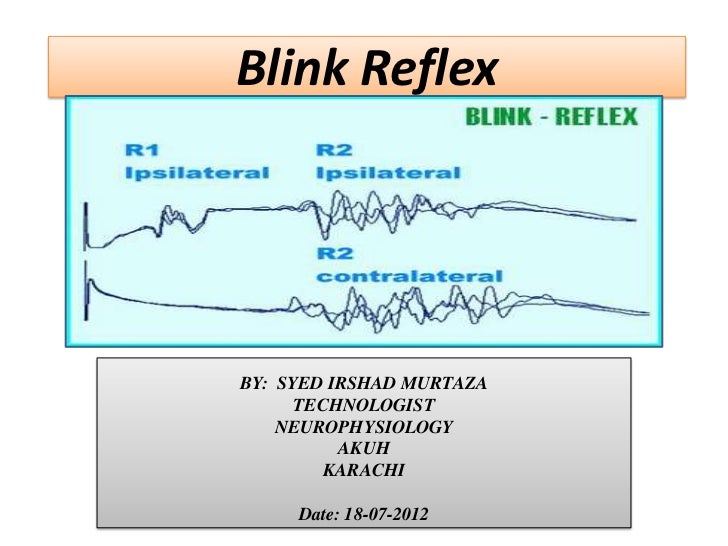
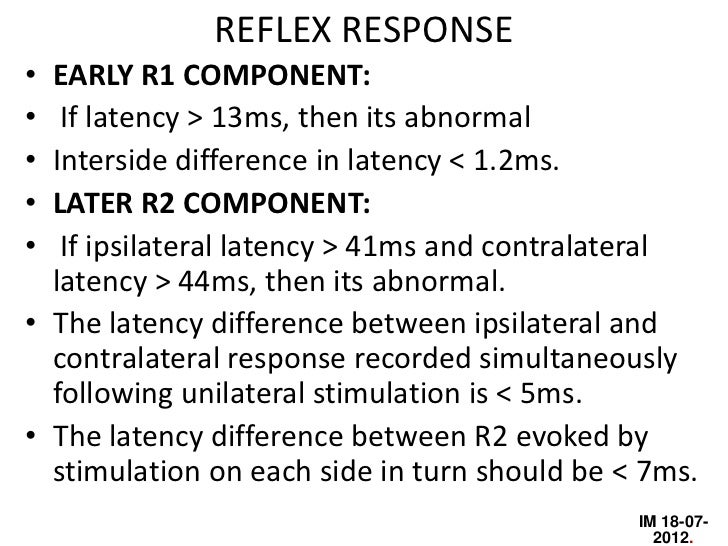
Blink Reflex R1 R2
Plos One Abnormal Control Of Orbicularis Oculi Reflex Excitability In Multiple Sclerosis

Recovery Cycle Of The R2 Component Of The Blink Reflex In Normal Download Scientific Diagram
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Late Blink Reflex Changes In Lesions Of Thalamus And Internal Capsule Neurology

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
Blink Reflex
Trigeminofacial (blink) reflex The neurophysiological data are shown in Table 1 In all studied subjects the R1 and R2 components of the blink reflex were obtained No statistically significant differences were found in the parameters of the blink reflex between both sides of the body and between the patient groups.
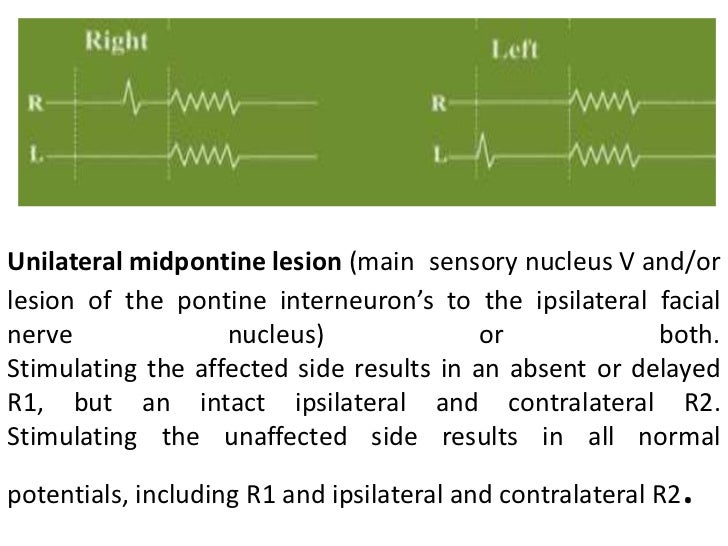
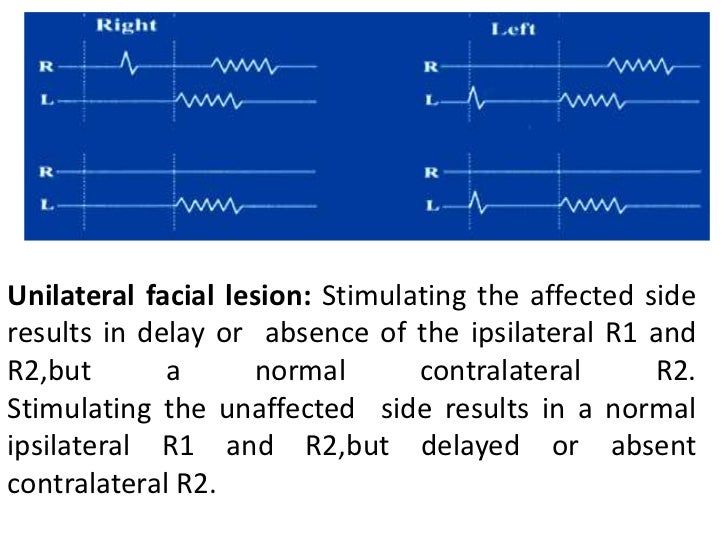
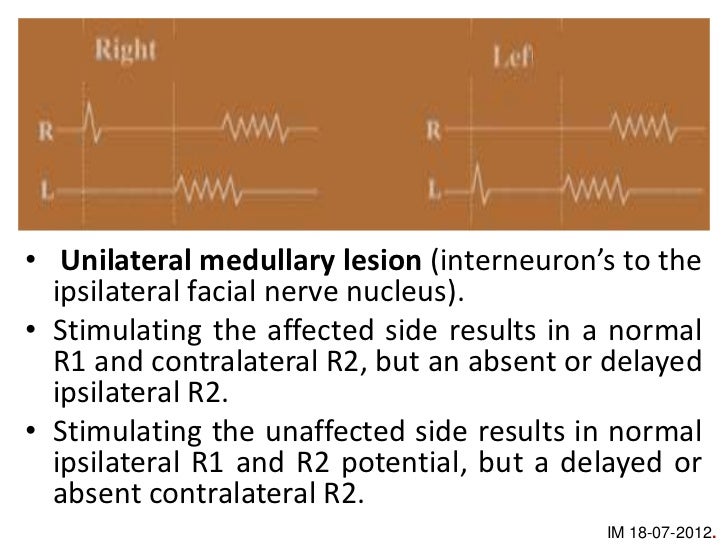
Blink reflex r1 r2. Stimulating unaffected side Normal R1 and ipsi R2, delayed or absent contra R2 Blink reflex abnormality pattern of a unilateral midpontine lesion Main sensory nucleus affected Absent/delayed R1 on affected side, with normal ipsi and contra R2. A blink reflex consists of an early unilateral component, R1, and a late bilateral component, R2 During an acute phase of hemispheric cerebrovascular accident, R1 and R2 were abnormal in 30 and 50 of 66 patients, respectively Paired stimuli usually corrected R1 but not R2, which was profoundly suppressed. Electrical blink reflexes had two components as R1 and R2, and ABR had one evoked potential in all volunteers There was no significant difference between gender, nor between right and leftsided.
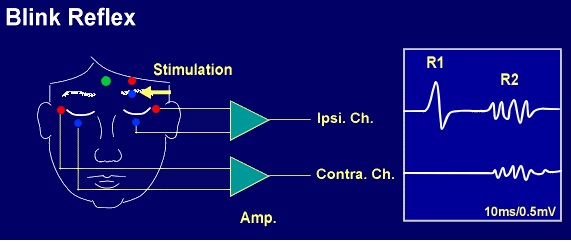
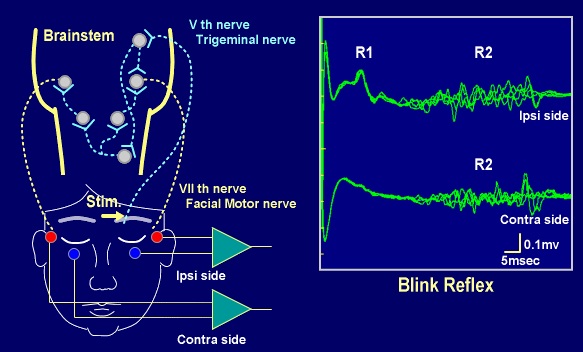
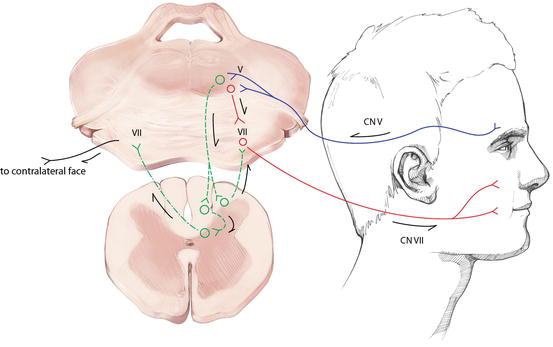
95% CI for difference, 006 to 094) R1, R2, and cR2 significantly improved at 4 months postoperatively. Blink reflex is elicited by stimulation of supraorbital nerve or infra orbital nerve or by glabellar tap using special reflex hammer that automatically triggers the oscilloscope sweep In normal response electrical stimulation elicits R1 response on the side ipsilateral to stimulation and R2 responses bilaterally. The blink reflex is characterized by an early component, R1, which lies ipsilateral to the site of stimulation and is conducted via an oligosynaptic pontine pathway It also has a bilateral component, R2, representing the medullary reticulum, which is mediated by a polysynaptic pathway via brainstem interneurons.
The blink reflex, also known as the orbicularis oculi reflex test, may be indicative of lesions or dysfunctions of the brainstem, and particularly assesses the trigeminalfacial arch This reflex is elicited by stimulation of the supraorbital nerve on one side of the face, leading to two ipsilateral responses (R1 and R2) and one contralateral. We examined the function of sensory processing mechanisms in patients with dystonic blepharospasm using the test of prepulse inhibition, or modification of the blink reflex 9,1317 The main findings of this study are as follows (1) The prepulse inhibition of the R2 was abnormal in 11 (647%) of 17 patients with blepharospasm (2) There was a. Blink reflex R2 changes and localisation of lesions in the lower brainstem (Wallenberg’s syndrome) BLINK REFLEX The blink reflex was evoked by stimulation of the supraorbital nerve Stimuli of 01 ms dura R1i slightly delayed (12,1 ms), loss of R2i /R2ci 5 Old lesion MCA complete 7 1, 2, 4, 6 Skew deviation R2i side diVerence.
Results Patients with DSPN had longer blink R1, R2, and contralateral R2 latencies (P , P = 0001, and P = 0031, respectively) and higher CAS (P ) Area under curve on receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in diagnosing occurrence of DSPN in blink R1 latency was 0772 (P ) Multiple linear regression analysis showed that blink R1 latency was independently associated with CAS. Three patients showed abnormality of the R1 response;. We recorded typical homolateral biphasic R1 and bilateral polyphasic R2 responses from both nerves, similar to those used by clinical neurophysiology laboratories as a diagnostic tool Clinically, the blink was more visible on the side of the stimulation, probably because the intensity of the stimulation (05 mA) was close to the R2 reflex.
R1 파형 (동측ipsilateral side) 와 R2 파형 (양쪽both sides) 는 순목반사 (blink reflex)에 의해 중재됩니다 안와상공 (supraorbital foramen) 에서, 삼차신경 (trigeminal nerve)의 상단 가지의 자극은 뇌간 (brainstem)을 향해 전달되고, 감각 핵 (sensory nucleus)에서 반사를 야기시킵니다. These data confirm the mediation of the R2 by WDR neurons and of the R1 by LTM neurons (Fig 4) The simultaneous occurrence of R1 and R2 components may help to differentiate nonnociceptive from nociceptive processes within the trigeminal system FIGURE 2 Blink reflex (BR) evoked by a weak electrical stimulus (top) and a laser heat pulse. R2 and contralateral R2 can be due to the pontine distortion due to the mechanical compression by the tumor, which is evident in our case The delay in early R1 reflex and late R2 reflex was seen in most cases with pontine lesions in the study by Kimura J 6 Post surgery improvement in the blink reflex latencies proves the same.
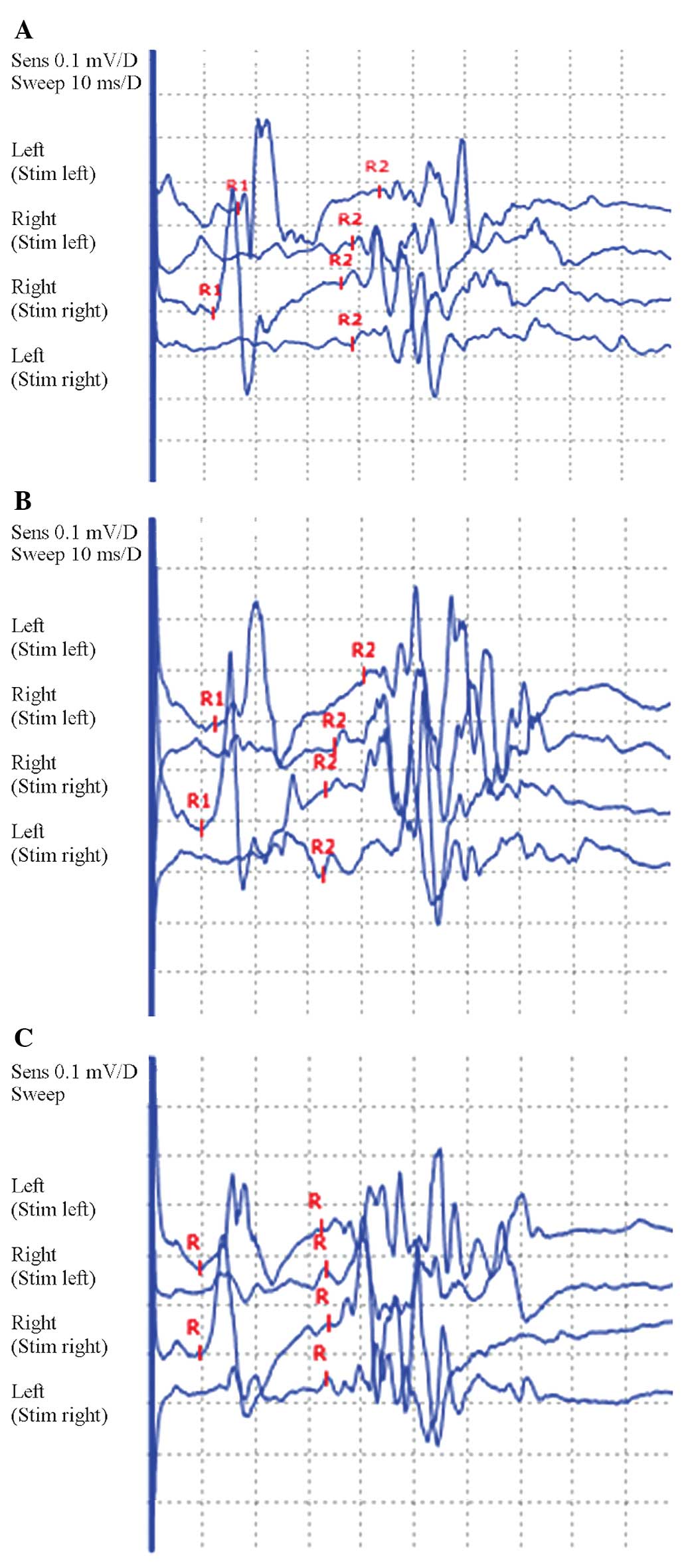
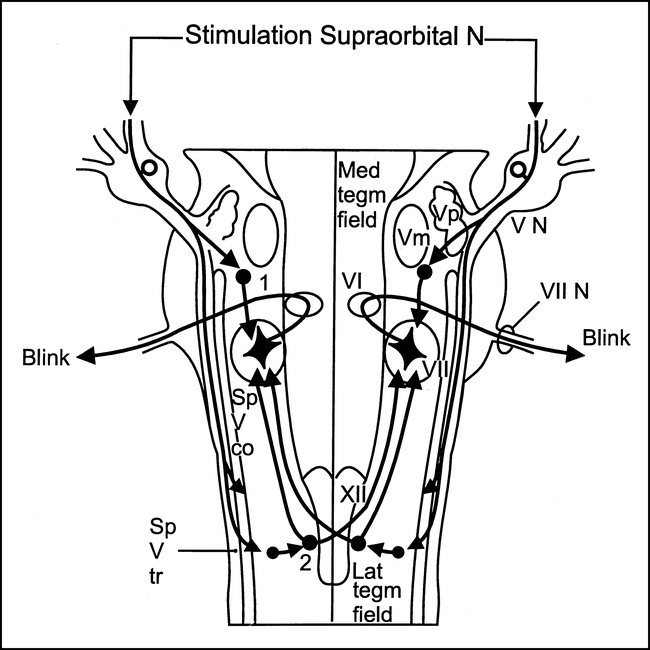
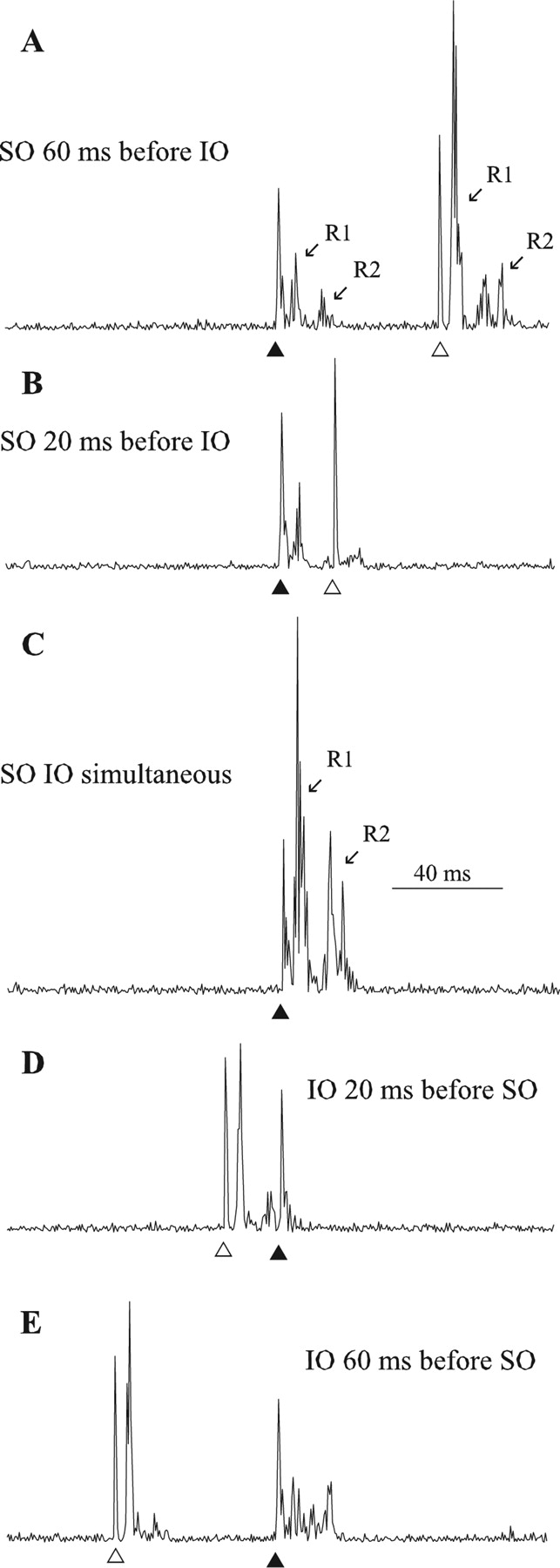
A , Responses of the orbicularis oculi of both sides to electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerve of either sideR1 refers to the ipsilateral early response whereas R2 and R2c refer to the late bilateral (ipsilateral and contralateral) responses B , Schematic representation of the brainstem circuit of the blink reflexThe input from the supraorbital nerve reaches the brainstem through. R1 R2 R2 R3 R3 C C Vµ ms Fig1 Example of an electromyographic record of an electrically evoked blink reflex and corneal reflex The stimulus is given on the vertical line on the left The upper two curves are from the blink reflex ipsilateral (upper) and contralateral (lower) The lower two curves are from the corneal reflex. Blink reflex (BR) test is an easy Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate (latency, amplitude or area of R1 and R2 components) in unconditioned (test) and.
The widespread use of MRI, allowing accurate localisation of brain lesions, particularly within the brainstem, tends to overshadow the usefulness of electrophysiology in evaluating functional loss This is the case of the blink reflex which explores trigeminal and facial nerves, and the brainstem Discrete lesions at sites along the structures involved in the reflex arc are associated with. The blink reflex consists of two responses R1, a synchronized response occurring ipsilateral to the stimulus with a disynaptic pathway between the main sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve in the midpons and the ipsilateral facial nucleus in the lower pontine tegmentum;. Trigeminofacial (blink) reflex The neurophysiological data are shown in Table 1 In all studied subjects the R1 and R2 components of the blink reflex were obtained No statistically significant differences were found in the parameters of the blink reflex between both sides of the body and between the patient groups.
The blink reflex physiology began to be better understood when Kugelberg performed the first electroneuromiograph (ENMG) study of the blink response 8 In his study, percussion of the glabela region triggered two ENMG responses an early, short latency response, considered proprioceptive R1, and a late response considered nociceptive R2. R1 and R2 blink reflex latencies were investigated blind in 10 patients with cervicogenic headache, 11 patients with chronic tension‐type headache, 11 patients with migraine, and 9 headache‐free controls There were no R1 or R2 latency differences between the four groups. R2 showed an increase of latency during task.
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye) The reflex occurs at a rapid rate of 01 seconds. The blink reflex has two components, an early R1 and a late R2 response The R1 response is usually present ipsilaterally to the side being stimulated, whereas the R2 response is typically present bilaterally The R1 response is thought to represent the disynaptic reflex pathway between the main sensory nucleus of V in the midpons and the ipsilateral facial nucleus in the lower pontine tegmentum. And R2, a bilateral response with a longer latency mediated by multisynaptic pathways between the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve in the ipsilateral pons and medulla with interneurons forming.
İn this study, the blink reflex was investigated in 13 patients with thalamic hemorrhage and in 12 normal subjects R1 was normal on both side stimulation but R2 and R2c obtained by stimulation on the paretic side slo wer in latency compared with responses of the non paretic side and the values of the normal subjects. In the remaining six patients, only R2 responses were affected Conclusions Subclinical abnormalities of both R1 and R2 can be seen in the context of SG of varying aetiologies, including paraneoplasia Performing the BR in patients with suspected of having SG may be helpful in providing. Three trigeminal divisions1,3 (R1 and R2 blink reflex after electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerve, SP1 and SP2 masseter inhibitory reflex after electrical stimulation of the infraorbital and mental nerves, and jaw jerk after chintaps), and normal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans Those assigned to the symptomatic TN.
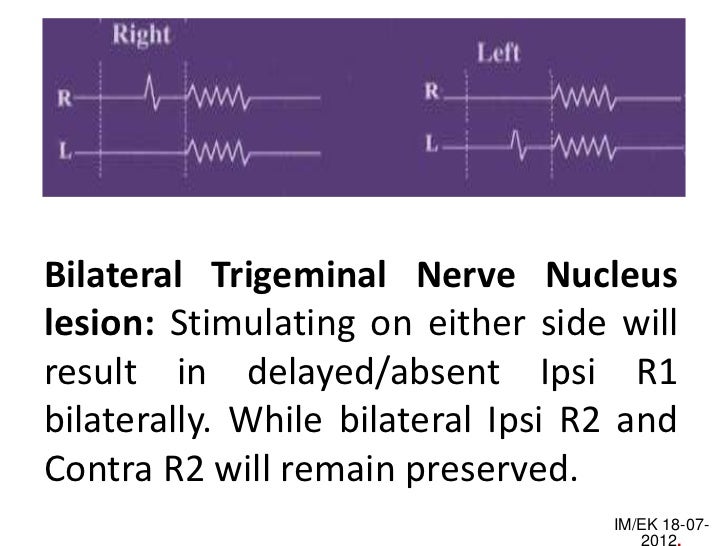
The blink reflex generated an R1 and an R2 component from each individual Blink reflexs were recorded and the supraorbital nerve was stimulated with single electrical shocks of increasing intensity until nearly stable R1 and R2 ipsilateral and R2 contralateral responses were obtained The. Blink Reflex True reflex proximal segments and visual and brainstem evoked potentials Stim affected side, delay or absence of ALL potentials (ispi R1, R2, contra R2)Stim unaffected side results in normal potentials, including the ipsilateral R1 and R2 and the contra R2. The blink reflex generated an R1 and an R2 component from each individual Blink reflexs were recorded and the supraorbital nerve was stimulated with single electrical shocks of increasing intensity until nearly stable R1 and R2 ipsilateral and R2 contralateral responses were obtained The.
R2 and contralateral R2 can be due to the pontine distortion due to the mechanical compression by the tumor, which is evident in our case The delay in early R1 reflex and late R2 reflex was seen in most cases with pontine lesions in the study by Kimura J 6 Post surgery improvement in the blink reflex latencies proves the same. R1 = early blink reflex, R2 = late blink reflex, SP1 = early masseter inhibitory reflex, SP2 = late masseter inhibitory reflex Introduction Thanks to the functional specificity of the nervous system, classic postmortem studies designed to correlate a clinical sign with a brain lesion remarkably advanced our understanding of nervous system. R1 is relayed centrally through an oligosynaptic arc including one to three interneurons in the mid pons, probably located in the vicinity of the main sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve R1 is not visible clinically but may have a preparatory function, by shortening the late blink re¯ex latency The R2 blink re¯ex correlates with.
The mechanisms underlying blink R1 latency, but not R2 or contralateral R2 latency, is a more sensitive parameter of blink reflex associated with DSPN occurrence and severity in type 2 diabetes. The latencies of the R1 and R2 components, the amplitude of the R1 component, and the area of the total power spectrum of the EMG discharges constituting the R2 component, the duration of the R2 component, and the latency of the R3 component were studied during the blink reflex. All 12 patients tested had blink reflex abnormalities absent and/or delayed R1 in 11 (917%), and absent and/or delayed R2 in 10 (3%) R1 latencies had strong positive correlations with serum anti‐NF155 antibody levels ( r = 09, P ≤ on both sides) and distal and F wave latencies of the median and ulnar nerves.
The electrophysiological investigation of the blink reflex allows evaluation of the different segments of the polysynaptically transmitted blinking response The electromyographic response of the orbicularis oculi muscle to electrical stimulation of the trigeminal nerve consists of an early response ipsilateral to electrical stimulation (R1. Objective To objectively evaluate the effects of maxillary lesions on the infraorbital nerve (ION) Methods We investigated the latencies (R1, R2) of the blink reflex, stimulating the infraorbital foramen electrically (18 mA, 02 millisecond) Twentytwo patients with unilateral maxillary lesions were enrolled Results Ten patients showed delayed or absent R1 on the lesion side. The latency of R1, R2, and R2′, the amplitude and size of the R2 and R2′ components of the blink reflex, the latency and duration of the ES1 and ES2 components, and the recovery curve of the ES2 component of the temporalis muscle activity did not differ between groups However, the recovery curve of the R2 component of the blink reflex diminished in patients with tension‐type headache compared with the other groups.
Blink Reflex Recovery MUSCLE & NERVE January 1996 11 RESULTS A conditioning test interval Neither peak amplitude nor area measurements of (s1 R1 and R2 responses, obtained by single stimulus 021 at two and three times R2 threshold, differed sig nificantly between the patients and controls. R1 and R2 blink reflex latencies were investigated blind in 10 patients with cervicogenic headache, 11 patients with chronic tension‐type headache, 11 patients with migraine, and 9 headache‐free controls There were no R1 or R2 latency differences between the four groups. Both R1 and R2 come from facial motor nucleus, but R1 is from the pons in the vicinity of the neurons of pontine sensory part of 5 th nerve R2 is from the reflex pathway in the pons If blink reflex is normal, it indicates that the 5 th nerve, interneurons in pons, caudal medulla and 7 th nerve are not interrupted in the above pathway In brain stem disorders, the data is less and results are inconsistent as it involves polysynaptic pathways in brainstem reticular formation.
Katsarava et al, 02a). Blink reflex is elicited by stimulation of supraorbital nerve or infra orbital nerve or by glabellar tap using special reflex hammer that automatically triggers the oscilloscope sweep In normal response electrical stimulation elicits R1 response on the side ipsilateral to stimulation and R2 responses bilaterally. And R2, a late bilateral response mediated through the polysynaptic medullary pathway.
The blink reflex was tested among all patients in accordance with electrophysiological laboratory standards Results The latency of the R1 response was significantly shorter among patients with migraine The latency of R2 and R2’ responses was similar in patients and controls A significant inverse correlation was observed between latency of R2. Three patients showed abnormality of the R1 response;. The blink reflex was elicited in 50 children from birth to 3 years of age In the awake state, the R1 response was always obtained;.
In some patients the R1 component was also present on the side contralateral to the stimulus, while in normal subjects it was present only on the ipsilateral side The excitability cycle of recovery of the R2 component of the blink reflex after a prior conditioning shock was enhanced in the patients. Electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerve, a sensory branch of the trigeminal nerve, elicits the blink reflex response, which consists of two separate components an early R1 and a late R2Visual and auditory stimuli give a response with only one component Whereas R1 is evoked only on the side of electrical stimulation, R2 is recorded bilaterally with unilateral electrical stimulation. A blink reflex consists of an early unilateral component, R1, and a late bilateral component, R2 During an acute phase of hemispheric cerebrovascular accident, R1 and R2 were abnormal in 30 and 50 of 66 patients, respectively Paired stimuli usually corrected R1 but not R2, which was profoundly suppressed.
The infraorbital blink reflex was significantly influenced only by time R1, R2, and cR2 at time 4 were significantly larger than at T0 (estimated difference, 050;. Contrary to the classical blink reflex which has two components (R1 and R2) and sometimes a third one (R3), the nBR is elicited by a special stimulation electrode with high current density activating rather selectively Aδ fibres and has only a R2 component (Kaube et al, 00;. R2 responses, especially contralateral ones, were more difficult to elicit under 9 months of age R1 latency and VIIth motor nerve conduction variations were a good witness of the peripheral nervous system maturation The influence of the different states of waking and sleeping on these reflex responses was studied.
Thresholds (R1, R2, R3) of the blink reflex components, the subjective perceptive threshold (Pth) and pain threshold (Path), electrical stimuli were given at unpredicted intervals, with electrical intensity increasing in 2mAsteps The length of interstimuli intervals was random but always longer than 40 s During this interval,. Our study was aimed at estimating normal time values for the EMG waves recorded in the blink reflex test The group examined included 400 healthy subjects (226 women and 174 men, with mean age about 50 years) There was no significant difference between the ages of the male and female subjects The mean latency of the R1 wave in the response was 103 msec, while R2 was obtained after 325 msec. A reflex contraction of the human orbicularis oculi muscles can be evoked by stimulation of either the supraorbital region (“blink reflex”) or the cornea (“corneal reflex”) We found that the latency of the corneal reflex was longer, and the duration was longer than the R2 component of the blink reflex The absolute refractory period of the R2 component of the blink reflex was longer.
Ited blink reflex consists of an early ipsilateral, R1, with a latency about 10 ms (range 813 ms) The late polysynaptic response, R2, has a latency of 3045 ms Latencies of the ipsilateral R1 and R2 and contralateral R2 were measured Delayed contralateral R2 response was considered indicative of impaired trigeminal nerve function. The blink reflex, elicited by stimulation of the supraorbital nerve, is an electrophysiological analogue of the corneal reflex, which indicates the excitability of brainstem interneurons and comprises two components R1, an early ipsilateral response mediated by the oligosynaptic pathway through the pons that is ipsilateral to the stimulation site;. R1 파형 (동측ipsilateral side) 와 R2 파형 (양쪽both sides) 는 순목반사 (blink reflex)에 의해 중재됩니다 안와상공 (supraorbital foramen) 에서, 삼차신경 (trigeminal nerve)의 상단 가지의 자극은 뇌간 (brainstem)을 향해 전달되고, 감각 핵 (sensory nucleus)에서 반사를 야기시킵니다.
Three trigeminal divisions1,3 (R1 and R2 blink reflex after electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerve, SP1 and SP2 masseter inhibitory reflex after electrical stimulation of the infraorbital and mental nerves, and jaw jerk after chintaps), and normal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans Those assigned to the symptomatic TN. R1 and R2 blink reflex latencies were investigated blind in 10 patients with cervicogenic headache, 11 patients with chronic tension‐type headache, 11 patients with migraine, and 9 headache‐free controls There were no R1 or R2 latency differences between the four groups. 95% CI for difference, 006 to 094) R1, R2, and cR2 significantly improved at 4 months postoperatively.
Our study was aimed at estimating normal time values for the EMG waves recorded in the blink reflex test The group examined included 400 healthy subjects (226 women and 174 men, with mean age about 50 years) There was no significant difference between the ages of the male and female subjects The mean latency of the R1 wave in the response was 103 msec, while R2 was obtained after 325 msec. Thresholds (R1, R2, R3) of the blink reflex components, the subjective perceptive threshold (Pth) and pain threshold (Path), electrical stimuli were given at unpredicted intervals, with electrical intensity increasing in 2mAsteps The length of interstimuli intervals was random but always longer than 40 s During this interval,. The infraorbital blink reflex was significantly influenced only by time R1, R2, and cR2 at time 4 were significantly larger than at T0 (estimated difference, 050;.
In the remaining six patients, only R2 responses were affected Conclusions Subclinical abnormalities of both R1 and R2 can be seen in the context of SG of varying aetiologies, including paraneoplasia Performing the BR in patients with suspected of having SG may be helpful in providing.

The Trigeminal And Facial Nerves The Facial And Blink Pdf Free Download

A B Blink Reflex Study Showed Normal Findings At Bot Open I

Optic Trigeminal And Facial Neuropathy Related To Anti Neurofascin 155 Antibody Ogata Annals Of Clinical And Translational Neurology Wiley Online Library
Blink Reflex Springerlink

The Study Of The Blink Reflex Excitability Recovery Curve In Download Scientific Diagram

Cluster Tic Syndrome As The Initial Manifestation Of Multiple Sclerosis The Journal Of Headache And Pain Full Text

Blink Reflex Recovery In Facial Weakness Neurology
Blink Reflex

Pdf Supratentorial Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Affect The Blink Reflex Test Semantic Scholar

Late Blink Reflex Changes In Lesions Of Thalamus And Internal Capsule Neurology
Gating Of Trigemino Facial Reflex From Low Threshold Trigeminal And Extratrigeminal Cutaneous Fibres In Humans Abstract Europe Pmc

Pdf The Blink Reflex Comparative Electrophysiologic Study In The Domestic Species Semantic Scholar

Blink Reflex To Supraorbital Nerve Electrical Stimulation R1 R2 And Download Table

Diagnostic Accuracy Of Trigeminal Reflex Testing In Trigeminal Neuralgia Neurology

Blink Reflex Changes And Sensory Perception In Infraorbital Nerve Innervated Areas Following Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures

Somatosensory Evoked Blink Reflex In Peripheral Facial Palsy El Tawab Ss Saba Ek Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil
순목검사 Blink Reflex 개요 네이버 블로그
Correlation Between Electromyographic Reflex And Mr Imaging Examinations Of The Trigeminal Nerve American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Vithas Salud Malaga Rosaleda Rincon Almunecar Granada Medical Center Neurofisiologia Dr Juan Jose Guzman Alvarez Electromiograma Emg Y Electroneurograma Eng Blink Reflex
Www nem Org Mxonline Resources Downloads Monograph 23 Edx studies of the facial nerve in peripheral facial palsy and hemifacial spasm Pdf

Blink Reflex By Ck Authorstream

Figure 6 From The Late Blink Reflex Response Abnormality Due To Lesion Of The Lateral Tegmental Field Semantic Scholar
Blink Reflex Springerlink
Gating Of Trigemino Facial Reflex From Low Threshold Trigeminal And Extratrigeminal Cutaneous Fibres In Humans Abstract Europe Pmc

Schematic Representation Of The Blink Reflex Pathways And Sites Of Download Scientific Diagram

Blink Reflex

View Image
Http Ddd Uab Cat Pub Tesis 02 Tdx 2514 Sat1de1 Pdf

Pathological Reflex An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Www Neurology Asia Org Articles Neuroasia 19 24 1 071 Pdf

Utility Of Intraoperative Electromyography In Microvascular Decompression For Hemifacial Spasm A Meta Analysis In Neurosurgical Focus Volume 27 Issue 4 09

Electrophysiological Investigation Of Hemifacial Spasm After Microvascular Decompression F Waves Of The Facial Muscles Blink Reflexes And Abnormal Muscle Responses In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 86 Issue 4 1997

Blink Reflex Comparison Of Latency Measurements In Different Human Races
Www et Info Docs Facial Trigeminal Pdf

Blink Reflex R2 Changes And Localisation Of Lesions In The Lower Brainstem Wallenberg S Syndrome An Electrophysiological And Mri Study Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry

Blink Reflex
Q Tbn And9gcr1bc3f7ratvy1zw0e Eoabwdwuvfpjms86h9zuto6f4oznssqa Usqp Cau
Blink Reflex

Trigeminal Reflexes For Diagnosing Symptomatic Trigemin Open I

Nociceptive Quality Of The Laser Evoked Blink Reflex In Humans Journal Of Neurophysiology

View Image

Figure 2 From The Late Blink Reflex Response Abnormality Due To Lesion Of The Lateral Tegmental Field Semantic Scholar
Blink Reflex
Blink Reflex
2
Experiential Modification Of The Trigeminal Reflex Blink Circuit Journal Of Neuroscience

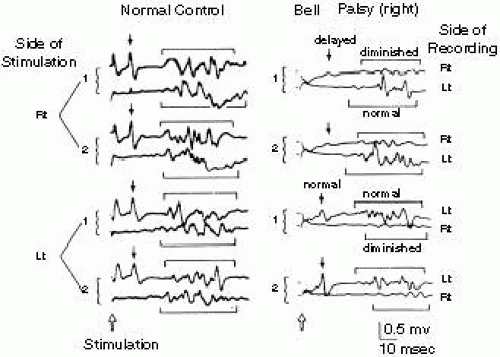
Blink Reflex Patient 1 R1 Was Elicited Ipsilaterally To The Stimulus Download Scientific Diagram

Nociceptive Quality Of The Laser Evoked Blink Reflex In Humans Journal Of Neurophysiology

Correlation Between Electromyographic Reflex And Mr Imaging Examinations Of The Trigeminal Nerve American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Figure 3 From Methods For Studying The Blink Reflex And Its Normative Parameters Semantic Scholar

An Explanation For Reflex Blink Hyperexcitability In Parkinson S Disease I Superior Colliculus Journal Of Neuroscience
Http Neurothai Org Media News File 338 02 Blink Reflex And Late Responses 1 Pdf

Blink Reflex Responses In The Second Patient With A Lesion On The Right Download Scientific Diagram

Blink Reflex

Facilitation And Inhibition Of The Human Startle Blink Reflexes By Stimulus Anticipation

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key

Figure 1 From Electrodiagnosis Of The Cranial Nerves Semantic Scholar

Blink Reflex Is Significantly Altered In Patients With Multisystem Atrophy Compared To Patients With Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Alzheimer S Disease And Frontotemporal Dementia A Pilot Study B Chandra Sr Ramanujam Nc Gohel A
순목검사 Blink Reflex 개요 네이버 블로그
Http Www Neurologic Theclinics Com Article S0733 8619 11 7 Pdf

Schematic Representation Of Various Lesions Within The Brainstem A ϫ Download Scientific Diagram

Multi Level Approach To Anaesthetic Effects Produced By Sevoflurane Or Propofol In Humans 1 Bis And Blink Reflex Sciencedirect
Reflex And Long Latency Musculoskeletal Key
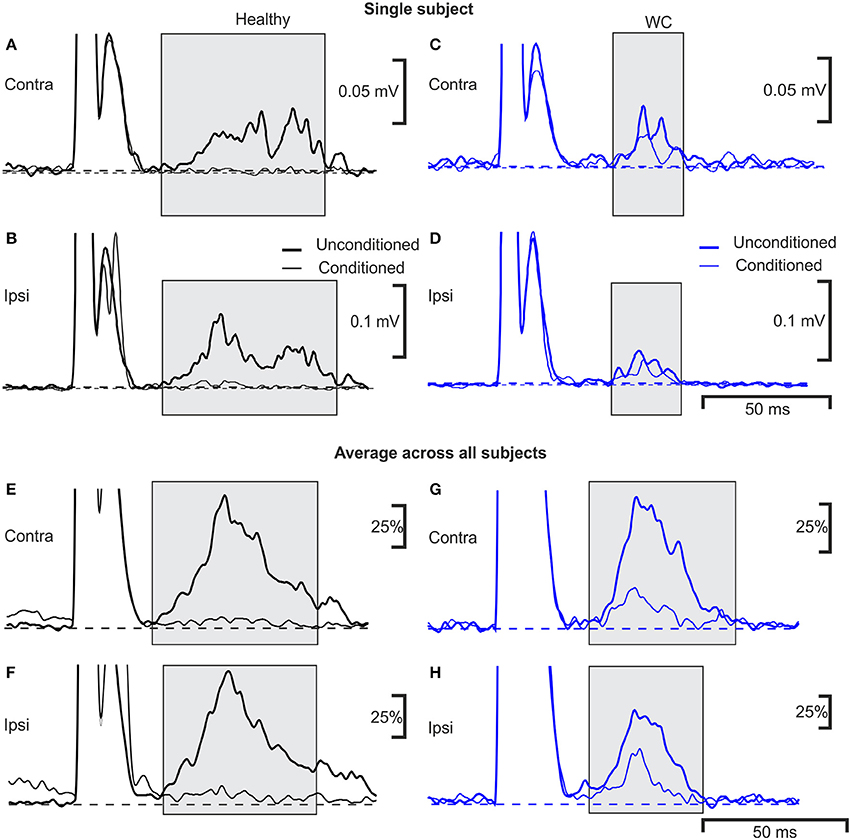
Frontiers Abnormal Blink Reflex And Intermuscular Coherence In Writer S Cramp Neurology

The Blink Reflex Arc The Circuit For The Oligosynaptic R1 Component Is Download Scientific Diagram
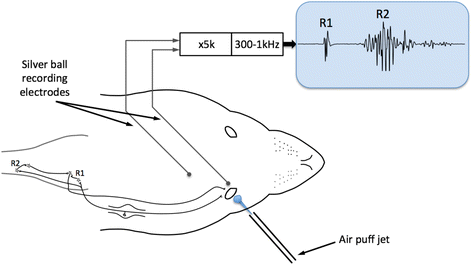
Pharmacology Of Reflex Blinks In The Rat A Novel Model For Headache Research The Journal Of Headache And Pain Full Text
2

Conduction Studies 21 Facial Nerve Conduction Studies
Q Tbn And9gcsv8wltanerpi23ufbb1adqwwmizej4gkc5 8ttup25ebdisi Usqp Cau
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf
Www Neurology Asia Org Articles Neuroasia 19 24 1 071 Pdf

Sensory Guillain Barre Syndrome A Case Report
Academic Oup Com Bja Article Pdf 98 6 737 Aem104 Pdf

Blink Reflex Role In Algorithmic Genetic Testing Of Inherited Polyneuropathies Wang 17 Muscle Amp Nerve Wiley Online Library
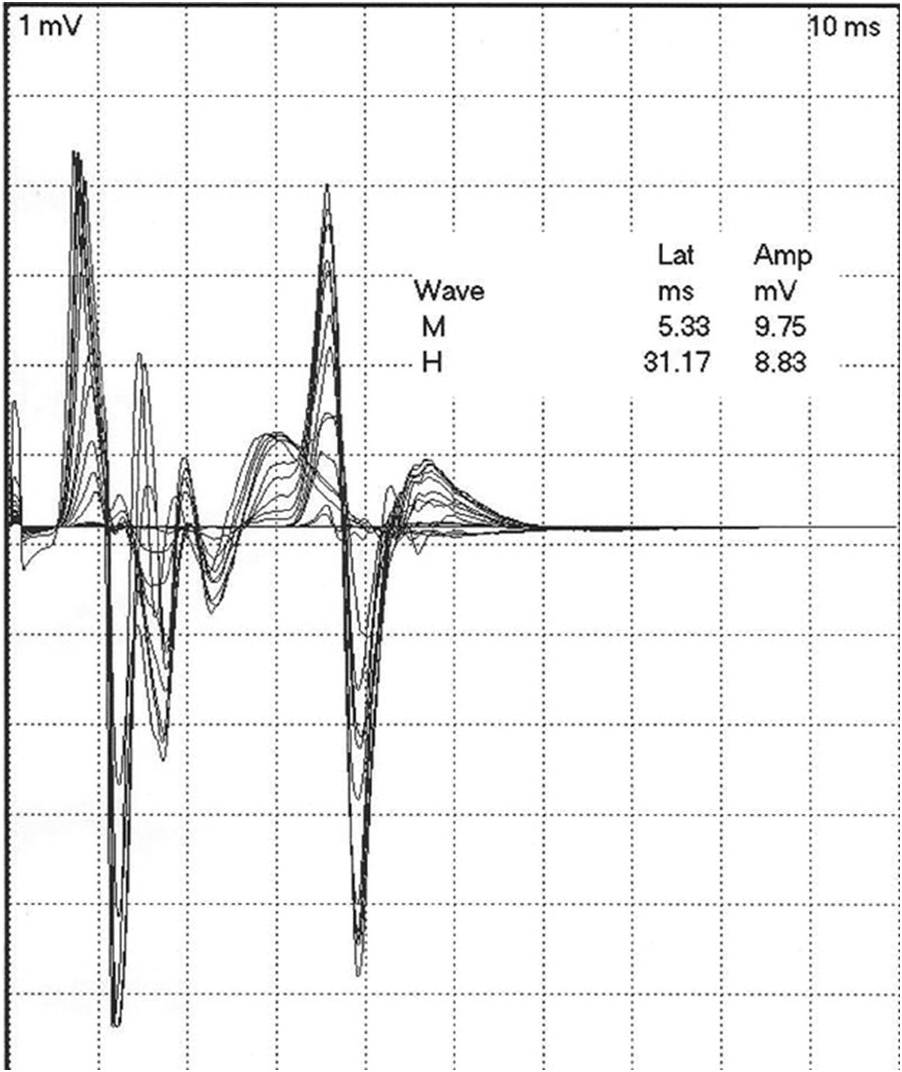
Late Responses And Blink Reflexes Chapter 11 Comprehensive Electromyography

Teach Neurology The Corneal Or Blink Reflex

Blink Reflex Recovery In Facial Weakness Neurology
Http Www Neurologic Theclinics Com Article S0733 8619 11 7 Pdf

Diagnostic Value Of Blink Reflex In Multisystem Atrophy Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinson Disease Sciencedirect
Q Tbn And9gcq8o Tsbkrnnqzquocephjten3vbuhaqwidvybpa0tcqpitmrzo Usqp Cau

Blink Reflex Is Significantly Altered In Patients With Multisystem Atrophy Compared To Patients With Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Alzheimer S Disease And Frontotemporal Dementia A Pilot Study B Chandra Sr Ramanujam Nc Gohel A

Xmlinkhub
Http Www Njppp Com Fulltext 28 Pdf
Academic Oup Com Brain Article Pdf 128 2 386 Awh366 Pdf
Blink Reflex Springerlink
Http Neurothai Org Media News File 338 02 Blink Reflex And Late Responses 1 Pdf
Q Tbn And9gctpwmheniumeaq90gpdzx2jivertdblx53 Ykyemjh6g9cqeds9 Usqp Cau
Blink Reflex

Blink Reflex Changes And Sensory Perception In Infraorbital Nerve Innervated Areas Following Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures

Blink Reflex Is Significantly Altered In Patients With Multisystem Atrophy Compared To Patients With Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Alzheimer S Disease And Frontotemporal Dementia A Pilot Study B Chandra Sr Ramanujam Nc Gohel A
Http Www Sciencedirect Com Science Article Pii S Pdf Md5 312d558dcdf5e76d50e5b01ddeeb1f Pid 1 S2 0 S Main Pdf

The Usefulness Of Blink Reflex In Diabetic Patients With Or Without

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
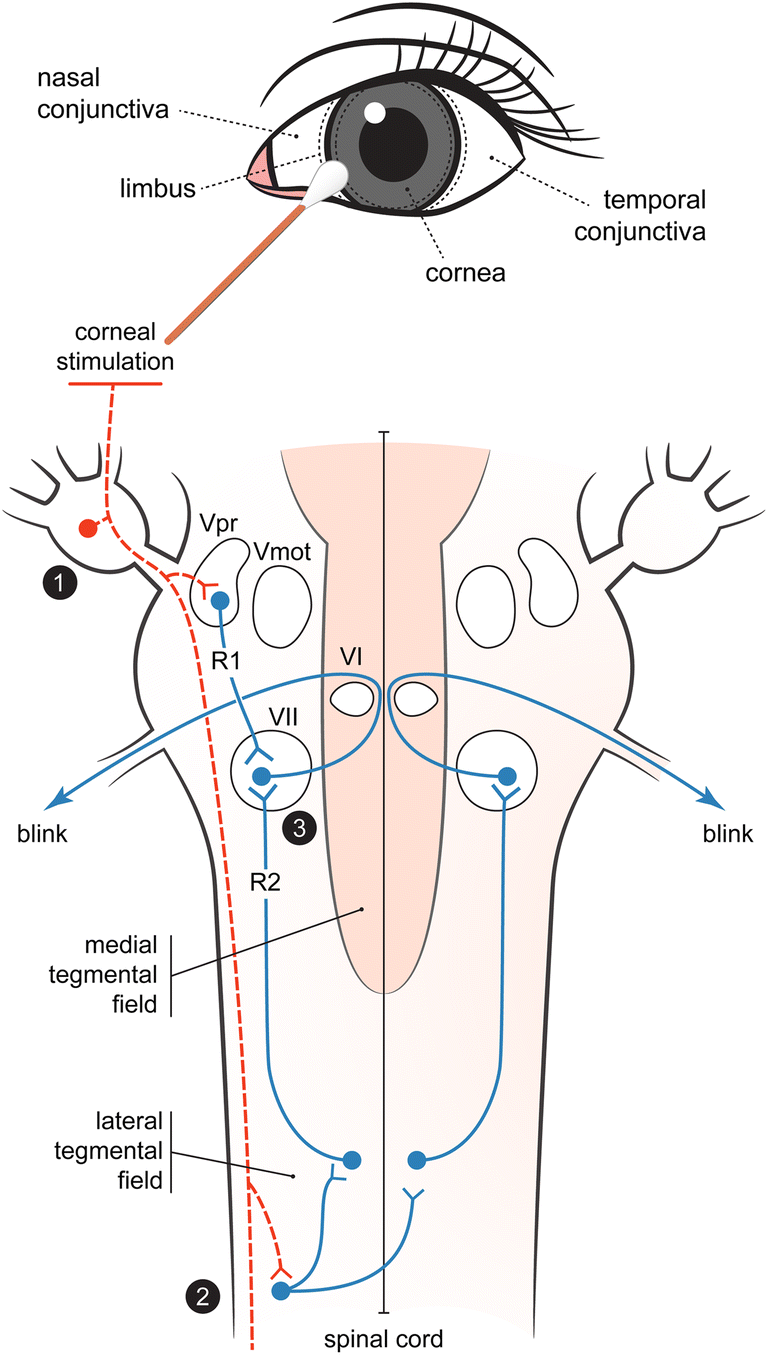
Figure 1 Corneal Reflex Testing In The Evaluation Of A Comatose Patient An Ode To Precise Semiology And Examination Skills Springerlink
Plos One Abnormal Control Of Orbicularis Oculi Reflex Excitability In Multiple Sclerosis

Ilsl Internacional Journal Of Leprosy And Other Mycobacterial Diseases Correspondence Using The Blink Reflex As Measured By Electromyogram To Assess Cranial Nerve Involvement In People Affected By Leprosy

Hyperekplexia And Stiff Man Syndrome Abnormal Brainstem Reflexes Suggest A Physiological Relationship Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
2



