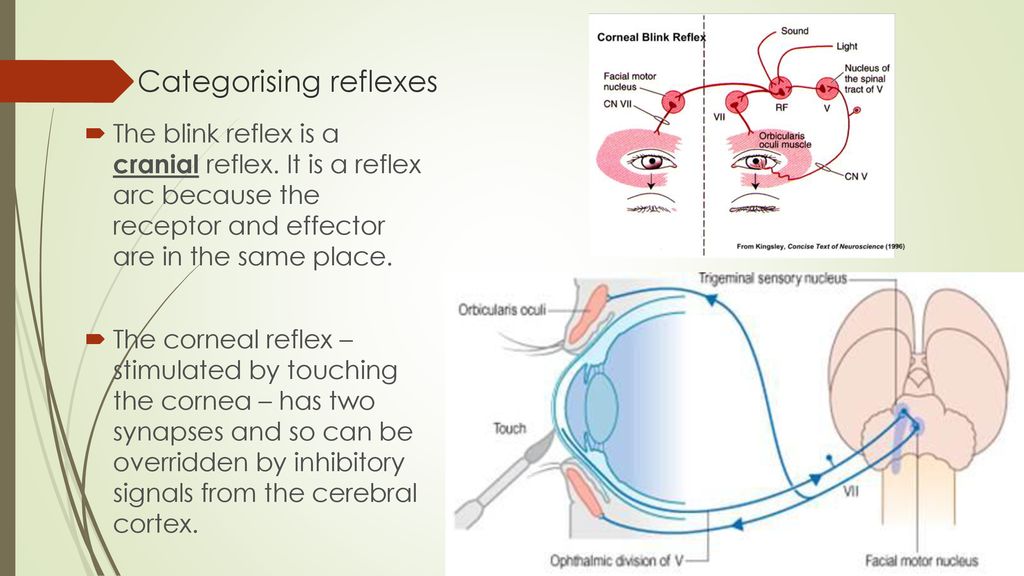
Blink Reflex Arc
Q Tbn And9gcroixwxexbyw4u8bnm3t2a4yys8tjmkhpskzyhm6u4u 2 Akvxm Usqp Cau

Chapter 19 Somatic Reflexes Types Of Reflexes Flashcards Quizlet

Reflex Arc Prezentaciya Onlajn

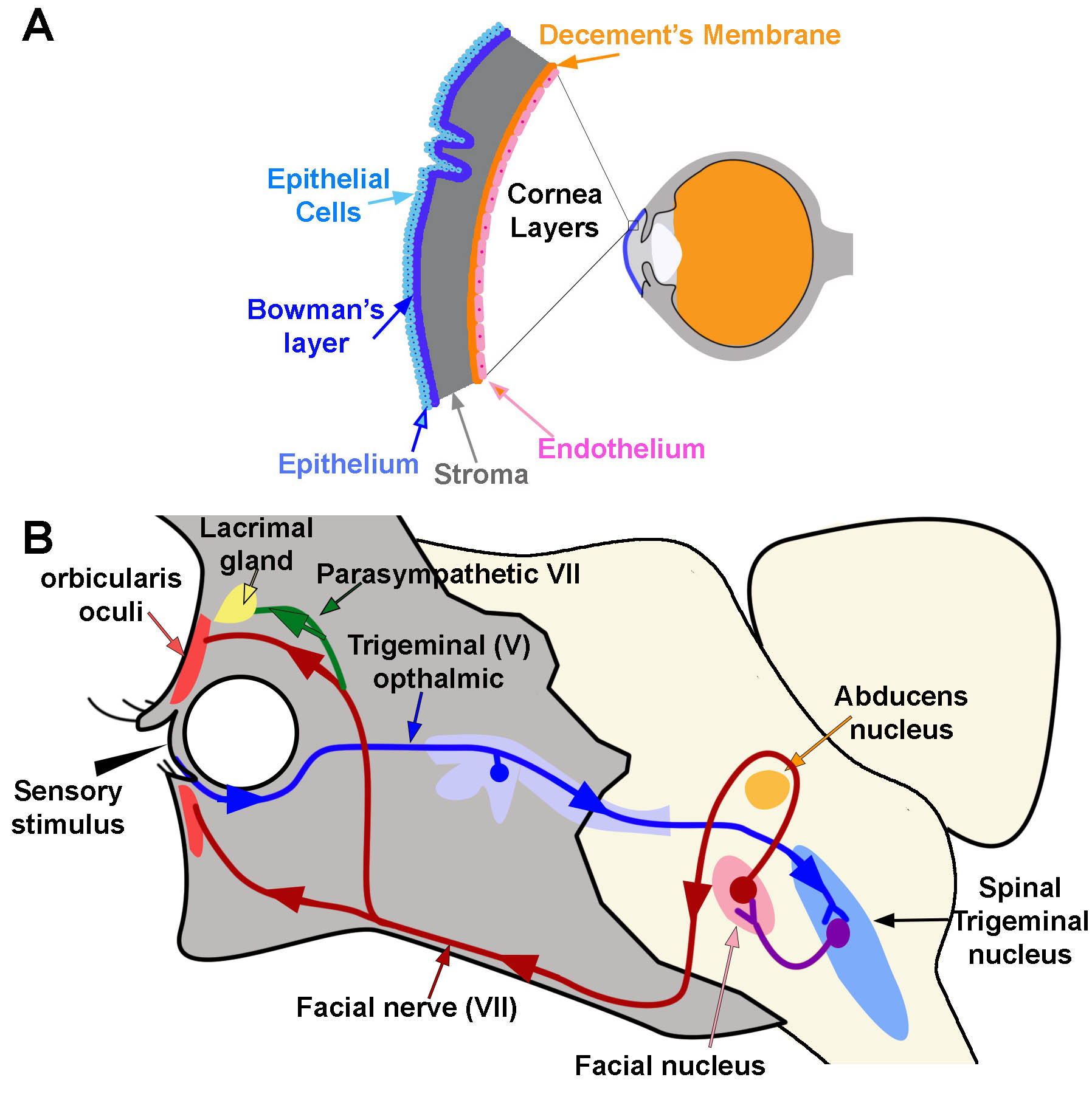
The Functional Unit Regulatory Systems Ocular Surface Center Berlin
What Is Reflex Action Quora
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf
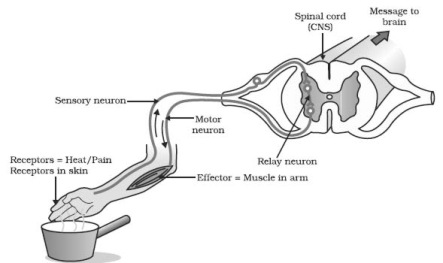
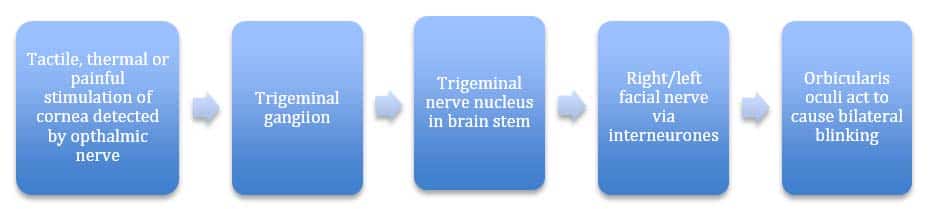
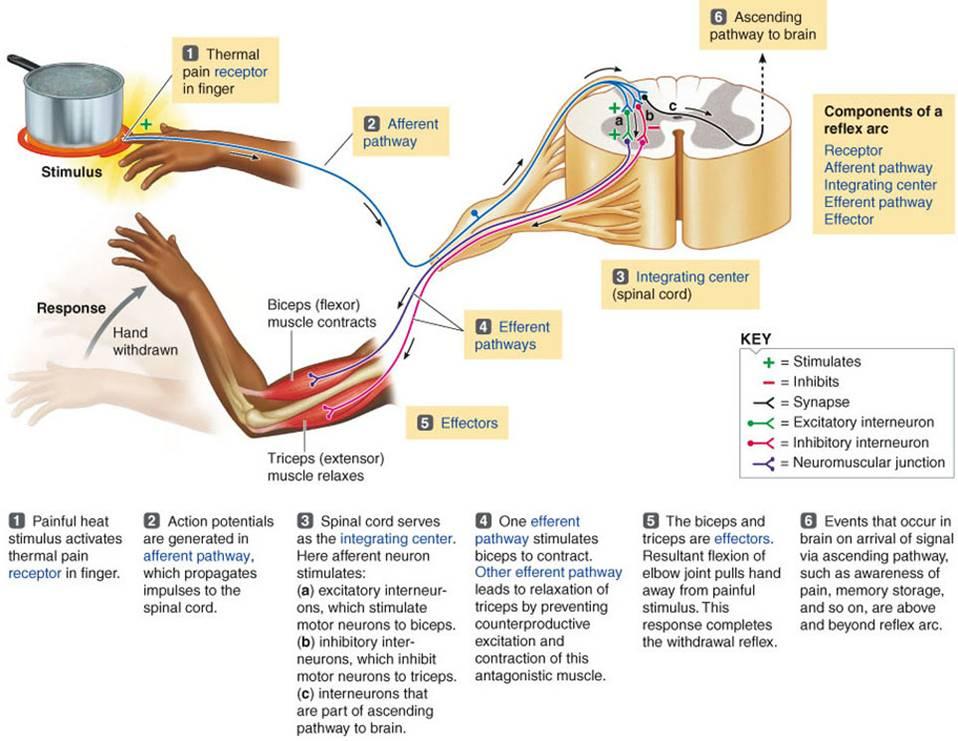
The nerve pathway followed by a reflex action is called a reflex arc For example, a simple reflex arc happens if we accidentally touch something hot Receptor in the skin detects a stimulus (the.
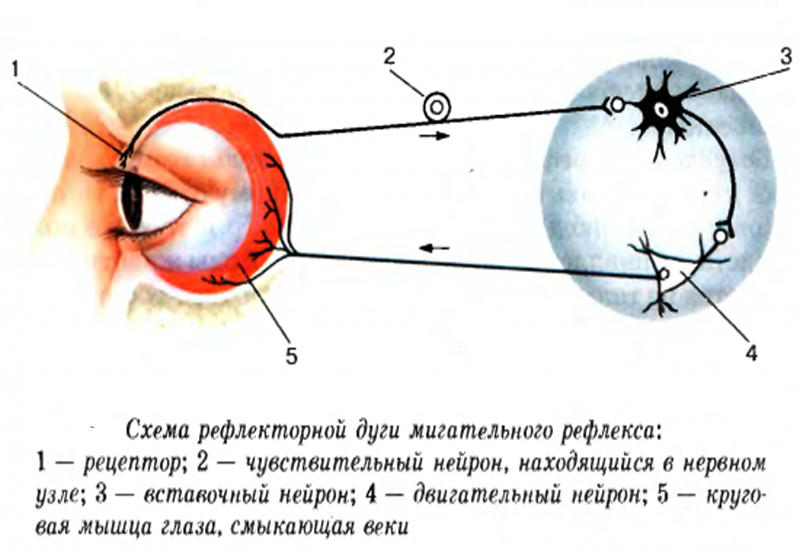
Blink reflex arc. A reflex is a rapid automatic response to a stimulus When you accidentally touch a hot object and automatically jerk your hand away, this is a reflex action It happens without you having to think about it Animals automatically blink when an object approaches the eye and cats twist their bodies in the air when falling so they land on their paws. A reflex blink is not necessarily a conscious blink either;. However, the interneuron of the blink reflex arc makes it possible to consciously keep the eyelid open when an object such as a contact lens touches the surface of the eyeball Doctors often test patients’ reflexes because an abnormal reflex can indicate nervous system malfunction.
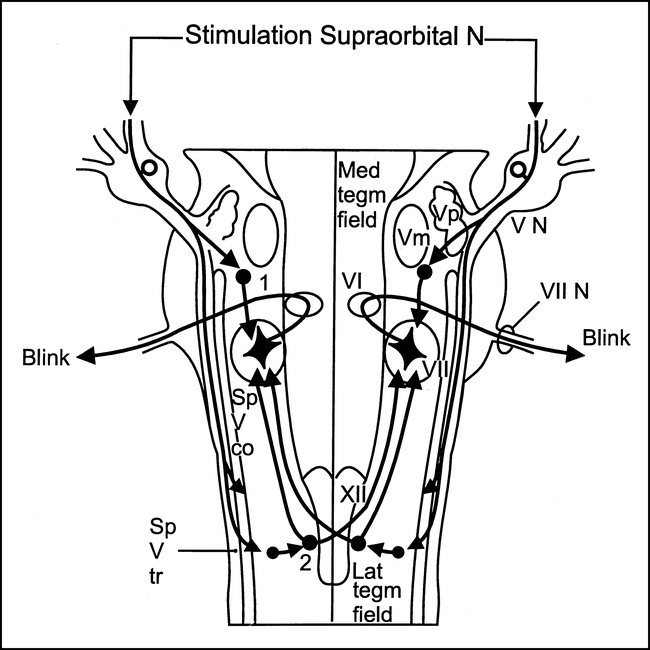
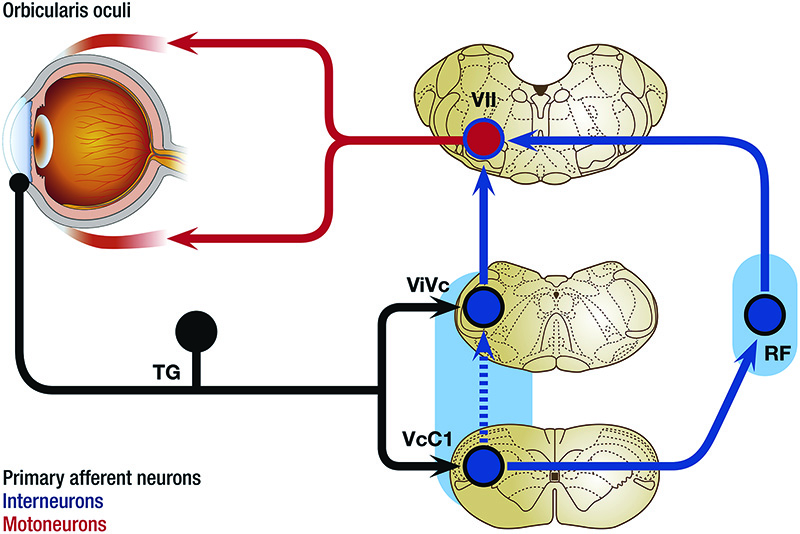
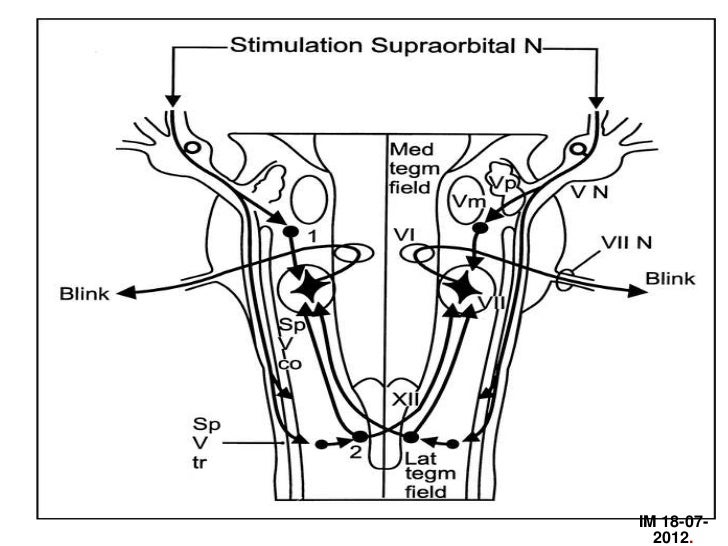
The blink reflex (BR) is a reflex contractionof the eyeclosingmuscleson bothsides whichcan be evoked withunilateralelectrical stimulationof the differentbranches of the TN The afferent arc of the cutaneousBR consists of the TNon the side of stimulationand the trigeminalsensory nuclei in the brainstemThe facial motornuclei in pons and the. Baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex — homeostatic countereffect to a sudden elevation or reduction in blood pressure detected by the baroreceptors in the aortic arch, carotid sinuses, etc BezoldJarisch reflex — involves a variety of cardiovascular and neurological processes which cause hypopnea and bradycardia. Monosynaptic reflex arc consists of only two neurons (one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron) **polysynaptic reflex arc **what does the blink reflex do This protects the eye from foreign bodies and bright lights The eye can adjust its optical power to.
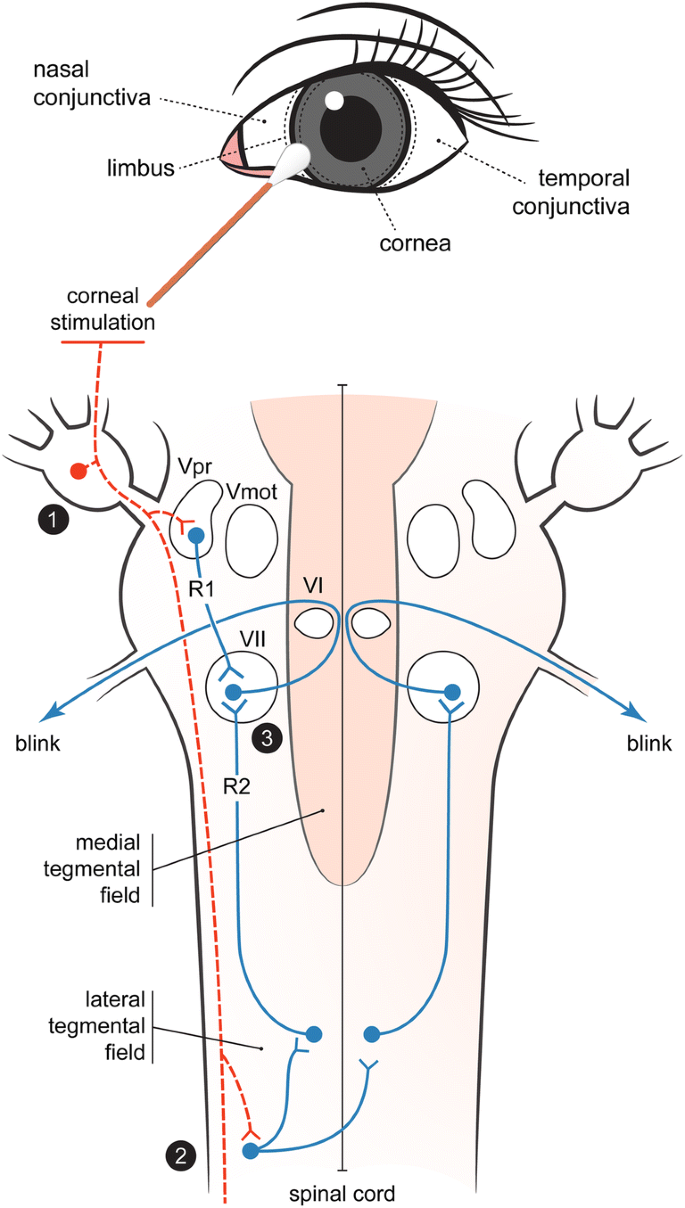
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). Considering the reflex arc, blink reflex (BR) might be useful in monitoring the sensory part of the trigeminal nerve, the brainstem connections and the facial nerve We describe the case of a patient who developed hemifacial hypoesthesia after microvascular decompression surgery for trigeminal neuralgia. A reflex that does not involve a complete reflex arc and hence is not a true reflex Its afferent and efferent limbs are branches of a single nerve fiber, the axon (axonlike dendrite) of a sensory neuron An example is vasodilation resulting from stimulation of the skin.
This is a video which explains the light reflex pathway and the accommodation reflex pathway of the eyes and also explains briefly 3 lesions found in these p. However it does happen faster than a spontaneous blink Reflex blink may occur in response to tactile stimuli (eg corneal, eyelash, skin of eyelid, contact with eyebrow), optical stimuli (eg dazzle reflex, or menace reflex) or auditory stimuli (eg, menace reflex) Voluntary blink. Apparently, this reflex has some sort of defensive role, moving the pupil under the lid in response to noxious corneal stimuli Apparently, the mesencephalic reticular nucleus is reponsible for integrating the eyelid and eye movements Ergo, a midbrain lesion may result in blinking without upward eye movement.
A reflex action or reflex is a biological control system linking stimulus to response and mediated by a reflex arc Reflexes can be builtin or learnt For example, a person stepping on a sharp object would initiate the reflex action through the creation of a nociceptive stimulus within specialized sense receptors located in the skin tissue of. Blink reflex If a foreign object touches either cornea (that’s the clear cover of your eyeball), both eyelids blink simultaneously The reflex is meant to protect your eye from being injured. Abstract Investigation of the blink reflex represents a contemporary and highly informative method in electroneurophysiological diagnosis Contradictory data from clinical studies of the blink.
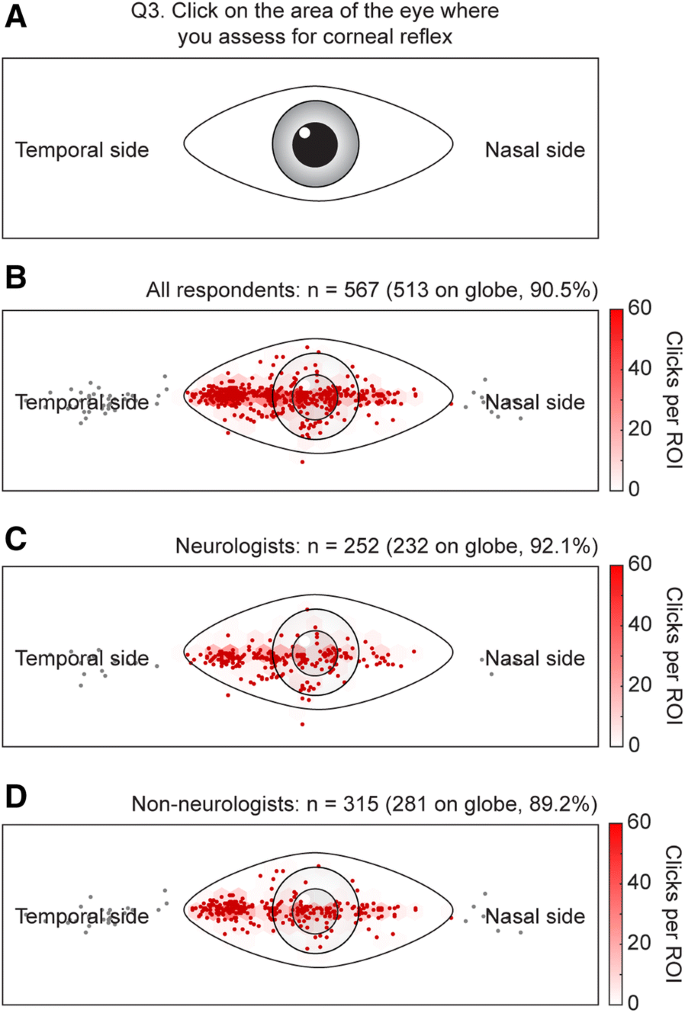
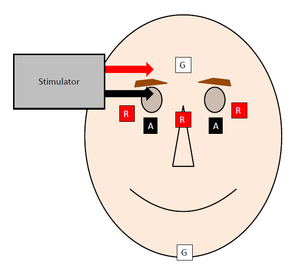
Reflex Action and Reflex Arc Reflex is a special ability that evolution gifted us to facilitate our survival Whenever part of your body comes in contact with an object capable of causing you harm, you tend to quickly withdraw that part of the body This happens before your brain gets the time it needs to process the threat. Reflex arc, neurological and sensory mechanism that controls a reflex, an immediate response to a particular stimulus The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells, which perform the reflex action. Test the corneal reflex Begin by telling the patient you are going to touch the eye gently in order to check the reflex Take a wisp of cotton and twist it into a point Ask the patient to look in the other direction, so you will not be testing the blink reflex Then gently but firmly touch the cornea at its junction with the sclera.
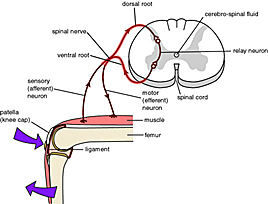
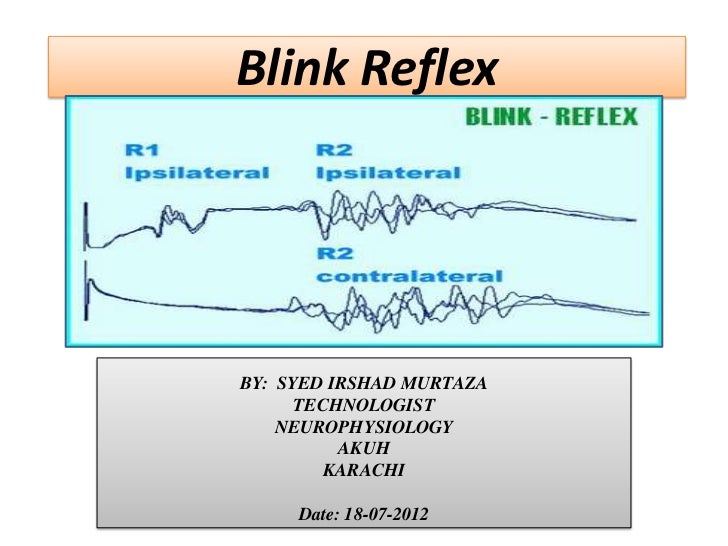
Probably This is the blink reflex and serves to protect our eyes from damage Materials Cotton balls (or rolledup paper towels) A transparent barrier (a wire screen, plastic or glass window) Did you know?. Reflex Arcs •In a kneejerk reflex arc the sensory neuron directly connects to the motor neuron in the spinal cord This is called a simple reflex arc • Follow the sensory neuron from the spindle (receptor) to where it connects with the motor neuron in the spinal cord • Follow the motor neuron to the muscle (effector). The blink reflex is a very practical reproducible electrical response, that can be used in comparative clinical studies and experimental models 13 At the beginning of XX th century, there was a dispute about the authorship of the original description of the blink reflex 4.
Reflex Arcs •In a kneejerk reflex arc the sensory neuron directly connects to the motor neuron in the spinal cord This is called a simple reflex arc • Follow the sensory neuron from the spindle (receptor) to where it connects with the motor neuron in the spinal cord • Follow the motor neuron to the muscle (effector). When something gets on in our eyes, we blink furiously to try and remove it This is a reflex action We don’t blink out of our own will It just happens REFLEX ARC Afferent neuron (receptor) and efferent neuron (effector or excitor) are the two neurons that dominate the pathway The events that take place during this. Considering the reflex arc, blink reflex (BR) might be useful in monitoring the sensory part of the trigeminal nerve, the brainstem connections and the facial nerve We describe the case of a patient who developed hemifacial hypoesthesia after microvascular decompression surgery for trigeminal neuralgia.
Blink reflex normative studies were made by many authors9,1113, although the work of Kimura et al1 is still accepted as the standard Despite many reports investigating the blink reflex in various neurological syndromes, the normative studies presented so far have not shown data for interracial comparison We do not know of normative studies. The blink reflex the blink reflex is absent in an UNCONCIOUS person, but the pupillary and corneal reflex are present since the blink reflex arc can be inhibited, what would be implied about the nerve pathway wiring of a reflex arc?. Reflex arc is the anatomical nervous pathway comprised of a receptor, afferent as the blink reflex It is an involuntary bli nking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation (such as.
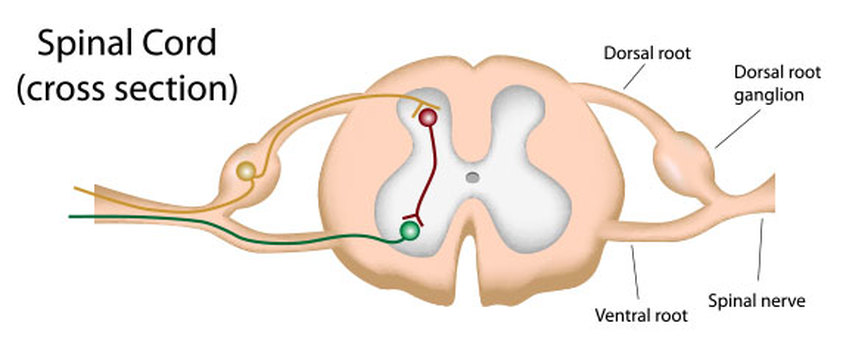
Whereas the basic circuit is a reflex arc, there are differences in the structure of those reflexes for the somatic and autonomic systems The Structure of Reflexes One difference between a somatic reflex , such as the withdrawal reflex, and a visceral reflex , which is an autonomic reflex, is in the efferent branch. This is a reflex action We don’t blink out of our own will It just happens REFLEX ARC Afferent neuron (receptor) and efferent neuron (effector or excitor) are the two neurons that dominate the pathway The events that take place during this. The reflex actions are listed below and you are to identify the sensory receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, and effector involved in each reflex arc Use simple terms in your explanations " Eye Blink Reflex Explanation " I just don't understand this question at all.
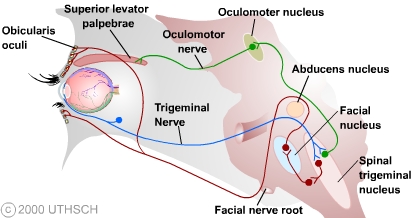
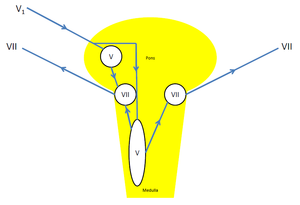
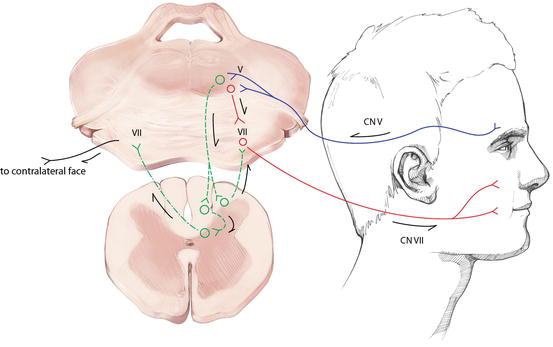
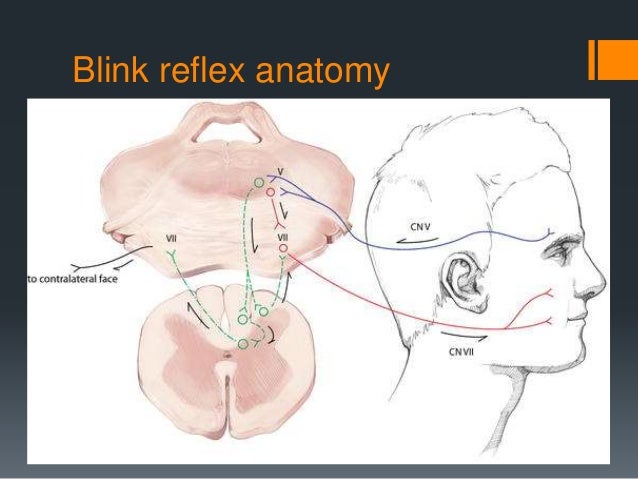
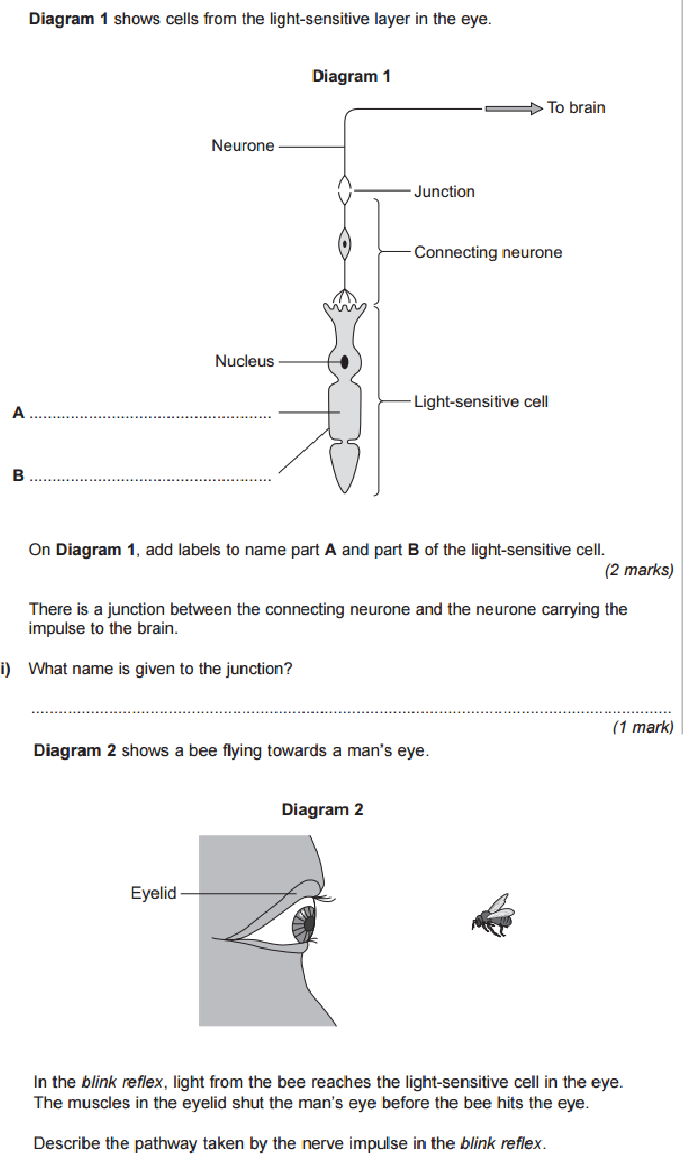
A reflex arc is a nerve pathway in the body of humans and some animals that connects certain muscle groups to others, without involving the brain These sorts of pathways primarily control involuntary movements in response to some sort of stimulus Rapidly blinking the eyes in response to dust or dirt in the air is one example;. The diagram shows a bee flying towards a man's eye In the blink reflex, light from the bee reaches the lightsensitive cell in the eye The muscles in the eyelid shut the man's eye before the bee. INTRODUCTION Blink reflex is essentially the electricalcorrelate of the clinically evoked cornealreflexBlink reflex is capable of evaluating the cranialnerves and their proximal segmentsThe afferent limb of blink reflex is ophthalmicdivision of trigeminal (V) nerve (which can bestimulated mechanically or electrically) andthe facial (VII) nerve mediates the efferentarc.
First of all, the sensory nerves take the impulses to the spinal cord through the reflex arc and then the spinal cord sends back the impulses in the form of motor impulse to the effector and then the body reacts It just triggers the effected organ to take the defensive action anyhow to protect the body. The reflex helps to maintain muscles at a constant length A common example of this reflex is the knee jerk that is elicited by a rubber hammer struck against the patellar ligament in a physical exam A specialized reflex to protect the surface of the eye is the corneal reflex, or the eye blink reflex When the cornea is stimulated by a tactile. An abnormal blink reflex may signal an underlying neurological problem Neurological exams can include a quick assessment of the blink reflex to see how a patient responds to stimuli This can be part of the process of checking on a patient who is believed to be nonresponsive or in a coma as well, because the reflex should kick in unless a patient has severe damage to the brainstem.
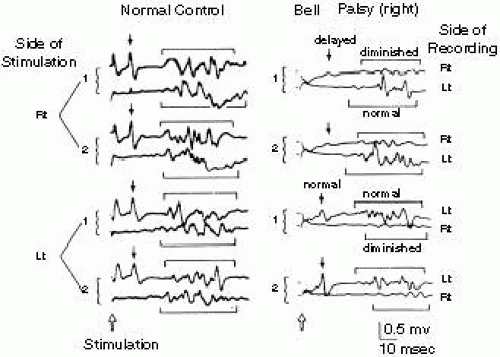
This reflex is especially visible in patients with Bell palsy, an acute disorder of the facial nerve, due to failure of adequate eyelid closure The presence or absence of Bell’s reflex can be useful in diagnosis of many systemic and local diseases In supranuclear palsy, which can occur with SteeleRichardson syndrome, Parinaud’s syndrome, and double elevator palsy, patients cannot elevate their eyes but can do so on attempting the Bell’s phenomenon. Whereas the basic circuit is a reflex arc, there are differences in the structure of those reflexes for the somatic and autonomic systems The Structure of Reflexes One difference between a somatic reflex , such as the withdrawal reflex, and a visceral reflex , which is an autonomic reflex, is in the efferent branch. First component of the blink reflex is conducted through an oligosynaptic arc including one or moreinterneurones There are different views on the reflex arc of the first component of the blink reflex in man Early descriptions have interpreted the origin of the blink reflex as a cutaneous (Overend, 16), periosteal (Bechterew, 1901;.
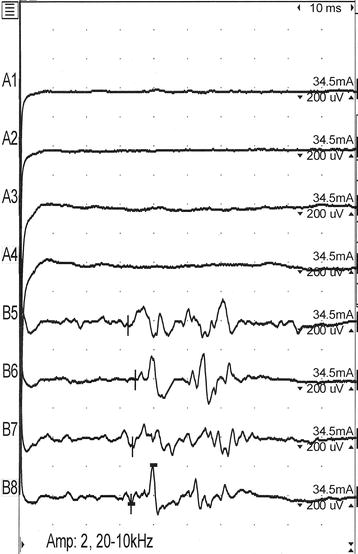
When something gets on in our eyes, we blink furiously to try and remove it This is a reflex action We don’t blink out of our own will It just happens REFLEX ARC Afferent neuron (receptor) and efferent neuron (effector or excitor) are the two neurons that dominate the pathway The events that take place during this. These are controlled by the reflex arc, which involves a sensory neuron bypassing the brain and sending a movement signal directly to the spinal cord to elicit a subconscious movement The knee reflex is a good example of this When the doctor strikes the patellar tendon below the knee cap with a reflex hammer, the lower leg subconsciously kicks. In all cases, prolonged latency, low amplitude, or the absence of the late component of the blink reflex was observed in the followup study These results indicate that prematurity and some congenital impairment mainly influence the maturation of the longloop reflex arc in the blink reflex.
Monosynaptic reflex arc consists of only two neurons (one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron) **polysynaptic reflex arc **what does the blink reflex do This protects the eye from foreign bodies and bright lights The eye can adjust its optical power to. People typically blink about 15 times per minute If you are awake for 16 hours each day, then you blink approximately. These are controlled by the reflex arc, which involves a sensory neuron bypassing the brain and sending a movement signal directly to the spinal cord to elicit a subconscious movement The knee reflex is a good example of this When the doctor strikes the patellar tendon below the knee cap with a reflex hammer, the lower leg subconsciously kicks.
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye) The reflex occurs at a rapid rate of 01 seconds. The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). Reflex arc is the anatomical nervous pathway comprised of a receptor, afferent as the blink reflex It is an involuntary bli nking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation (such as.
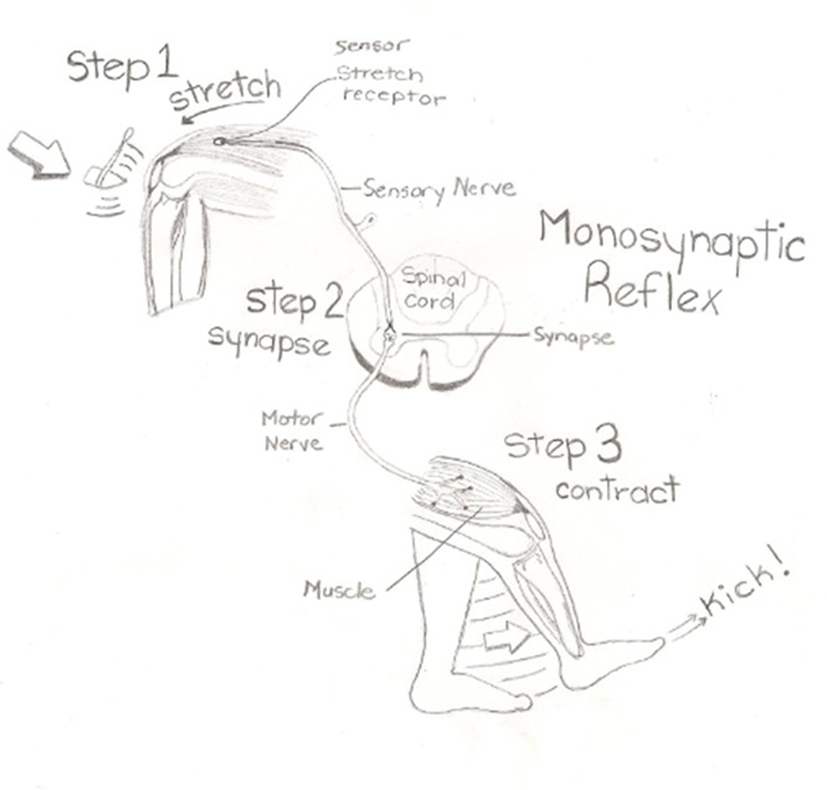
First component of the blink reflex is conducted through an oligosynaptic arc including one or moreinterneurones There are different views on the reflex arc of the first component of the blink reflex in man Early descriptions have interpreted the origin of the blink reflex as a cutaneous (Overend, 16), periosteal (Bechterew, 1901;. The nerve pathway followed by a reflex action is called a reflex arc For example, a simple reflex arc happens if we accidentally touch something hot Receptor in the skin detects a stimulus (the. In its simplest form, a reflex is viewed as a function of an idealized mechanism called the reflex arc The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensorynerve cells (or receptors) that receive stimulation, in turn connecting to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action In most cases, however, the basic physiological mechanism behind a reflex is more complicated than the reflex arc theory would suggest.
The sequence of neural events that gives rise to reflexive behaviors is called the reflex arc The sequence of neural events that gives rise to reflexive behaviors is called the reflex arc 1 A receptor organ (skin, eye, mouth) receives a stimulus from the external environment (hot touch, bright light, sour taste). Afferent nasociliary branch of ophthalmic branch (V1) of trigeminal nerve (5th nerve) Efferent facial nerve (7th nerve) Abdominal reflex Contraction of superficial abdominal muscles when stroking abdomen lightly. Override response by using inhibitory neurons.
The blink reflex is a powerful tool to measure the excitability of the trigeminofacial reflex arc and, through that, the physiologic correlates of certain functions (and the pathophysiology of dysfunctions) that are either integrated in, or mediated by, the brainstem There are two main techniques for using the blink reflex to measure. When something gets on in our eyes, we blink furiously to try and remove it This is a reflex action We don’t blink out of our own will It just happens REFLEX ARC Afferent neuron (receptor) and efferent neuron (effector or excitor) are the two neurons that dominate the pathway The events that take place during this. Allows the VestibularOcular Reflex Arc to function effectively, which maintains visual stability during head movement Symptoms of Retained HRR Impairment of balance, controlled eye movements and visual perception Poor Posture;.
Corneal reflex (blink reflex) Involuntary blinking in response to corneal stimulation;.

Some Medical Thoughts Reflexes A No Brainer

Difference Between Somatic And Visceral Reflex Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Reflex Arc Crossword Wordmint

Corneal Reflex Wikipedia

Anatomy Of The Corneal Reflex Youtube

Neural Reflexes Human Physiology Openstax Cnx

Usmle Tutorial The Corneal Reflex Youtube
Draw The Labelled Diagram Of Reflex Homework Help Mycbseguide

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key

The Reflex Ppt Download

Chapter 15 Reflexes
Www Asu Edu Courses Pgs461 Reflexes arcs Pgs 461 Pdf

The Clinical Use Of Brainstem Reflexes And Hand Muscle Reflexes Sciencedirect

Reflex Arc

Lesson Video Reflex Actions

Schematic Representation Of Various Lesions Within The Brainstem A ϫ Download Scientific Diagram

Reflex Wikiwand

Schematic Representation Of The Blink Reflex Pathways And Sites Of Download Scientific Diagram
Reflexes Psychology Wiki Fandom

Reflex Physiology Britannica
Correlation Between Electromyographic Reflex And Mr Imaging Examinations Of The Trigeminal Nerve American Journal Of Neuroradiology
3
Corneal Reflex Testing In The Evaluation Of A Comatose Patient An Ode To Precise Semiology And Examination Skills Springerlink
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 41 6 538 Full Pdf
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf
Ocular Motor System Section 3 Chapter 7 Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston

Experiment The Patellar Reflex And Reaction

2 Minute Neuroscience Corneal Reflex Youtube

Blink Reflex
Blink Reflex

Blink Reflex Physiopedia
Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Blink Reflex Responses In The Second Patient With A Lesion On The Right Download Scientific Diagram

Plant And Animal Responses Reflex Actions Diagram Quizlet

Schematic Representation Of The Blink Reflex Pathways And Sites Of Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn And9gcqzqgojnj 6judjio9 Yhw5 170uzrddnmejhopprhy84cukx7n Usqp Cau

Neurons And Reflex Arcs Sciencemusicvideos
Blink Reflex Springerlink
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Eyelid Reflex An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Blink Reflex By Ck Authorstream

Control Of Eye Movements Flashcards Quizlet

Show Digrammatically The Reflex Arc In The Case Of Blinking Of Eyes Science Control And Coordination Meritnation Com

Blink Reflex
Http Www Sciencedirect Com Science Article Pii S Pdf Md5 312d558dcdf5e76d50e5b01ddeeb1f Pid 1 S2 0 S Main Pdf
Blink Reflex 1

Reflex Arc Prezentaciya Onlajn
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf

Basal Ganglia To Brainstem Pathways Influencing Reflex Open I

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
Reflex And Long Latency Musculoskeletal Key

Neural Reflexes Human Physiology Openstax Cnx

Chapter 29 33 Chapter 29 Reflex Arc And Reflexes Reflexes Automatic Response Without A Conscious Thought Involuntary Predictable Responses These Occur Course Hero
When Kicking The Doctor Is Good A Simple Reflex Frontiers For Young Minds
Tfos Dews Ii Report Pain And Sensation Tfos Tear Film Ocular Surface Society
Journals Viamedica Pl Neurologia Neurochirurgia Polska Article Download

Blink Reflex

Question Video Determining The Correct Pathway Of Nerve Impulses In A Reflex Action

Trigeminofacial Reflex A Means Of Detecting Proximity To Ophthalmic And Maxillary Divisions Of The Trigeminal Nerve During Surgery In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 121 Issue 5 14
The Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Course Divisions Teachmeanatomy
Blink Reflex
Reflexes

Reflexes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Reflexes 3 Corneal Reflex Youtube

Neuroanatomy Trigeminal Reflexes Article

Ag Remnev
Reflex Arc Of The First Component Of The Human Blink Reflex A Single Motoneurone Study Abstract Europe Pmc
Think Tank Centre The Reflex Arc
Blink Reflex Springerlink
Ready To Unlearn Nature

Reflexes And The Eye Eyewiki
13 8 Reflexes A Level Biology Student

Blink Reflex Authorstream
Www Asu Edu Courses Pgs461 Reflexes arcs Pgs 461 Pdf
Module 5 Communication Homeostasis Energy Ppt Download

Figure 3 From New Insights Into Mononuclear Phagocyte Biology From The Visual System Semantic Scholar
Blink Reflex Physiopedia
Corneal Reflex Testing In The Evaluation Of A Comatose Patient An Ode To Precise Semiology And Examination Skills Springerlink

The Blink Reflex Arc The Circuit For The Oligosynaptic R1 Component Is Download Scientific Diagram

Reflex Action And Reflex Arc Concepts Solved Questions And Videos

Reflex Physiology Britannica

Ocular Movements Visual Reflexes Medatrio
Reflex Arc Components Reflex Arc Arc Links
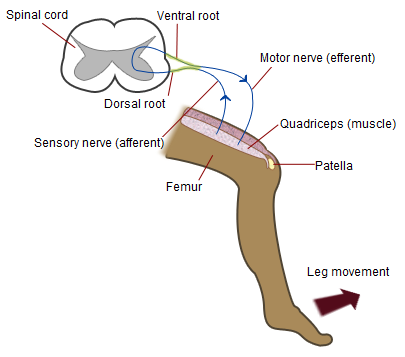
Patellar Reflex Wikipedia

The Corneal Reflex The Corneal Reflex Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook

Trigeminofacial Reflex A Means Of Detecting Proximity To Ophthalmic And Maxillary Divisions Of The Trigeminal Nerve During Surgery In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 121 Issue 5 14

Neural Reflexes Human Physiology Openstax Cnx

The Corneal Reflex The Corneal Reflex Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook

The Corneal Reflex The Corneal Reflex Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook

What Is Reflex Action And Reflex Arc Justscience
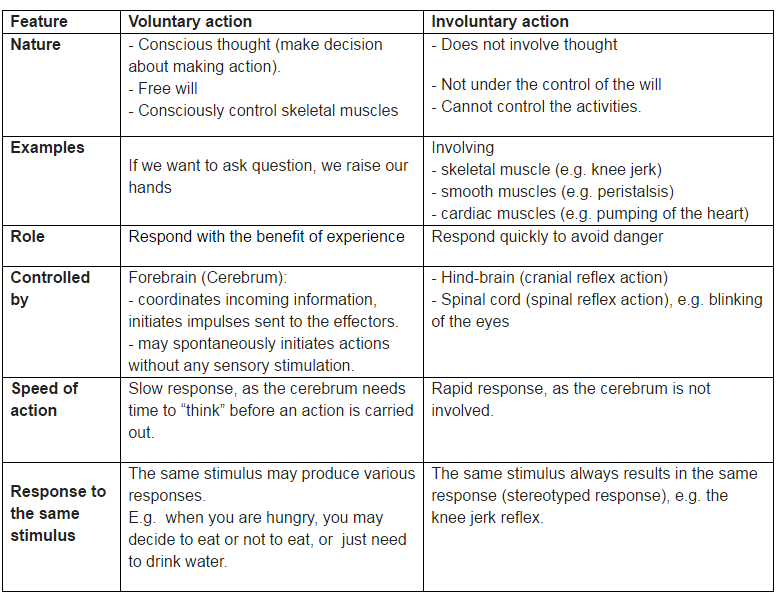
Reflexes And Reflex Action Definition Examples Diagrams

Solved 1 The Parasympathetic Division Of The Autonomic N Chegg Com
Q Tbn And9gcrj86uf3j5zfg 3jspwc3wmrglql95r J02qxhme8ndzzmlxqfg Usqp Cau
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Reflex Action Hourlybook

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
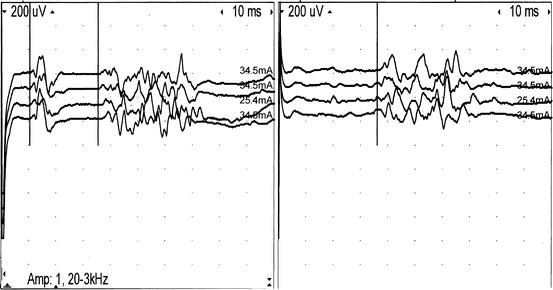
Blink Reflex Springerlink



