A Point Mutation

Point Mutation Mouse Models Knockins Precision Targeting
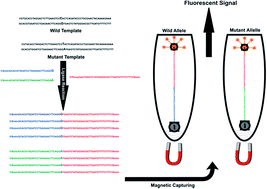
Fluorescent Detection Of Point Mutation Via Ligase Reaction Assisted By Quantum Dots And Magnetic Nanoparticle Based Probes Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing
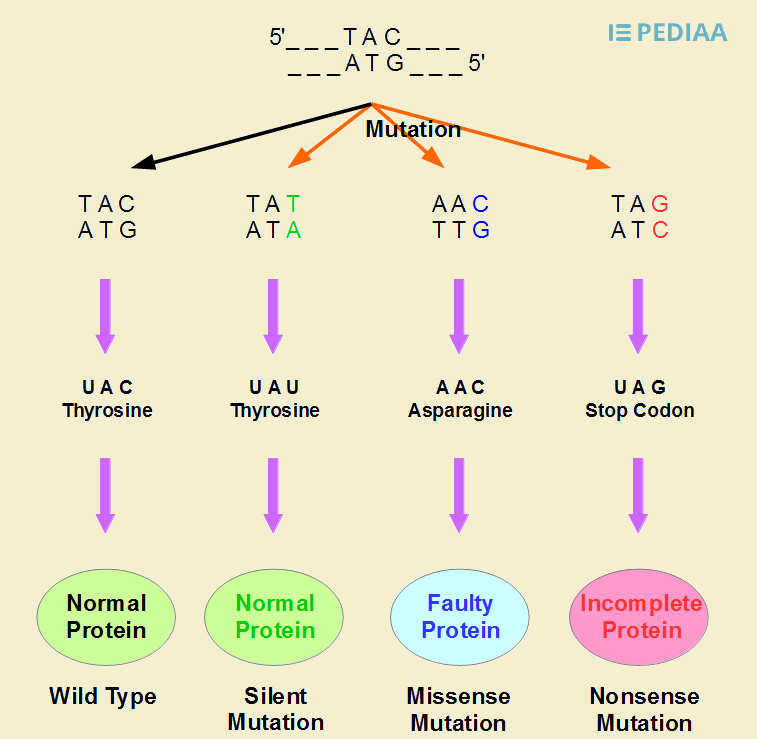
Difference Between Point Mutation And Frameshift Mutation Definition Types Features Diseases Caused

Point Mutation High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Point Mutation Models Creative Biolabs

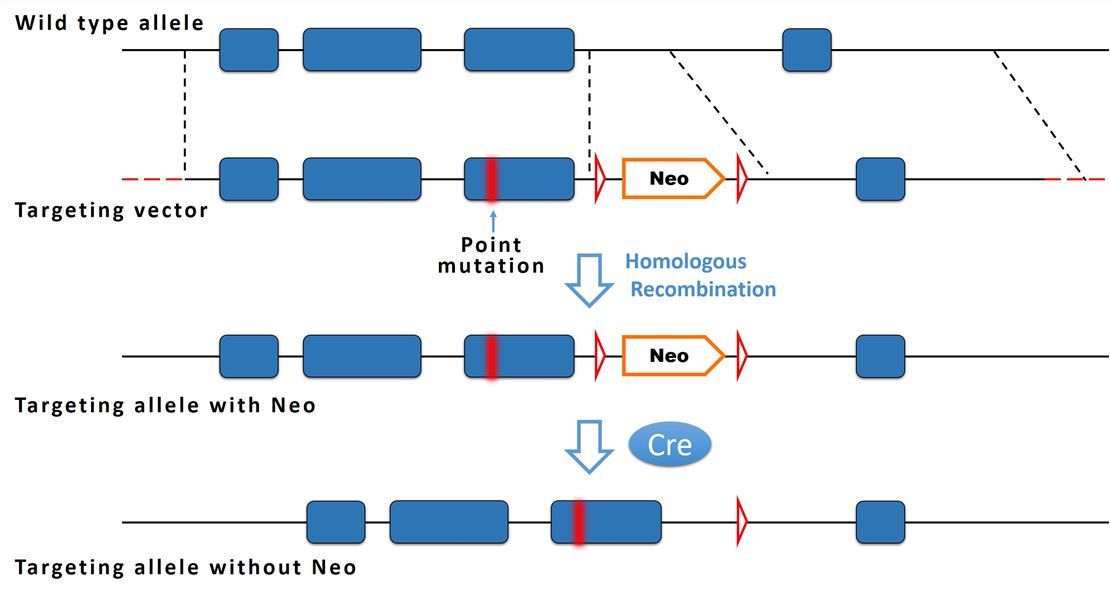
Introduction Of A Point Mutation Using The Cre Lox P System A The Download Scientific Diagram
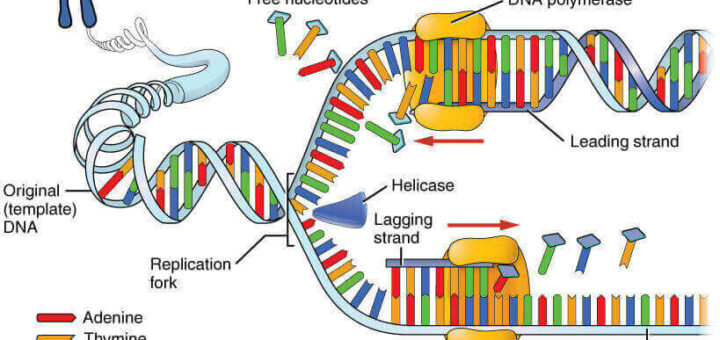
A point mutation is a mutation that only affects a single nucleotide of nucleic acid In this type of mutation in DNA or RNA there is a change within a gene in which one base pair in the DNA sequence is altered Point mutations are frequently the result of mistakes made during DNA replication.

A point mutation. The 9V mutation of PSEN1 gene can cause Alzheimer's disease Somatic cells of patients with Alzheimer's disease are induced into pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and then the mutant gene is modified by replacing the point mutation with a wildtype sequence. The mutation is located at a specific site on what’s called the “receptor binding domain” — the part of the viral spike protein that latches on to human cells. They're point mutations in which one nitrogenous.
What is a point mutation?. Define point mutation point mutation synonyms, point mutation pronunciation, point mutation translation, English dictionary definition of point mutation n A mutation that changes one nucleotide in a gene or DNA sequence by substitution, deletion, or addition. What is a Point Mutation?.
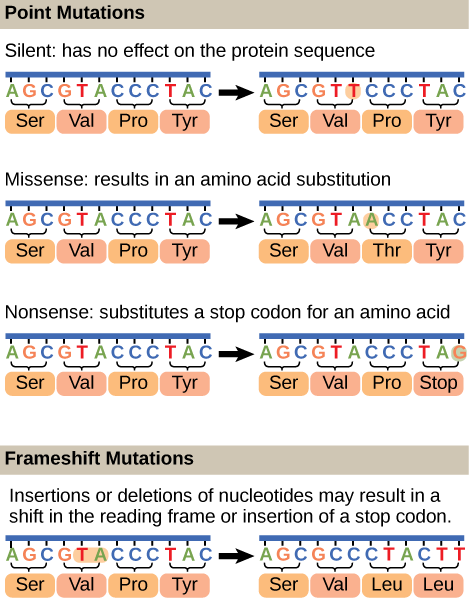
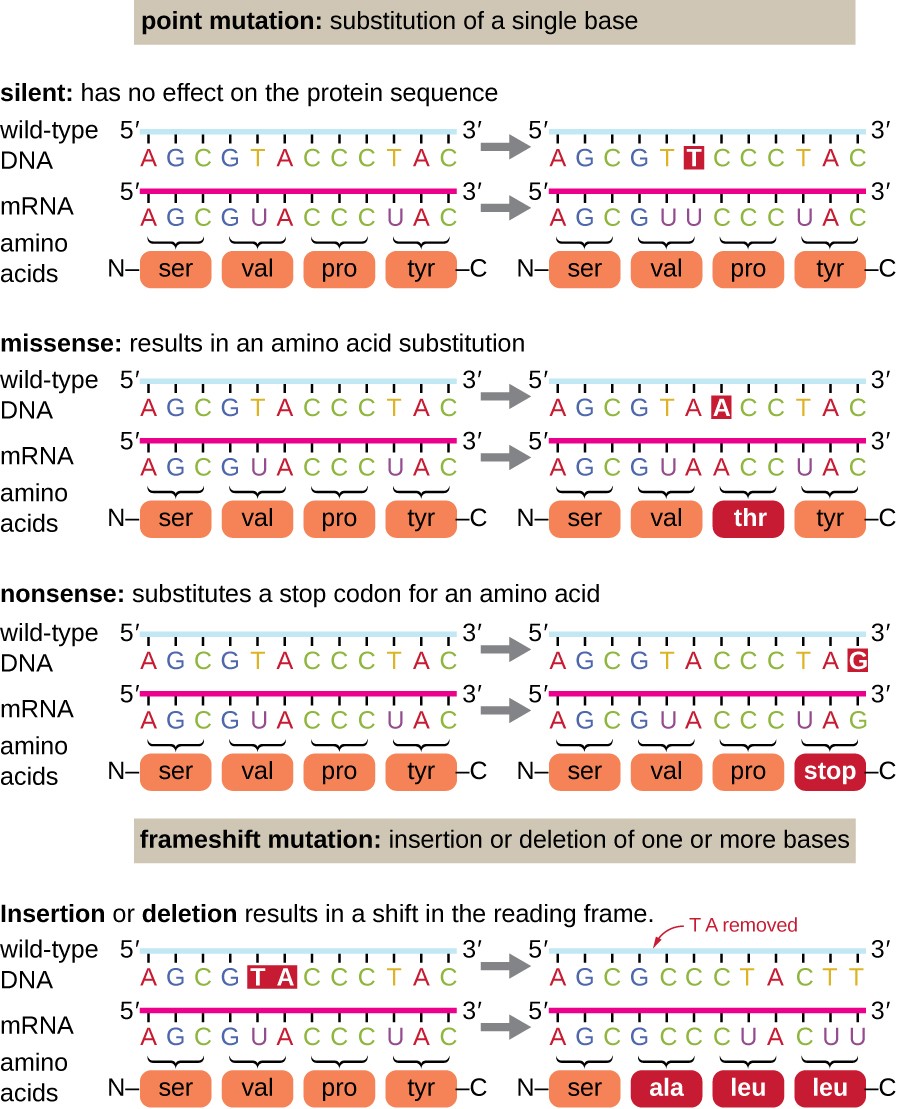
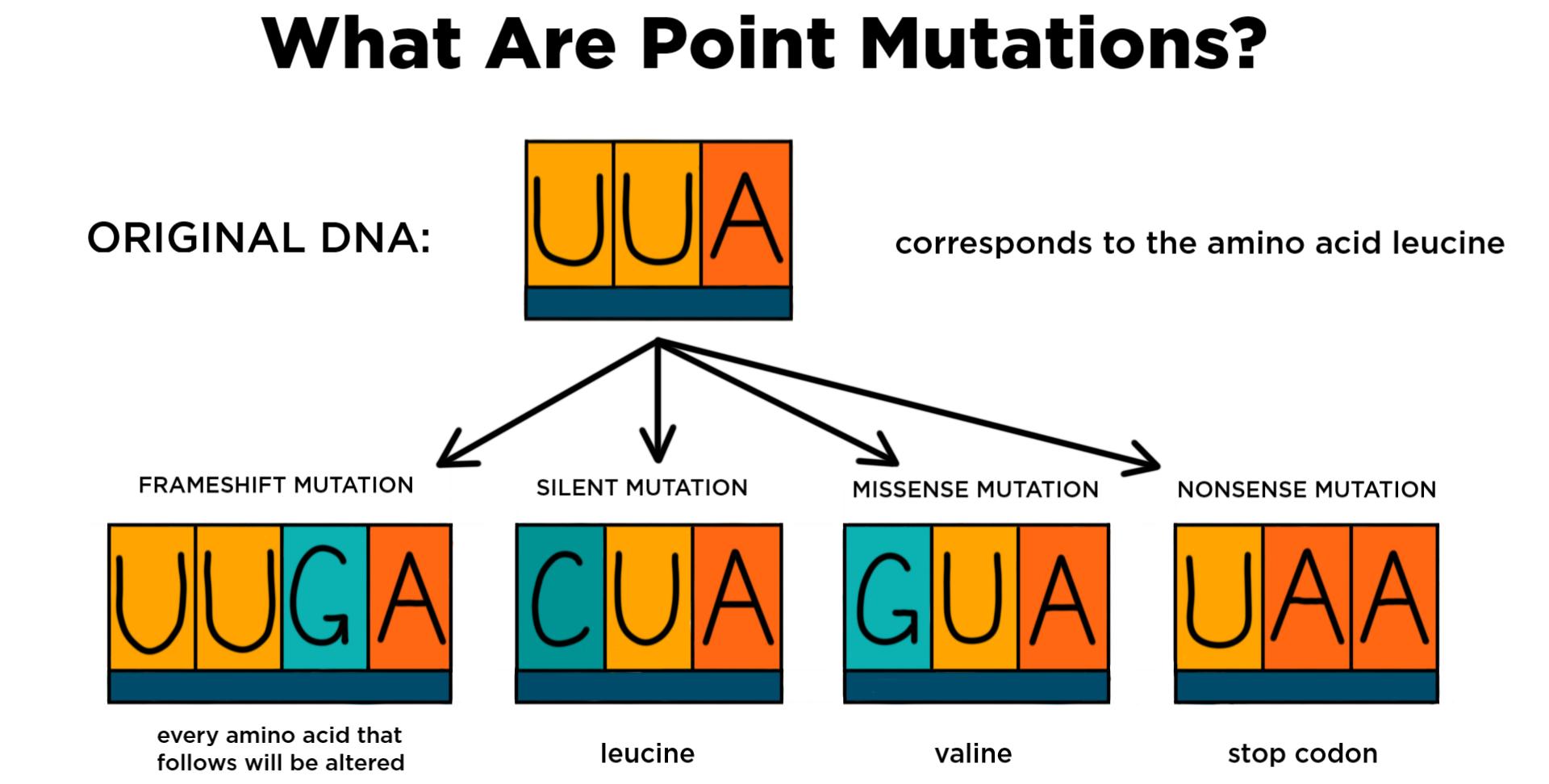
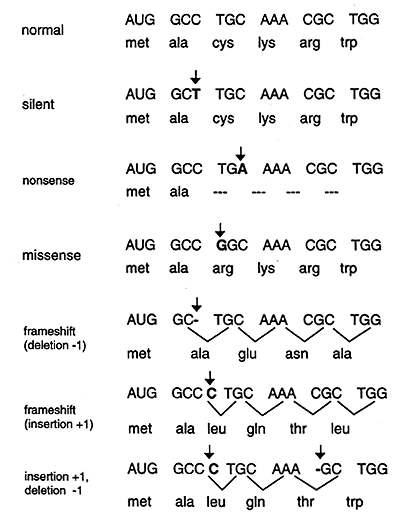
Definition, Causes & Types Point Mutations Have you ever thought that you could be a mutant?. Explain the difference between a frameshift mutations and a point mutation A frameshift mutation is an insertion or deletion of a nucleotide base that changes the reading frame A point mutation does not change the frame and only changes one amino acids Which type of mutation, a frameshift or a point mutation, has more effect on the organism?. Point mutations that occur in DNA sequences encoding proteins are either silent, missense or nonsense Silent If abase substitution occurs in the third position of the codon there is a good chance that a synonymous codon will be generated Thus the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene is not changed and the mutation is said to be silent.
Usually the term "mutation" is used if the change has an impact on the phenotype The "P" in "SNP" means "polymorphism" A lot of people use this term if more than 1% of the individual in a given population have this variant My recommendation only use "mutation" if you are sure that your variant has an important impact on the phenotype. Join the Amoeba Sisters as they explain gene and chromosome mutations, and explore the significance of these changes This updated video has improved audio a. Using all available deep sequencing data of complete genome from all over the world (NCBI repository), we identified several hundreds of point mutations or SNPs in SARSCoV2 all across the genome This could be the cause for the constant change and differed virulence with an increase in mortality and morbidity.
Define point mutation point mutation synonyms, point mutation pronunciation, point mutation translation, English dictionary definition of point mutation n A mutation that changes one nucleotide in a gene or DNA sequence by substitution, deletion, or addition. In order to enhance NE blocking capacity, we analyzed the KD sequence from a structurefunction point of view and designed specific point mutations in order to enhance NE affinity We substituted the P1 site residue at the reactive site for a leucine (termed RLKD), given its central role for KD’s inhibition to NE. Recently, mutations in the E gene (CT) and N gene (C290T) were reported affecting the detection of target genes by two commercial assays in 8 and 1 patients, respectively Interestingly, both mutations are of C>T type, a common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that may be associated with strong host cell mRNA editing mechanisms known.
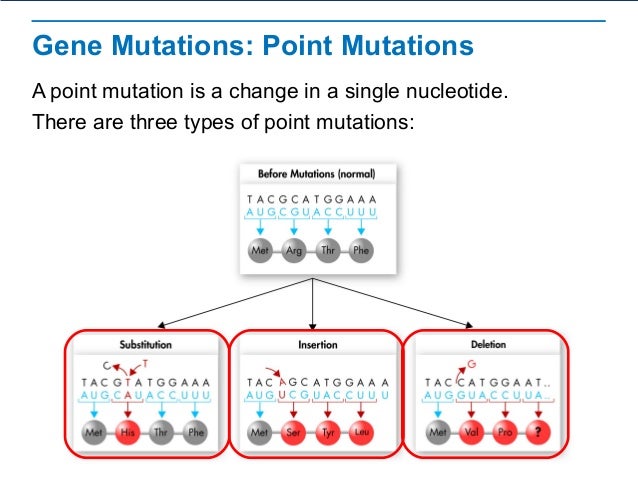
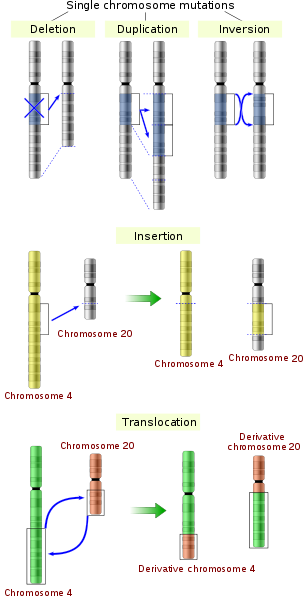
There are several types of mutations that are classified according to how the DNA molecule is altered One type, called a point mutation, affects a single base and most commonly occurs when one base is substituted or replaced by another. Point mutations, also called somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs), refer to changes in the sequence of DNA bases and include substitutions, insertions, and deletions of one or a few bases. A point mutation can develop when a double stranded DNA molecule creates two separate single strands In addition, radiation and chemical reactions can lead to a point mutation when the reactions are severe enough Environmental properties such as extreme heat and other temperature changes may also be a factor.
Recently, mutations in the E gene (CT) and N gene (C290T) were reported affecting the detection of target genes by two commercial assays in 8 and 1 patients, respectively Interestingly, both mutations are of C>T type, a common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that may be associated with strong host cell mRNA editing mechanisms known. Maybe if you were a Base Substitutions Base substitutions are just what they sound like;. Have you ever wished you were?.
Smallscale mutations affect a gene in one or a few nucleotides (If only a single nucleotide is affected, they are called point mutations). A point mutation is a natural change in a DNA or RNA sequence that only effects a single nucleotide – it changes just one letter These mutations can be passed from parent to child. A point mutation affects the DNA of more genes than a chromosomal mutation B A point mutation can involve a insertion or deletion, but cannot result in a frameshift***.
Definition of point mutation in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of point mutation What does point mutation mean?. A point mutation in LTT1 enhances cold tolerance at the booting stage in rice The cold tolerance of rice at the booting stage is a main factor determining sustainability and regional adaptability However, relatively few cold tolerance genes have been identified that can be effectively used in breeding programmes. Point mutations are changes in the genetic sequence that occur at a specific point along the DNA strand There are lots of different ways a point mutation can come about They're caused by random.
The optimal fragment length for the detection of point mutations varies between 0 and 600 bp;. A point mutation decouples the lipid transfer activities of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein Meredith H Wilson, Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. The optimal fragment length for the detection of point mutations varies between 0 and 600 bp;.
Mutation is the sudden heritable change in the genetic sequence of the organisms Two main types of mutation are frame shift mutation and point mutation The point mutation occurs due to the change in the single nucleotide sequence or base Frame shift mutation refers to the deletion or insertion of the basepair in the sequence. Point mutations are a large category of mutations that describe a change in single nucleotide of DNA, such that that nucleotide is switched for another nucleotide, or that nucleotide is deleted, or a single nucleotide is inserted into the DNA that causes that DNA to be different from the normal or wild type gene sequence. A single point mutation in carR downregulates the expression of almE, almF, and almG The carRcarS twocomponent system has been reported to regulate the expression of the almEFG operon mRNA Hence, we checked whether the point mutation at nucleotide position 265 in carR was able to change its regulatory.
Point mutation, change within a gene in which one base pair in the DNA sequence is altered Point mutations are frequently the result of mistakes made during DNA replication, although modification of DNA, such as through exposure to Xrays or to ultraviolet radiation, also can induce point. Definition of point mutation a gene mutation involving the substitution, addition, or deletion of a single nucleotide base. We discovered that a point mutation in the cotton bollworm, one of the world’s most voracious pests, confers dominantly inherited resistance to the Bt protein produced by transgenic cotton grown in China This mutation increased 100fold in frequency from 06 to 16 in China.
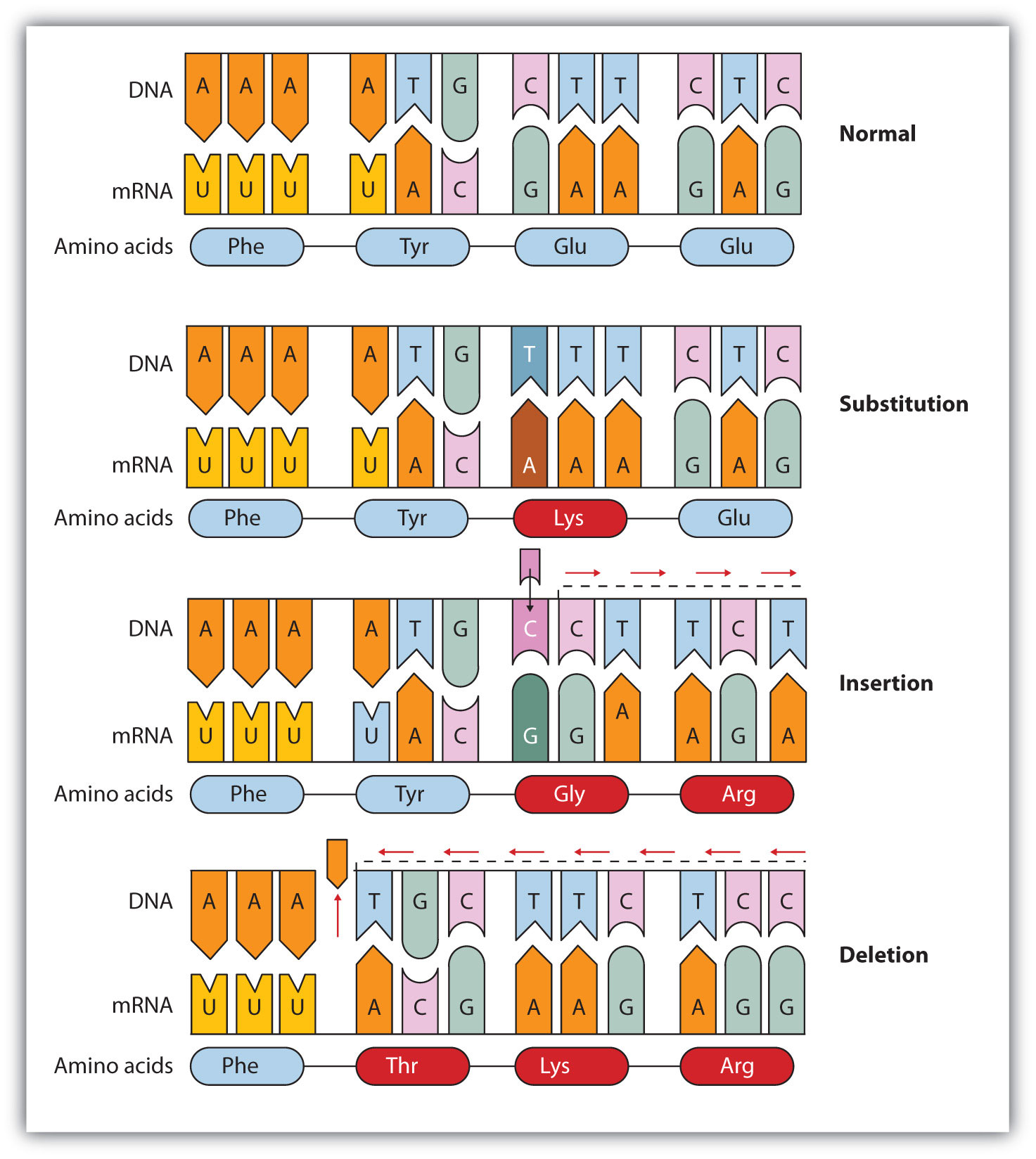
The detection of mutations in PCR fragments of up to 900 bp has been reported (25) (26). A point mutation occurs when one nucleotide within the strand of DNA is replaced with another A point mutation affects a single nucleotide There are four different nucleotides that make up DNA, which are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cystine (C). A point mutation usually involves a _____, which can be a nonsense or _____ 3 Frameshift mutations can either be an _____ or _____ In the chart below, transcribe the DNA sequence into mRNA Then use your codon chart to indicate what amino acids are being coded.
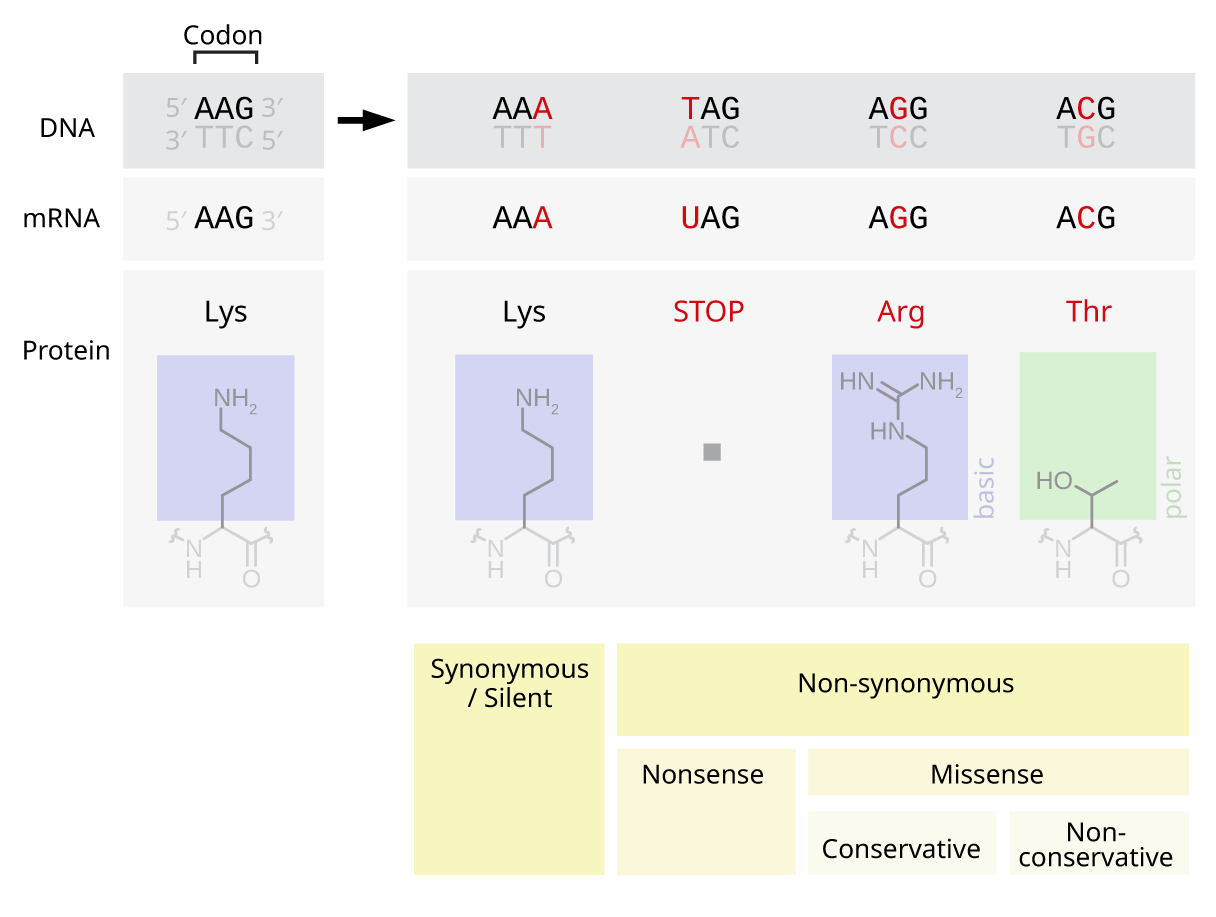
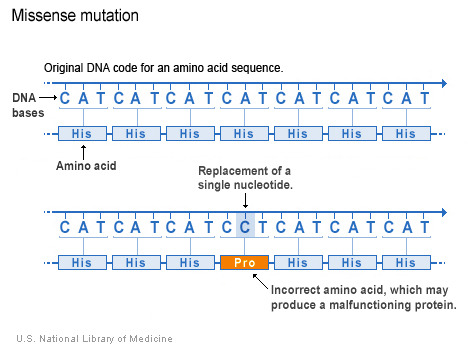
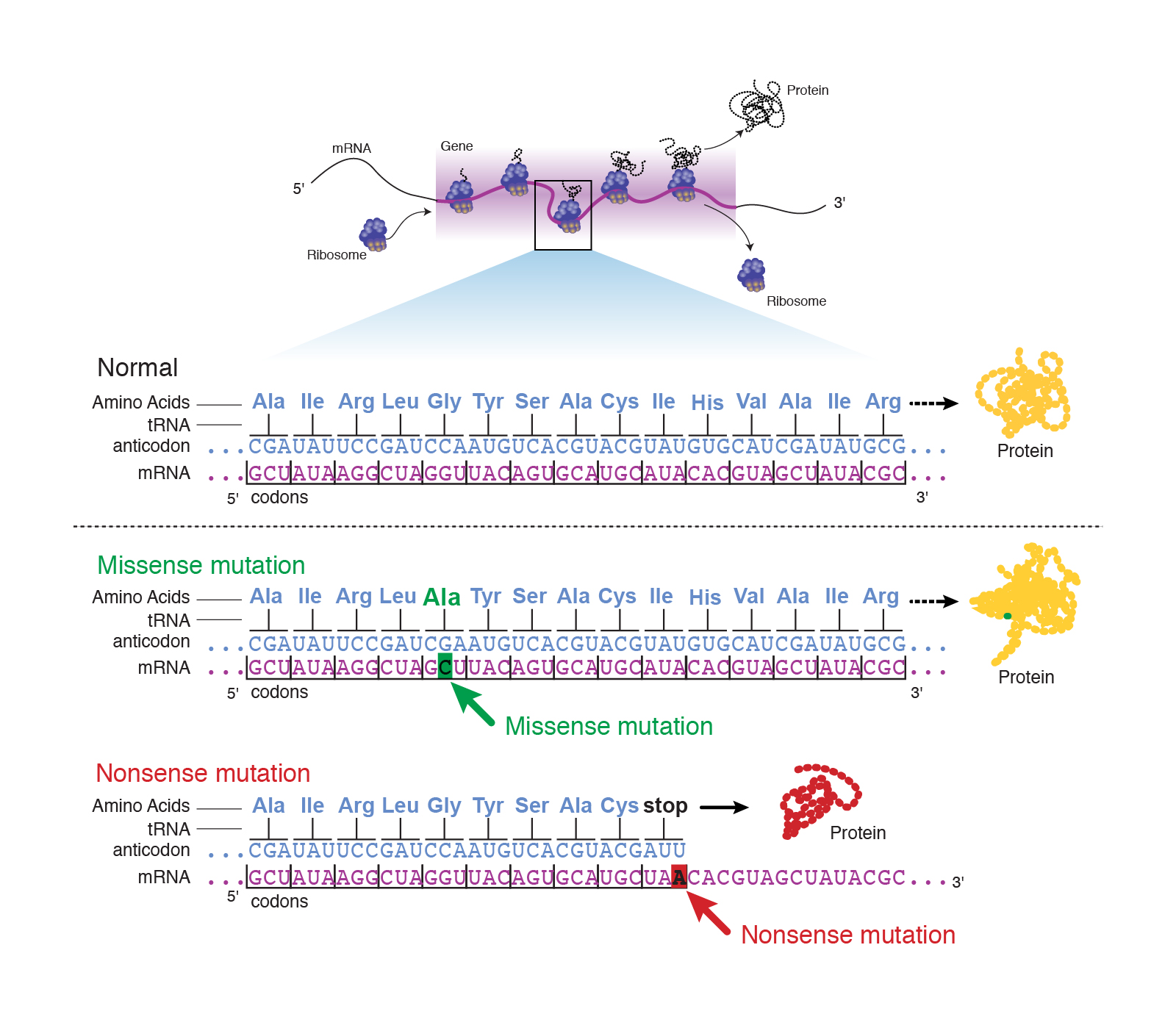
A point mutation or substitution is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. A single point mutation in carR downregulates the expression of almE, almF, and almG The carRcarS twocomponent system has been reported to regulate the expression of the almEFG operon mRNA (18) Hence, we checked whether the point mutation at nucleotide position 265 in carR was able to change its regulatory function. Missense mutation is a point mutation which results in the substitution of a different amino acid in the amino acid sequence due to the change of a single nucleotide in the mRNA sequence Nonsense mutation is a point mutation which results in a truncated, incomplete, nonfunctional protein product due to the introduction of a premature stop.
Point Mutation Point Mutation Definition A point mutation is a type of mutation in DNA or RNA, the cell ’s genetic material, in which From DNA to Protein DNA and RNA have a double helix structure Phosphate groups and 5carbon sugars make up the Types of Point Mutations A substitution. In a missense mutation, a different amino acid causes slightly different function, even though it may be conservative and similar to the original The different is that the change is noticeable While this may be a point mutation, or a change of one nucleotide, a point mutation can be the source of any mutation. Point mutations refer to changes to a single nucleotide These usually take place during DNA replication, and their consequences can be benign, or can be devastating This depends on the location of the mutation Point mutations occur through insertion, substitution or deletion.
Information and translations of point mutation in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. Changes within genes are called point mutations The simplest kinds are changes to single base pairs, called basepair substitutions Many of these substitute an incorrect amino acid in the corresponding position in the encoded protein, and of these a large proportion result in altered protein function. The detection of mutations in PCR fragments of up to 900 bp has been reported Detectable mutations Though the method is widely used for screening purposes, relatively few systematic studies on the fraction of mutations detectable have been published.
What is Point Mutation Silent Mutations In silent mutations, though a single base pair has changed in a particular codon, the same amino acid Missense Mutations In missense mutations, once the alteration occurs in a particular codon by a nucleotide Nonsense Mutations In nonsense mutations,. Mutations Types of Mutations There are a variety of types of mutations Two major categories of mutations are germline mutations Chromosomal Alterations Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure They occur when a Point Mutations A point mutation is a change in. Recently, mutations in the E gene (CT) and N gene (C290T) were reported affecting the detection of target genes by two commercial assays in 8 and 1 patients, respectively Interestingly, both mutations are of C>T type, a common single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) that may be associated with strong host cell mRNA editing mechanisms known.
A point mutation can result in the wrong amino acid getting produced, which alters the protein Remember, a protein is made when a bunch of amino acids are linked together, and if the protein gets. Single point mutations in DNA are linked with various diseases including Alzheimer’s and macular degeneration They can also play a role in resistance to drugs The ability to readily detect these mutations in genetic sequences could have a profound impact on the way that genetic diseases are diagnosed, and enable more targeted prescription. A point mutation can develop when a double stranded DNA molecule creates two separate single strands In addition, radiation and chemical reactions can lead to a point mutation when the reactions are severe enough Environmental properties such as extreme heat and other temperature changes may also be a factor.
Point mutation is an alteration in a single nucleotide in a DNA or RNA sequence It can happen due to changing, inserting or deleting a single base pair in the nucleic acid Most point mutations occur due to the errors in the DNA replication process. The next step was to emulate individual point mutations that tend to emerge in the real world by generating a pseudotype virus with the use of the B117 variant spike sequence Viral pseudotype. Point mutations can be subdivided into three types 1) Nonsense mutations are the ones which code for the same amino acid 2) Missense mutations occur in the genes which code for different amino acid 3) Silent mutations do not affect the function of the proteins and code for different or same amino acid.
The following points highlight the three types of point mutation The types are 1 NonSense Mutations 2 Missense Mutation 3 Silent Mutation Type # 1 NonSense Mutations Nonsense mutation is one type of point mutation. Nonsense mutation is one type of point mutation There are 64 codons that code for amino acid out of which three codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) are known as termination codons that do not encode for any amino acid If any change occurs in any codon, it brings about changes in amino acids which specify an amino acid to termination codon. A point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide in DNA This type of mutation is usually less serious than a chromosomal alteration An example of a point mutation is a mutation that changes the codon UUU to the codon UCU Point mutations can be silent, missense, or nonsense mutations, as shown in Table below.
Single point mutations in DNA are linked with various diseases including Alzheimer’s and macular degeneration They can also play a role in resistance to drugs. Initially, a series of point mutations were made to modify the amino acids in SARSCoV2 to match those at analogous position in SARSCoV (ie, a causative agent of the original SARS outbreak in. Causes of point mutation Causes of point mutation Types of point mutation Examples of point mutation Detection of point mutation Conclusion.
Smallscale mutations affect a gene in one or a few nucleotides (If only a single nucleotide is affected, they are called point mutations).
Plos One Pofut1 Point Mutations That Disrupt O Fucosyltransferase Activity Destabilize The Protein And Abolish Notch1 Signaling During Mouse Somitogenesis

What Is A Mutation

Ak Lectures Point Mutations Base Pair Substitutions

Rosalind Glossary Point Mutation
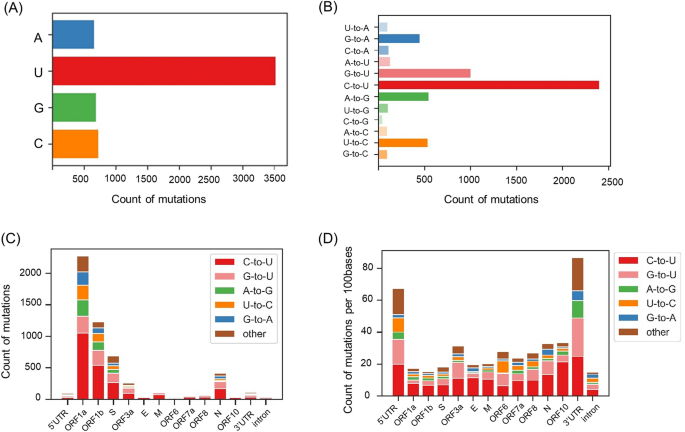
Point Mutation Bias In Sars Cov 2 Variants Results In Increased Ability To Stimulate Inflammatory Responses Scientific Reports

A Point Mutations
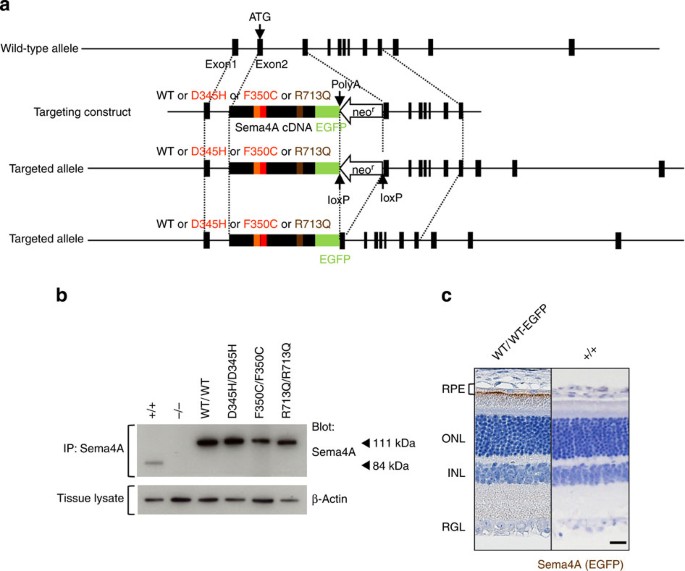
A Point Mutation In Semaphorin 4a Associates With Defective Endosomal Sorting And Causes Retinal Degeneration Nature Communications

Point Mutation Genetics Britannica

In Silico Analyses Of The Effects Of A Point Mutation And A Pharmacological Chaperone On The Thermal Fluctuation Of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Sciencedirect

A Point Mutation In Sec61a1 Leads To Diabetes And Hepatosteatosis In Mice Diabetes

Genetic Variation Of Viruses Part 2 Lecture 3 1 Types Of Viral Mutation A Point Mutations Point Mutations Occur When A Single Nucleotide Is Changed Ppt Download

10 Mutation With Binary String A Single Point Mutation B Multi Download Scientific Diagram
28 Mutations Biology Libretexts
Mutations And Genetic Diseases
How Does Mutation Affect Dna Replication Socratic
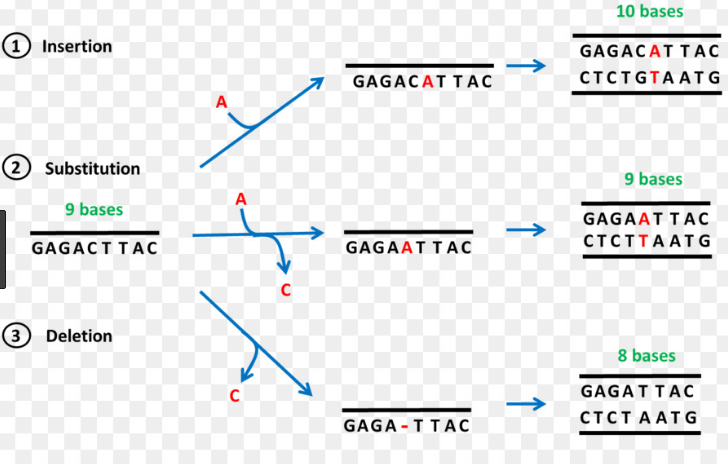
5 Difference Between Frameshift And Point Mutations Viva Differences

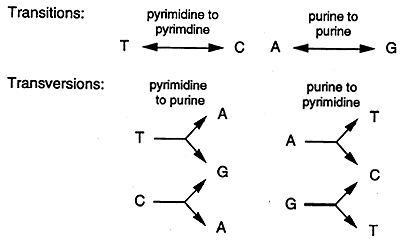
A Point Mutation Where Guanine Is Replaced By Cytosine Is Also Called

Types Of Mutations Point Mutations And Frameshift Mutations Mutations In Genetics Youtube
Biology Lower Secondary Ydp Animation Sequence Of Proteins And Point Mutations

Genetic Mutation Dna Mutation Point Mutation Youtube
Mutations Microbiology
Q Tbn And9gctpw Jizoe Eisllkx0tzslqrq1mw1dpg7ptkg4bxp0nhet5m9v Usqp Cau
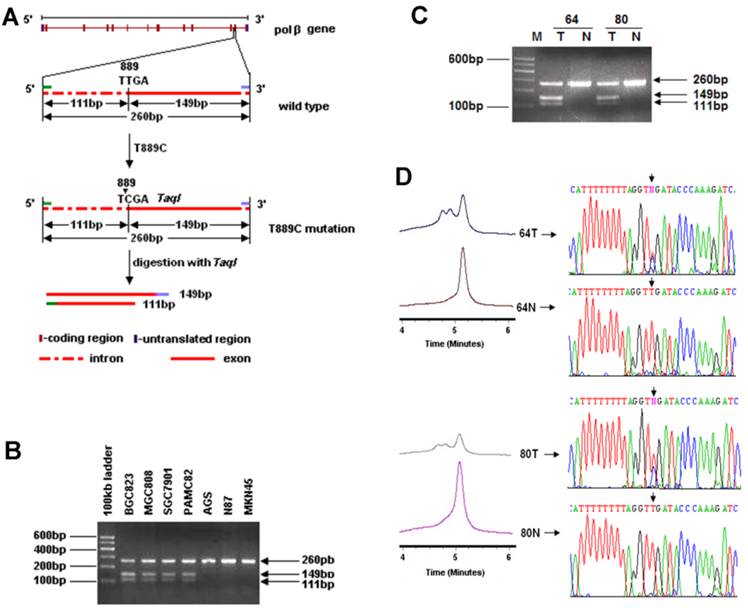
Clinical Significance Of A Point Mutation In Dna Polymerase Beta Polb Gene In Gastric Cancer
Point Mutation Wikipedia
Point Mutation Definition Types Expii
Point Mutation Wikipedia
Is A Point Mutation Always Damaging Quora

What Is A Mutation

What Is Point Mutation Give One Example Youtube
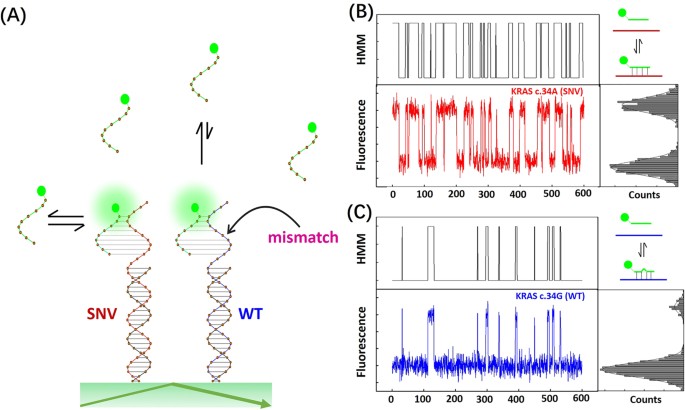
Single Molecule Counting Of Point Mutations By Transient Dna Binding Scientific Reports

Mutation Pattern In The Coding Region Of Sars Cov 2 A Point Mutation Download Scientific Diagram

Point Mutation Definition Types Expii
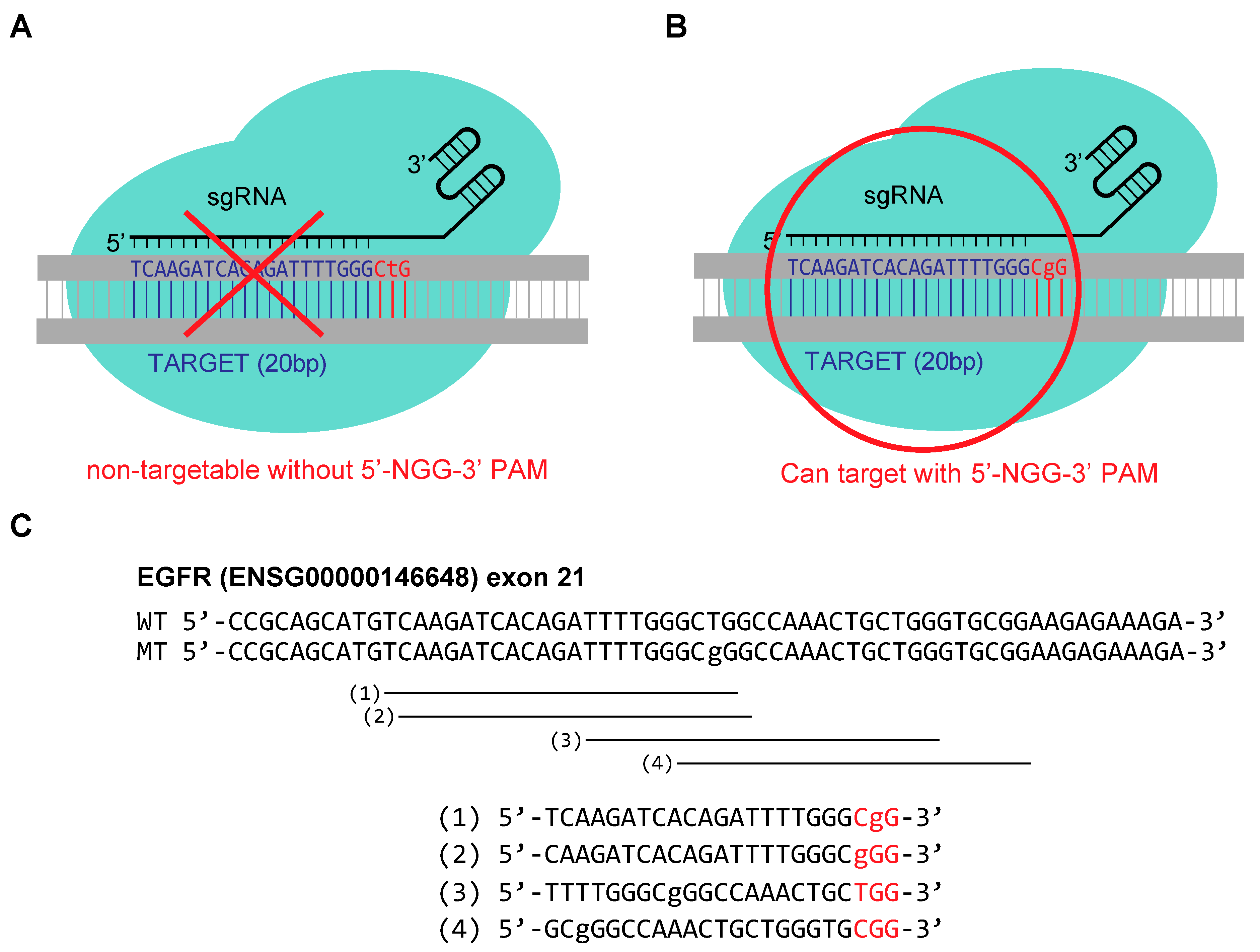
Molecules Free Full Text Specificity Assessment Of Crispr Genome Editing Of Oncogenic Egfr Point Mutation With Single Base Differences

Mutations B 2 3 1 Flashcards Quizlet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-932732476-5c4a21ce46e0fb0001d85d03.jpg)
Types And Examples Of Dna Mutations

Computational Design Of Thermostabilizing Point Mutations For G Protein Coupled Receptors Elife

What Is A Point Mutation And Why Should You Know About It

A Point Mutation In The Dynein Heavy Chain Gene Leads To Striatal

Point Mutations In Dna Types Diseases Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
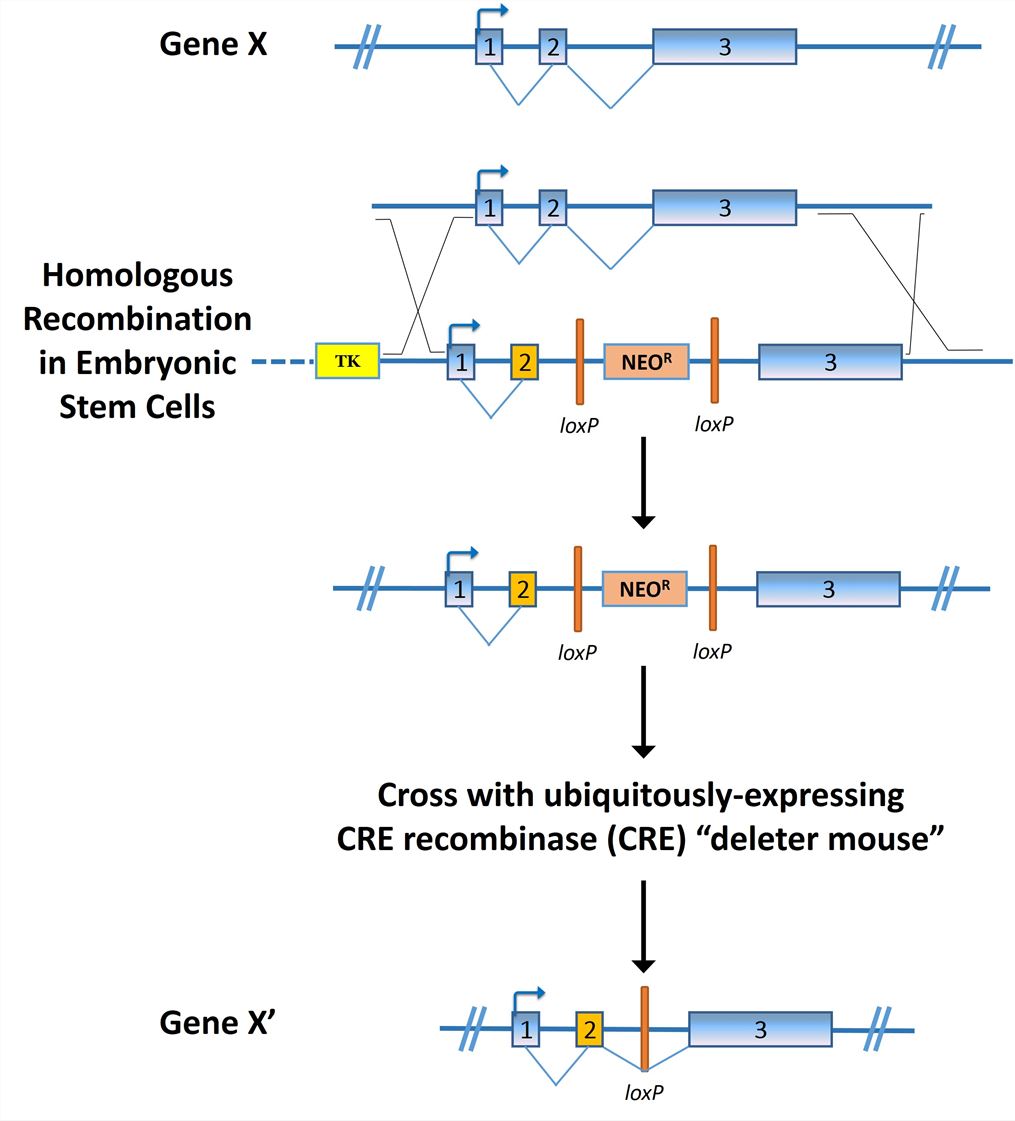
Tissue Specific Point Mutation Models Creative Biolabs

Which Disease Is Caused By Point Mutation

Point Mutation Knockin Biocytogen

Types Of Gene Mutation

Pdf A Point Mutation Within A Distinct Conserved Region Of The Herpes Simplex Virus Dna Polymerase Gene Confers Drug Resistance Semantic Scholar

Machine Learning Techniques For Classifying The Mutagenic Origins Of Point Mutations Genetics
Solved Question 1 Of 10 10 Points Determine Whether The S Chegg Com

Solved 2 Point Mutations One Type Of Mutation Is Called Chegg Com
Plos Genetics A Point Mutation In A Lincrna Upstream Of Gdnf Is Associated To A Canine Insensitivity To Pain A Spontaneous Model For Human Sensory Neuropathies
Dna Mutation And Repair

What Is A Point Mutation
Markov Point Mutation Diagram Left Diagram Shows 16 Genetic Cell Download Scientific Diagram
My Notes For Usmle Missense Mutation Is A Point Mutation In Which
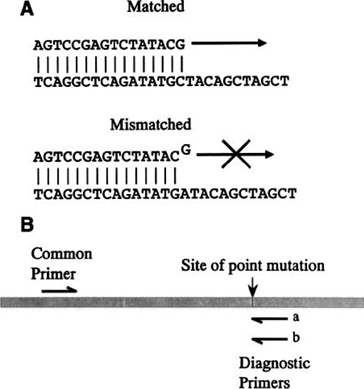
Pcr Methods For Identification Of Point Mutations And Gene Rearrangements Springerlink
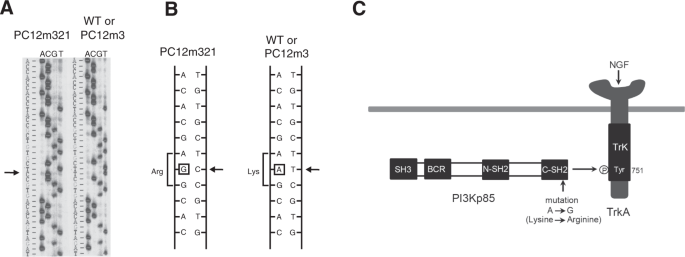
C Sh2 Point Mutation Converts P85b Regulatory Subunit Of Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase To An Anti Aging Gene Scientific Reports

Molecular Genetic Point Mutation

The Point Mutation Verified By Sanger Sequencing A Was The Download Scientific Diagram

Effect Of Site Directed Point Mutations On Protein Misfolding A Simulation Study Kumar 19 Proteins Structure Function And Bioinformatics Wiley Online Library
Mutations

Point Mutations Biology Mrs Harper 2 2 Ppt Download

Point Mutation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Point Mutation Cell Lines Customized Cell Lines Cyagen Us Inc

Ls What Is Point Mutation Name A Disease That Is Caused By Point Mutation Ecur 164 Is This A Course About Science Wiki

What Is A Point Mutation Definition Causes Types Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Q Tbn And9gcruhf4ytgcndpyp447jzjj3dbtrmhil5g Fsrbekz9uw Kdjren Usqp Cau

Mutation Analysis Of Patient 1 Showed A Point Mutation Of Clcnkb A Download Scientific Diagram

Solved What Impact Can A Point Mutation Have On The Amino Chegg Com

The Microglia Defect In Biluo Mutants Is Caused By A Point Mutation In Download Scientific Diagram

Point Mutations Youtube
Point Mutation

Point Mutation Wikipedia

Identification Of A Point Mutation Underlying Feps A Sequence Download Scientific Diagram

What Is A Point Mutation

What Is A Point Mutation With Picture
.PNG)
Mutations Presentation Biology

Point Mutations Practices Worksheets Mutation Relationship Worksheets

A Point Mutation L1015f Of The Voltage Sensitive Sodium Channel Gene Associated With Lambda Cyhalothrin Resistance In Apolygus Lucorum Meyer Dur Population From The Transgenic Bt Cotton Field Of China Sciencedirect
A Point Mutation Leads To An Amino Acid Exchange In The Coding Region Download Scientific Diagram

What Is A Point Mutation

What Is A Point Mutation
Point Mutation Cell Models Focus On One Function At A Time Genoway

What Types Of Mutation Are There Facts Yourgenome Org

A Point Mutation In The Regulatory Light Chain Reduces The Step Size Of Skeletal Muscle Myosin Pnas
Plos Genetics A Point Mutation Decouples The Lipid Transfer Activities Of Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein

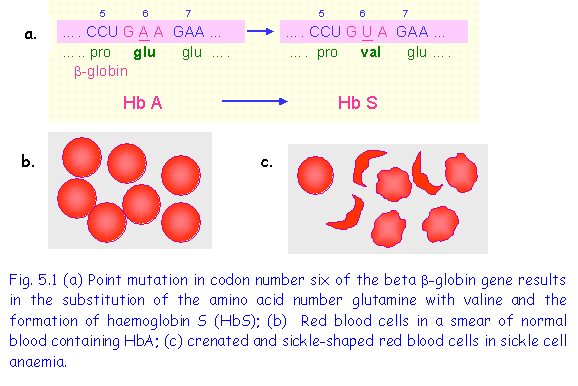
Sickle Cell Anemia Is Caused By A Point Mutation Knows As A Substitution Course Hero
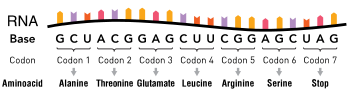
Point Mutation Wikipedia

New Dna Base Editors Advance Towards Curing Cystic Fibrosis And Other Human Point Mutation Diseases Nextbigfuture Com
Difference Between Point Mutation And Chromosomal Mutation Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Familial Creutzfeldt Jakob Disease Associated With A Point Mutation At Codon 210 Of The Prion Protein Gene

Point Mutations Bioninja

Effects Of Mutations On Protein Function Missense Nonsense And Silent Mutations Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Dna Mutation And Repair
Point Mutation Science Online

Point Mutations In Dna Types Diseases Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Solved Why Are Frameshift Mutations Likely To Be More Det Chegg Com

Point Mutations Types Processes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Q Tbn And9gcqnhx4pxhutouj1niunxesyaqfnqtt8qztlv1uhsqhf3mtxzmvs Usqp Cau

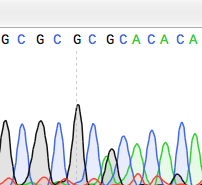
Can Anyone Verify Whether This Is An Artifact Or A Point Mutation In These Sanger Sequencing Results



