Adenocarcinoma In Situ Lung
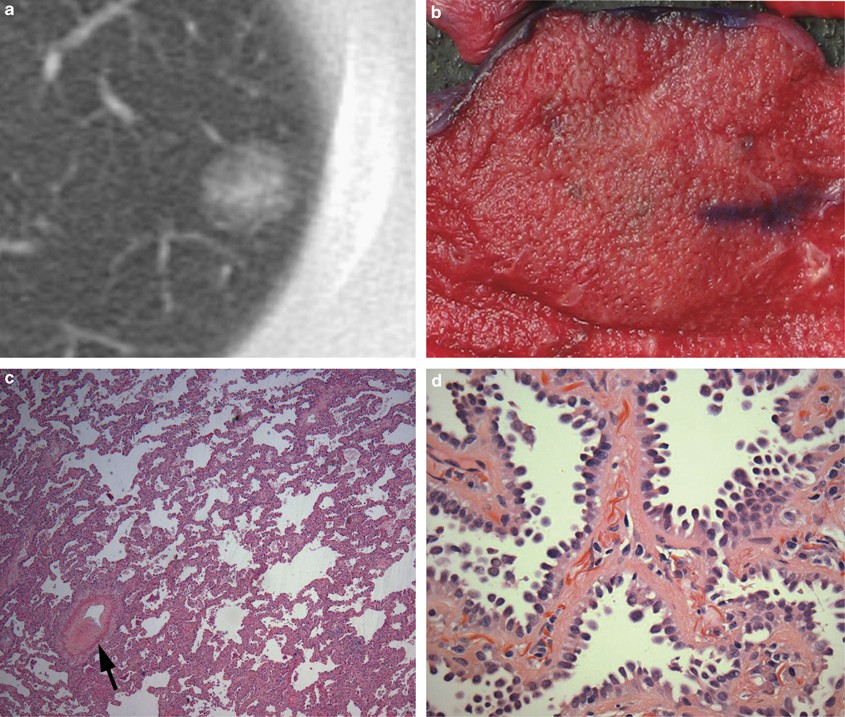
Assessment Of Invasion In Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification Including Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Modern Pathology

Diagnosis Of Lung Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma From Intraoperative Frozen Sections An Analysis Of 136 Cases Journal Of Clinical Pathology

The Many Faces Of Lung Adenocarcinoma A Pictorial Essay Pascoe 18 Journal Of Medical Imaging And Radiation Oncology Wiley Online Library

Adenocarcinoma Situ Lung Lepidic Growth Pattern Stock Photo Edit Now
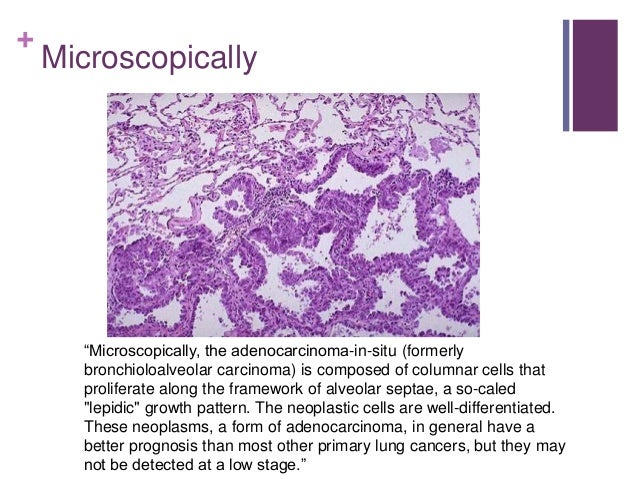
Lung Cancer Pathology Clinical

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Lung Wikipedia
Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of lung is a newlydescribed entity that is preinvasive AIS partly replaces noninvasive ‘bronchoalveolar carcinoma’ (BAC) AIS is found more commonly in nonsmokers, in women and individuals of Asian ethnicity The definition of Adenocarcinoma insitu is a ‘localized’ mass that is less than 3 cm in diameter.

Adenocarcinoma in situ lung. Adenocarcinoma of the lung from BAC to the future Abstract Adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma and invasive Key points To familiarise radiologists with the new pathological classification of adenocarcinoma of the lung The artist. What can you do to decrease the risk of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS)?. Abstract Although the clinical entity of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) has been reclassified into adenocarcinoma in situ, lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma, and mucinous adenocarcinoma, it continues to merit special consideration based on its distinct natural history and response to therapy.
The term carcinoma in situ is a term used to define and describe a cancer that is only present in the cells where it started and has not spread to any nearby tissues Carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of a cancer, and is, at this stage, considered "noninvasive" With regard to staging, carcinoma in situ is considered stage 0 cancer. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the uterine cervix is caused by infection with highrisk human papillomavirus and is the recognized precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma of the cervix Because most AIS lesions are caused by HPV 16/18 infection, prophylactic HPV vaccination is an important step toward prevention of AIS, potentially reducing the incidence of invasive adenocarcinoma. Carcinoma in situ, or stage 0 cancer, refers to precancerous cells in a limited area It is not cancer and may not become malignant Still, doctors usually recommend surgery to prevent future.
Adenocarcinoma of the lung is a type of nonsmall cell lung cancer It occurs when abnormal lung cells multiply out of control and form a tumor Eventually, tumor cells can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body including the lymph nodes around and between the lungs. AIS is a newer name for BAC which is usually slow growing (hence in situ) on the CT BAC looks cloudy instead of the solid white of typical lung cancer It can grow throughout the lungs but doesn't usually metastasize outside the lungs BAC can change behavior and become more like a typical lung cancer where the rate of growth usually changes. NCI's Dictionary of Cancer Terms provides easytounderstand definitions for words and phrases related to cancer and medicine.
ADENOCARCINOMA IN SITU (SEE COMMENT) Comment Multiple deeper sections into the paraffin block were obtained in this case Only adenocarcinoma in situ is identified in the histologic sections examined Adenocarcinoma in situ was previously known as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma No invasion is identified in the tumor present for evaluation. The cancer is only in the lining of the bronchus and not in lung tissue This is also called carcinoma in situ Stage 1 The cancer is only in the lung. Adenocarcinoma is the most common histological subtype of primary lung cancer and has recently been reorganized into a spectrum ranging from preinvasive lesions to invasive adenocarcinoma.
Briefly, Multifocal Adenocarcinoma (MAC) of the lung is a clinical entity of multiple synchronous (less than 6 months) or metachronous (more than 6 months), often groundglass opacities (GGO) on CT scan, typically indolentbehaving cancers There is a scarce amt of clinical data to guide treatment decisions. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of lung is a newlydescribed entity that is preinvasive AIS partly replaces noninvasive ‘bronchoalveolar carcinoma’ (BAC) AIS is found more commonly in nonsmokers, in women and individuals of Asian ethnicity The definition of Adenocarcinoma insitu is a ‘localized’ mass that is less than 3 cm in diameter. For tumors categorized previously as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC), criteria and terminology had not been uniform, so the 11 classification provided four new terms (a) adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), representing histopathologically a small (≤3cm), noninvasive lepidic growth, which at computed tomography (CT) is usually nonsolid;.
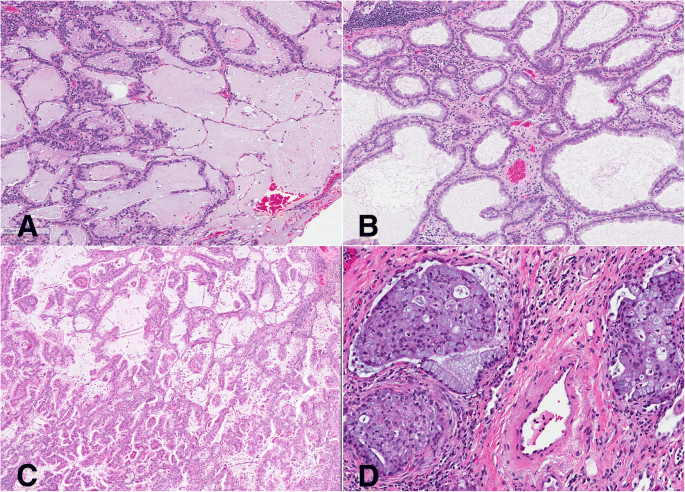
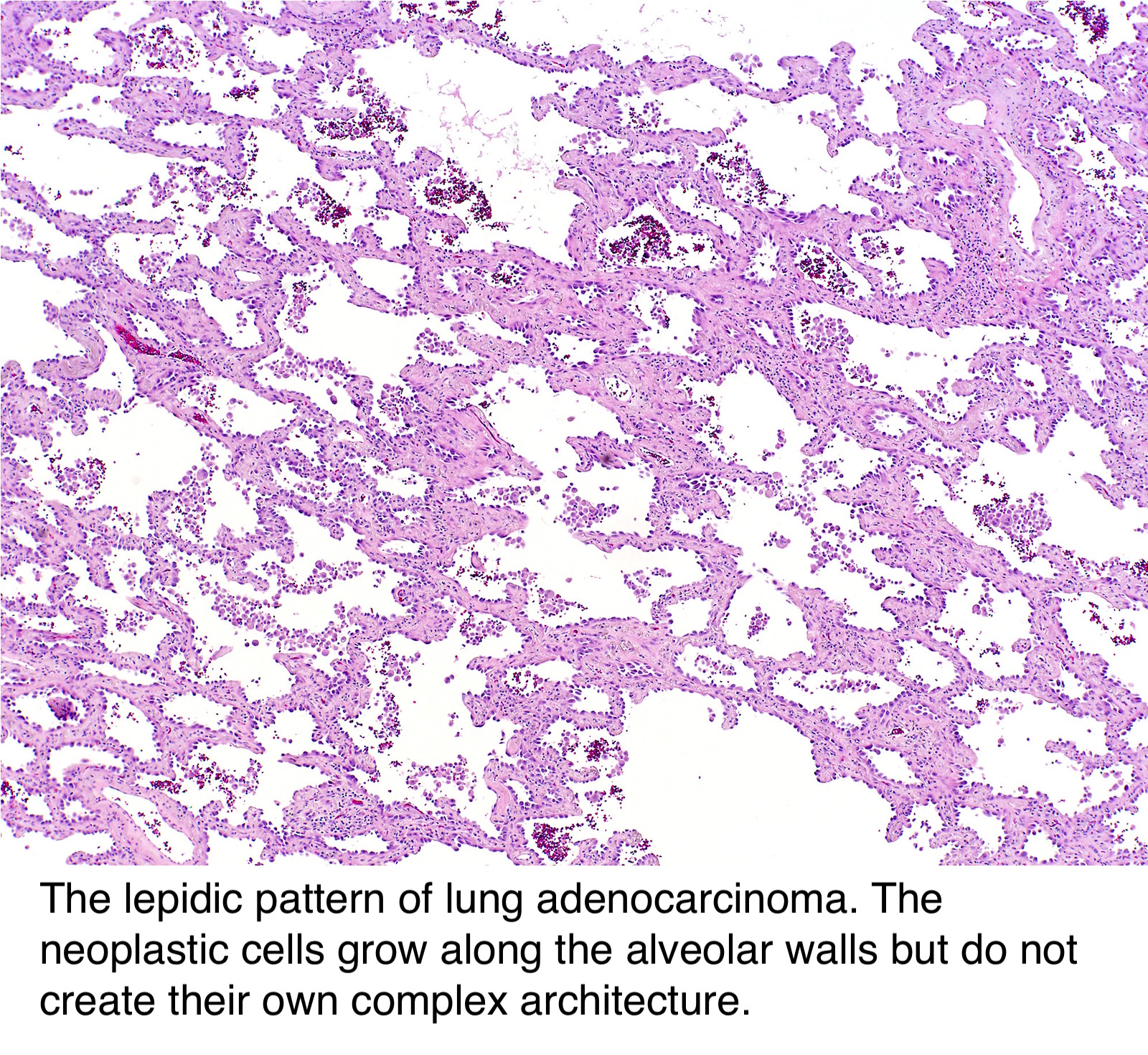
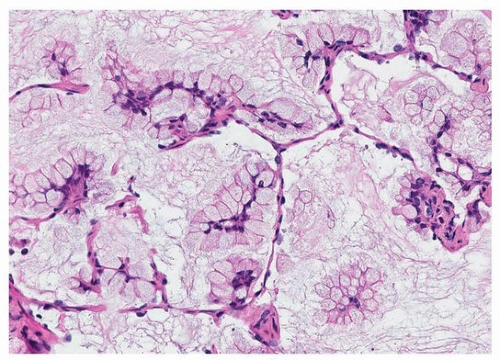
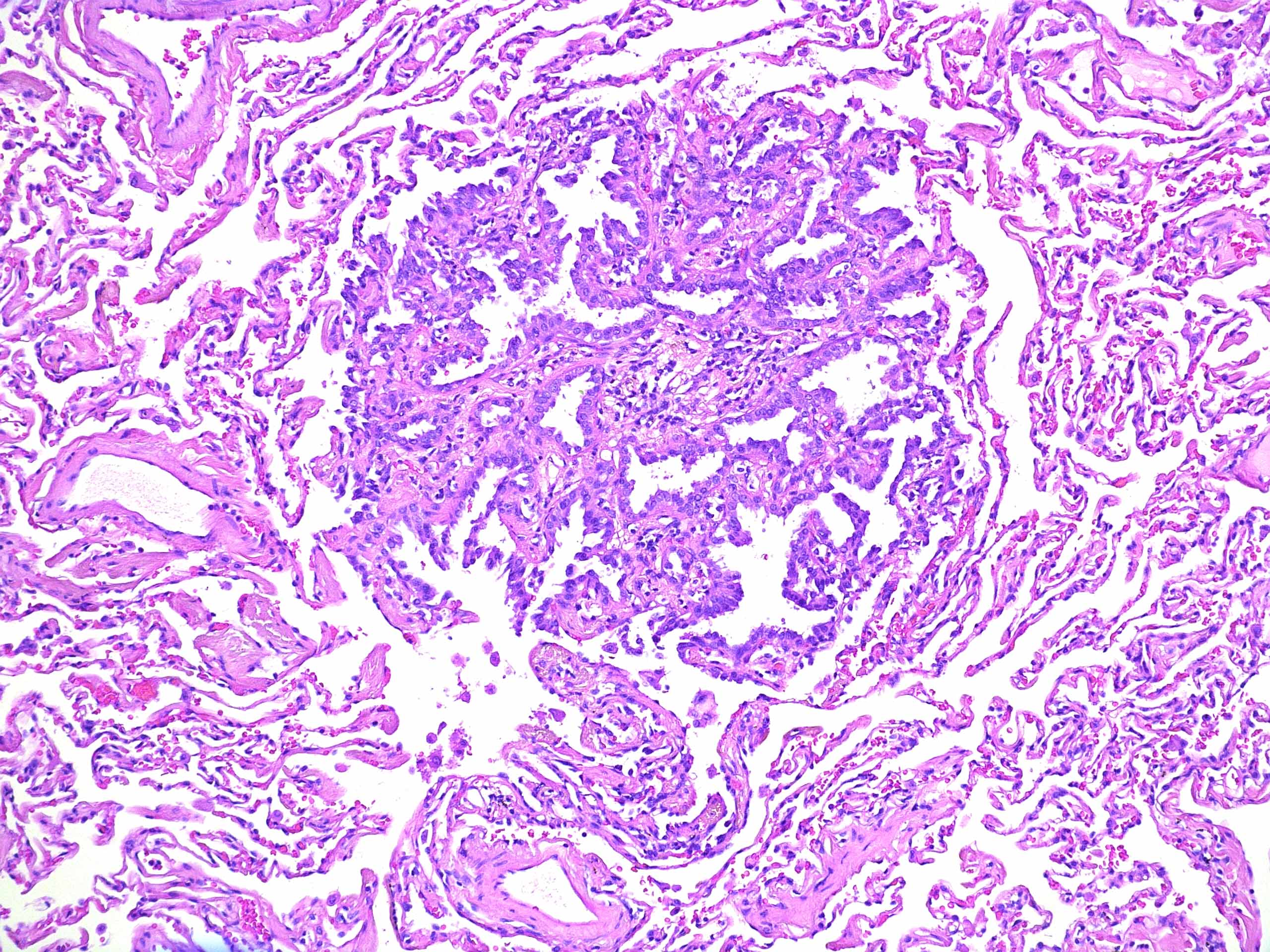
Lung adenocarcinoma has a spectrum of appearances on CT, many of which mimic non‐malignant processes The general radiologist has a major role in guiding the management of abnormalities detected on chest CT and an awareness of these appearances is vital We describe the protean imaging manifestations of lung adenocarcinoma. AIS is a newer name for BAC which is usually slow growing (hence in situ) on the CT BAC looks cloudy instead of the solid white of typical lung cancer It can grow throughout the lungs but doesn't usually metastasize outside the lungs BAC can change behavior and become more like a typical lung cancer where the rate of growth usually changes. Adenocarcinoma in Situ Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) was adopted by the WHO for the first time in the 15 classification of lung tumors 5 Like AAH, AIS demonstrates purely lepidic growth of neoplastic type II pneumocytes or Clara cells along intact septae and lacks stromal, vascular, and pleural invasion 12 AAH and AIS are a morphologic continuum, with AIS demonstrating more cellular and structural atypia than AAH, but their histologic distinction can be challenging 13 While AIS can be.
Adenocarcinoma is cancer that forms in mucussecreting glands throughout the body The disease may develop in many different places, but it is most prevalent in the following cancer types Lung cancer Nonsmall cell lung cancer accounts for 80 percent of lung cancers, and adenocarcinoma is the most common type. Thus, the most important change to the classification of lung adenocarcinoma was proposed for a tumor no greater than 30 cm in size with a pure lepidic growth pattern and lacking stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion, which should now be categorized as in situ adenocarcinoma At the same time, a category of minimally invasive adenocarcinoma was proposed for tumors with a predominantly lepidic growth pattern,. "In stage IA lung adenocarcinoma characterized by GGNs, the SUVmax of GGNs with invasive CT features was high," Shao wrote, adding that HRCT can be used in diagnosing the subtypes of lung.
Adenocarcinoma of the lung usually evolves from the mucosal glands and represents about 40% of all lung cancers It is the most common subtype to be diagnosed in people who have never smoked Lung adenocarcinoma usually occurs in the lung periphery, and in many cases, may be found in scars or areas of chronic inflammation. D0222 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of left bronchus and lung The code D0222 is valid during the fiscal year 21 from October 01, through September 30, 21 for the submission of HIPAAcovered transactions The ICD10CM code D0222 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like carcinoma in situ of bronchus and lung, carcinoma in situ of bronchus and lung, carcinoma in situ of bronchus of left lower lobe, carcinoma in. Adenocarcinoma in situ Adenocarcinoma in situ is defined as a tumour of ≤ 3 cm with pure lepidic growth but no lymphatic, vascular or pleural invasion and no tumour necrosis The word lepidic means ‘scaly’ and is used to describe the growth of bland, pneumocytictype tumour cells along alveoli without lymphovascular invasion.
We examined DNA methylation in 249 tissue samples from 93 subjects, spanning the putative spectrum of peripheral lung adenocarcinoma development histologically normal adjacent nontumor lung, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH), adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS, formerly known as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma), and invasive lung adenocarcinoma Comparison of DNA methylation levels between the lesion types suggests that DNA hypermethylation of distinct loci occurs at different time points. Adenocarcinoma in situ AIS is a preinvasive lesion and is defined as a small (≤3 cm) solitary adenocarcinoma with pure lepidic (in situ) growth and no stromal, vascular, air space, or pleural invasion 42,52,62 AIS is usually an incidental finding on CT scan where it classically appears as a small groundglass opacity in the lung parenchyma. The most common paraneoplastic syndromes associated with adenocarcinoma of the lung are described below Hypercalcemia of malignancy is more common in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, but can occur in adenocarcinoma as Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPO) is fairly rare in.
Lung adenocarcinoma has increased in prevalence compared to other subtypes of lung cancer 1 Increasing numbers of non‐smokers and never‐smokers are developing lung adenocarcinoma 2 The classification of lung adenocarcinoma was revised in 11 at which time the term bronchoalveolar carcinoma was removed Four new terms were introduced to replace this term – adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma and lepidic predominant. Aims To determine the diagnostic accuracy and contraindications for intraoperative diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) from frozen sections Methods A retrospective analysis of data from 136 patients pathologically diagnosed with earlystage (T1N0M0) AIS or MIA from paraffinembedded sections. Adenocarcinoma The 15 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors has undergone significant changes since the publication of 04 WHO Classification These changes have resulted from advances in molecular testing and radiology as well as greater use of immunohistochemistry in subtyping tumors The major changes in the 15 WHO classification of adenocarcinomas of the lung (resected tumors) are 1) Discontinuing the terms bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and mixed subtype adenocarcinoma;.
ADENOCARCINOMA IN SITU (SEE COMMENT) Comment Multiple deeper sections into the paraffin block were obtained in this case Only adenocarcinoma in situ is identified in the histologic sections examined Adenocarcinoma in situ was previously known as bronchioloalveolar carcinoma No invasion is identified in the tumor present for evaluation. Lung adenocarcinoma is a subtype of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Lung adenocarcinoma is categorized as such by how the cancer cells look under a microscope Lung adenocarcinoma starts in glandular cells, which secrete substances such as mucus, and tends to develop in smaller airways, such as alveoli. For resection specimens, new concepts are introduced such as adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) for small solitary adenocar cinomas with either pure lepidic growth (AIS) or predominant lepidic growth with 5 mm invasion (MIA) to define patients who, if they undergo complete resection, will have 100% or near 100% disease specific survival, respectively.
Purpose Knowledge regarding programmed deathligand 1 (PDL1) expression in lung cancer is limited We aim to clarify PDL1positive expression in nonsmallcell lung cancer (NSCLC), including adenocarcinoma subtypes Methods In all, 90 NSCLC specimens containing various adenocarcinoma subtypes, in addition to squamous cell carcinoma and largecell carcinoma were selected. Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis Carcinomas occur when the DNA of a cell is damaged or altered and the cell begins to grow. Invasive adenocarcinoma of lung is the most commonly diagnosed type of lung cancer It is a type of nonsmall cell lung cancer that usually develops in the peripheral region of the lungs (peripheral airways) It can be broadly subdivided into invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma and invasive nonmucinous adenocarcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma makes up about 40% of lung cancers It's most often found in the outer part of the lungs and grows more slowly than other types of lung cancer You usually get it if you're a smoker. Carcinoma in situ, also called in situ cancer, is different from invasive carcinoma, which has spread to surrounding tissue, and from metastatic carcinoma, which has spread throughout the body to other tissues and organs In general, carcinoma in situ is the earliest form of cancer, and is considered stage 0. Diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma in situ and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma from intraoperative frozen sections an analysis of 136 cases (1)Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China (2)Breast Center, Nanfang Hospital, Southern.
The cancer is only in the lining of the bronchus and not in lung tissue This is also called carcinoma in situ Stage 1 The cancer is only in the lung. Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is very common in both women and men Of the more than 100 types of this virus, about 30 are spread from person to person through sexual contact. Adenocarcinoma Malignant epithelial tumor with glandular differentiation, mucin production, or pneumocyte marker expression Lung Cancer (including other carcinoma types) is the most common cause of cancer death worldwide Strong association with tobacco smoking.
(b) minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, representing histopathologically a small (≤3cm) and predominantly lepidic growth that has 5mm or smaller. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ is the precancer that can become invasive squamous cell carcinoma (a type of nonsmall cell lung cancer) Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is the precancer that can become adenocarcinoma (another type of nonsmall cell lung cancer). Growth (adenocarcinoma in situ) and predominant lepidic growth with invasion of 5 mm or less (minimally invasive adenocarcinoma), to define the condition of patients who will have 100% or near 100% diseasespecific survival,.
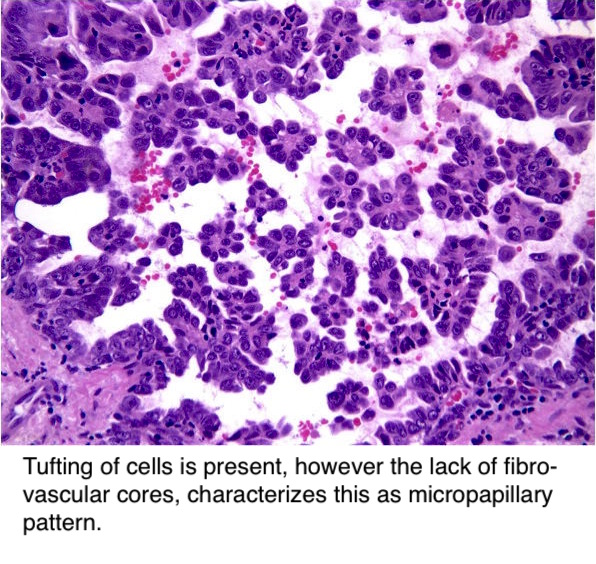
KRASmutations vary widely in adenocarcinoma of the lung, from only 3% in the papillary subtype, to 10%–30% in the solid subtype, to 33% in the micropapillary subtype, to the remarkable levels of 80%–100% in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (1). ADENOCARCINOMA Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of major cancer incidence and mortality worldwide1,2 Adenocarcinoma is the most common histologic subtype of lung cancer in most countries, accounting for almost half of all lung cancers3 A widely divergent clinical, radiologic, molecular, and pathologic spectrum exists within lung adenocarcinoma. Revised classification of lung adenocarcinoma Restricted the diagnosis of large cell carcinoma only to resected tumors that lack any clear morphologic or immunohistochemical differentiation with reclassification of the remaining former large cell carcinoma subtypes into different categories.
Lung adenocarcinoma in situ Atypical epithelial cells line thickened alveolar walls in a lepidic pattern and show cellular crowding, nuclear pleomorphism, and hyperchromasia (hematoxylineosin, original magnification X10) Genomic Alterations in Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma In Situ in an Adolescent Patient. Lung adenocarcinoma in situ (Concept Id C) A localized noninvasive adenocarcinoma of the lung measuring 3 cm or less It is characterized by a pure lepidic growth pattern and the lack of stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion Lung adenocarcinoma in situ. In situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (AIS)—previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a noninvasive growth pattern This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung If completely removed by surgery, the prognosis is excellent with up to 100% 5year survival Although the entity of.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer found in nonsmokers and is usually seen as a peripheral lesion in the lungs In the past several years, many genetic and environmental factors have been identified as causative factors for lung cancer. Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis Carcinomas occur when the DNA of a cell is damaged or altered and the cell begins to grow. Adenocarcinoma of the lung General Adenocarcinoma is the most common (primary lung cancer) Adenocarcinoma is the nonsmoker tumour SCLC and Gross Classically peripheral lesions May be multifocal Lung adenocarcinoma Microscopic May be absent in mucinous tumours may look similar to.
Adenocarcinoma (AdehnohKARsihNOHmuh) is a type of cancer that forms in glandular cells (cells in our glands) Glandular cells release substances like mucus, for example, in the body Adenocarcinomas occur in several parts of the body, including the lungs. Lung tumor Adenocarcinomageneral Terminology of lung adenocarcinoma has been significantly revised in the new WHO classification (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart (Medicine), 4th Edition, 15, J Thorac Oncol 15;) Discontinuing the terms bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) and mixed subtype adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma should not be used in the reporting of small biopsies and cytology Tumours with a noninvasive pattern are referred to by their pattern, eg lepidic growth, not as AIS Lung, Right Upper Lobe, Core Biopsy INVASIVE ADENOCARCINOMA, NONMUCINOUS.
Carcinomas are named based on how the cells look under the microscope Adenocarcinoma is a type of nonsmall cell lung cancer where the cells resemble gland cells, such as the glands that secrete mucus in the lungs This is the most common type of lung cancer in the United States. Adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and invasive adenocarcinoma of lung Terminology Epidemiology AIS and MIA are an uncommon type of bronchial carcinoma which occurs most frequently among nonsmokers, Clinical presentation Presentation is often insidious, and a large. Adenocarcinomas in situ (AIS) of the lung refer to a relatively new entity for a preinvasive lesion in the lung This entity partly replaces the noninvasive end of the previous term bronchoalveolar carcinoma.
For adenocarcinoma in situ, particularly mucinous adenocarcinoma in situ, great care must be taken to be sure the lesion is solitary and sharply circumscribed without miliary spread in adjacent lung parenchyma The criteria for adenocarcinoma in situ can be applied in the setting of multiple tumors only if the other tumors are. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) AIS refers to purely lepidic growth without stromal, vascular or pleural invasion It is equivalent to carcinoma in situ Like AAH it is a preinvasive tumour but is typically larger Most measure between 5 and mm but AIS can be as large as 3 cm Although still a GGN, AIS is typically of greater attenuation than AAH. Revised classification of lung adenocarcinoma Restricted the diagnosis of large cell carcinoma only to resected tumors that lack any clear morphologic or immunohistochemical differentiation with reclassification of the remaining former large cell carcinoma subtypes into different categories.
Diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma in situ and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma from intraoperative frozen sections an analysis of 136 cases He P (1), Yao G (2), Guan Y (3), Lin Y (1), He J (4).
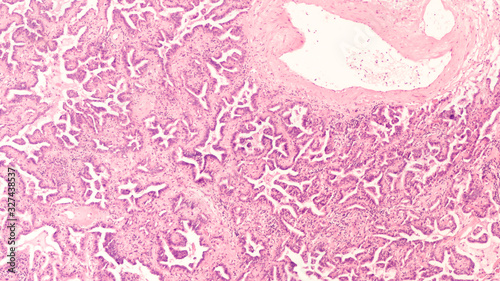
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Lung Lepidic Growth Pattern Formerly Bronchoalveolar Carcinoma The Cancer Cells Grow Along The Scaffolding Of Preexisting Pulmonary Alveoli Without Stromal Invasion Buy This Stock Photo And Explore
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiol
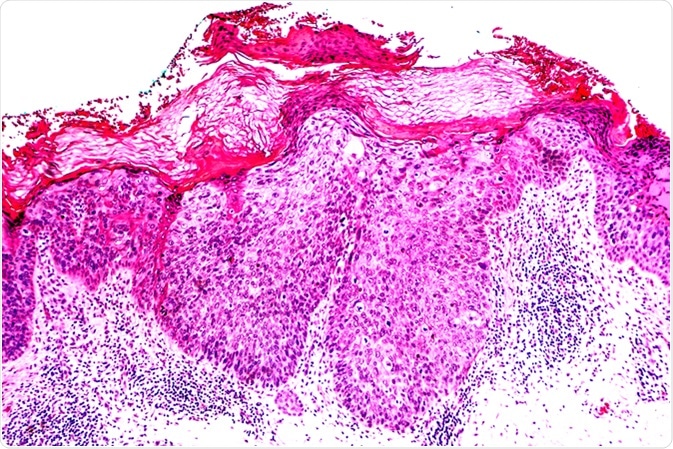
Bowen S Disease Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ

Multidisciplinary Management Of Lung Cancer Nejm
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
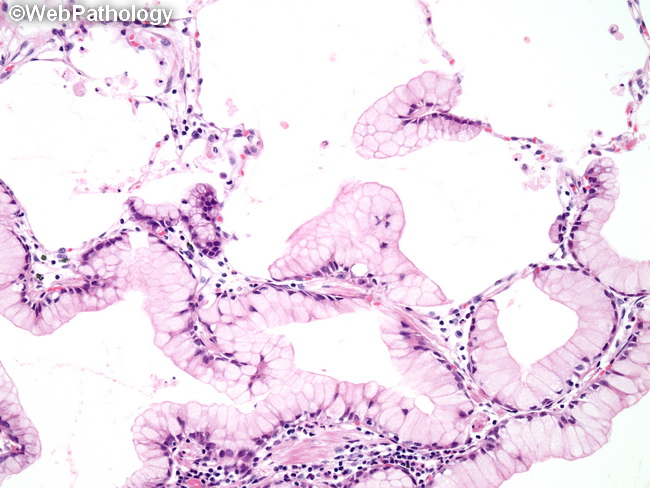
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images

Histotypes Of Lung Adenocarcinoma And The Corresponding Anaplastic Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn And9gcr0qscwv Wuwcmxi8tkwnmcwiw06o1ws49matztcclxjpchfbcn Usqp Cau

Pdf Transition From Adenocarcinoma In Situ To Invasive Adenocarcinoma Then To Large Cell Lung Carcinoma With Rhabdoid Phenotype Immunohistochemical And Molecular Findings Case Report And Literature Review Semantic Scholar

Pdf Transition From Adenocarcinoma In Situ To Invasive Adenocarcinoma Then To Large Cell Lung Carcinoma With Rhabdoid Phenotype Immunohistochemical And Molecular Findings Case Report And Literature Review Semantic Scholar

Variable Imaging Presentations Of Lung Cancer Thoracic Key
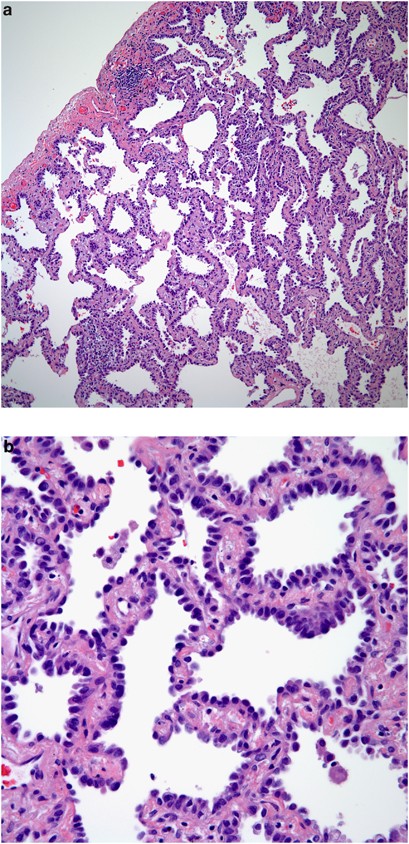
Early Stage Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma T1n0m0 A Clinical Radiological Surgical And Pathological Correlation Of 104 Cases The Md Anderson Cancer Center Experience Modern Pathology
Plos One Dna Methylation Changes In Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Lung Adenocarcinoma

A Nonmucinous Adenocarcinoma In Situ B Tumor Shows Continuous Download Scientific Diagram

Pulmonary Pathology
Www Jto Org Article S1556 0864 15 1 Pdf
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
Www Jto Org Article S1556 0864 15 1 Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcrl86u2p6jgw Haogciymb4fym6cxyjsmrrxb0bgb Z00 Itu0k Usqp Cau

The New Iaslc Ats Ers Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification From A Clinical Perspective Current Concepts And Future Prospects Zugazagoitia Journal Of Thoracic Disease

Small Cell Carcinoma Wikipedia
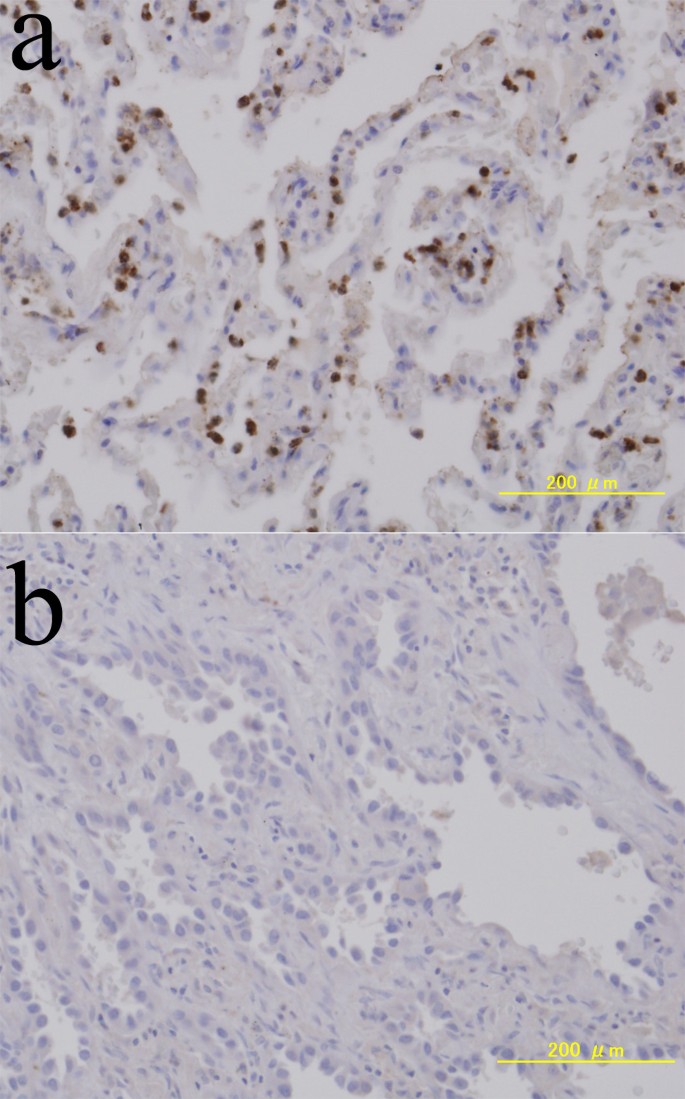
Bronchioloalveolar Invasion In Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Is Associated With Expression Of Transforming Growth Factor B1 World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text
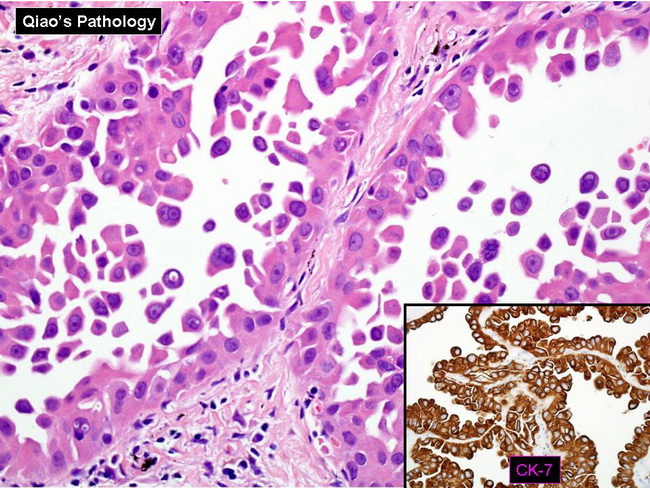
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
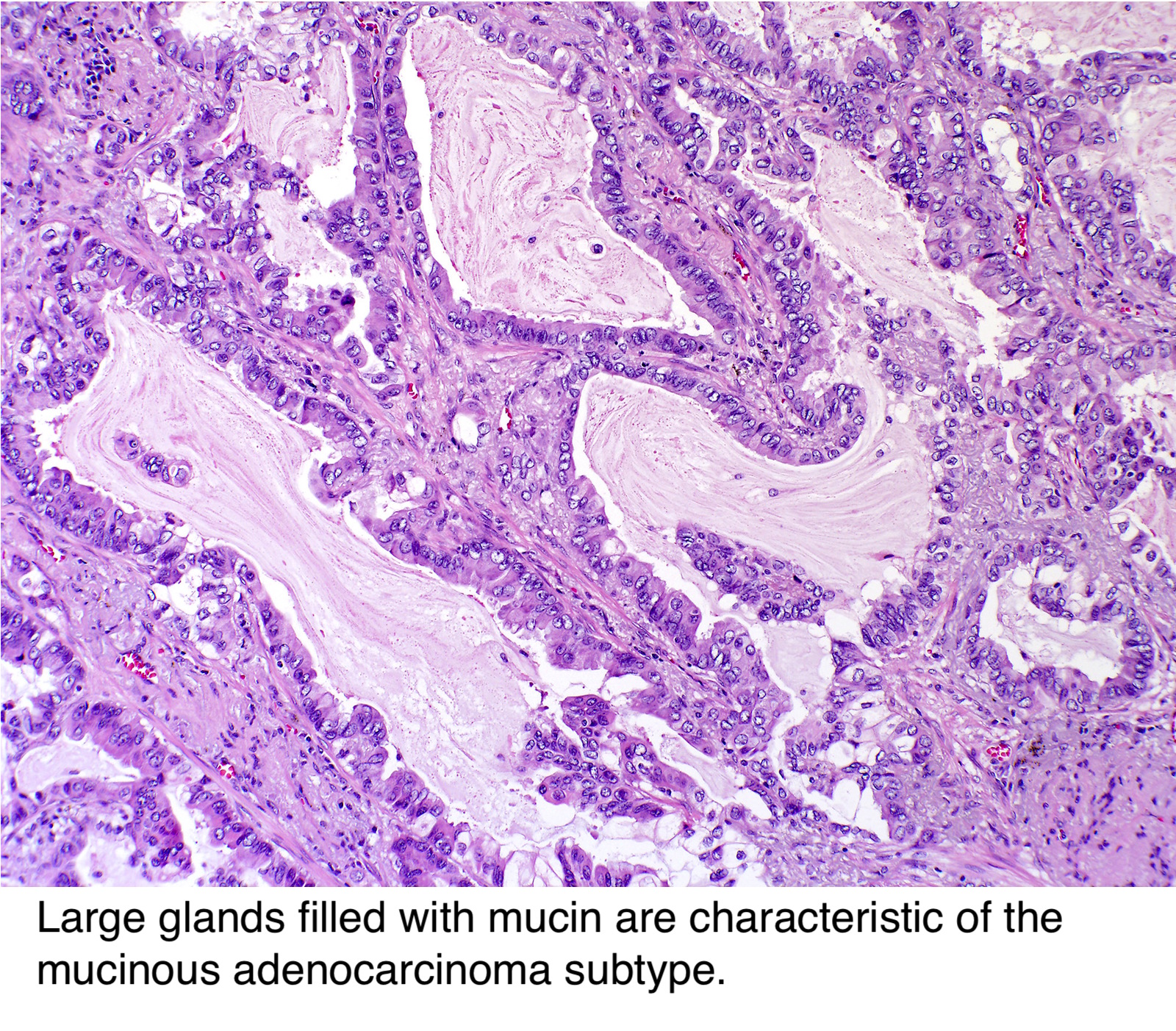
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview

A Chemically Induced Model For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lung In Mice Cancer Research

Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Adjacent To Lung Adenocarcinoma In Situ Download Scientific Diagram

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Adenocarcinoma Of Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Adenocarcinoma In Situ In 52 Year Old Woman A Transverse Lung Window Download Scientific Diagram
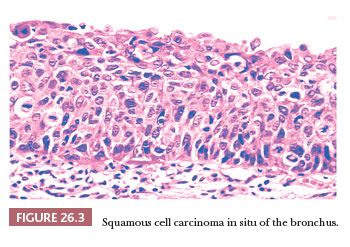
Pulmonary Neoplasms Basicmedical Key

Prognostic Considerations Of The New World Health Organization Classification Of Lung Adenocarcinoma European Respiratory Society
Q Tbn And9gcqnemssgievr4hzgc B I8cnyrtp6qshg8urpmcxguoehjvh6qw Usqp Cau
Pulmonary Mucinous Adenocarcinomas A Clinicopathologic Series With Emphasis On The Prognostic Significance Of Spread Through Alveolar Spaces And Presence Of Solid Growth Component Surgical And Experimental Pathology Full Text
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview

Lung Carcinoma In Situ Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials
3

1 Tuberculosis 2 Cancer Of The Lung Second Practical Respiratory Block Pathology Dept Ksu Ppt Download

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Non Mucinous A This Tumor Shows A Download Scientific Diagram

Radiologic Implications Of The 11 Classification Of Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung Radiology
Www Thoracic Org Statements Resources Lcod Adenocarcinoma Pdf

Why Do Pathological Stage Ia Lung Adenocarcinomas Vary From Prognosis A Clinicopathologic Study Of 176 Patients With Pathological Stage Ia Lung Adenocarcinoma Based On The Iaslc Ats Ers Classification Sciencedirect
Mucinous Adenocarcinoma Thoracic Key
Pathology Outlines Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
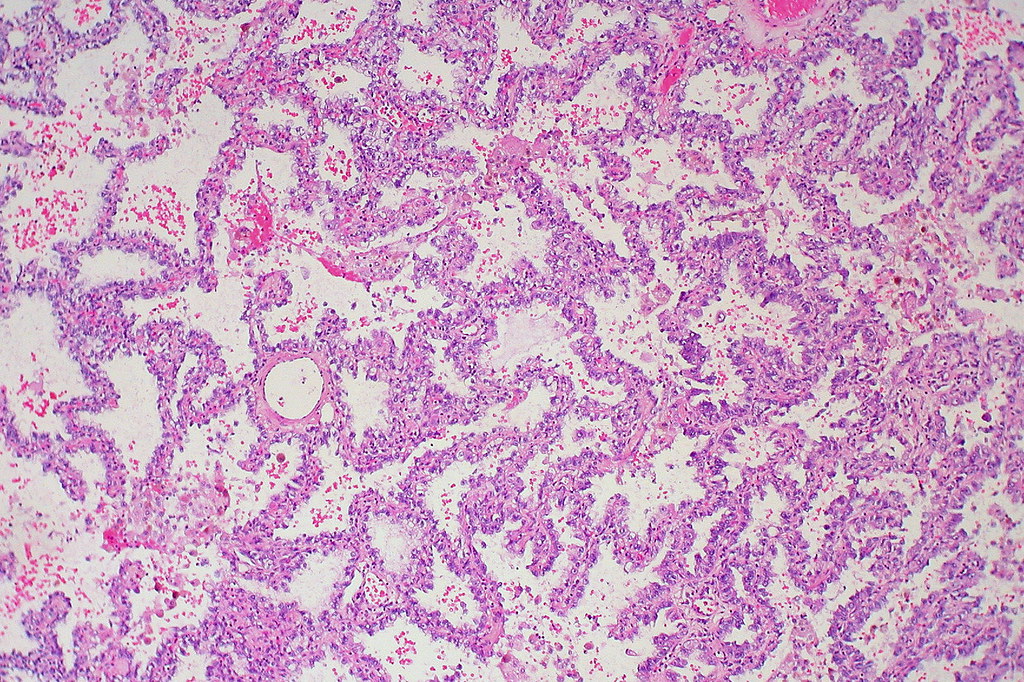
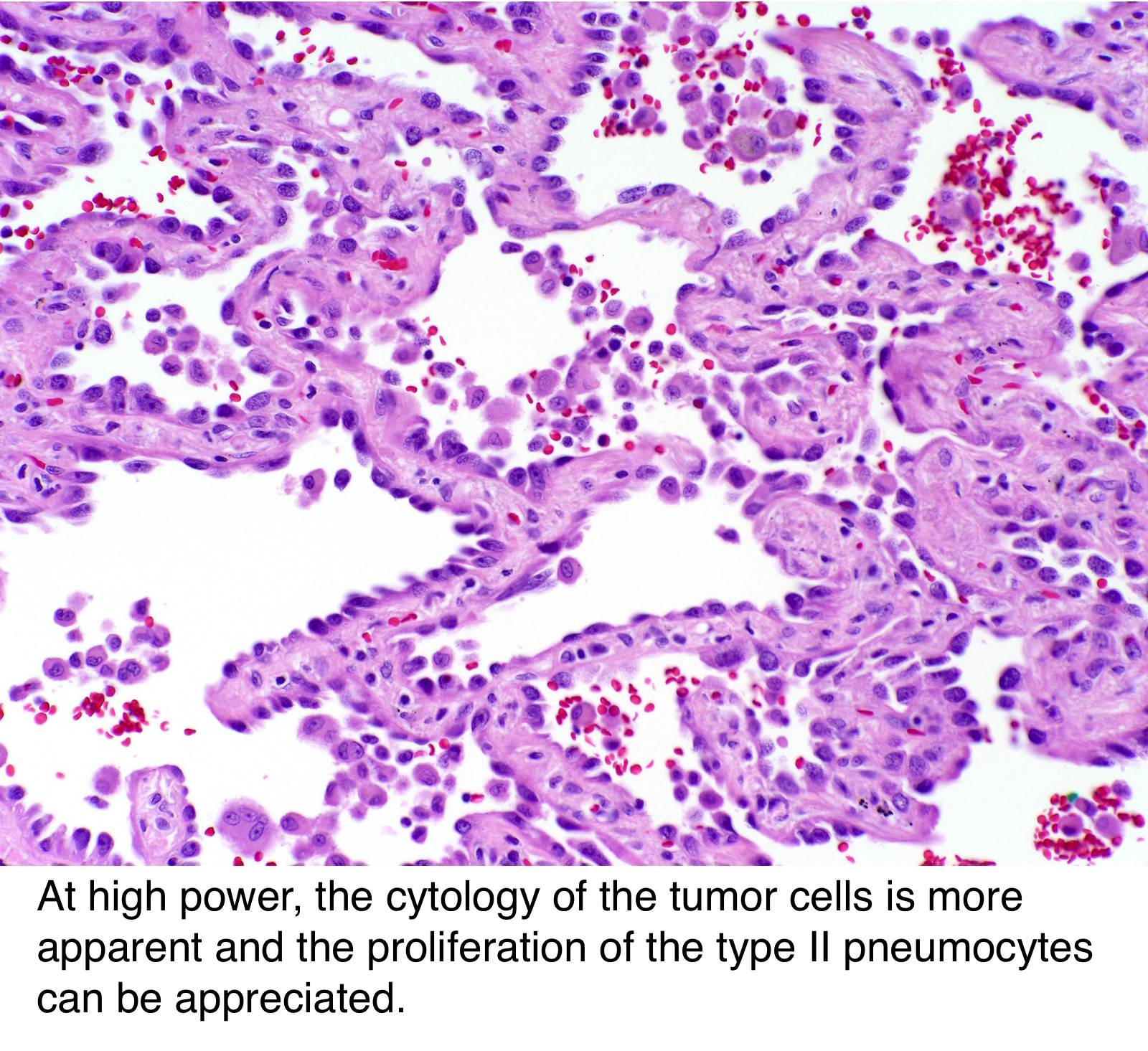
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Lung Histology

Current Concepts In Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Biology Clinical Cancer Research

Do All Lung Adenocarcinomas Follow A Stepwise Progression Lung Cancer
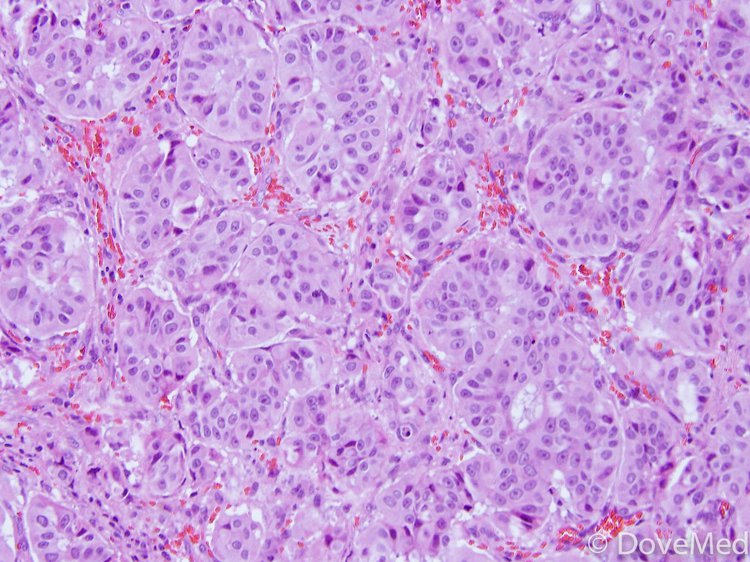
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Lung

Small Cell Carcinoma Wikipedia
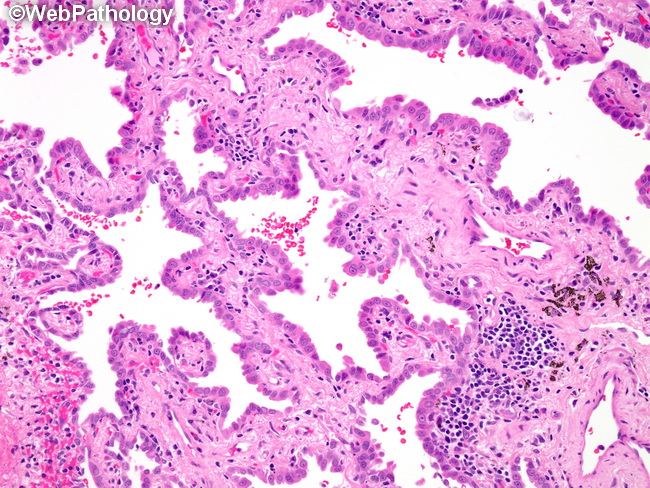
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
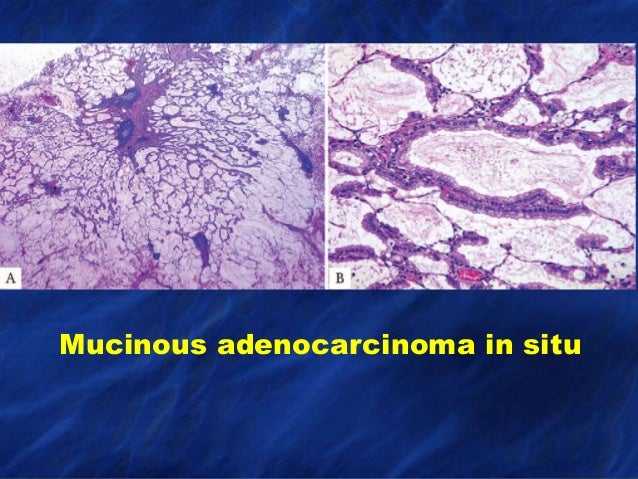
Recent Advances In Lung Tumors And Tumor Like Lesions
Plos One Transcriptome Profiles Of Carcinoma In Situ And Invasive Non Small Cell Lung Cancer As Revealed By Sage

The Pivotal Role Of Pathology In The Management Of Lung Cancer Davidson Journal Of Thoracic Disease

A Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma Differentiation Is Evident Based On Download Scientific Diagram

Adenocarcinoma Situ Lung Lepidic Growth Pattern Stock Photo Edit Now
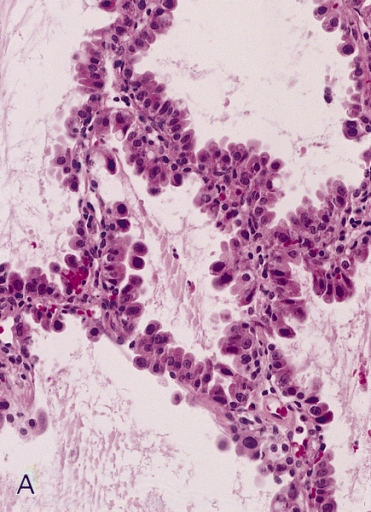
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Lung Wikiwand

Adenocarcinoma In Situ The Goblet Cell Proliferation Has Occupied The Download Scientific Diagram
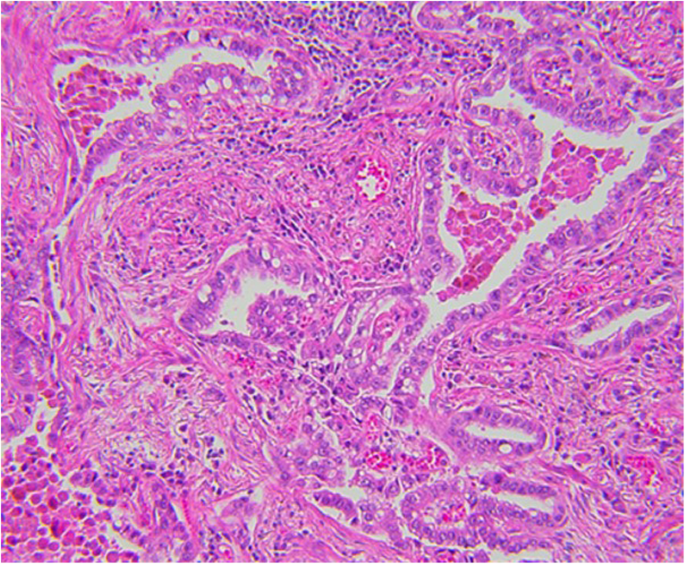
Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung From Bac To The Future Insights Into Imaging Full Text

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais Formerly Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Bac Thoracic Pathology A Volume In The High Yield Pathology Series Expert Consult Online And Print 1st Edition
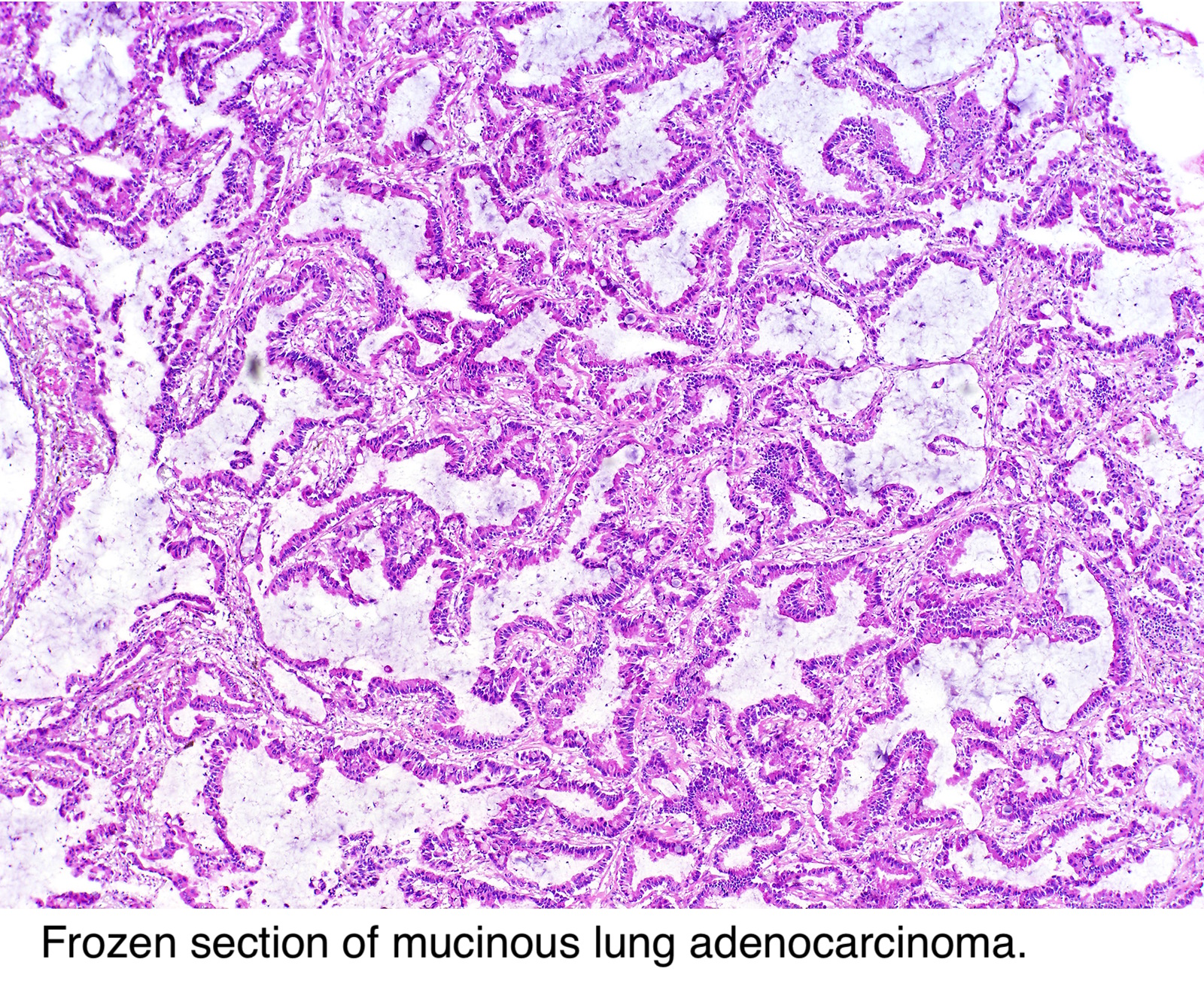
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
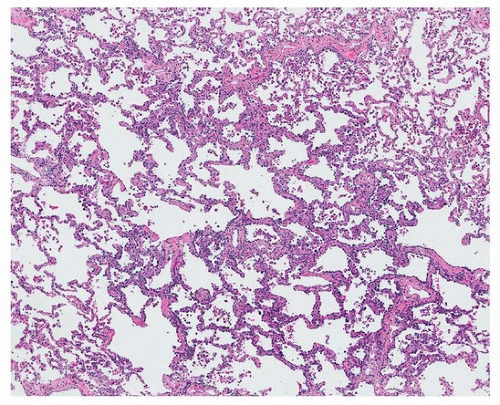
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Nonmucinous Thoracic Key

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
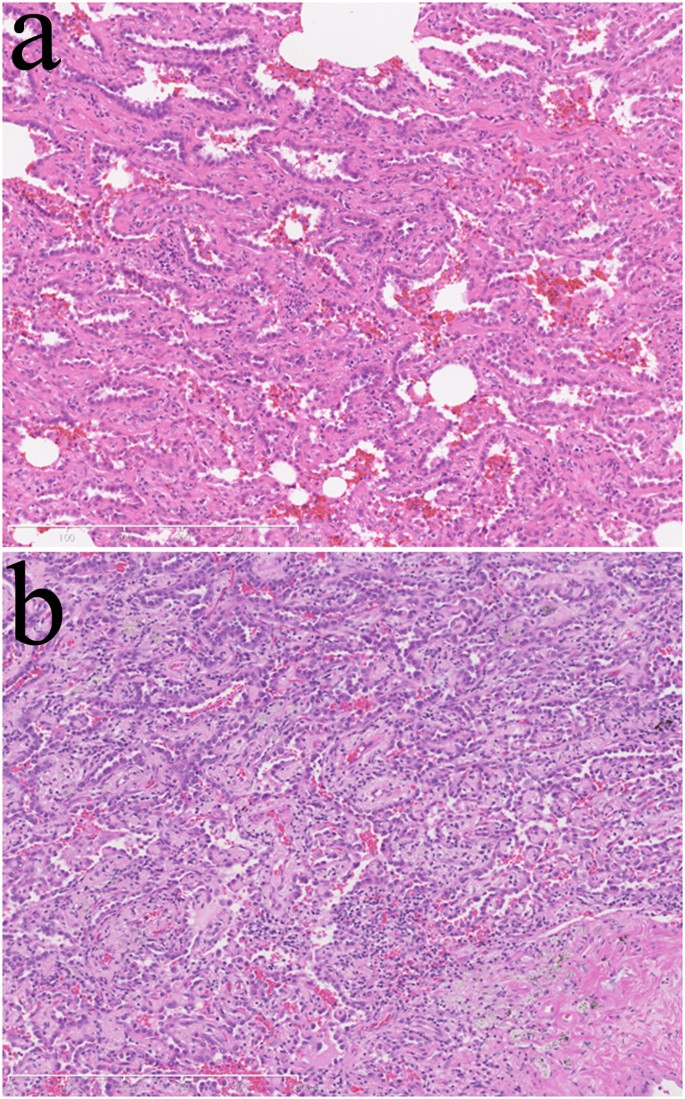
Bronchioloalveolar Invasion In Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Is Associated With Expression Of Transforming Growth Factor B1 World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text
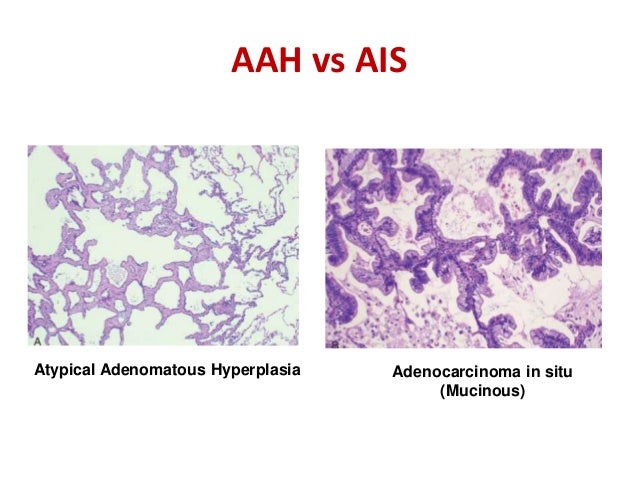
Classification Of Lung Tumors

Pathology Walker Auto Tweet Bot Adenocarcinoma In Situ Lung Partial Pulmonectomy Pathology

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Diagnosis Of Lung Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma From Intraoperative Frozen Sections An Analysis Of 136 Cases Journal Of Clinical Pathology

Medpix Case Adenocarcinoma In Situ Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma
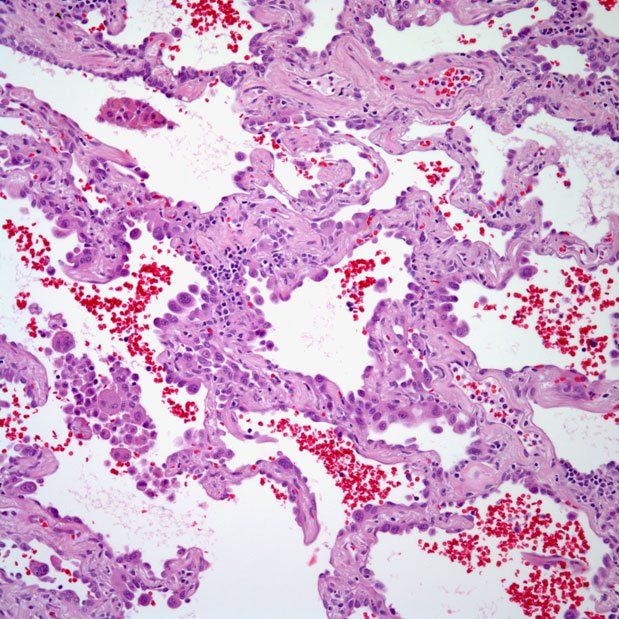
Slide Show Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Pathology Cancer Network
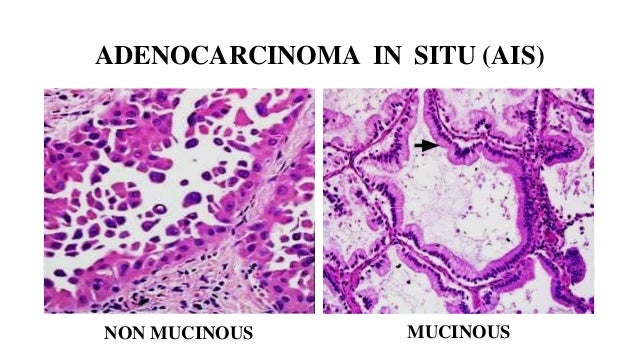
Histopathological Subtypes And Molecular Alterations In Pulmonary Ade

International Association For The Study Of Lung Cancer American Thoracic Society European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Classification Of Lung Adenocarcinoma Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
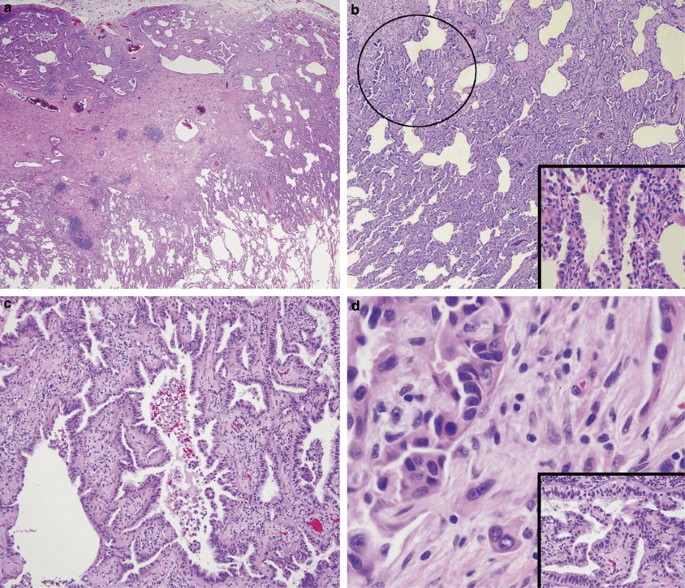
Assessment Of Invasion In Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification Including Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Modern Pathology
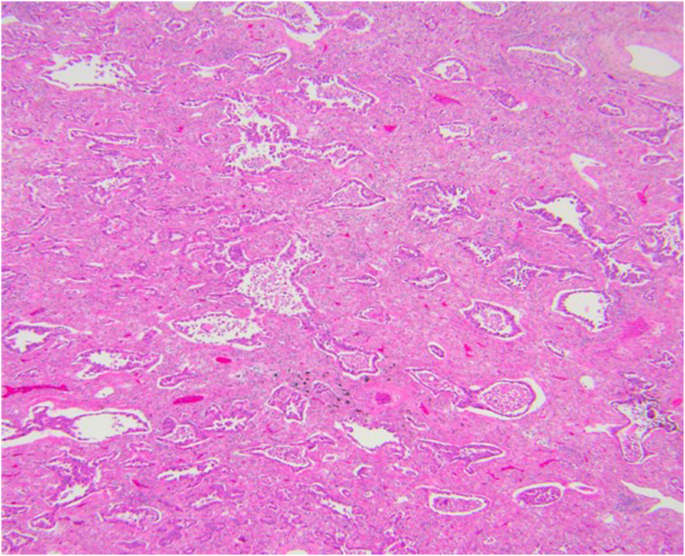
Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung From Bac To The Future Insights Into Imaging Full Text
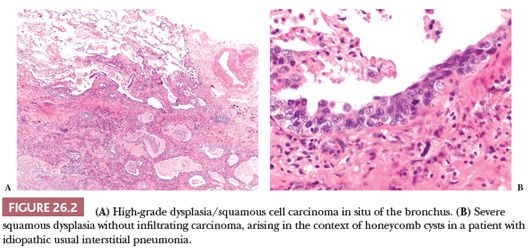
Pulmonary Neoplasms Basicmedical Key

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Angel Panizo Md Phd How Would You Classify This Lung Tumor Adenocarcinoma In Situ Ais Or Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Mia Pulmpath Pathology Smlungpathguy Yro854 Lara Pijuan Sansanovalero T Co Z7agtut9wy

Lung Adenocarcinomas Correlation Of Computed Tomography And Pathology Findings Sciencedirect

The Lung Adenocarcinoma Guidelines What To Be Considered By Surgeons Sardenberg Journal Of Thoracic Disease

Diagnosis Of Lung Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma From Intraoperative Frozen Sections An Analysis Of 136 Cases Journal Of Clinical Pathology

Microenvironmental Changes In The Progression From Adenocarcinoma In Situ To Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Lepidic Predominant Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung Lung Cancer

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Adenocarcinoma Of Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Lung Wikiwand

Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
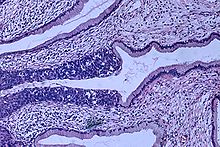
Carcinoma In Situ Wikipedia
Www Pathologica It Article Download 36 60

Pulmonary In Situ Adenocarcinoma With Mosaic Paving Pattern

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Adenocarcinoma Of Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
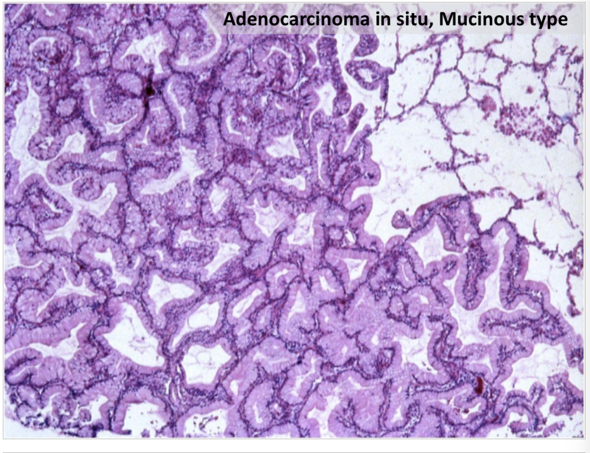
P 3pat1 Lung Cancer Pathology Pulmonary Flashcards Memorang

The Many Faces Of Lung Adenocarcinoma A Pictorial Essay Pascoe 18 Journal Of Medical Imaging And Radiation Oncology Wiley Online Library

Pulmonary Pathology
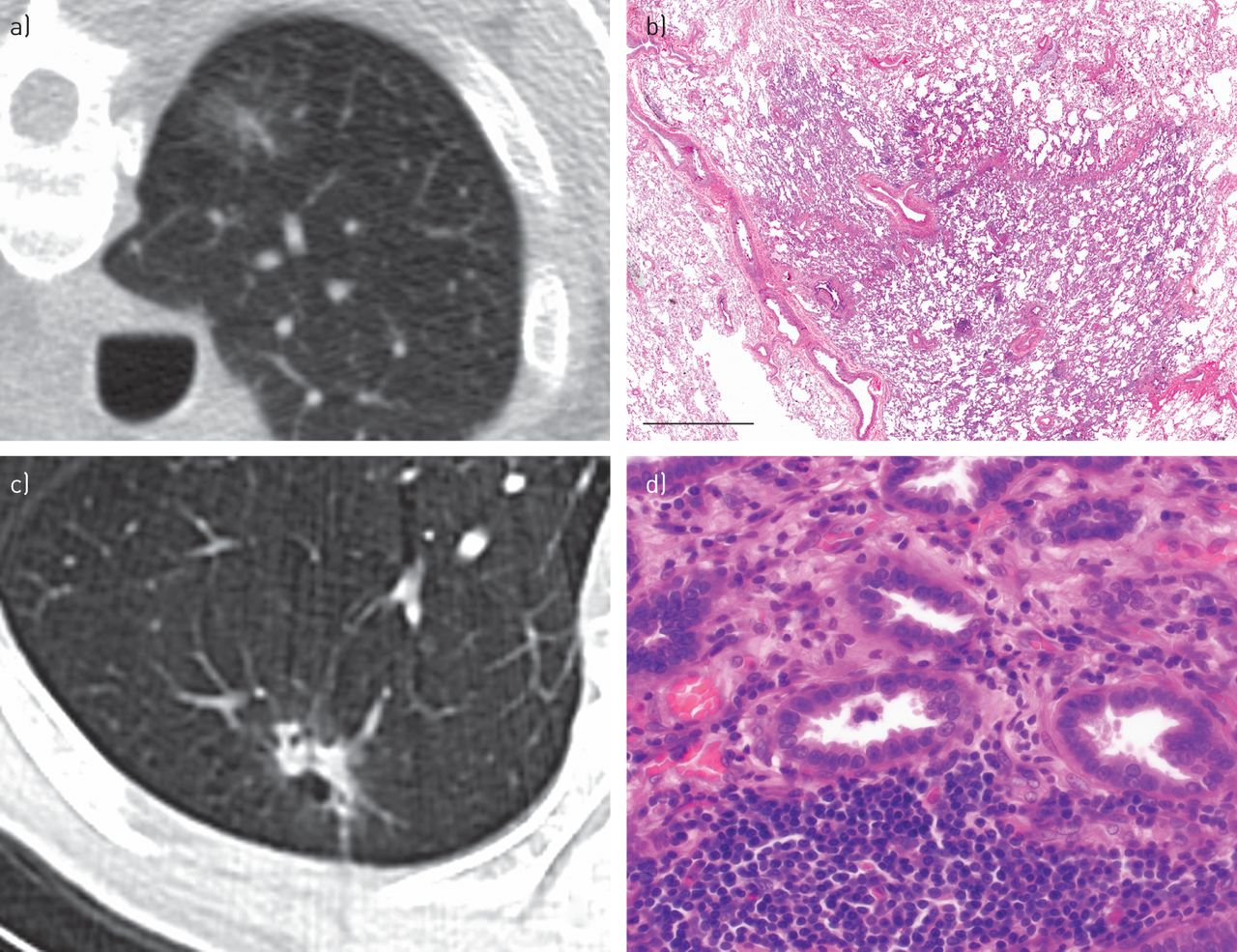
Prognostic Considerations Of The New World Health Organization Classification Of Lung Adenocarcinoma European Respiratory Society
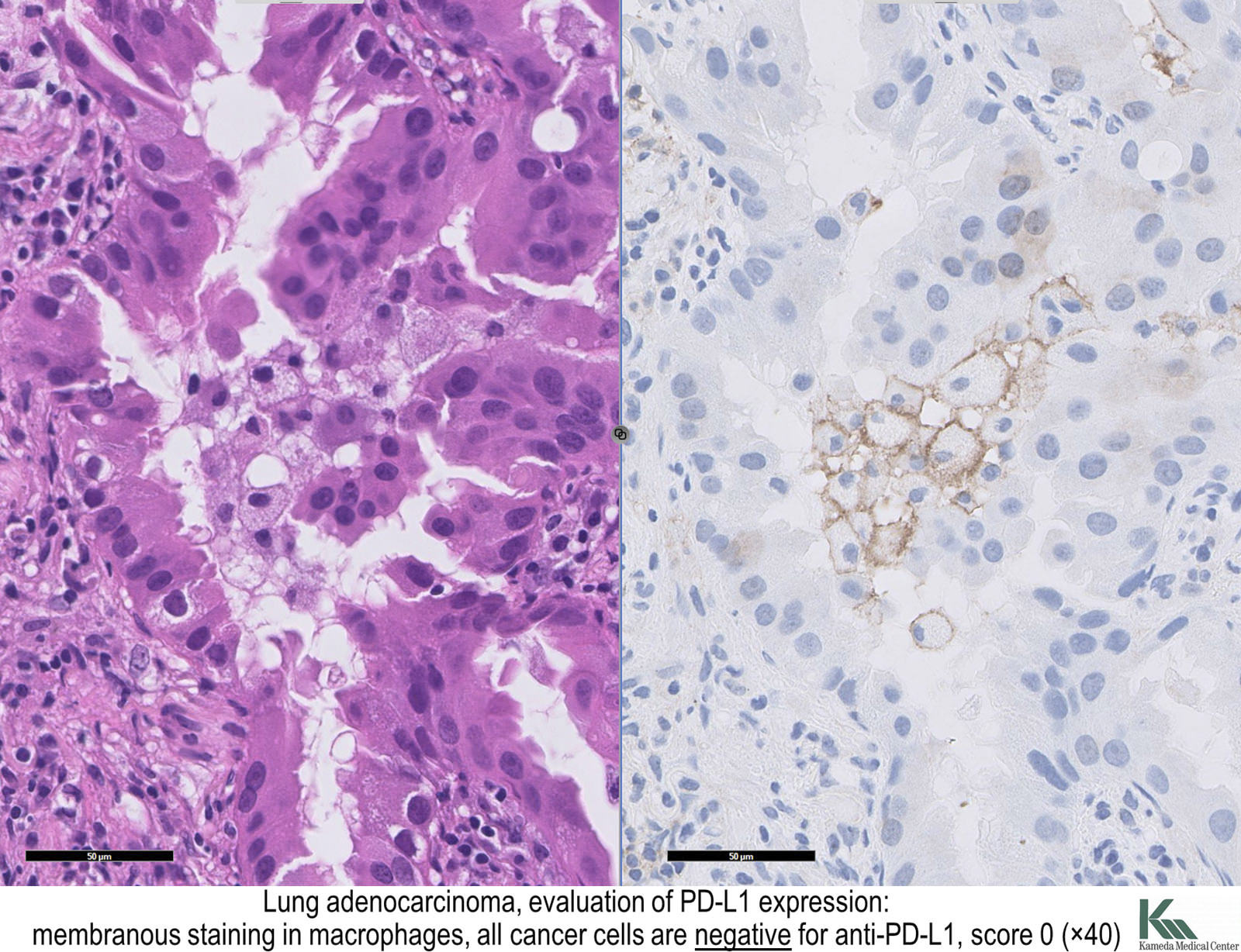
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Lung Wikipedia

A Chemically Induced Model For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lung In Mice Cancer Research
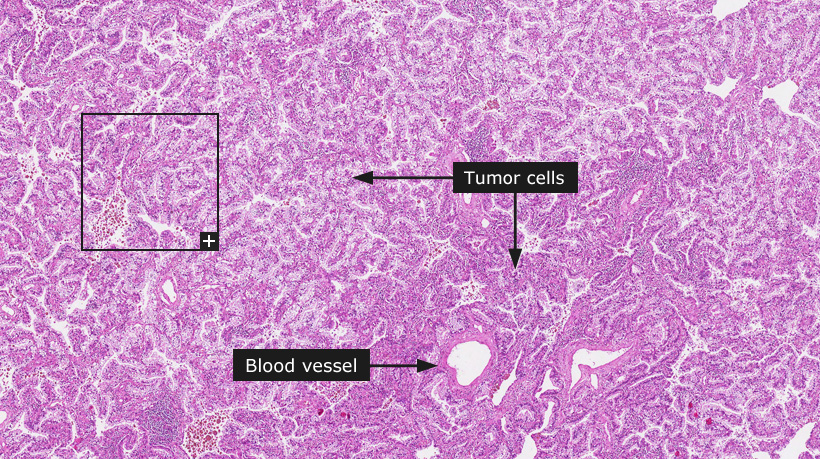
Dictionary Cancer Lung Cancer The Human Protein Atlas
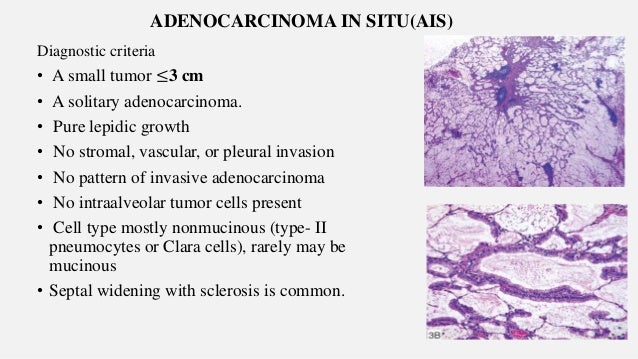
Lung Carcinoma 16 Update

Adenocarcinoma In Situ In 52 Year Old Woman A Transverse Lung Window Download Scientific Diagram

Slow Growing Lung Cancer As An Emerging Entity From Screening To Clinical Management European Respiratory Society
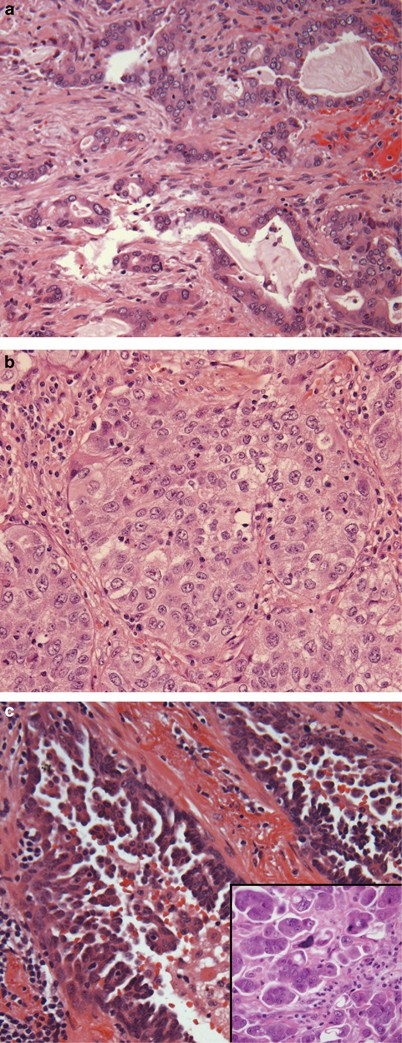
Assessment Of Invasion In Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification Including Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Modern Pathology

Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Cancer Therapy Advisor



