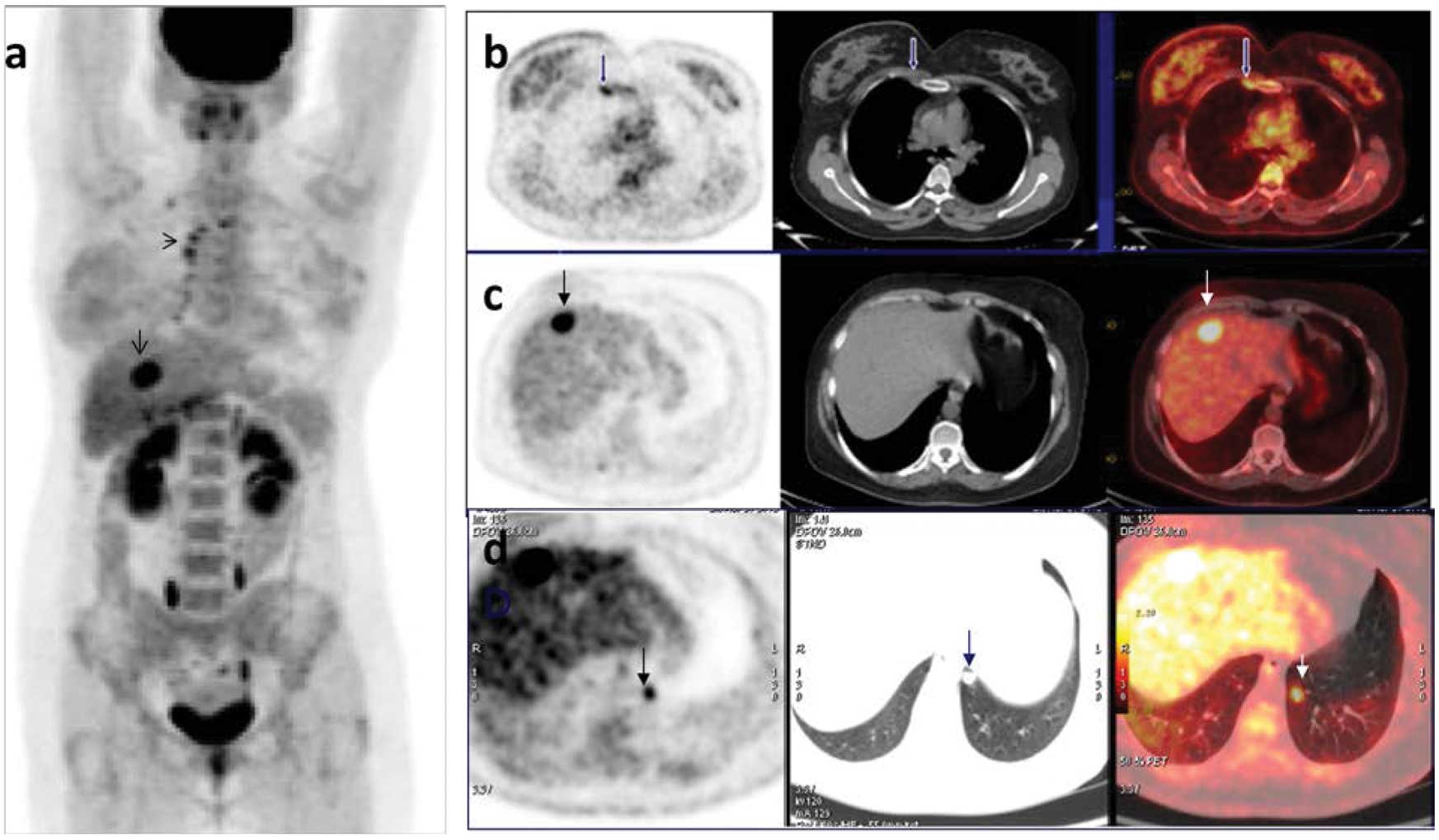
Clinical Impact Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct On Initial Staging And Therapy Planning For Breast Cancer

Fact Sheet What Is Pet Snmmi

Fdg Pet Ct Scan Mesorfa Information And Press Releases
Q Tbn And9gctkucjsjhxfwerokk1wbohpgtl1f9xag5dfdo1ypjonbcuncn1h Usqp Cau
Pet Ct Scan Details Ct Scan Machine
Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In The Diagnosis Of Inflammatory And Infectious Vascular Disease Chrapko Nuclear Medicine Review

Full Text Lugano 14 Criteria For Assessing Fdg Pet Ct In Lymphoma An Operatio Dddt



