Fdg Pet
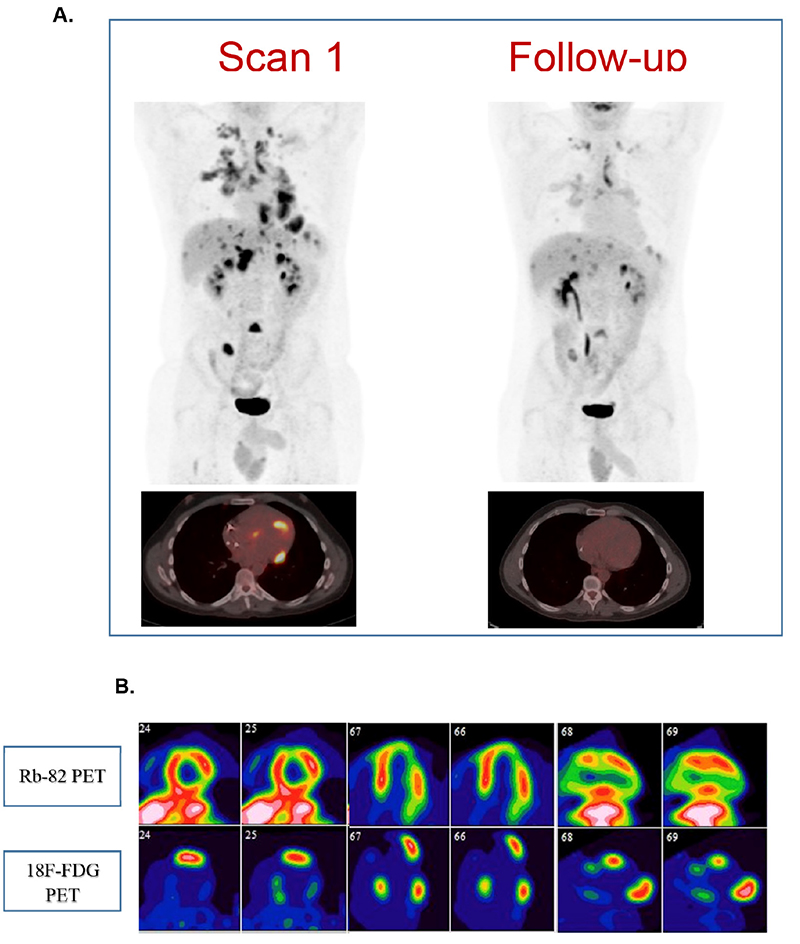
The Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Cardiac Sarcoidosis
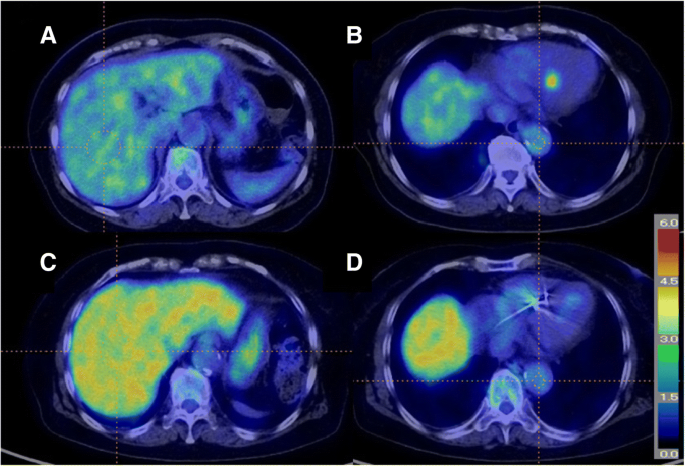
Which Is The Proper Reference Tissue For Measuring The Change In Fdg Pet Metabolic Volume Of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Before And After Steroid Therapy Ejnmmi Research Full Text
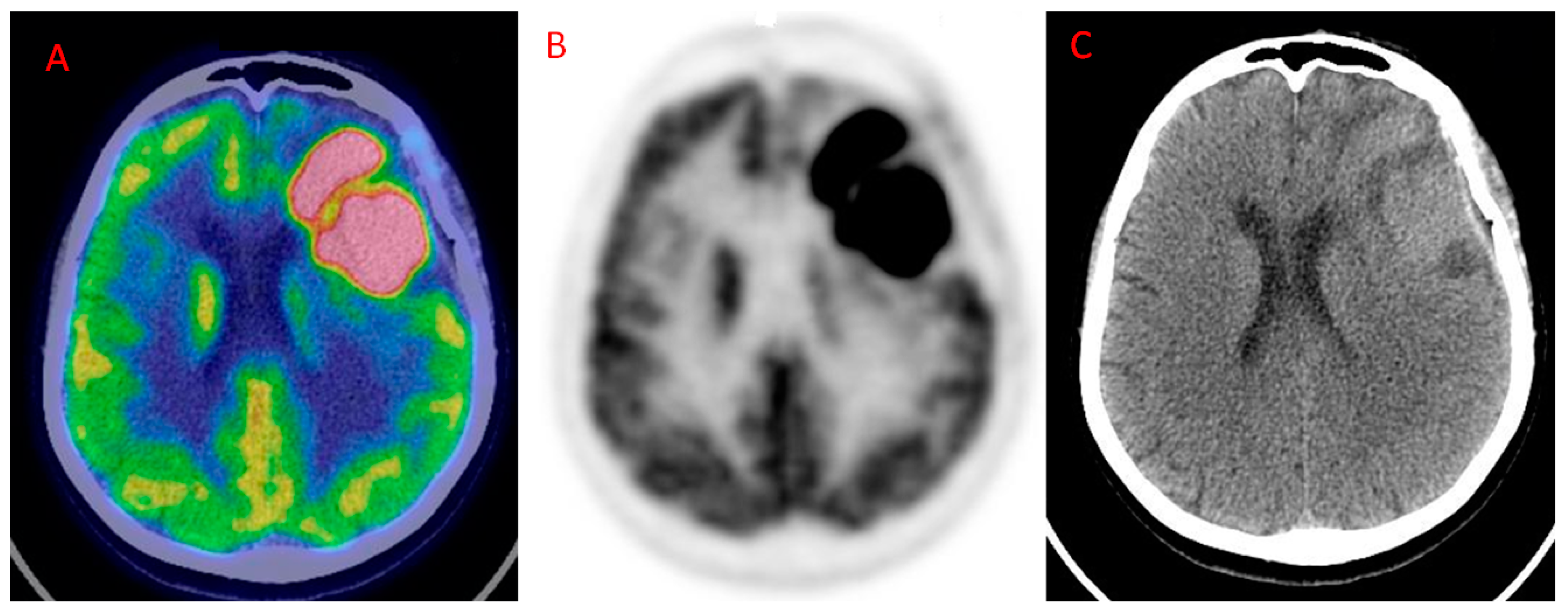
Diagnostics Free Full Text The Additional Value Of 18f Fdg Pet And Mri In Patients With Glioma A Review Of The Literature From 15 To

Increased Muscle Fdg Pet Uptake In Dermatomyositis Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
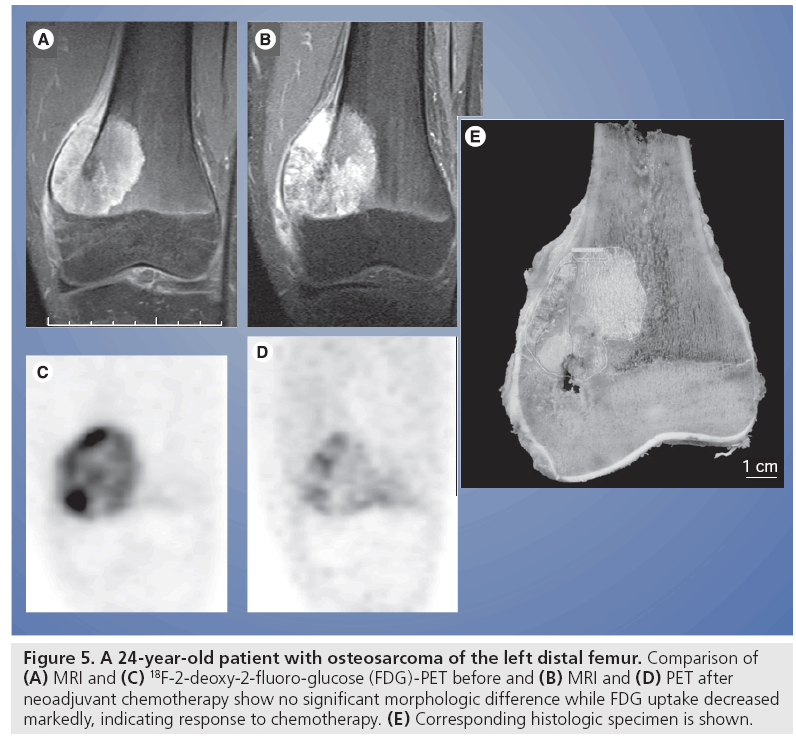
Imaging Primary Musculoskeletal Tumors Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct
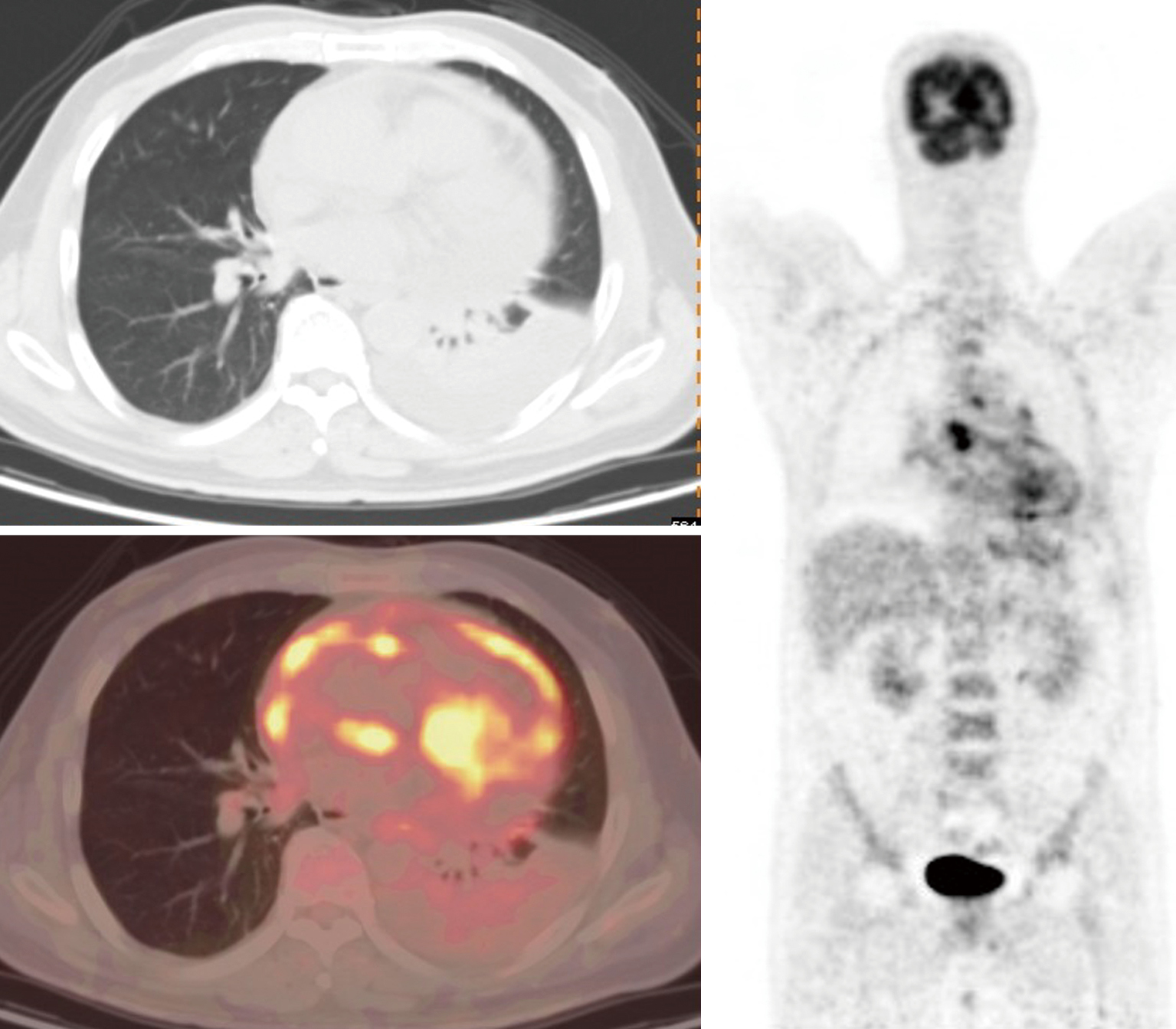
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery
Radiopharmaceutical F18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) for viability PETCT and either Tc99m tetrofosmin (Myoview) or Tc99m sestamibi (Cardiolite) for cardiac rest perfusion.
Fdg pet. As a metabolic viability test, cardiac PET imaging with FDG can assess the myocardium in either a fasting or a glucoseloaded state A fasting protocol is preferred when one wants to suppress FDG uptake in normal tissue, as in the detection of inflammatory or infectious diseases, including cardiac sarcoidosis, vasculitis, and infection of intravascular devices, pacemakers, and catheters. FDG PET/CT is useful in early detection of occult lesions in myeloid sarcoma which are nondetectable by conventional imaging techniques as CT or MRI It identifies extramedullary sites of involvement which facilitates biopsy and diagnosis. These benign etiologies may produce abnormalities on 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT), or both However, the skin is also the site of primary malignancies such as melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma ( Fig 52 ), as well as lymphoma ( Fig 53 ) or metastases ( Fig 54 ).
METHODS Fortysix patients undergoing 18FFDG PET/CT and WBMRI were reviewed by a nuclear medicine physician and radiologist, respectively, for the presence of myeloma bone disease Blinded clinical and imaging data were reviewed by two haematologists in consensus and management recorded following clinical data ± 18FFDG PET/CT or WBMRI. Preoperative 18 FFDG PET and CT were reviewed retrospectively for primary tumors of the stomach and lymph node metastases Any increased 18 FFDG uptake exceeding that of the adjacent normal gastric wall was considered positive for the primary tumor Lymph nodes were classified into 3 groups based on their anatomic sites. FDGPET had a sensitivity of 963%, a specificity of 90%, and an accuracy of 93% Study finds FDGPET 93% accurate in diagnosing chronic osteomyelitis The finding of negative FDGPET results in patients who showed no signs of disease within nine months or more of followup was important, Dehdashti notes Detecting Colorectal Cancer Spread.
FDGPET has also been shown to provide more rapid response data than anatomical measurements FDGPET/CT has also been successfully used to modify disease management by preventing futile thoracotomies in patients with lung cancer 55 and in stratifying patients with colorectal cancer into surgical versus palliative groups 53. A glucose molecule which has been tagged with a small amount of radioactive element is known as FDG This product is injected into the body during a PET scan. Abstract This handout explains a positron emission tomography (PET)/CT FDG brain scan, which allows doctors to see your brain while it is working This scan is often used to check for tumors and to find the reason for memory problems Included are how to prepare for the scan, what to expect, and how to get your results.
This handout explains a positron emission tomography (PET)/CT FDG brain scan, which allows doctors to see your brain while it is working This scan is often used to check for tumors and to find the reason for memory problems Included are how to prepare for the scan, what to expect, and how to get your results. A FDGPET scan is a medical imaging procedure It involves an injection of radioactive tracer liquid inside the body that congregates at tumors and other sites where the cells divide more quickly than usual The acronym FDGPET scan stands for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET), where the FDG is the radioactive liquid and the PET is the scanning machinery. FDGPET has also been shown to provide more rapid response data than anatomical measurements FDGPET/CT has also been successfully used to modify disease management by preventing futile thoracotomies in patients with lung cancer 55 and in stratifying patients with colorectal cancer into surgical versus palliative groups 53.
PET scanning with the tracer 18FFDG, is widely used in clinical oncologyFDG is a glucose analog that is taken up by glucoseusing cells and phosphorylated by hexokinase (whose mitochondrial form is significantly elevated in rapidly growing malignant tumours) Metabolic trapping of the radioactive glucose molecule allows the PET scan to be utilized The concentrations of imaged FDG tracer. Pet Scan FDG, Information, Cost Tweet PET scan images can provide important information about many disorders that affect the heart, lung, brain, bones, liver etc and will help the doctor plan appropriate treatment for you. Normal F18 FDG Distibution in PET/CT Imaging This radiotracer, which enters cells through glucose transporters and thus represents glycolytic rate of cells, is used to find many forms of cancers PET imaging is based on detecting coincident gamma photos from annhiliation events, thus providing higher resolution images than single photon imaging.
Positron emission tomography (PET) and combined PET/computed tomography (CT) are increasingly used for oncologic imaging Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET demonstrates abnormal metabolic features associated with malignancy that often precede morphologic findings demonstrated with anatomic imaging. Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection,USP is indicated in PET (positron emission tomography) for Identification of regions of abnormal glucose metabolism associated with foci of epileptic seizures Assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist in the evaluation of malignancy in patients with known. Given the MRI results as well as the history of VT followed by 3rd degree AV block, a fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) (cardiac and whole body) scan was subsequently performed and showed a mismatch between perfusion and metabolic imaging to further confirm the diagnosis and provide an imaging reference for future followup.
METHODS Fortysix patients undergoing 18FFDG PET/CT and WBMRI were reviewed by a nuclear medicine physician and radiologist, respectively, for the presence of myeloma bone disease Blinded clinical and imaging data were reviewed by two haematologists in consensus and management recorded following clinical data ± 18FFDG PET/CT or WBMRI. PET scanning with the tracer 18FFDG, is widely used in clinical oncology FDG is a glucose analog that is taken up by glucoseusing cells and phosphorylated by hexokinase (whose mitochondrial form is significantly elevated in rapidly growing malignant tumours) Metabolic trapping of the radioactive glucose molecule allows the PET scan to be utilized. METHODS Fortysix patients undergoing 18FFDG PET/CT and WBMRI were reviewed by a nuclear medicine physician and radiologist, respectively, for the presence of myeloma bone disease Blinded clinical and imaging data were reviewed by two haematologists in consensus and management recorded following clinical data ± 18FFDG PET/CT or WBMRI.
Background 18 FFDG PET and 131 I scans are important in the detection of metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) The relationship of FDG and radioiodine (RAI) metabolism in bone metastases (BMs) from DTC and its prognostic value on RAI treatment is not clear. General Aspects of Tumor Visualization on FDGPET FDG is currently the most commonly used radiotracer in clinical PET imaging Tumor imaging with FDG is based on the principle of increased glucose metabolism of cancer cells, which are more dependent on anaerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect) Like glucose, FDG is taken up by the cancer cells through facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs). Positron emission tomography (PET) and combined PET/computed tomography (CT) are increasingly used for oncologic imaging Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET demonstrates abnormal metabolic features associated with malignancy that often precede morphologic findings demonstrated with anatomic imaging.
Use of FDGPET or FDGPET/CT in both nonHodgkin’s and Hodgkin’s lymphoma continues to expand FDGPET is widely used to assess response to treatment after completion of chemotherapy in these. Before your PETCT, you’ll get a radioactive medication with glucose called a tracer through an intravenous (IV) line in your arm This is done to show differences between healthy tissue and diseased tissue Your PETCT will use FDG as the tracer FDG is taken up by your cells and doesn’t stay in your body long Contrast. FDG PET brain scans were obtained and visually graded by an experienced nuclear medicine physician as to the presence of classic bilateral temporoparietal hypometabolism as seen in Alzheimer's type dementia.
FDG PET scans involve a specialized sugar that shows up on PET scans This sugar injected into your body And since most tumors will take up more of it, it allows the tumor to show up on the PET scan Besides helping to diagnose cancer, FDG PET scans can also tell you if your cancer consumes a lot of sugar (ie if it’s “glucose avid” or not). FDG PET/CT EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging version The purpose of these guidelines is to assist physicians in recommending, performing, interpreting and reporting the results of FDG PET/CT for oncological imaging of adult patients PET is a quantitative imaging technique and therefore requires a common quality control (QC)/quality assurance (QA) pro. Fluorodeoxyglucose (18 F) , or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 (USAN and USP), also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated 18 FFDG, 18 FFDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical used in the medical imaging modality positron emission tomography (PET).
The lung is the most common site of IFIs, but IFIs can affect any part of the body Imaging plays an essential role in the management of IFIs Fluorine18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography integrated with computed tomography (18 FFDG PET/CT) has been used in the management of IFIs 5,618 FFDG PET/CT, as a wholebody hybrid imaging technique, allows functional data from. Purpose To determine the prognostic and predictive value of early metabolic response assessed by a change in standardized uptake value (SUV) on interim FFDG PET in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Methods PubMed and Embase were searched up until 10 September, , for studies evaluating a change in SUV on interim FFDG PET for predicting a. Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection is a positron emitting radiopharmaceutical that is used for diagnostic purposes in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging The active ingredient 2deoxy2 18 FfluoroDglucose has the molecular formula of C 6 H 11 18 FO 5 with a molecular weight of , and has the following chemical structure.
As a metabolic viability test, cardiac PET imaging with FDG can assess the myocardium in either a fasting or a glucoseloaded state A fasting protocol is preferred when one wants to suppress FDG uptake in normal tissue, as in the detection of inflammatory or infectious diseases, including cardiac sarcoidosis, vasculitis, and infection of intravascular devices, pacemakers, and catheters. FDGPET has also been shown to provide more rapid response data than anatomical measurements FDGPET/CT has also been successfully used to modify disease management by preventing futile thoracotomies in patients with lung cancer 55 and in stratifying patients with colorectal cancer into surgical versus palliative groups 53. PET scan has the ability to identify tumors in their very early phase The PET scan can also detect the spread of cancer in other parts of the body What is FDG?.
Purpose To determine the prognostic and predictive value of early metabolic response assessed by a change in standardized uptake value (SUV) on interim FFDG PET in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Methods PubMed and Embase were searched up until 10 September, , for studies evaluating a change in SUV on interim FFDG PET for predicting a. Purpose To determine the prognostic and predictive value of early metabolic response assessed by a change in standardized uptake value (SUV) on interim FFDG PET in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Methods PubMed and Embase were searched up until 10 September, , for studies evaluating a change in SUV on interim FFDG PET for predicting a. FDG PET is a biomarker for neuronal degeneration in dementia 4 , in addition to being an oncologic imaging biomarker 5 – 9.
An FDG PET scan is one of the most powerful tools we have to detect and monitor disease Most often used in conjunction with CT or MRI, it helps radiologists distinguish between healthy tissue and diseased tissue so that cancer can be accurately diagnosed, correctly staged, and appropriately treated. METHODS Fortysix patients undergoing 18FFDG PET/CT and WBMRI were reviewed by a nuclear medicine physician and radiologist, respectively, for the presence of myeloma bone disease Blinded clinical and imaging data were reviewed by two haematologists in consensus and management recorded following clinical data ± 18FFDG PET/CT or WBMRI. Positron emission tomography, also called PET imaging or PET scan, is a test that images the function of cells to show differences between healthy tissue and diseased tissue It uses a small amount of a radioactive chemical which is combined with sugar This combination is called F18 fluorodeoxyglucose or FDG, so the test is sometimes called an FDGPET scan.
FDG (2 F18 fluoro2deoxyDglucose) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a minimallyinvasive diagnostic imaging procedure used to evaluate glucose metabolism in normal tissue as well as in diseased tissues in conditions such as cancer, ischemic heart disease, and some neurologic disorders FDG is an injected radionuclide (or radiopharmaceutical) that emits subatomic particles, known as positrons, as it decays. PET imaging with 18FFDG takes advantage of the fact that the brain is normally a rapid user of glucose Standard 18FFDG PET of the brain measures regional glucose use and can be used in neuropathological diagnosis Examples Brain pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease greatly decrease brain metabolism of both glucose and oxygen in tandem. 18 FFDG PET imaging, which stands for 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography, uses a radioactively labeled glucose molecule to identify parts of the body or brain that have unusual amounts of activity Glucose is the body’s main source of energy, so PET scans allow doctors to visualize areas that have high energy metabolism, or hypermetabolism.
METHODS Fortysix patients undergoing 18FFDG PET/CT and WBMRI were reviewed by a nuclear medicine physician and radiologist, respectively, for the presence of myeloma bone disease Blinded clinical and imaging data were reviewed by two haematologists in consensus and management recorded following clinical data ± 18FFDG PET/CT or WBMRI. FDG (2 F18 fluoro2deoxyDglucose) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a minimallyinvasive diagnostic imaging procedure used to evaluate glucose metabolism in normal tissue as well as in diseased tissues in conditions such as cancer, ischemic heart disease, and some neurologic disorders. Purpose To determine the prognostic and predictive value of early metabolic response assessed by a change in standardized uptake value (SUV) on interim FFDG PET in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy Methods PubMed and Embase were searched up until 10 September, , for studies evaluating a change in SUV on interim FFDG PET for predicting a.
If you do not follow the diet, the results of the FDG PET Scan could be incorrect or abnormal Following this diet greatly increases the reliability of test results by limiting uptake of the radioactive medication (FDG) used in the test only to tissues that are affected by sarcoidosis and/or inflammation. PETCT FDG Cardiac Viability Special Instructions Consult with the atte nding radiologist about the appropriateness of the examination and regarding the patient’s blood sugar measurements during the examination. FDGPET has also been shown to provide more rapid response data than anatomical measurements FDGPET/CT has also been successfully used to modify disease management by preventing futile thoracotomies in patients with lung cancer 55 and in stratifying patients with colorectal cancer into surgical versus palliative groups 53.
The uptake of 18 FFDG by tissues is a marker for the tissue uptake of glucose, which in turn is closely correlated with certain types of tissue metabolism After 18 FFDG is injected into a patient, a PET scanner can form twodimensional or threedimensional images of the distribution of 18 FFDG within the body Since its development in 1976, 18 FFDG had a profound influence on research in. In follicular lymphoma (FL), detection of bone marrow (BM) involvement (BMI) by 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) improves the accuracy of staging vs BM biopsy (BMB) alone. 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality for cancer imaging, assisting diagnosis, staging of patients with newly diagnosed malignancy, restaging following therapy and surveillance Interpretation requires integration of the metabolic and anatomic findings provided by the PET and CT components which transcend the knowledge base isolated in the worlds of nuclear medicine and radiology, respectively.
Those abbreviations stand for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)positron emission tomography (PET) The role of this procedure is to detect metabolically active malignant lesions including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, brain cancer and multiple myeloma FDGPET scan may also be used to stage and monitor the response to therapy of malignant disease. FDG PET studies have shown that adipose tissue becomes insulin resistant in obesity and type 2 diabetes (Virtanen et al, 01 ;. The lung is the most common site of IFIs, but IFIs can affect any part of the body Imaging plays an essential role in the management of IFIs Fluorine18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography integrated with computed tomography (18 FFDG PET/CT) has been used in the management of IFIs 5,618 FFDG PET/CT, as a wholebody hybrid imaging technique, allows functional data from.
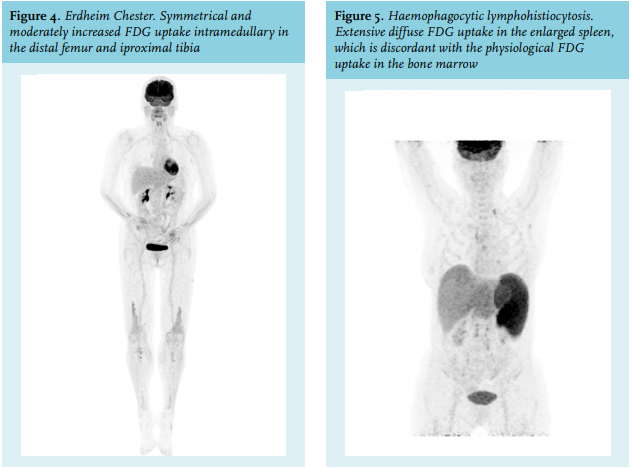
Article The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Scans To Evaluate Bone Marrow In Haemato Oncological Conditions Full Text September 19 Njm

Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Cardiac Viability Perth Envision
Fdg Pet Ct In Clinical Decision Making Science 2 0
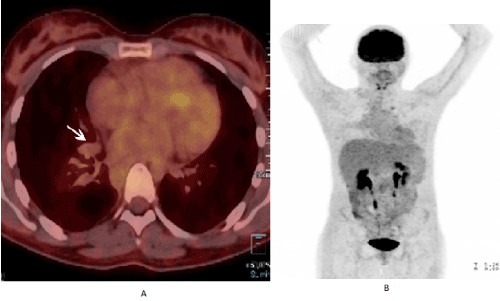
Whole Body Mri With Diffusion Sequence Versus Fdg Pet Ct Correlation Study On Children Adolescents And Young Adults With Hodgkin Lymphoma
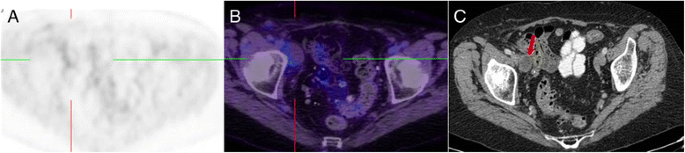
How We Read Oncologic Fdg Pet Ct Cancer Imaging Full Text
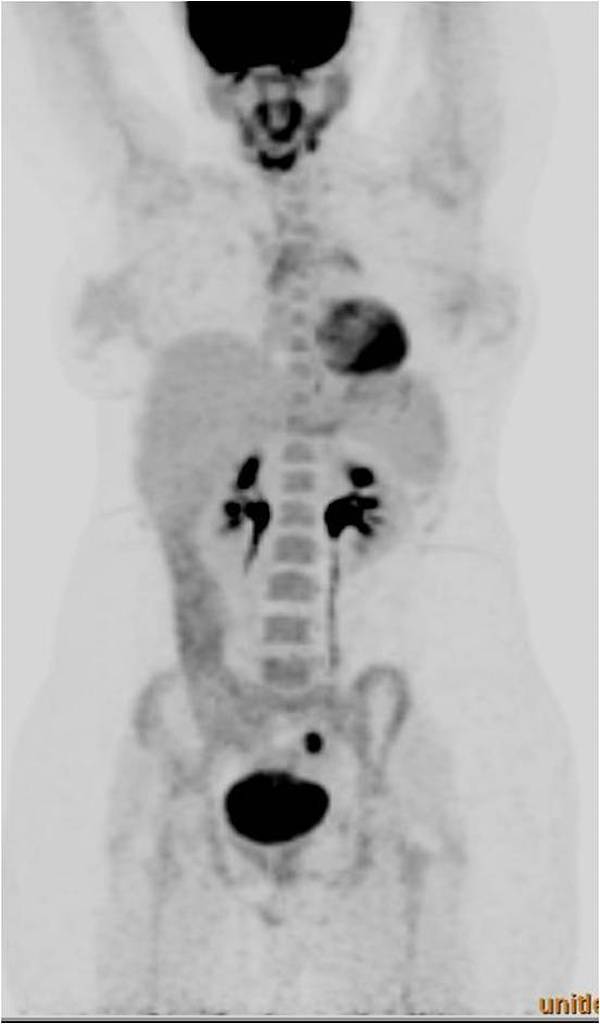
Physiologic Fdg Uptake In Corpus Luteal Cyst Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

The Basic Principles Of Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Pet Clinics
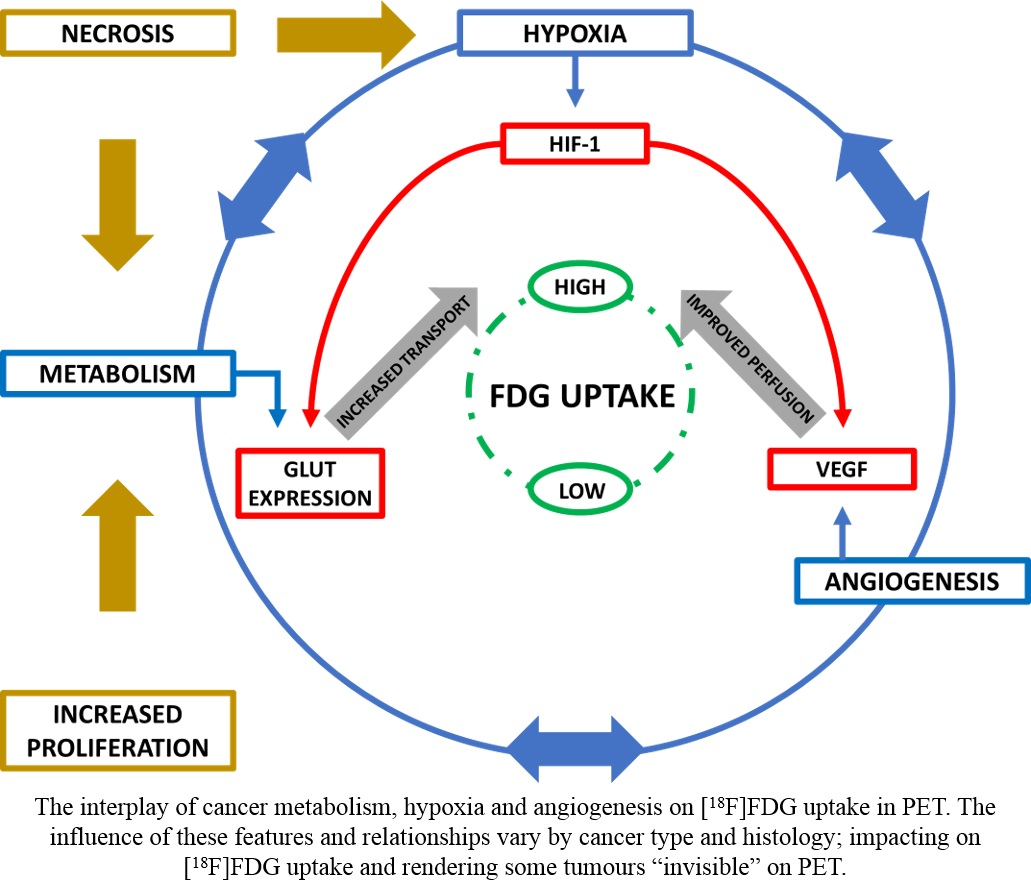
Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text Can The Efficacy Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Clinical Oncology Be Enhanced By Screening Biomolecular Profiles Html

Fdg Pet Predicts Outcomes In Paediatric Osteosarcoma Physics World
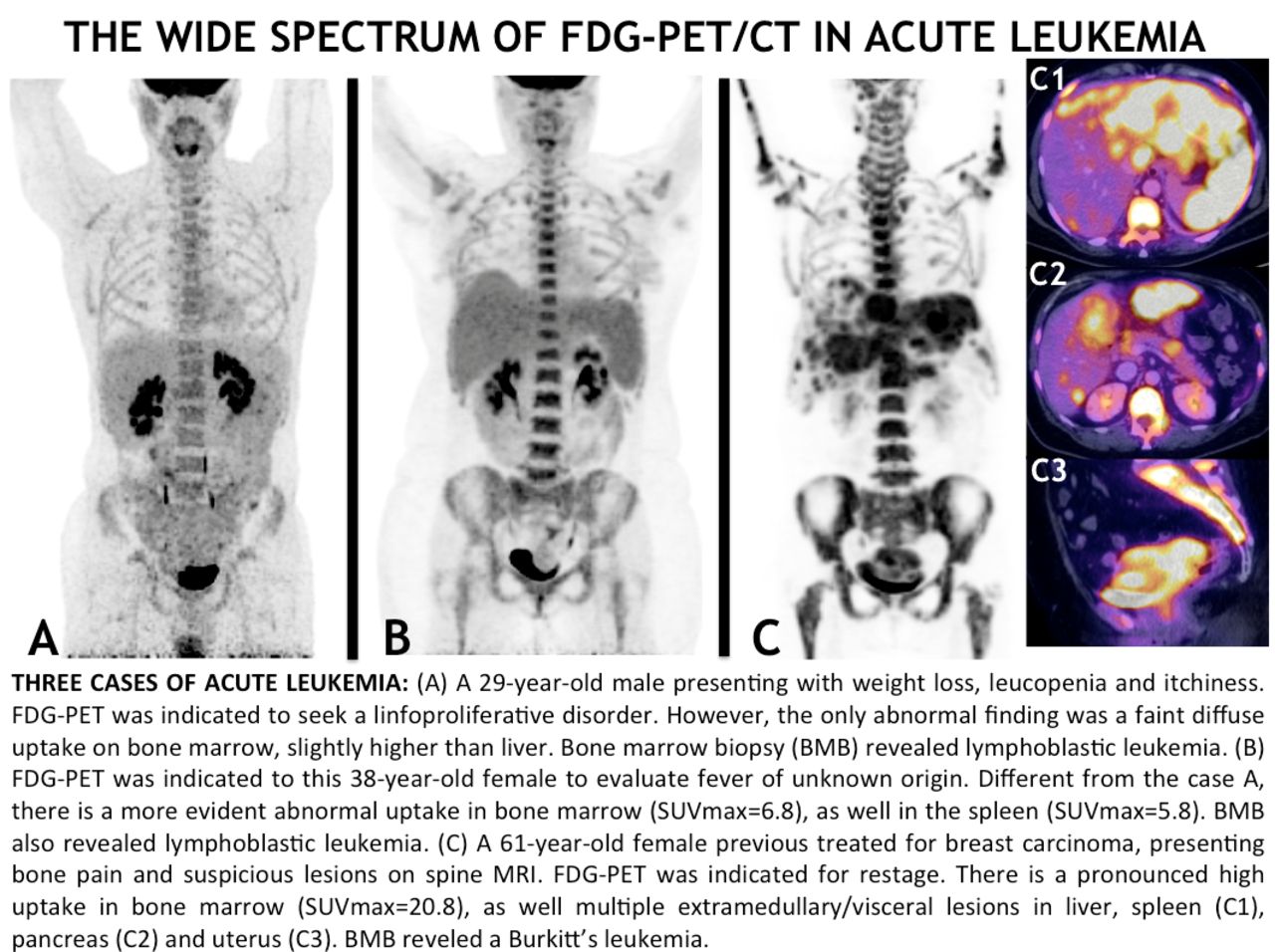
Acute Leukemia The Wide Spectrum Of Imaging Findings On An Fdg Pet Ct Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Fdg Pet And Mri In The Evolution Of New Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus American Journal Of Neuroradiology
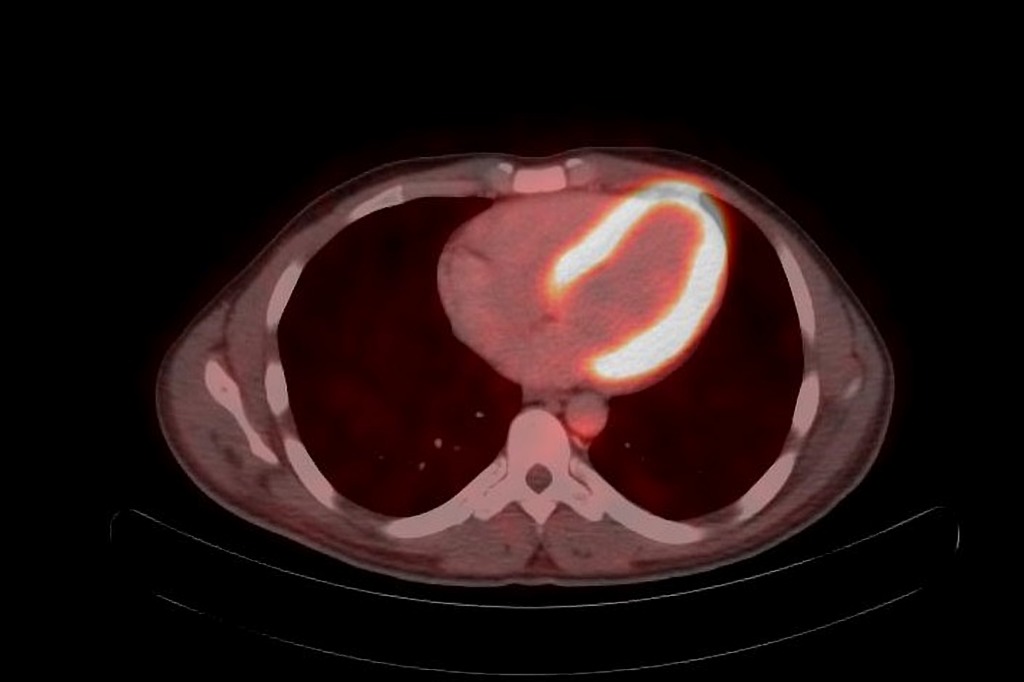
Normal Physiological Cardiac Uptake In F 18 Fdg Pet Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
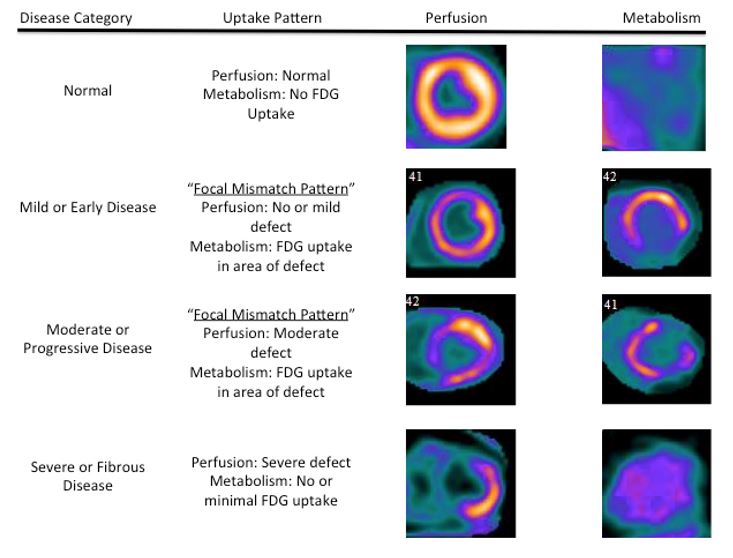
Fdg Pet Is A Superior Tool In The Diagnosis And Management Of Cardiac Sarcoidosis American College Of Cardiology

Flt Pet Is Superior To Fdg Pet For Very Early Response Prediction In Npm Alk Positive Lymphoma Treated With Targeted Therapy Cancer Research
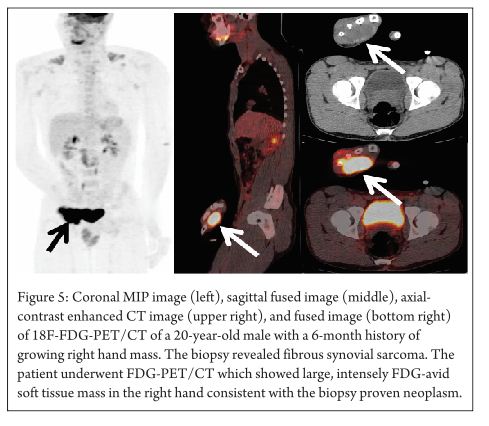
Current Role Of Fdg Pet In Bone And Soft Tissue Tumors Journal Of Bone Soft Tissue Tumors
Artifacts And Normal Variants In Fdg Pet Radiology Key
Q Tbn And9gcqmb6cff 1xe18vnoqntqqyxunenn9eqvxbrmcvtaueevkxq2ay Usqp Cau

Fdg Pet Found Effective At Evaluating Alzheimer S Severity Axis Imaging News
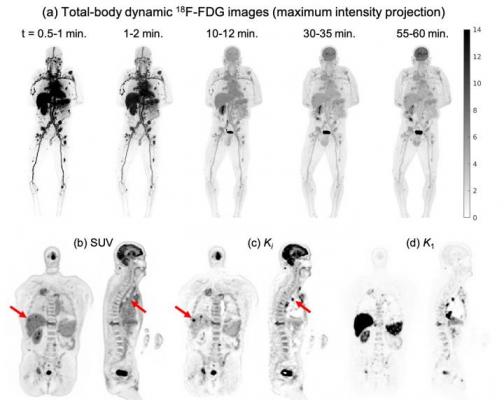
Total Body Dynamic Pet Successfully Detects Metastatic Cancer Imaging Technology News

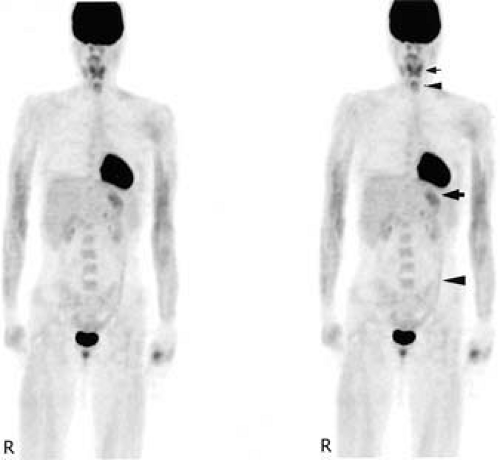
Whole Body 18f Fdg Pet Ct In The Diagnosis Of Neurosarcoidosis Mayo Clinic Proceedings

Diagnostic Efficacy Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Adrenal Incidentaloma In Endocrine Connections Volume 8 Issue 7 19

The Fdg Pet Study Youtube
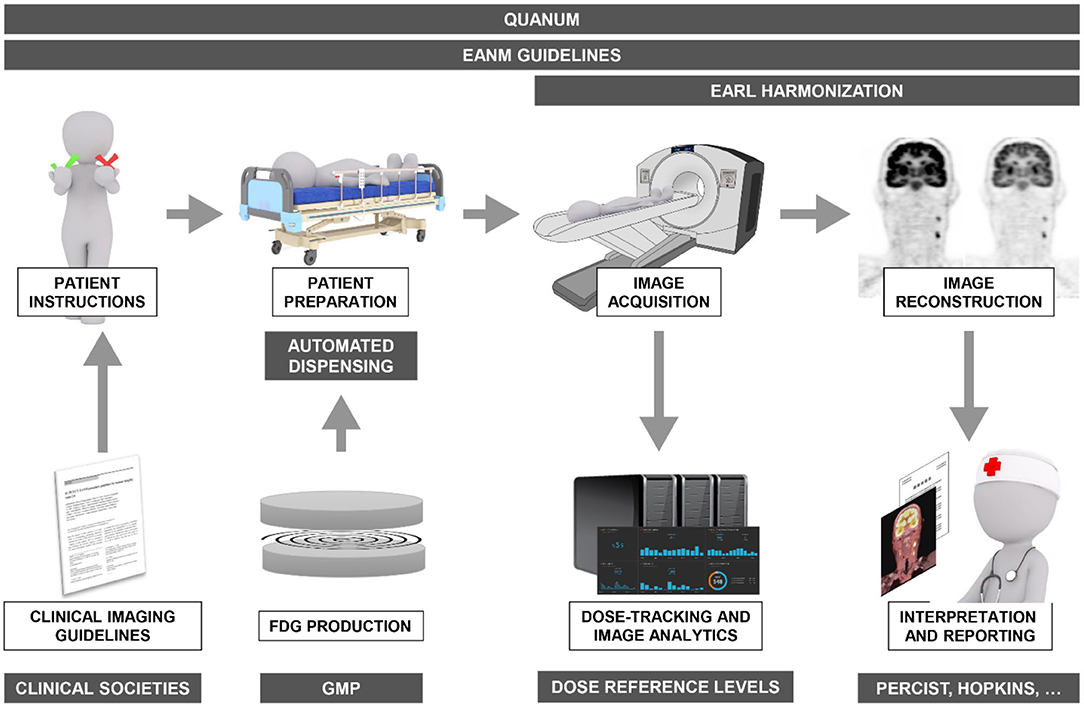
Frontiers Quality Assessment In Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of Head And Neck Cancer One Home Run Is Better Than Two Doubles Oncology

18f Fdg Pet Ct Normal Variants Artefacts And Pitfalls In Lymphoma Radiology Key

Advanced Fdg Pet Image Analysis Identifies Cell Mutations In Cancer Patients Imaging Technology News

Fdg Pet The Jagust Lab

Pdf Common Pitfalls In Oncologic Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Semantic Scholar

Prognostic Pet 18f Fdg Uptake Imaging Features Are Associated With Major Oncogenomic Alterations In Patients With Resected Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Cancer Research

Inguinal And Scrotal Extramammary Paget S Disease 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging
Q Tbn And9gctl4i6z5fzghcdvnea1hyysxoib3b0yxekob3w Yqbn6ndk6wdi Usqp Cau
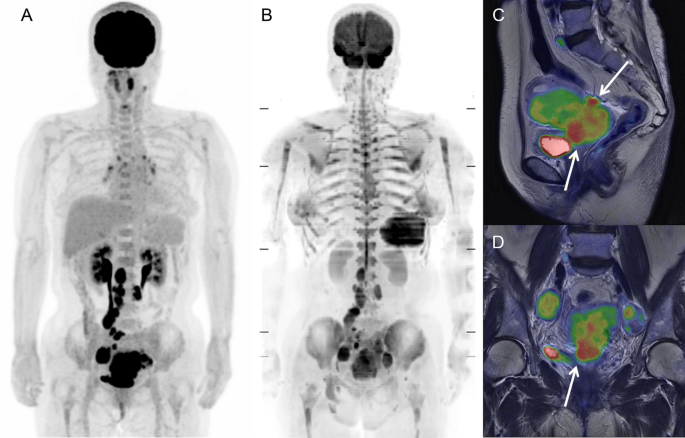
Integrated 18 F Fdg Pet Mri Demonstrates The Iron Related Bone Marrow Physiology Scientific Reports

Normal F 18 Fdg Pet Ct Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Use Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct To Predict Short Term Outcomes Early In The Course Of Chemoradiotherapy In Stage Iii Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung

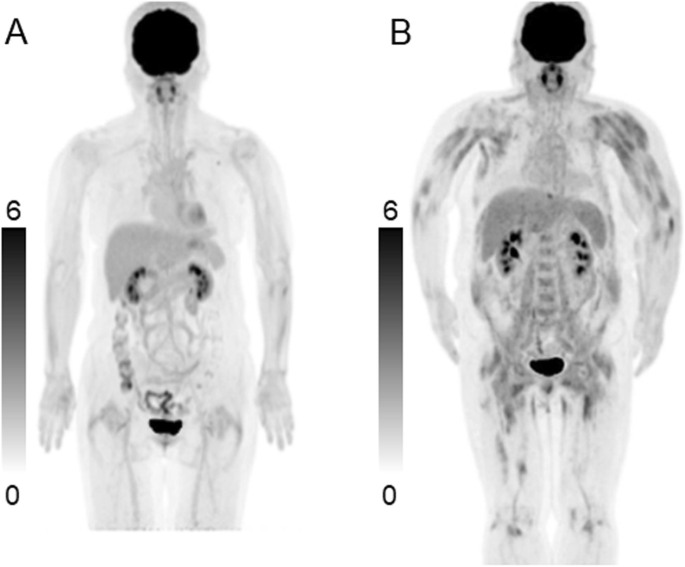
Clinical Values Of Fdg Pet In Polymyositis And Dermatomyositis Syndromes Imaging Of Skeletal Muscle Inflammation Bmj Open

Novel Strategy For A Cocktail 18f Fluoride And 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Evaluation Of Malignancy Results Of The Pilot Phase Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Clinical Relevance Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In The Postoperative Follow Up Of Patients With History Of Medullary Thyroid Cancer In Radiology And Oncology Ahead Of Print
1

Fdg Pet Is A Superior Tool In The Diagnosis And Management Of Cardiac Sarcoidosis American College Of Cardiology

18 F Fdg Pet Results From Patient No 4 The Pre Treatment Pet Image Download Scientific Diagram

Evaluation Of Wilson Disease With 18f Fdg Pet Ct Insight Medical Publishing

Integrated 18f Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging 18f Fdg Pet Mri A Multimodality Approach For Comprehensive Evaluation Of Dementia Patients A Pictorial Essay Jena A Renjen Pn Taneja S Gambhir A Negi P
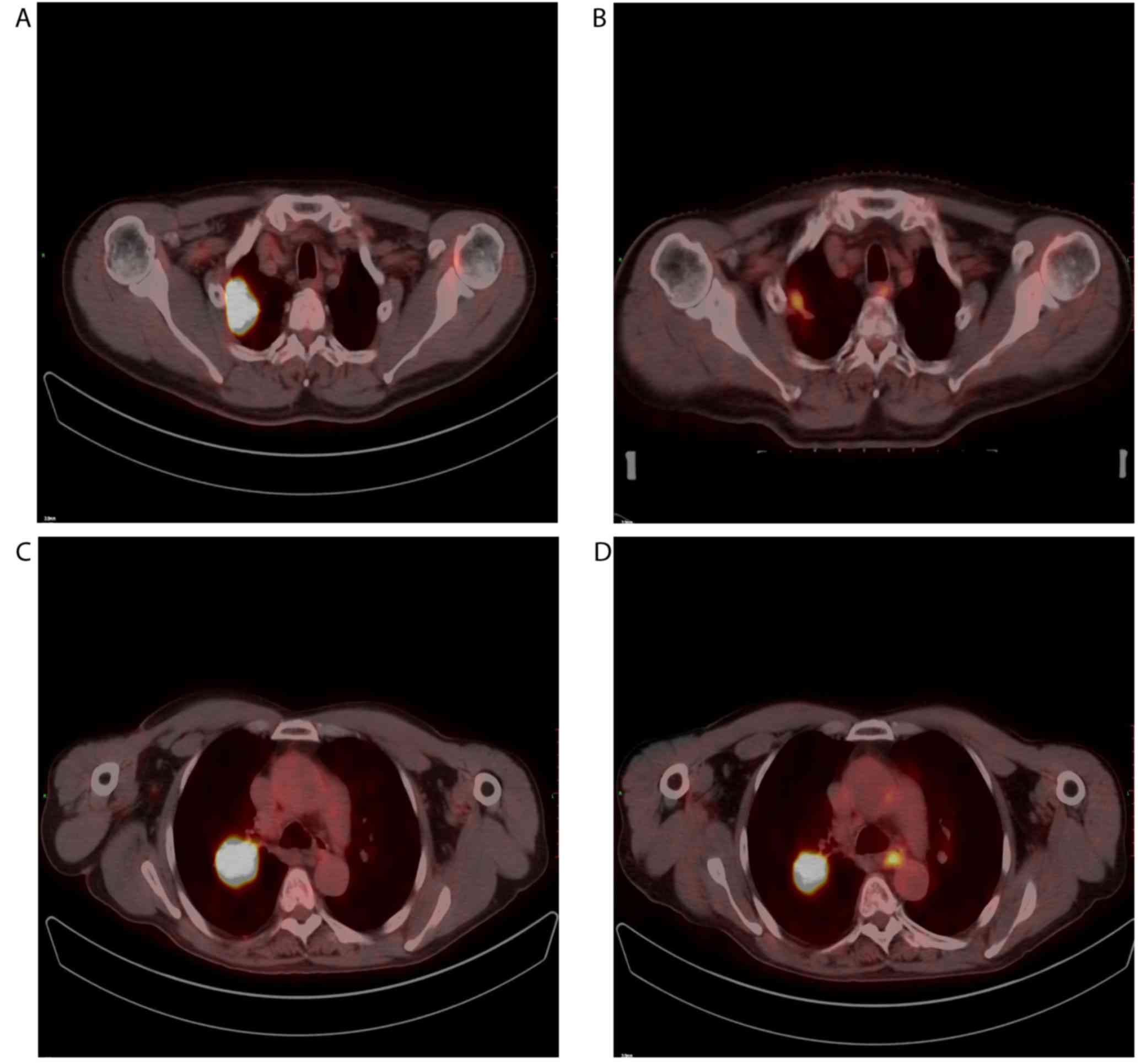
18 F Fdg Pet Ct In Patients With Polymyositis Dermatomyositis Correlation With Serum Muscle Enzymes European Journal Of Hybrid Imaging Full Text
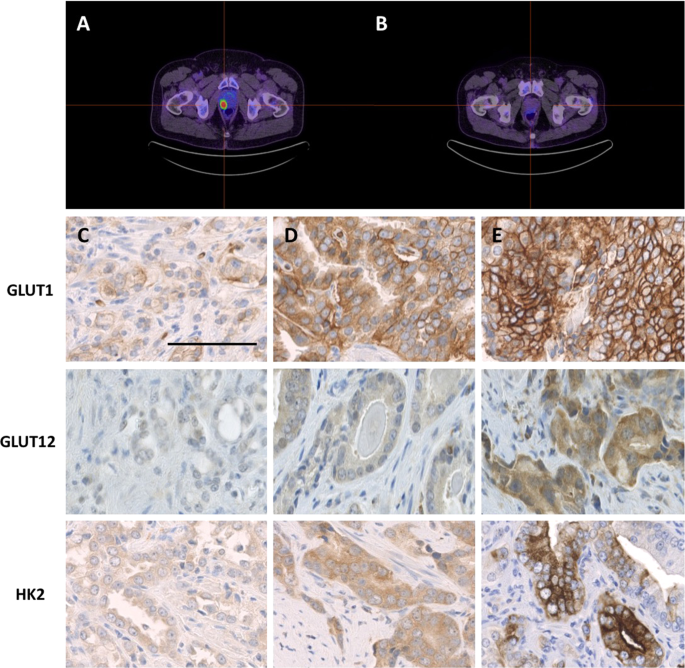
Glut1 Expression In High Risk Prostate Cancer Correlation With 18 F Fdg Pet Ct And Clinical Outcome Prostate Cancer And Prostatic Diseases

18f Fdg Pet Ct For Monitoring The Response Of Breast Cancer To Mir 143 Based Therapeutics By Targeting Tumor Glycolysis Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids

18 F Fdg Pet Imaging Evaluation On Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease And Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model Treated With Sorafenib

Fdg Pet Ct And Breast Cancer Siemens Healthineers Malaysia

Fdg Pet Scan At The Time Of Initial Diagnosis The Tumor Of The Download Scientific Diagram

Utilizing 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging And Quantitative Histology To Measure Dynamic Changes In The Glucose Metabolism In Mouse Models Of Lung Cancer Protocol

Novel Strategy For A Cocktail 18f Fluoride And 18f Fdg Pet Ct Scan For Evaluation Of Malignancy Results Of The Pilot Phase Study Journal Of Nuclear Medicine

Lymphoma Severity And Type Are Associated With Aortic Fdg Uptake By 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Jacc Cardiooncology
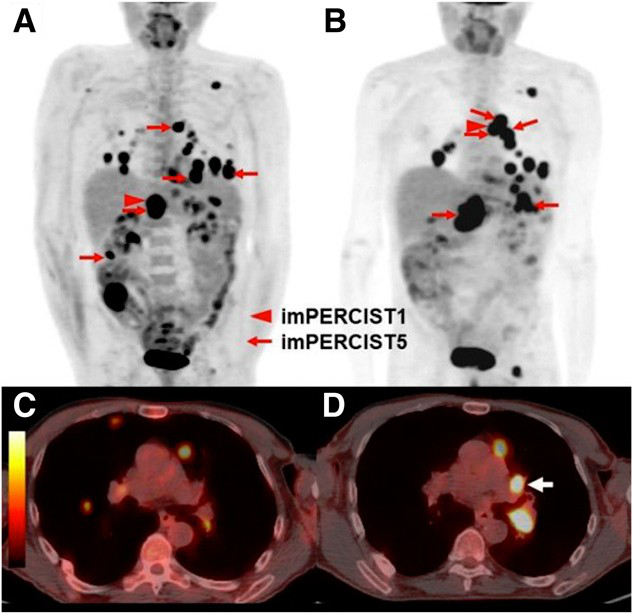
Fdg Pet Ct Aids In Melanoma Treatment Assessment
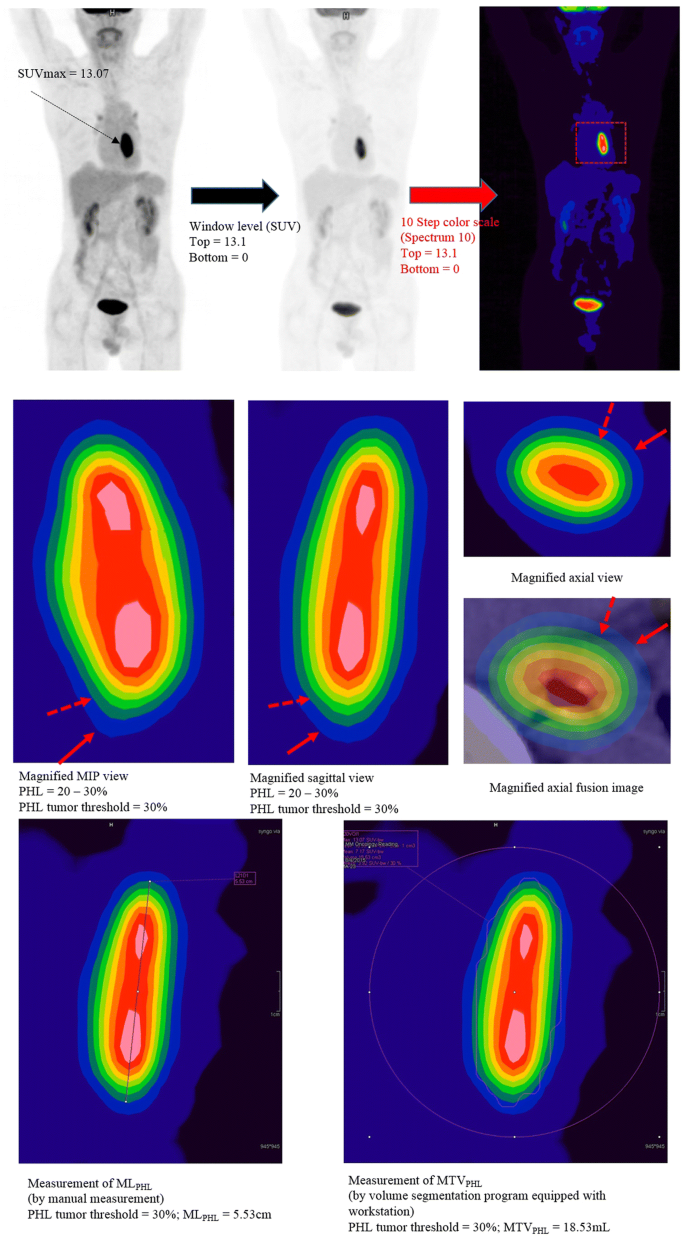
Accurate Fdg Pet Tumor Segmentation Using The Peritumoral Halo Layer Method A Study In Patients With Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cancer Imaging Full Text

Accuracy Of Positron Emission Tomography Ecr Journal

Fig 4 4 Mip Fdg Pet And Fused Diseases Of The Abdomen And Pelvis 18 21 Ncbi Bookshelf

A Preliminary 18f Fdg Pet Mri Study Shows Increased Vascular Inflammation In Moderate To Severe Atopic Dermatitis The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Increasing Cardiac 18f Fluorodeoxyglucose Fdg Uptake On Pet Ct As A Biomarker For Cardiotoxicity Of Chemo Radiotherapy In Cancer A Myth Or A Reality Radiotherapy And Oncology

Pet Approaches For Diagnosis Of Dementia American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Amyloid Pet And 18f Fdg Pet In The Diagnostic Investigation Of Alzheimer S Disease And Other Dementias The Lancet Neurology

Fdg Pet Scan Cedars Sinai

Non Malignant Cardiac Findings On Fdg Pet Ct

Figure 1 From 11c Dtbz And 18f Fdg Pet Measures In Differentiating Dementias Semantic Scholar

18f Fdg Pet The Early Phases And The Delivery Rate Of 18f Av45 Pet As Proxies Of Cerebral Blood Flow In Alzheimer S Disease Validation Against 15o H2o Pet Sciencedirect
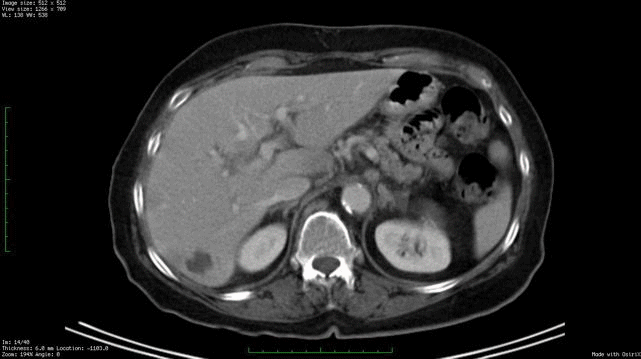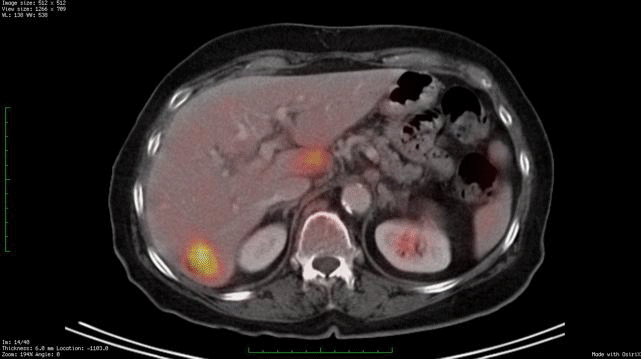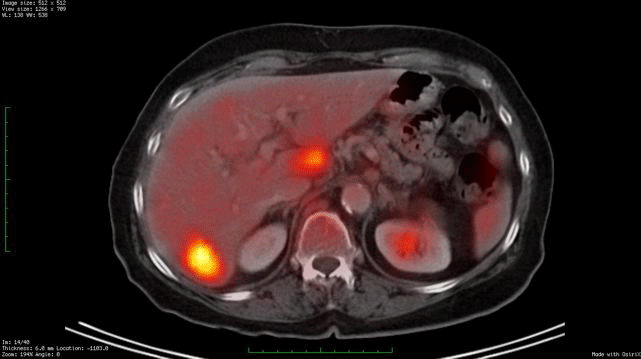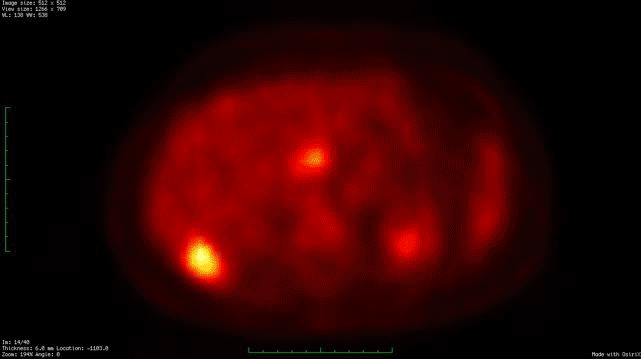
Whole Body Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Cancer New York Eye Cancer Center
Understanding Your Fdg Pet Scan

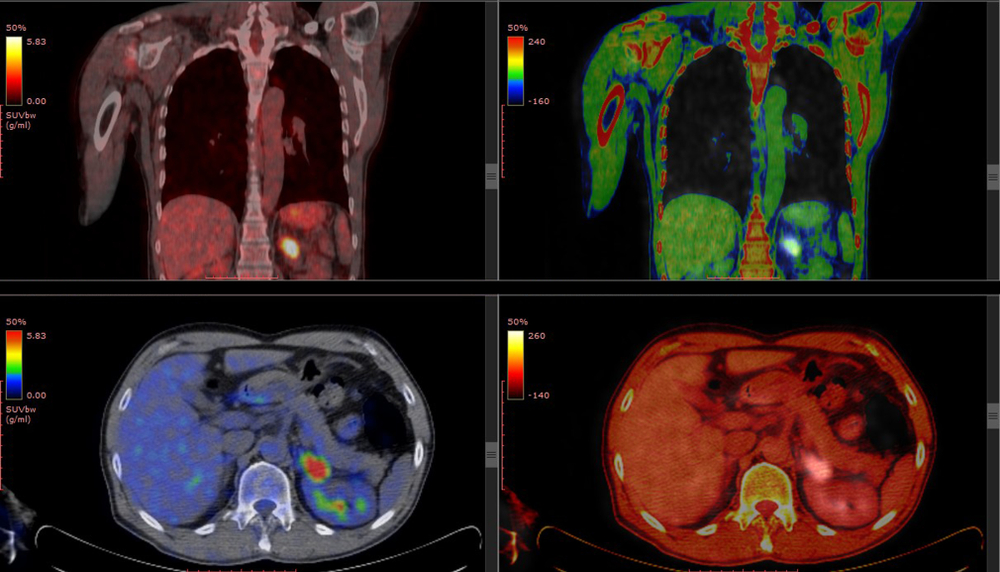
Diffuse Bone Marrow Uptake Pattern In 18 F Fdg Pet Ct A And B Download Scientific Diagram

Delayed 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In The Assessment Of Residual Tumors After Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Cancer Radiology
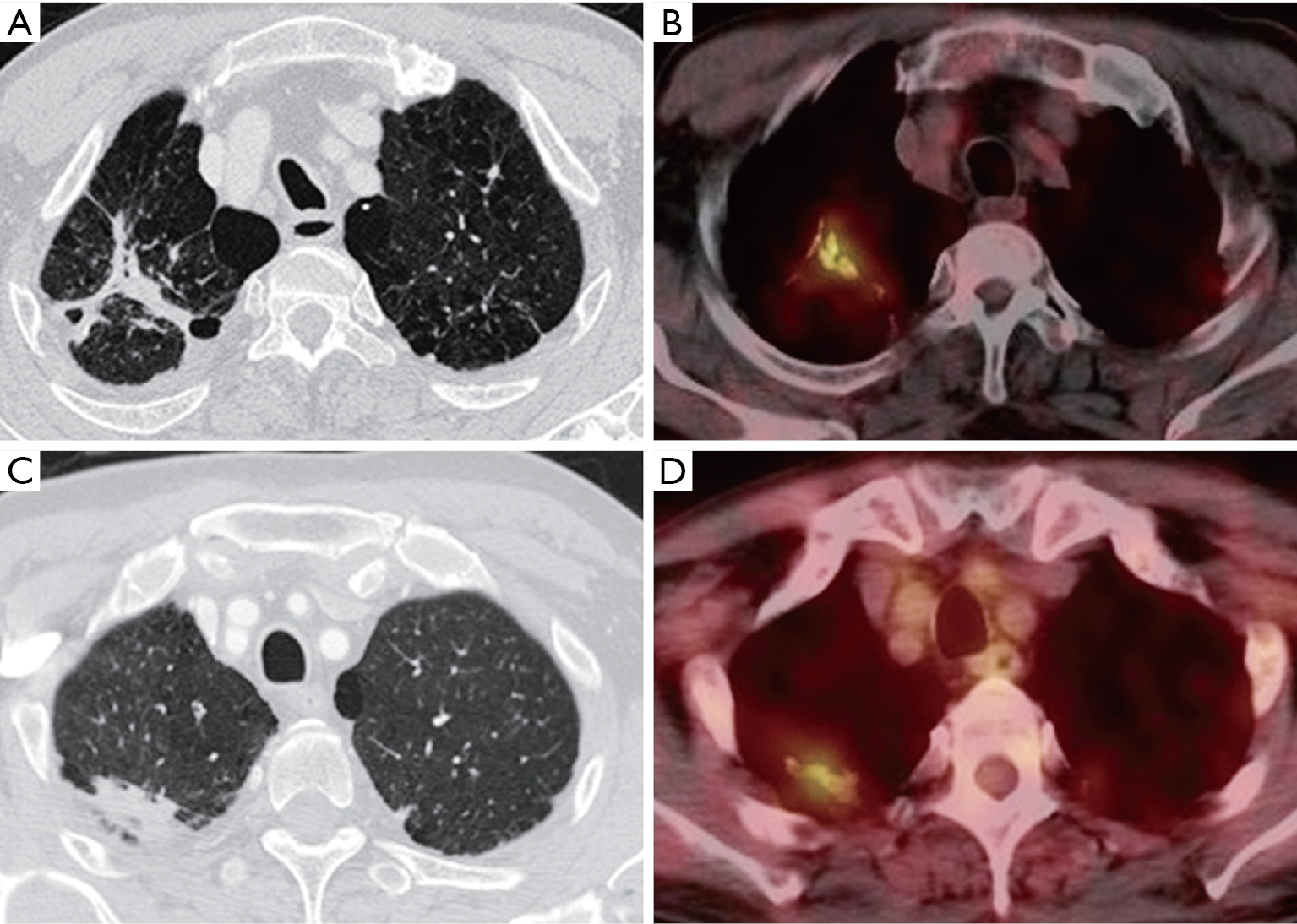
Updates On 18 F Fdg Pet Ct As A Clinical Tool For Tuberculosis Evaluation And Therapeutic Monitoring Yu Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery

Abnormal Brain Metabolism On Fdg Pet Ct Is A Common Early Finding In Autoimmune Encephalitis Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation

Pet Scans And Alzheimer S Bluegrass Regional Imaging

Common Causes Of False Positive F18 Fdg Pet Ct Scans In Oncology

Eposters 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Cervical Cancer Assessment

Comparison Of F 18 Fluoride Pet Ct F 18 Fdg Pet Ct And Bone Scintigraphy Planar And Spect In Detection Of Bone Metastases Of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Nagoya University Research Seeds For Needs Unite
The Value Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Breast Cancer Staging Bosnian Journal Of Basic Medical Sciences
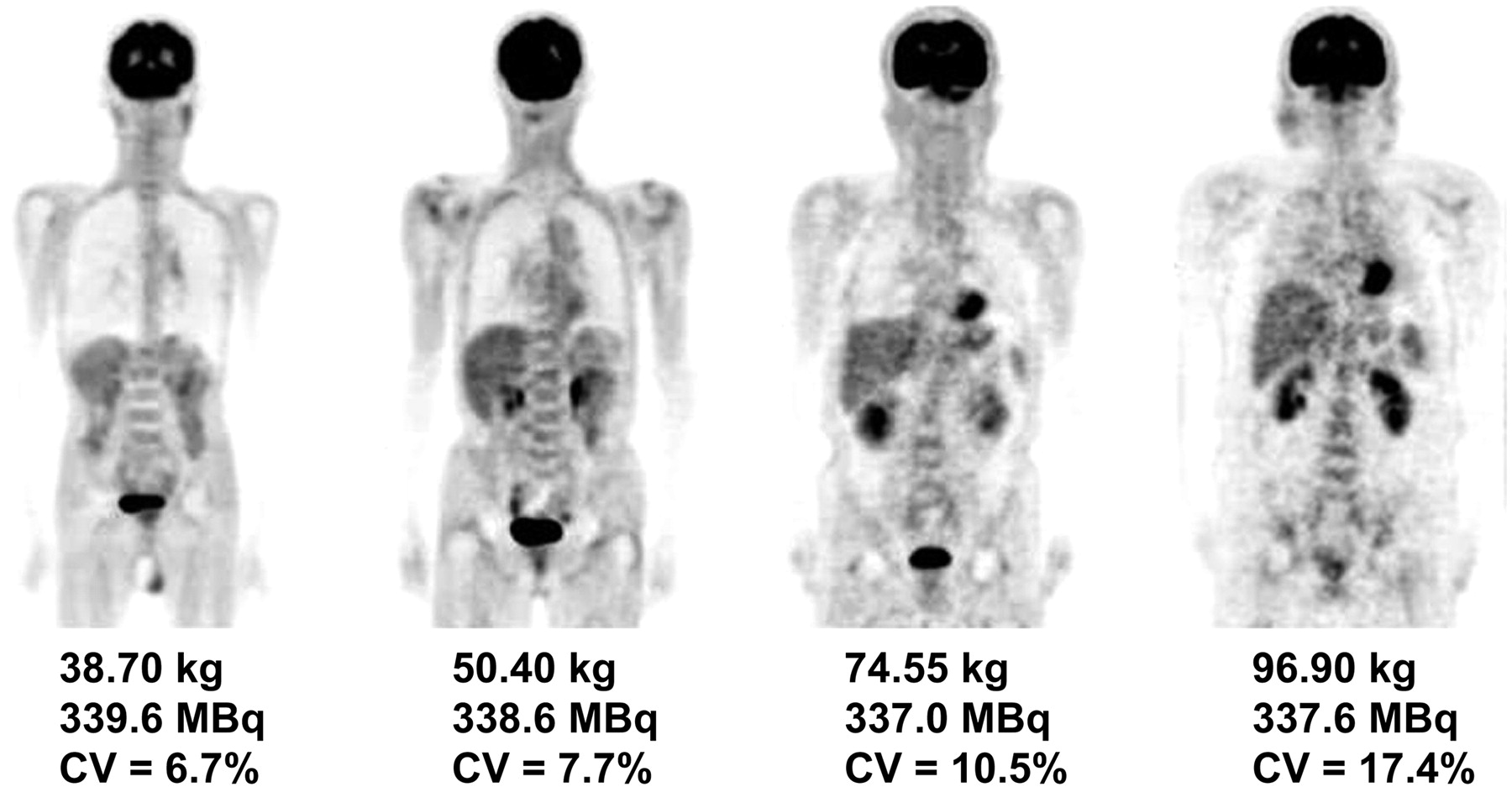
Patient Weight Based Acquisition Protocols To Optimize18f Fdg Pet Ct Image Quality Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology

Diagnostic Errors In Clinical Fdg Pet Ct European Journal Of Radiology
Generative Fdg Pet And Mri Model Of Aging And Disease Progression In Alzheimer S Disease

The Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct In Cardiac Sarcoidosis
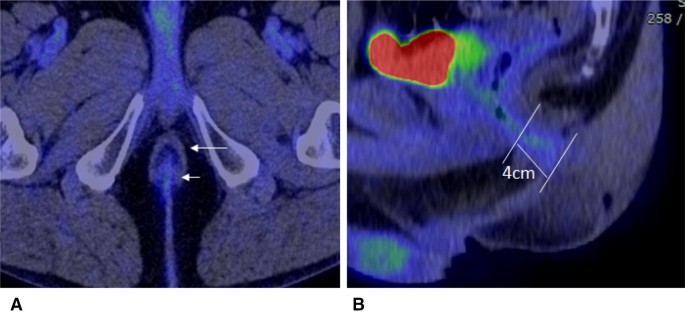
Physiological 18f Fdg Uptake In The Normal Adult Anal Canal Evaluation By Pet Ct Springerlink

Comparison Of 18f Naf Pet Ct And 18f Fdg Pet Ct For Detection Of Skull Base Invasion And Osseous Metastases In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Nasopharyngeal Tuberculosis Incidentally Diagnosed On 18f Fdg Pet Ct International Journal Of Infectious Diseases

Fever Of Unknown Origin The Value Of Fdg Pet Ct Sciencedirect

Usefulness And Pitfalls Of F 18 Fdg Pet Ct For Diagnosing Extramedullary Acute Leukemia European Journal Of Radiology

Fdg Pet Ct Imaging Of Fibrous Dysplasia Left Maximum Intensity Download Scientific Diagram
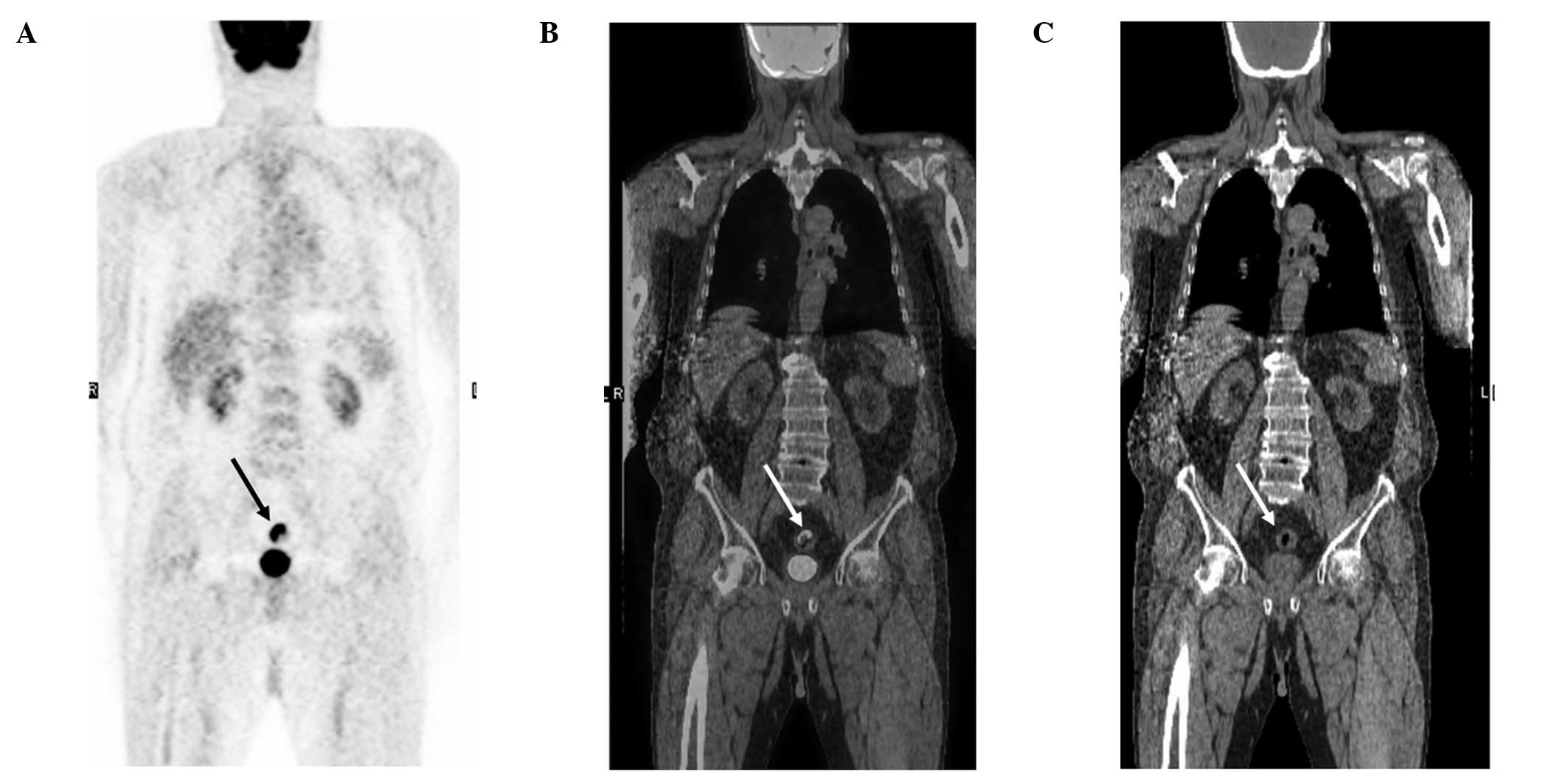
Correlation Between Incidental Fdg Pet Ct Colorectal Observations And Endoscopic And Histopathological Results
Q Tbn And9gcthwpzjmkg9ocldhqds3xub4enzp2 Yr65sl 1y3pxbwy2djxdi Usqp Cau
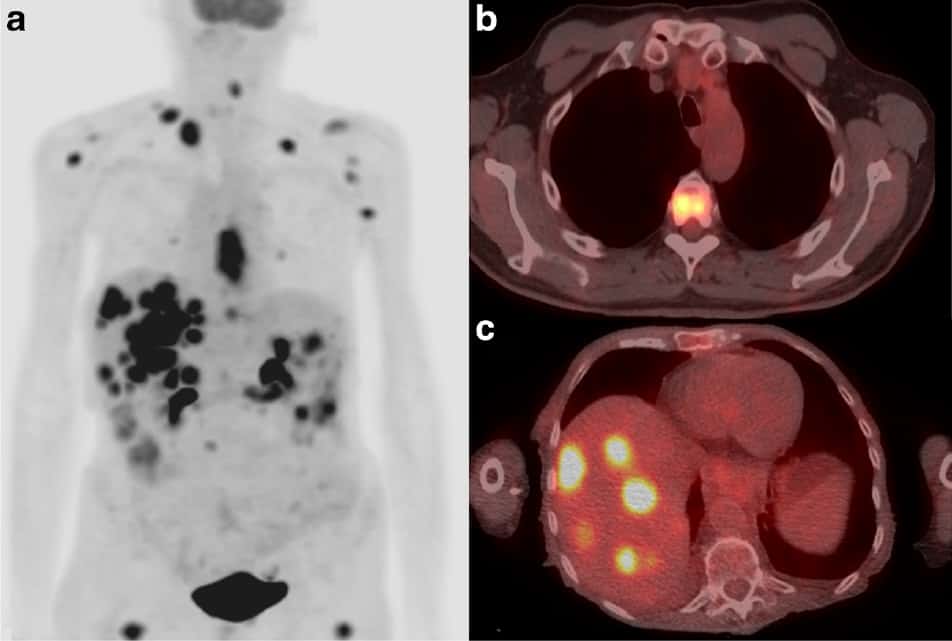
Fdg Pet Ct Provides Valuable Oesophageal Cancer Updates Physics World
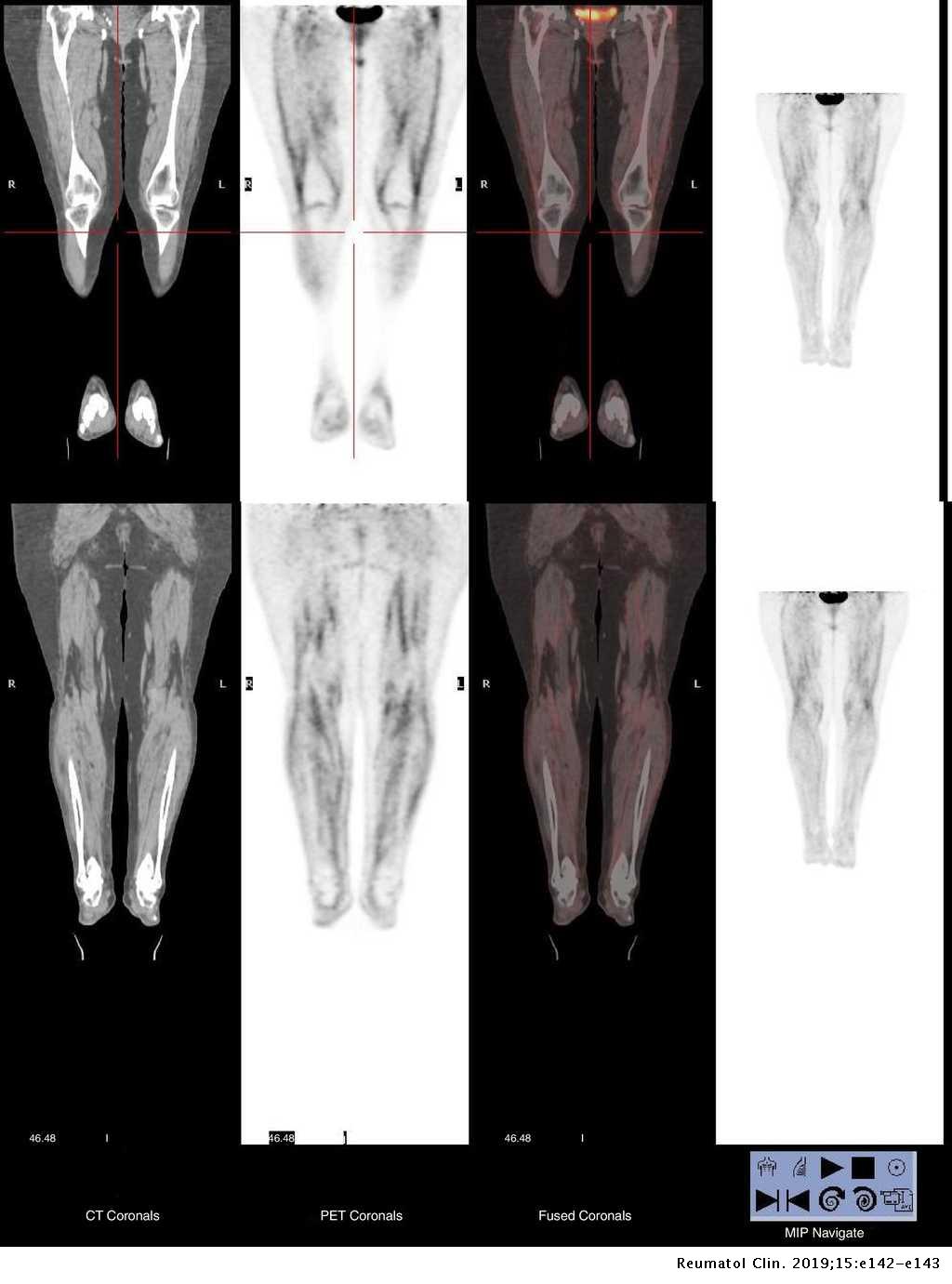
18f Fdg Pet Ct May Be A Useful Adjunct In Diagnosis Of Eosinophilic Fasciitis Reumatologia Clinica

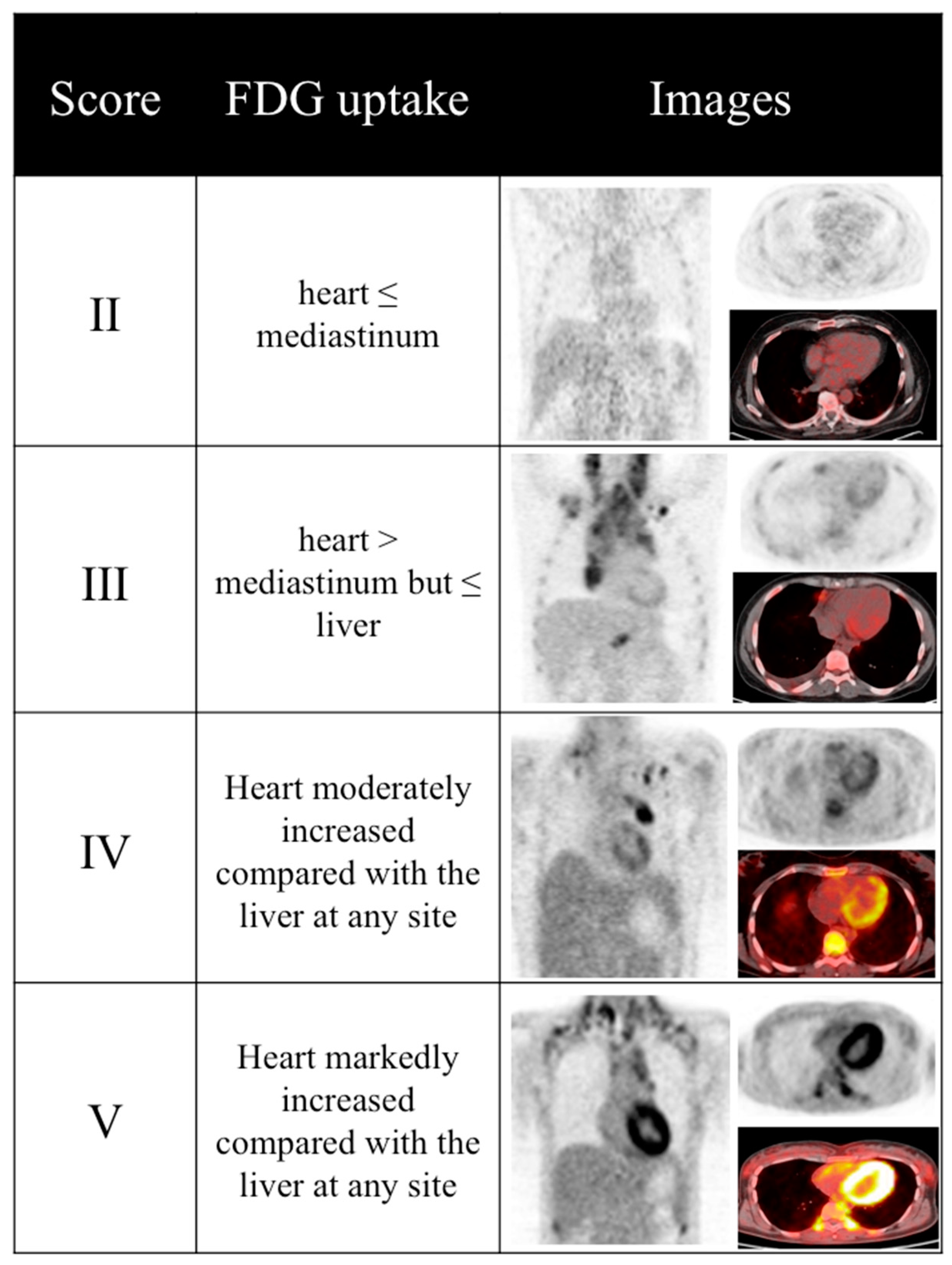
Diagnostics Free Full Text A Score Based Approach To 18f Fdg Pet Images As A Tool To Describe Metabolic Predictors Of Myocardial Doxorubicin Susceptibility Html
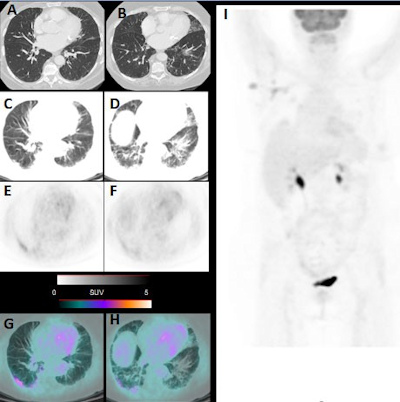
Incidental Covid 19 Findings Seen On Routine Fdg Pet Ct

Fdg Pet Ct Infinity Medical Centre

18f Fdg Pet Brain In Parkinsonism Mds Abstracts
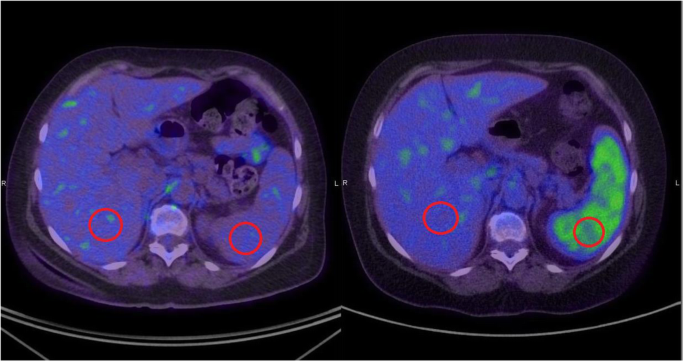
18 F Fdg Pet Ct Based Spleen To Liver Ratio Associates With Clinical Outcome To Ipilimumab In Patients With Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Imaging Full Text

Eposters Clinical Helpfulness Of F 18 Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Diabetic Patients With Malignant Otitis Externa
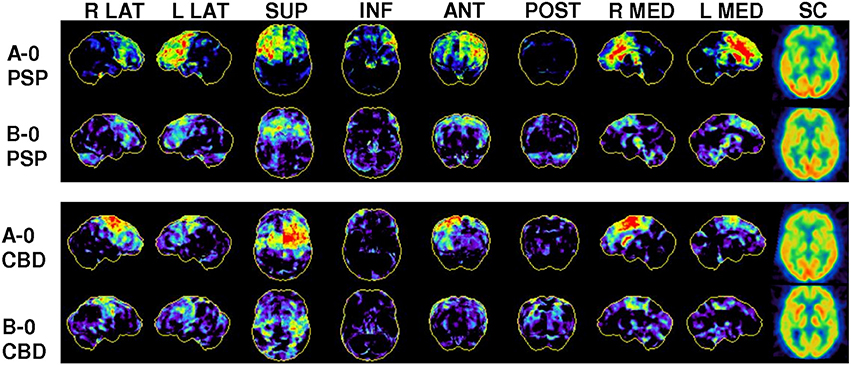
Frontiers Clinical Routine Fdg Pet Imaging Of Suspected Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Corticobasal Degeneration A Gatekeeper For Subsequent Tau Pet Imaging Neurology

Clinical Usefulness Of Fdg Pet For Management Of Well Differentiated Digestive Neuroendocrine Tumors Digestive And Liver Disease
Http Www Ranzcp Org Ranzcp Media Conference Presentations Son 18 Rowe Pet For Clinicians Nov 18 Pdf

Fdg Pet Imaging Reliable In Identifying Abnormalities In Parkinson Disease Neurology Advisor
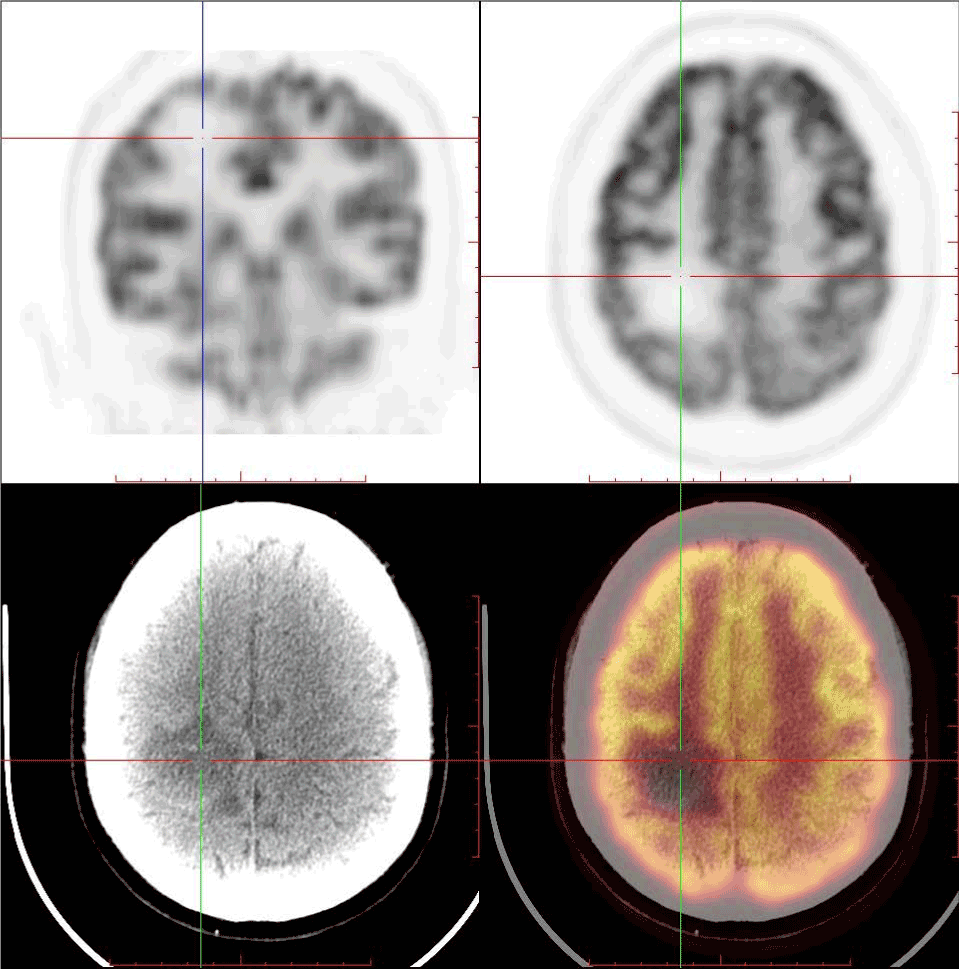
Cerebral Metastasis With Sup 18 Sup F Fdg Uptake Deficiency From Non Small Cell Lung Cancer



