Anti Vegf Mechanism Of Action

Novel Pharmacotherapies In Diabetic Retinopathy Current Status And What S In The Horizon
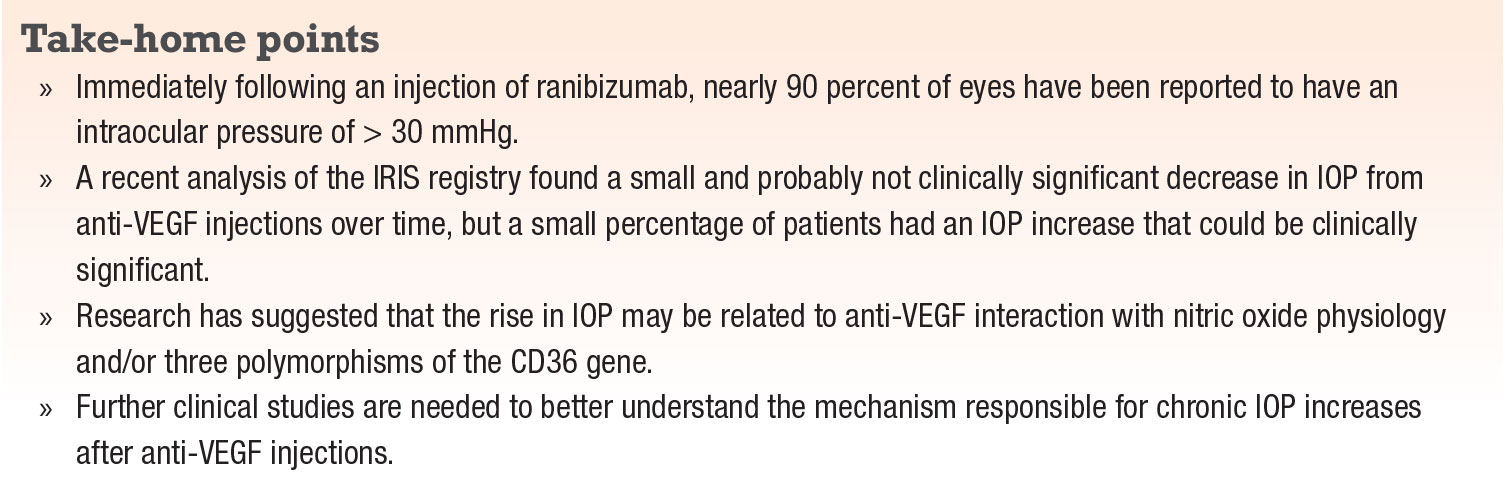
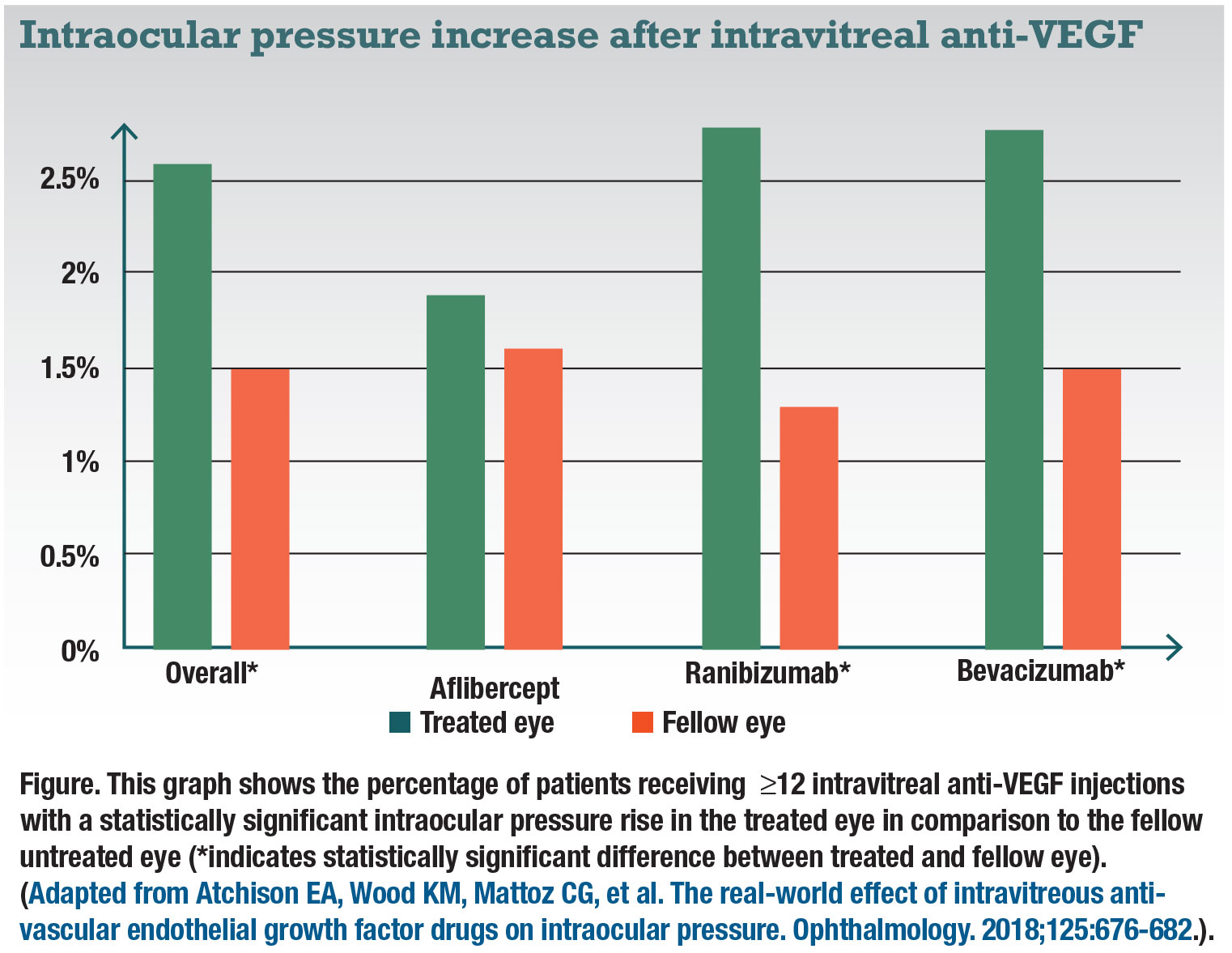
Iop And Anti Vegf Drugs What We Know So Far

Retinal Edema Mode Of Action Of Anti Vegf Therapies Ppt Download
Q Tbn And9gcqganpvqidhwl6c4ein7marvevlvm0tzrifpnjmdc17o1g1yj 9 Usqp Cau
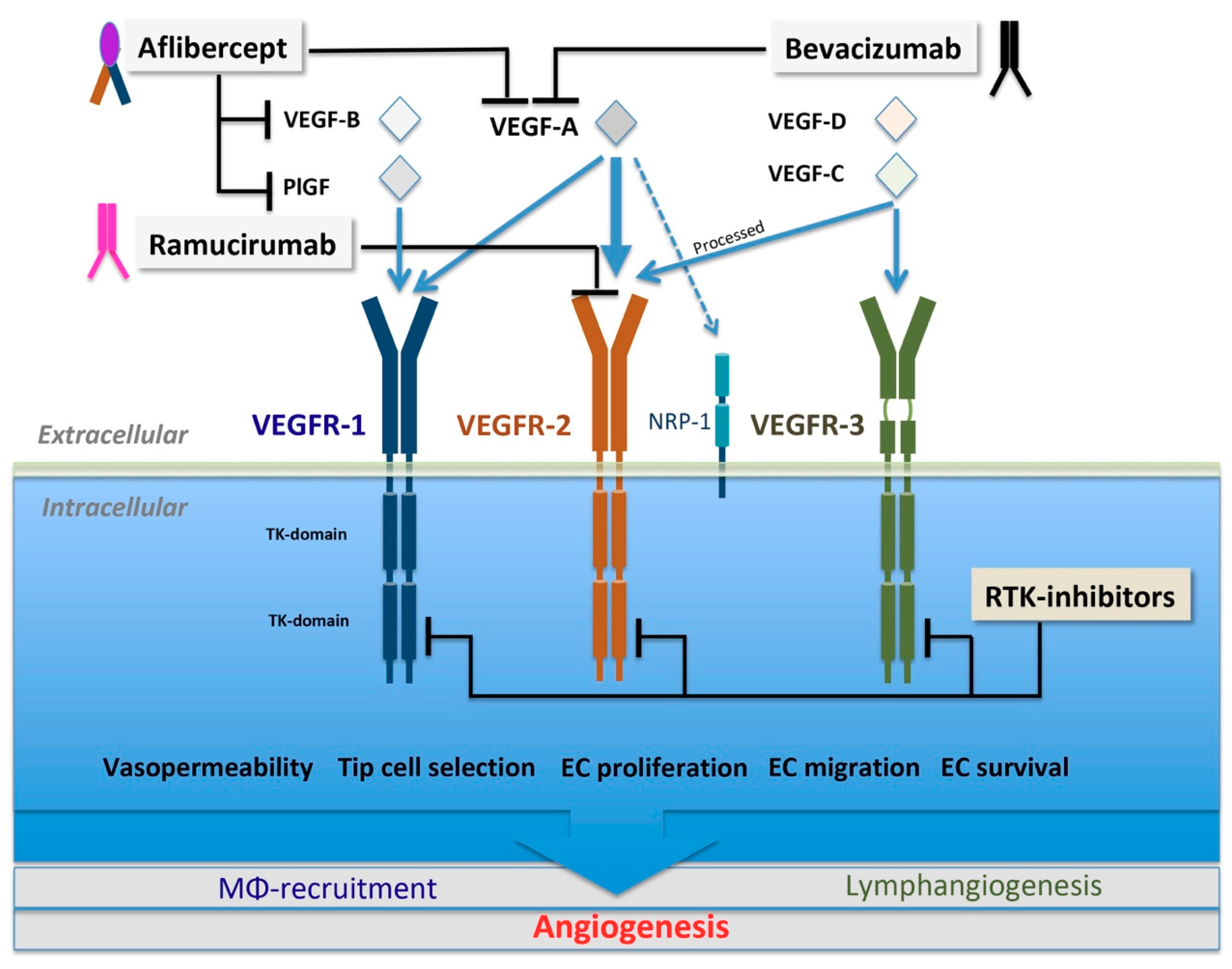
Cells Free Full Text Trends And Challenges In Tumor Anti Angiogenic Therapies Html
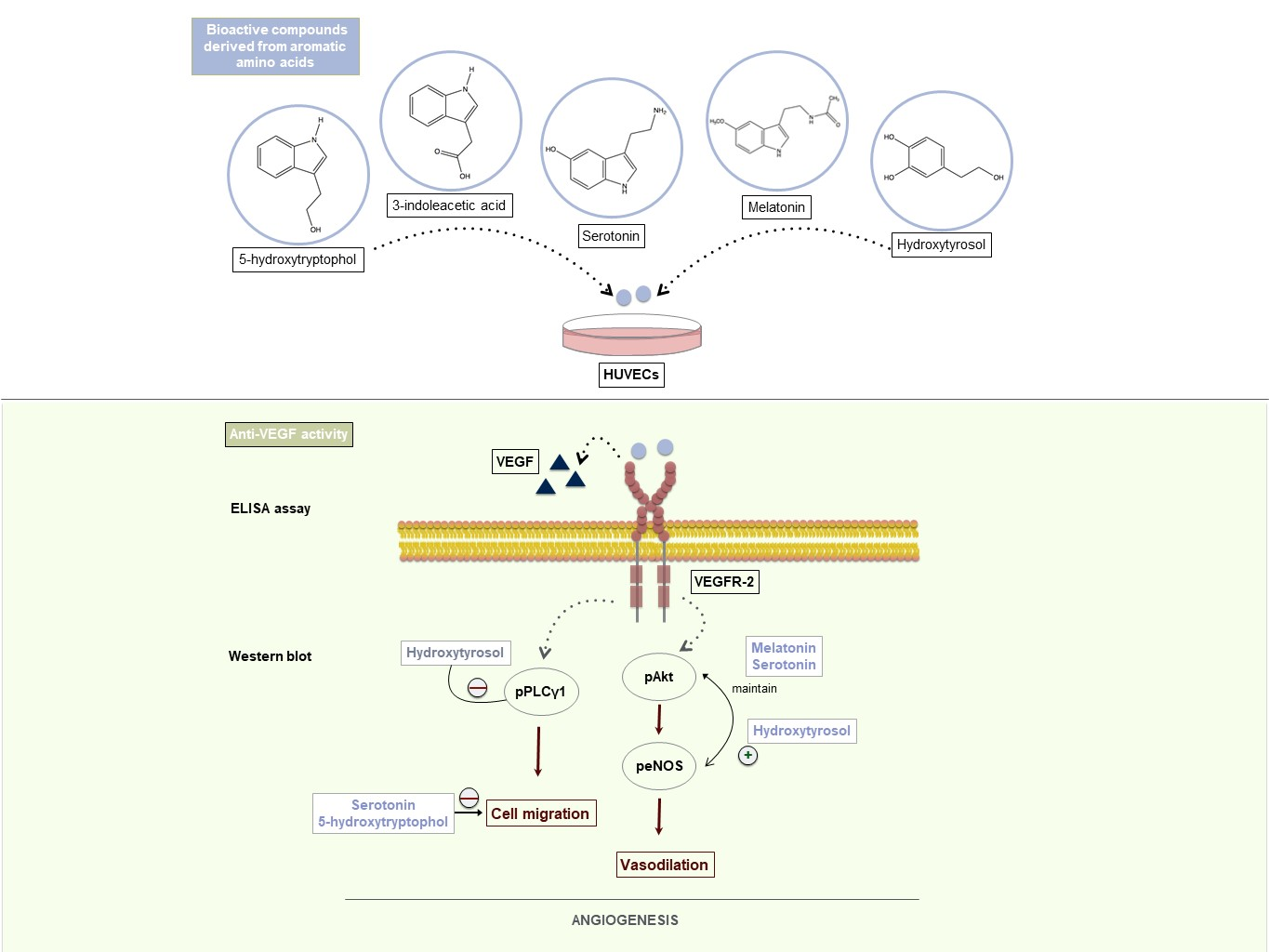
Nutrients Free Full Text Anti Vegf Signalling Mechanism In Huvecs By Melatonin Serotonin Hydroxytyrosol And Other Bioactive Compounds Html
First, to understand the mechanisms of action of antiVEGF agents further and, second, to identify and validate biomarkers for antiVEGF therapy Achieving this would enable optimization of different treatment protocols, establishment of appropriate tumor response criteria and, possibly, reduction of the adverse effects.
Anti vegf mechanism of action. AntiVEGF strategies show promise as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of CNV and are currently undergoing active clinical investigation Such strategies include antiVEGF antibodies, antiVEGF aptamer, gene therapy and protein kinase C inhibition This article reviews the mechanism of action and rationale for antiVEGF drugs in ARMD. Importantly, the mechanisms of action of antiVEGF therapy remain unknown Here, we discuss several potential mechanisms of action such as tumor vascular normalization, bone marrowderived cell recruitment blockade and cytostatic effects of antiVEGF therapy. However, these agents bring with them a set of side effects attributable to their unique mechanisms of action The anti VEGF agentsbevacizumab, aflibercept and ramucirumab, can result in renal and vascular complications such as hypertension, arterial thrombotic events (ATE), proteinuria and GI perforations.
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of visual impairment and preventable blindness, and represents a significant socioeconomic cost for health care systems worldwide Therefore, new approaches beyond current standards of diabetes care are needed Based on the crucial pathogenic role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the development of diabetic macular edema (DME. Purpose VEGFA blockade has been clinically validated as a treatment for human cancers Angiopoietin2 (Ang2) expression has been shown to function as a key regulator of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis Experimental Design We have applied the recently developed CrossMab technology for the generation of a bispecific antibody recognizing VEGFA with one arm based on bevacizumab (Avastin. 8579 Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM Vascular permeability factor/vascular.
Proposed Mechanism of Action Bevacizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody (initially it came from the mouse) that targets VEGFA, an isoform of VEGF that stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and subsequent migration 2 Bevacizumab specifically binds to the VEGFA protein, thereby inhibiting the process of angiogenesis (Fig 1). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/ vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitors are agents that inhibit the activity of VEGF and VEGFR VEGR and VEGFR (a tyrosine kinase receptor) signaling modulates angiogenesis, which involves making of new blood vessels from existing blood vessels. While expressed in normal tissues, VEGF is also present at physiologically relevant levels in tumors 28,29 A VEGF ligand binds to receptors on endothelial cells to help drive angiogenesis 3032 The mechanism of action of Avastin has been elucidated in preclinical models Its clinical significance is unknown.
TitleAntiVEGF Strategies – from Antibodies to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Background and Clinical Development in Human Cancer VOLUME 18 ISSUE 19 Author(s)Grzegorz Korpanty and Elizabeth Smyth AffiliationDepartment of Medical Oncology, Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, Ireland KeywordsTumour angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor, antiangiogenic therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bevasirinab (Opko, Inc) is another drug in clinical development with a different mechanism of action Bevasirinab utilizes siRNA technology to target the mRNA of VEGF, not the VEGF molecule itself Each siRNA molecule can inactivate hundreds to thousands of mRNAs. INLYTA (axitinib) and the VEGF pathway RCC is a highly vascular tumor, in which VEGF plays a key role VEGF acts on 3 receptors VEGFR1, 2, and 3, which are implicated in pathologic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression 9.
Mechanism of Action Aflibercept is a 115 kDa fusion protein It consists of an IgG backbone fused to extracellular VEGF receptor sequences of the human VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 As a soluble decoy receptor, it binds VEGFA with a greater affinity than its natural receptors. AntiVEGF strategies show promise as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of CNV and are currently undergoing active clinical investigation Such strategies include antiVEGF antibodies, antiVEGF aptamer, gene therapy and protein kinase C inhibition This article reviews the mechanism of action and rationale for antiVEGF drugs in ARMD. Interference with the action of vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor may play a central role in the placental hypoperfusion seen in preeclampsia VEGFtargeted therapy mechanisms of antitumour activity Nat Rev Cancer 08;.
During this live webinar, Dr Kazlauskas discusses how antiVEGF agents provide benefit by temporarily reducing the level of VEGF and overcoming vascular per. Mechanisms of action of the antiVEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells By Jakub Bogusz, Agata Majchrzak, Aleksandra Mędra, Barbara CebulaObrzut, Tadeusz Robak and Piotr Smolewski. In summary, the proposed mechanisms of action of antiVEGF therapy include normalization of tumor vasculature shortly after the initiation of treatment, direct action upon tumor cells, and.
In summary, the proposed mechanisms of action of antiVEGF therapy include normalization of tumor vasculature shortly after the initiation of treatment, direct action upon tumor cells, and. One type of treatment for DMO is antiVEGF This drug is given by means of an injection into the eye It can reduce the swelling at the back of the eye and prevent visual loss There are three main types of antiVEGF drugs in use aflibercept (Eyelea TM), bevacizumab (Avastin) and ranibizumab (Lucentis TM). When VEGF is attached to these drugs, it is unable to activate the VEGF receptor Other angiogenesis inhibitors bind to VEGF and/or its receptor as well as to other receptors on the surface of endothelial cells or to other proteins in the downstream signaling pathways, blocking their activities.
Education Lab Intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor (antiVEGF) treatment regimens have provided significant improvements to longterm visual outcomes in neovascular agerelated macular degeneration (nAMD) However, some patients do not receive an optimal response with current antiVEGF therapies, while poor adherence due to treatment burden remains a significant problem. TitleAntiVEGF Strategies – from Antibodies to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Background and Clinical Development in Human Cancer VOLUME 18 ISSUE 19 Author(s)Grzegorz Korpanty and Elizabeth Smyth AffiliationDepartment of Medical Oncology, Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, Ireland KeywordsTumour angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor, antiangiogenic therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The first work on antiVEGF aptamers, published in 1994, reported an initial set of high affinity RNA ligands selected for their ability to inhibit the binding of 125 IVEGF to its receptors in a concentrationdependent manner in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) Competition experiments on candidate antiVEGF aptamers revealed that they all bound to a similar site within the.
Types of anti angiogenesis treatment There are different types of drugs that block blood vessel growth Drugs that block blood vessel growth factor Some drugs block vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from attaching to the receptors on the cells that line the blood vessels This stops the blood vessels from growing. INLYTA (axitinib) and the VEGF pathway RCC is a highly vascular tumor, in which VEGF plays a key role VEGF acts on 3 receptors VEGFR1, 2, and 3, which are implicated in pathologic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression 9. Sorafenib (BAY ) is a pankinase inhibitor of raf kinase, VEGF receptor 2, and PDGF receptor β and is proposed to have a dual mechanism of action through targeting of tumor vasculature Sorafenib monotherapy has shown activity in tumors expressing wildtype and mutant ras, as well as mutant Braf.
In the case of bevacizumab, the mechanism of action is inhibition of a cell surface protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) This VEGF helps tumors to form new blood vessels and. The Ang2 inhibitor was administered alone or in combination with an antihuman VEGF antibody that neutralized the action of tumor cell–derived VEGF The Colo5 tumor model was used because of its documented sensitivity to Ang2 inhibitors (13). BI 60 is a humanized bispecific nanobody® (antibody fragments consisting of a single variable antibody domain) comprising blocking domains for VEGF and Ang2 and an additional portion for extending the halflife 1 By binding to VEGF and Ang2, BI 60 inhibits tumor angiogenesis and vascularization, and enhances the tumor microenvironment to support Tcell trafficking and function in the tumor, 1 making it a potential candidate for use in combination with PD1 inhibitors (eg BI ).
Development with a different mechanism of action Bevasirinab utilizes siRNA technology to target the mRNA of VEGF, not the VEGF molecule itself Each siRNA molecule can inactivate hundreds to thousands of mRNAs A phase 2 trial compared multiple doses of bevasirinab, with injections administered at baseline and 4 weeks. However, despite the known antiangiogenic mechanism of antiVEGF antibodies, relatively little is known about their effects on the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of other antibodies This study aimed to measure the disposition properties, with a particular emphasis on tumor uptake, of trastuzumab in the presence or absence of antiVEGF. VEGFaxis dependent and nonVEGF mediated mechanisms of resistance to antiangiogenic therapies NonVEGF axis receptors include TGFβ receptor, Tie2, PDGFR, FGFR, and Dll4Notch General mechanisms of action for zivAflibercept, bevacizumab, VEGFaxis dependent resistance mechanisms.
The decrease in tumor uptake of IgG confirms that at least one mechanism of action for antiVEGF is to produce vascular permeability changes in the tumor, whereas that of most normal organs was unaffected (Figs 3 and 4) This is an important observation, as it suggests that antiVEGF treatment has the potential to reduce antibody distribution. AntiVEGF strategies show promise as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of CNV and are currently undergoing active clinical investigation Such strategies include antiVEGF antibodies, antiVEGF aptamer, gene therapy and protein kinase C inhibition This article reviews the mechanism of action and rationale for antiVEGF drugs in ARMD. Mechanism of Action (proposed) Bevacizumab binds to soluble VEGF and inhibits the binding of VEGF molecules to its receptors on the surface of endothelial cells Bevacizumab is a nonspecific VEGF inhibitor with two binding sites per molecule Bevacizumab prevents all VEGFA isoforms from binding to endothelial cell receptors.
We review articles describing intravitreal injection of antiVEGF drug trials, while discussing the mechanisms of the action of antiVEGF antibodies, and also evaluating their outcomes Intraocular injections of antiVEGF drug are considered to be an effective treatment for macular edema after retinal vein occlusion, however, recurrent/persistent edema is common. Based on the antiVEGF mechanism of action for aflibercept see Clinical Pharmacology (121), treatment with Eylea may pose a risk to human embryofetal development Eylea should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Mans (9) Both BDNF and VEGF signaling converge on the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway (4, 18), which has also been implicated in ketamine’s mechanism of action (19, ) Understanding at a subcellular level how these ligands and their receptor systems interact, particularly with other proposed mechanisms of action.
Mans (9) Both BDNF and VEGF signaling converge on the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway (4, 18), which has also been implicated in ketamine’s mechanism of action (19, ) Understanding at a subcellular level how these ligands and their receptor systems interact, particularly with other proposed mechanisms of action. Additional studies are needed to better understand the mechanisms by which VEGF inhibition enhances ET expression and action There is limited evidence of a role of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in VSP inhibitor–induced hypertension. Mechanisms of action of the antiVEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells By Jakub Bogusz, Agata Majchrzak, Aleksandra Mędra, Barbara CebulaObrzut, Tadeusz Robak and Piotr Smolewski.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the most abundant and important mediator of angiogenesis in glioblastoma Multiple strategies have been developed to target VEGF/VEGF receptor (VEGFR)–mediated angiogenesis, including VEGF blockade, VEGF Trap, and suppression of VEGFR signaling via receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Mechanisms of resistance to antiangiogenic therapies can be broadly categorized into VEGFaxis dependent alterations, nonVEGF pathways, and stromal cell interactions Complimentary combinations of agents that inhibit alternative mechanisms of blood vessel formation may optimize inhibition of angiogenesis and improve clinical benefit for patients. Mechanisms of Action of Combination Therapies that Include AntiVEGF Targeting Effective antiVEGF agents should block the formation of new tumor vessels and prune the existing ones.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/ vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitors are agents that inhibit the activity of VEGF and VEGFR VEGR and VEGFR (a tyrosine kinase receptor) signaling modulates angiogenesis, which involves making of new blood vessels from existing blood vessels. In the case of bevacizumab, the mechanism of action is inhibition of a cell surface protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) This VEGF helps tumors to form new blood vessels and. TitleAntiVEGF Strategies – from Antibodies to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Background and Clinical Development in Human Cancer VOLUME 18 ISSUE 19 Author(s)Grzegorz Korpanty and Elizabeth Smyth AffiliationDepartment of Medical Oncology, Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, Ireland KeywordsTumour angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor, antiangiogenic therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Mans (9) Both BDNF and VEGF signaling converge on the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway (4, 18), which has also been implicated in ketamine’s mechanism of action (19, ) Understanding at a subcellular level how these ligands and their receptor systems interact, particularly with other proposed mechanisms of action. VEGF Trap (aflibercept) is a decoy of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 fused to an Fc segment of immunoglobulin G1 that prevents activation of the VEGFR by “trapping” circulating VEGF 39 Studies using preclinical models showed that VEGF Trap exerts antivascular effects by inducing rapid regression of existing tumor vessels 40 together with inhibiting the formation of new vessels and remodeling of the surviving vasculature 41. Additional studies are needed to better understand the mechanisms by which VEGF inhibition enhances ET expression and action There is limited evidence of a role of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in VSP inhibitor–induced hypertension.
Prompt panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) or antivascular endothelial growth factor (antiVEGF) treatment not required AND investigator and potential participant are willing to wait for development of highrisk characteristics (defined in protocol) to treat PDR. Mechanisms of action of the antiVEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells By Jakub Bogusz, Agata Majchrzak, Aleksandra Mędra, Barbara CebulaObrzut, Tadeusz Robak and Piotr Smolewski. In summary, the proposed mechanisms of action of antiVEGF therapy include normalization of tumor vasculature shortly after the initiation of treatment, direct action upon tumor cells, and inhibition of NO and the resulting tumor vasoconstriction.
Multiple cellular pathways influence the growth and metastatic potential of tumors This creates heterogeneity, redundancy, and the potential for tumors to bypass signaling pathway blockade, resulting in primary or acquired resistance Combining therapies that inhibit different signaling pathways has the potential to be more effective than inhibition of a single pathway and to overcome tumor. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a mitogen that plays a crucial role in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis It is involved in tumor survival through inducing tumor angiogenesis and by increasing chemoresistance through autocrine signaling Because of its importance in tumor formation and survival, several medications have been developed to inhibit VEGF and reduce blood vessel. Mechanism of action of angiogenesis inhibitors Bevacizumab binds to VEGF inhibiting its ability to bind to and activate VEGF receptors Sunitinib and Sorafenib inhibit VEGF receptors Sorafenib also acts downstream.
Although the precise mechanism of action may differ between these two classes of drugs, each ultimately inhibits EGFR signaling and the related downstream biologic effects The development of skin reactions that resemble acne or folliculitis appears to be a class effect related to EGFR inhibition. TitleAntiVEGF Strategies – from Antibodies to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Background and Clinical Development in Human Cancer VOLUME 18 ISSUE 19 Author(s)Grzegorz Korpanty and Elizabeth Smyth AffiliationDepartment of Medical Oncology, Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, Ireland KeywordsTumour angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor, antiangiogenic therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Mechanism of Action Humanized monoclonal antibody to VEGFA, inhibits VEGFAinduced ocular neovascularization Absorption Peak plasma time ~1 day Peak plasma concentration 17 ng/mL (05 mgdose) Excretion Halflife ~9 days (vitreous).
When VEGF is attached to these drugs, it is unable to activate the VEGF receptor Other angiogenesis inhibitors bind to VEGF and/or its receptor as well as to other receptors on the surface of endothelial cells or to other proteins in the downstream signaling pathways, blocking their activities. This appears to occur in 35 percent to 11 percent of patients receiving chronic antiVEGF agents 1719 It is unclear whether the etiology of this is mediated by the drugs’ mechanisms of action on the trabecular meshwork, hydrostatic damage to the trabecular meshwork, outflow impairment, a combination of these, or due to some other. INLYTA (axitinib) and the VEGF pathway RCC is a highly vascular tumor, in which VEGF plays a key role VEGF acts on 3 receptors VEGFR1, 2, and 3, which are implicated in pathologic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression 9.
What are VEGF/VEGFR inhibitors?.

Mechanisms Of Vegf Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Associated Hypertension And Vascular Disease Hypertension

Novel Pharmacotherapies For Diabetic Macular Edema Based On Mechanisms Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn And9gctws5a1yhj2ymkyyxw1vzczsykzyurnboo Jowxfdtjnzhfg8se Usqp Cau
Clinical Development Of Targeted And Immune Based Anti Cancer Therapies Journal Of Experimental Clinical Cancer Research Full Text

Targeting Vegf In Eye Neovascularization What S New A Comprehensive Review On Current Therapies And Oligonucleotide Based Interventions Under Development Sciencedirect
Iop And Anti Vegf Drugs What We Know So Far

Treat Science Of Dme
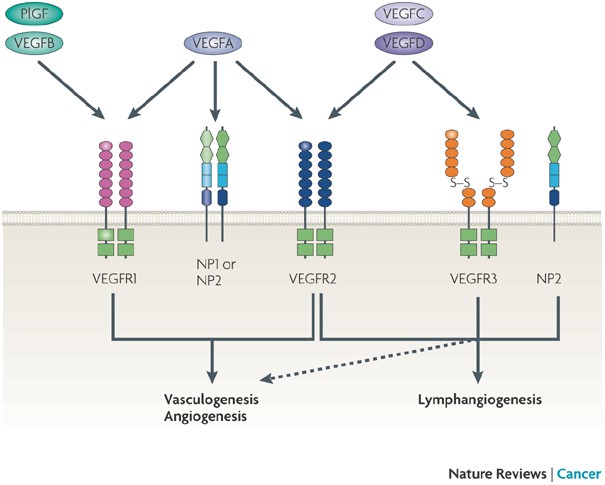
Vegf Targeted Therapy Mechanisms Of Anti Tumour Activity Nature Reviews Cancer

Colorectal Cancer
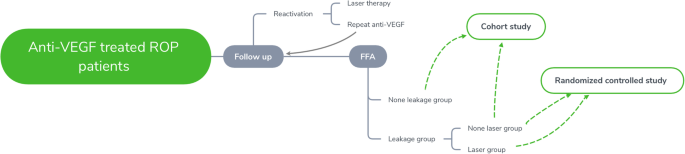
Study Protocol For Prognosis And Treatment Strategy Of Peripheral Persistent Avascular Retina After Intravitreal Anti Vegf Therapy In Retinopathy Of Prematurity Trials Full Text

Rationally Combining Anti Vegf Therapy With Checkpoint Inhibitors In Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy

Vegf Ang2 Inhibitor Investigational Compounds Inoncology

Vascular Toxicities With Vegf Inhibitor Therapies Focus On Hypertension And Arterial Thrombotic Events Sciencedirect

Avastin Bevacizumab Proposed Moa Mcrc Treatment

Mechanism Of Action Of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Vegf Download Scientific Diagram
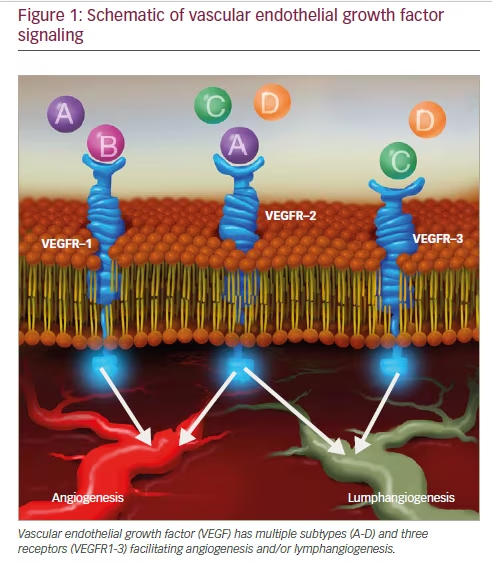
The Role Of Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Agents In The Management Of Retinopathy Of Prematurity Touchophthalmology

Retinal Physician Wet Amd In 18 Drugs In Development
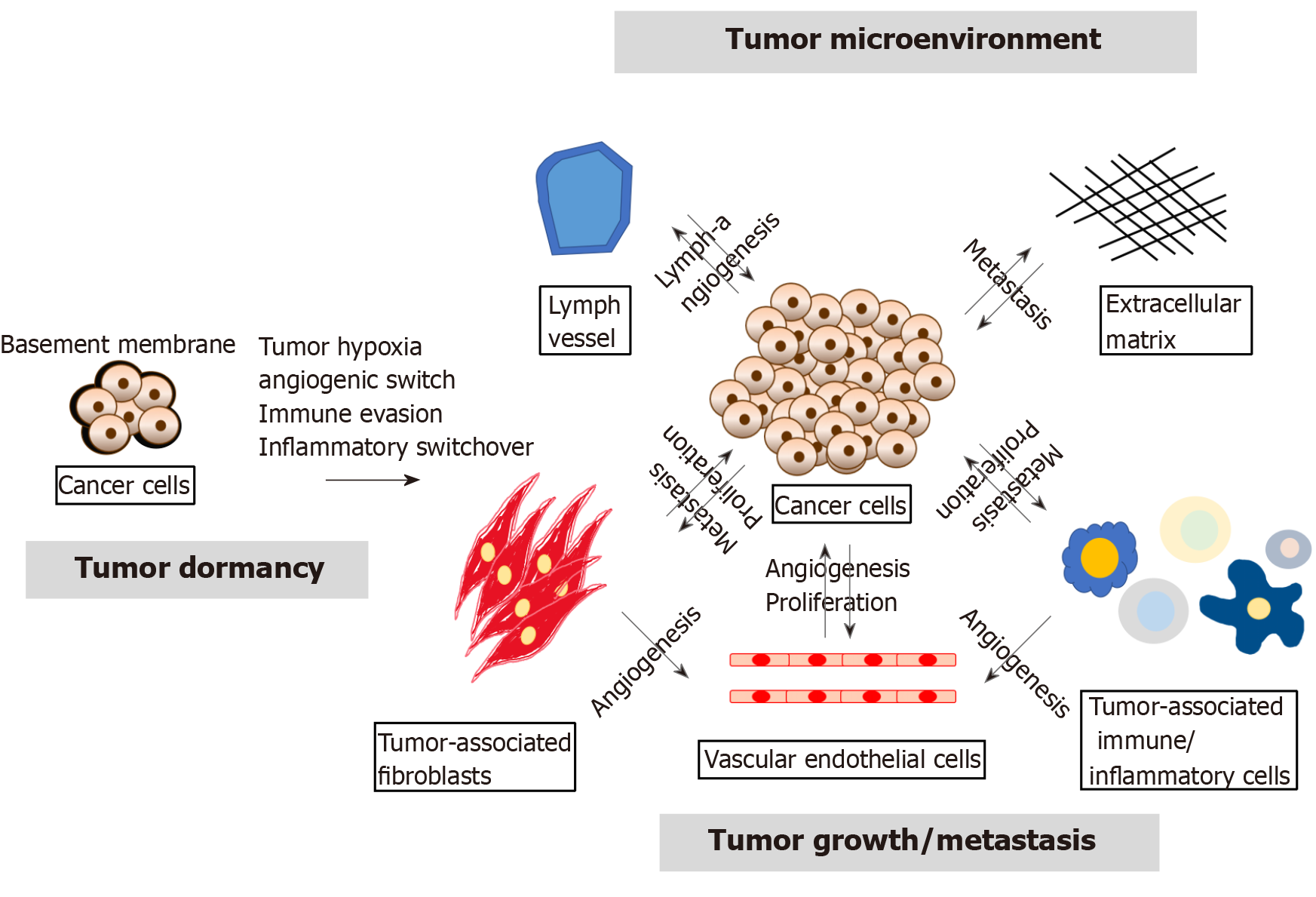
Tumor Progression Dependent Angiogenesis In Gastric Cancer And Its Potential Application
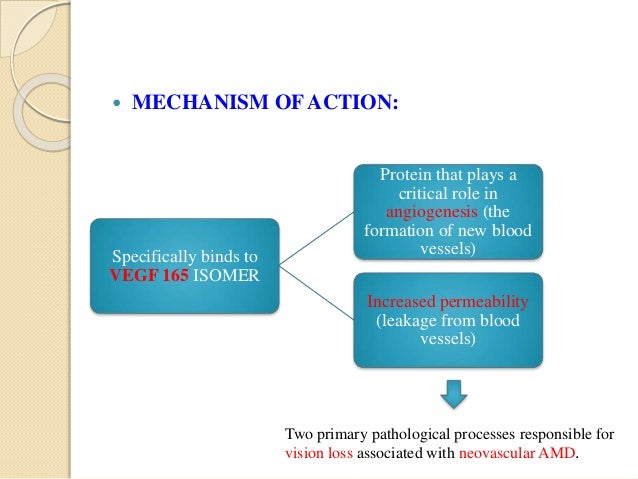
Anti Vegf S In Ophthalmology

Anti Vegf Molecular Targeted Therapies In Common Solid Malignancies Comprehensive Update For Radiologists Radiographics

Effects Of Novel Angiogenesis Inhibitors For The Treatment Of Cancer On The Cardiovascular System Circulation
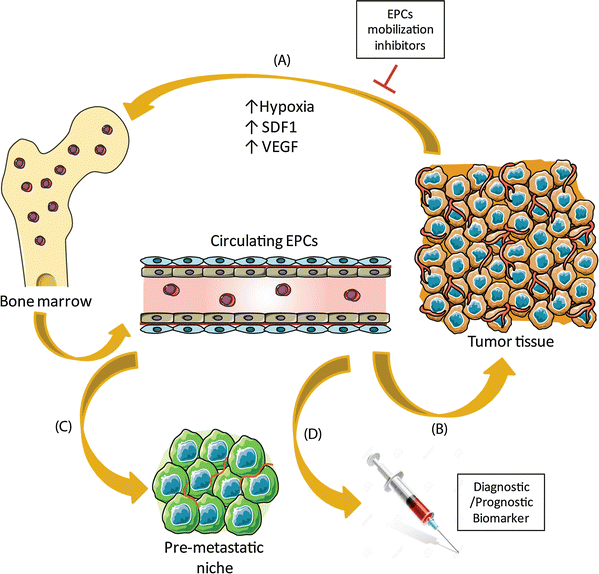
Mechanisms Of Anti Angiogenic Therapy Springerlink

Inoncology About Nintedanib
Www Cancertreatmentreviews Com Article S0305 7372 14 6 Pdf

The Role Of Vegf And Egfr Inhibition Implications For Combining Anti Vegf And Anti Egfr Agents Molecular Cancer Research
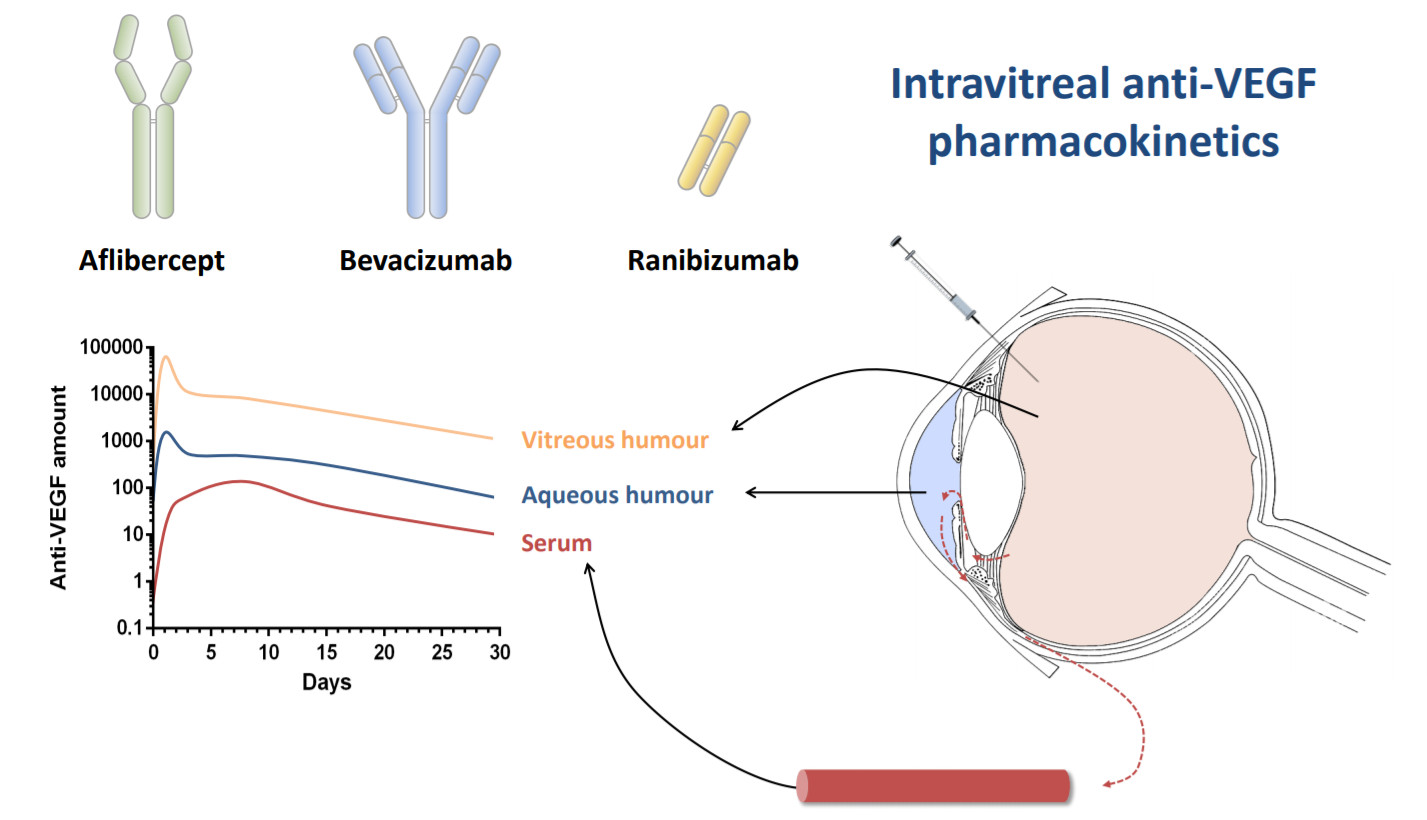
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Pharmacokinetics Of Intravitreal Anti Vegf Drugs In Age Related Macular Degeneration Html

Bevacizumab Classes Of Monoclonal Antibodies Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitors

Novel Therapeutic Targets In Diabetic Macular Edema Beyond Vegf Sciencedirect

Beovu Brolucizumab For The Treatment Of Wet Macular Degeneration

Aflibercept Clinical Cancer Research

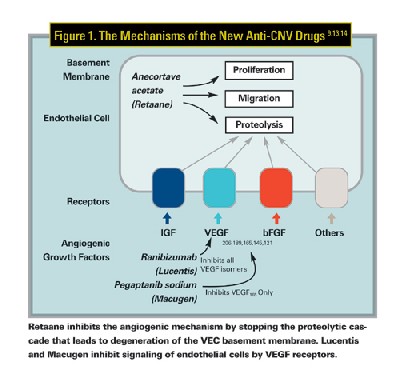
Pdf Introduction Mechanism Of Action And Rationale For Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Drugs In Age Related Macular Degeneration Semantic Scholar

Mechanism Of Action Of Anti Vegf Agents In Colorectal Cancer Adapted Download Scientific Diagram
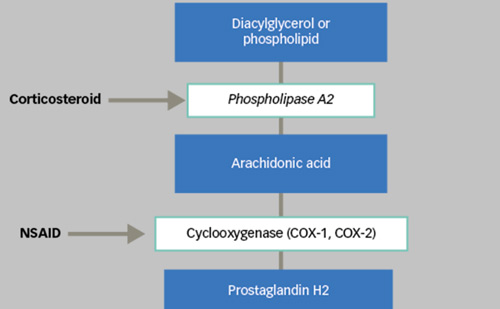
The Role Of Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Agents In The Management Of Retinopathy Of Prematurity Touchophthalmology

Ifor Williams Ar Twitter Bonus Mechanism Of Action For Anti Vegf In Cancer Paper By Kim Et Al From Kaist In Sciimmunology Hints That Anti Vegf Approved As Tumor Angiogenesis Inhibitor Blocks Tox Dependent Cd8
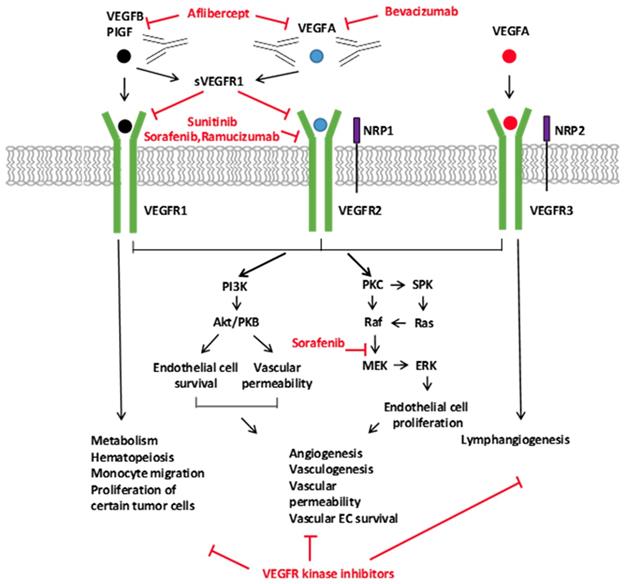
Angiogenesis In Breast Cancer Progression Diagnosis And Treatment
Http Www Ijbcp Com Index Php Ijbcp Article Download 1349 12

Off Tumor Targets Compromise Antiangiogenic Drug Sensitivity By Inducing Kidney Erythropoietin Production Pnas
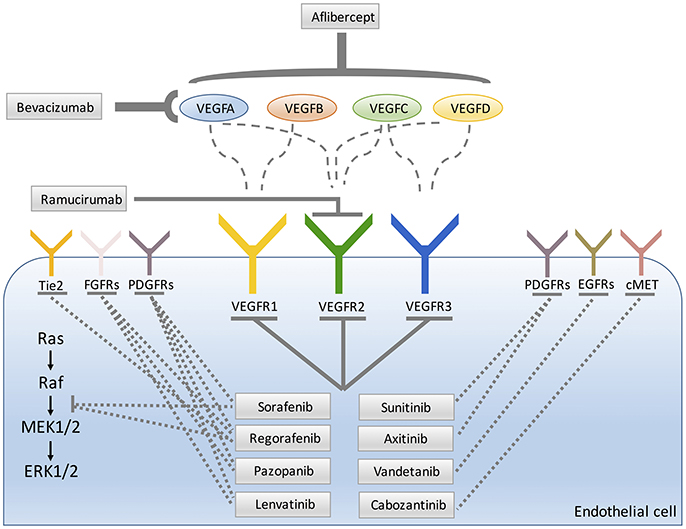
Frontiers Therapy For Cancer Strategy Of Combining Anti Angiogenic And Target Therapies Cell And Developmental Biology

Angiogenesis Inhibitor Wikipedia

Treat Science Of Dme

Ocular Anti Vegf Therapy For Diabetic Retinopathy The Role Of Vegf In The Pathogenesis Of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes Care

Aflibercept Mechanism Of Action Aflibercept Binds To Vegf A D And Pigf Download Scientific Diagram
1

Anti Vegf For The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
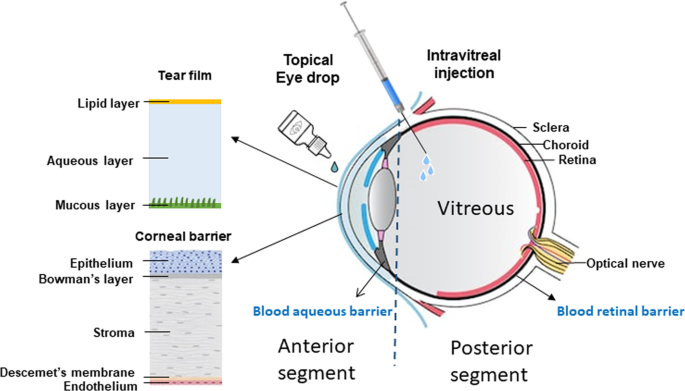
Use Of Biomaterials For Sustained Delivery Of Anti Vegf To Treat Retinal Diseases Eye

Retinal Physician Topical Delivery Of Retinal Drugs

Using The Past To Inform The Future Anti Vegf Therapy As A Road Map To Develop Novel Therapies For Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes
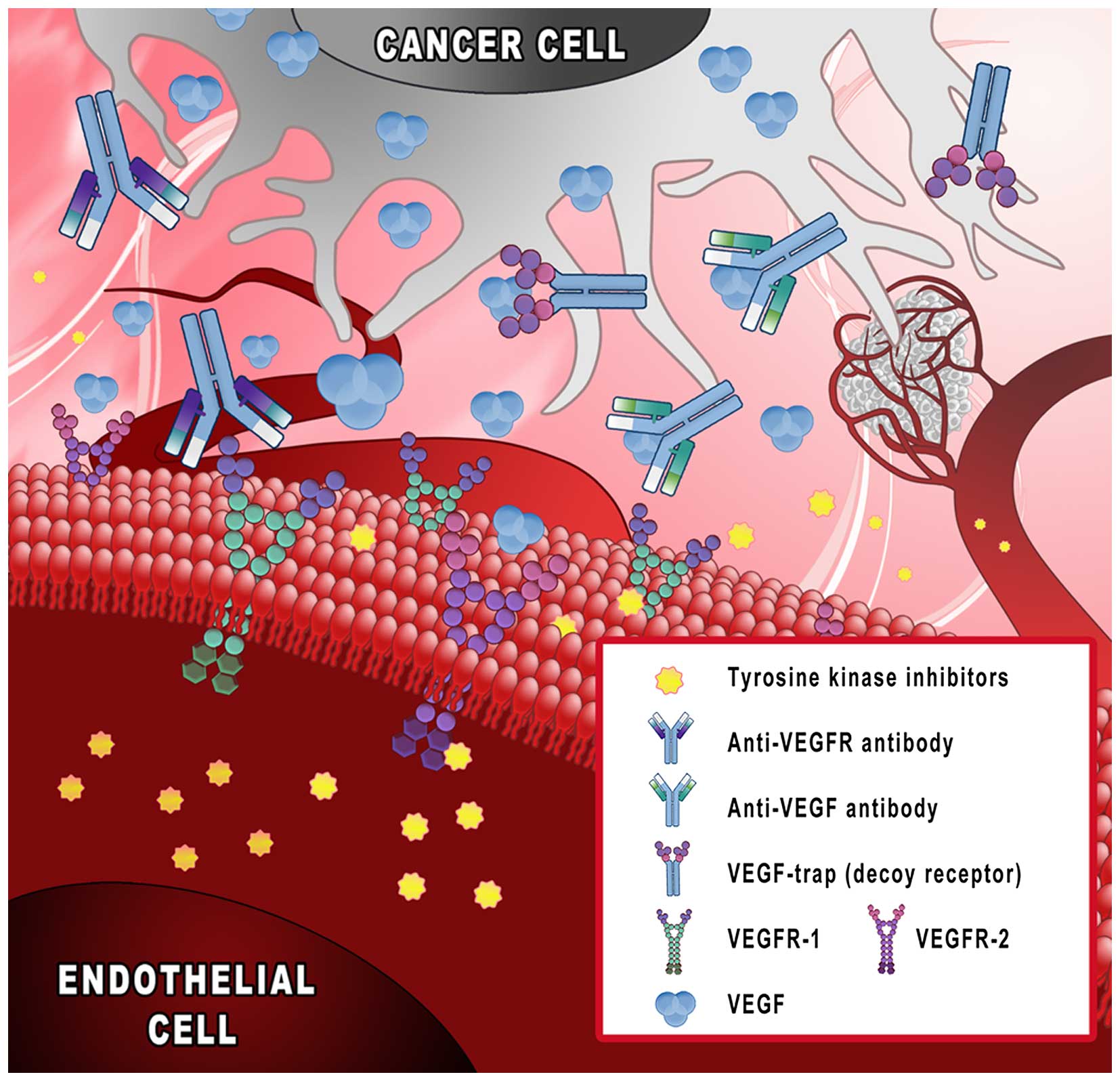
Antiangiogenic Cancer Treatment The Great Discovery And Greater Complexity Review

Direct Effects Of Anti Angiogenic Therapies On Tumor Cells Vegf Signaling Trends In Molecular Medicine

Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Targeted Therapy In Renal Cell Carcinoma Current Status And Future Directions Clinical Cancer Research
Mp0250 A Vegf And Hgf Neutralizing Darpin Molecule Shows High Anti Tumor Efficacy In Mouse Xenograft And Patient Derived Tumor Models Oncotarget

Anti Angiogenic Alternative And Complementary Medicines For The Treatment Of Endometriosis A Review Of Potential Molecular Mechanisms

Targeting Vegf In Eye Neovascularization What S New A Comprehensive Review On Current Therapies And Oligonucleotide Based Interventions Under Development Sciencedirect
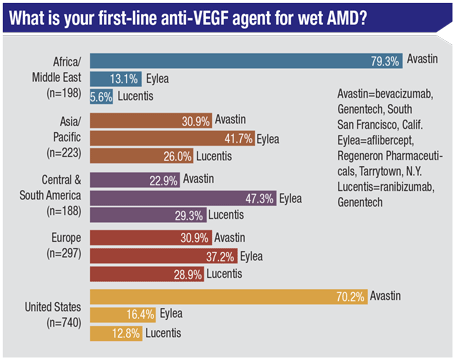
Anti Vegf 19 The State Of The Art
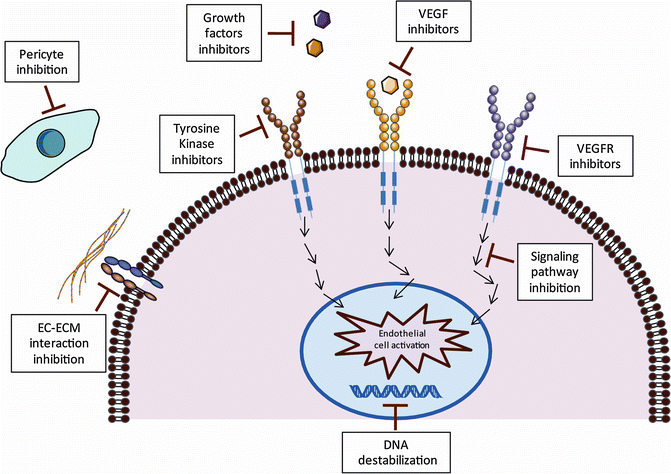
Mechanisms Of Anti Angiogenic Therapy Springerlink
Gale Onefile Health And Medicine Document Anti Vegf For The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema

Swiss Medical Weekly Role Of Tumour Angiogenesis In Haematological Malignancies

Anti Vegf S In Ophthalmology
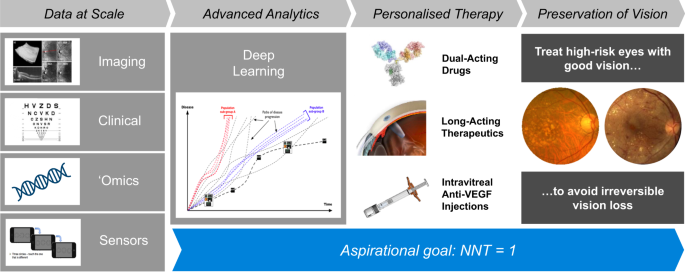
Building On The Success Of Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy A Vision For The Next Decade Eye
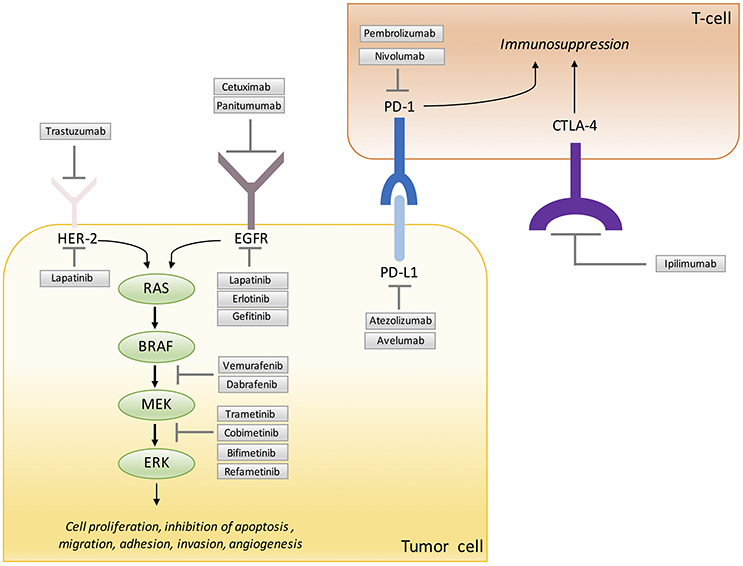
Frontiers Therapy For Cancer Strategy Of Combining Anti Angiogenic And Target Therapies Cell And Developmental Biology

Full Text Resistance To Anti Vegf Therapy In Neovascular Age Related Macular Deg Dddt

Amd New Therapies New Mechanisms
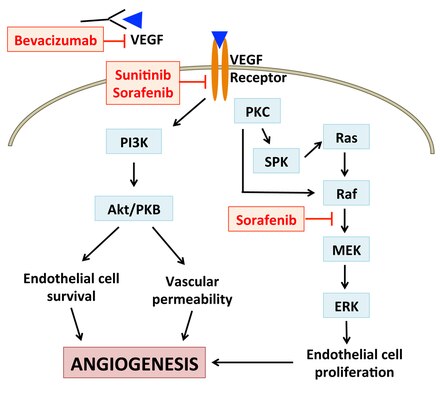
Angiogenesis Inhibitor Wikiwand

Ocular Anti Vegf Therapy For Diabetic Retinopathy The Role Of Vegf In The Pathogenesis Of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes Care

Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Vegf Sigma Aldrich
Focus Opthea Wet Amd And Dme Therapies
Q Tbn And9gctwa2chdm7lcdakvyg0sgvh8wum25btq8x8psqtt5e7hpliwqyj Usqp Cau

Anti Angiogenic And Anti Scarring Dual Action Of An Anti Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Aptamer In Animal Models Of Retinal Disease Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
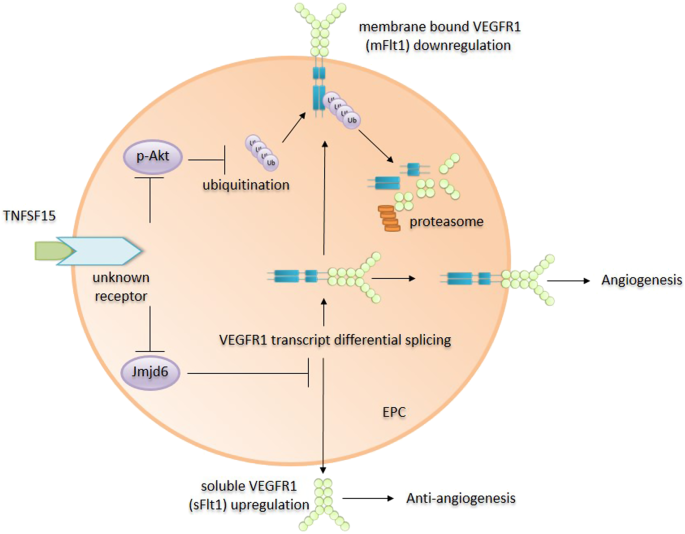
Counterbalance Modulation Of Vegf Vegfr Activities By Tnfsf15 Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy
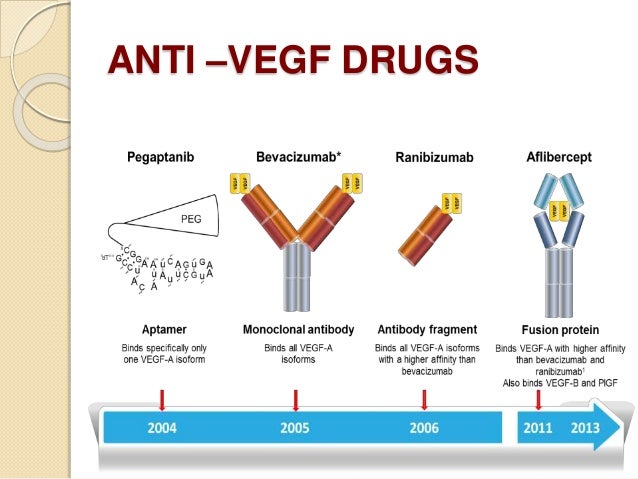
Anti Vegf Facts Myths
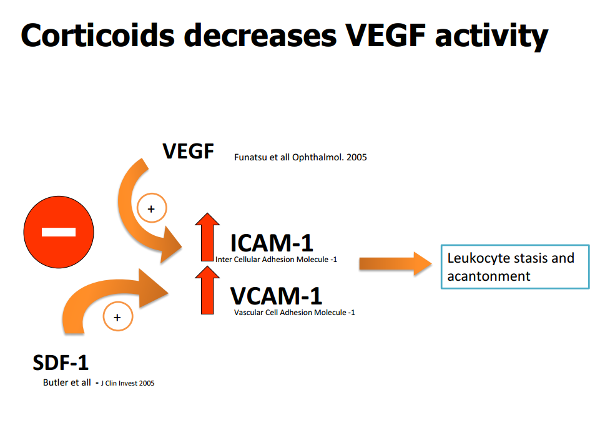
Combined Treatment Www Amdbook Org
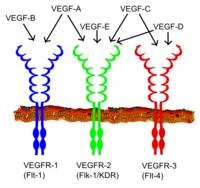
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Wikipedia

Current Treatment
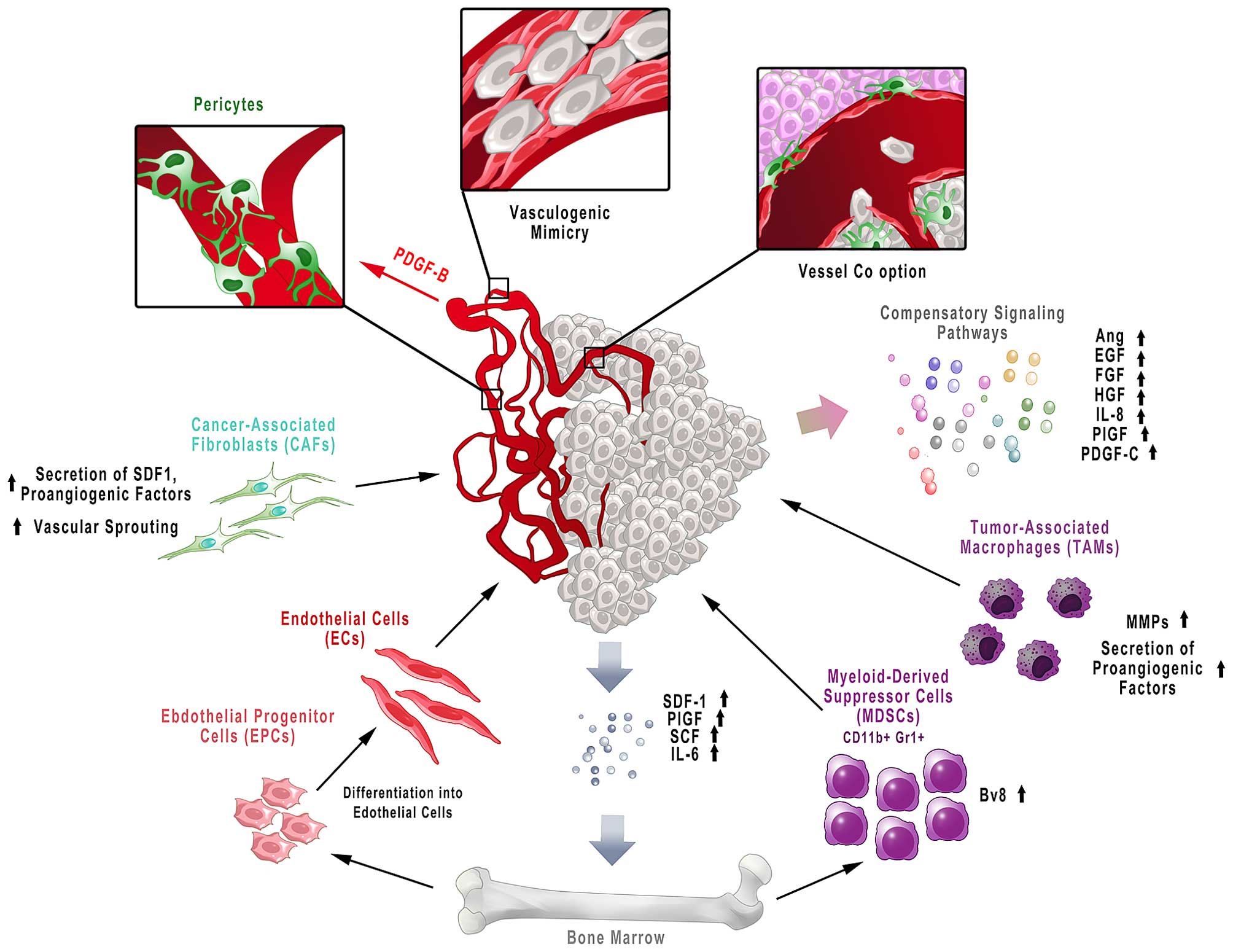
Antiangiogenic Cancer Treatment The Great Discovery And Greater Complexity Review

Mechanism Of Action Cabometyx Cabozantinib For Healthcare Professionals
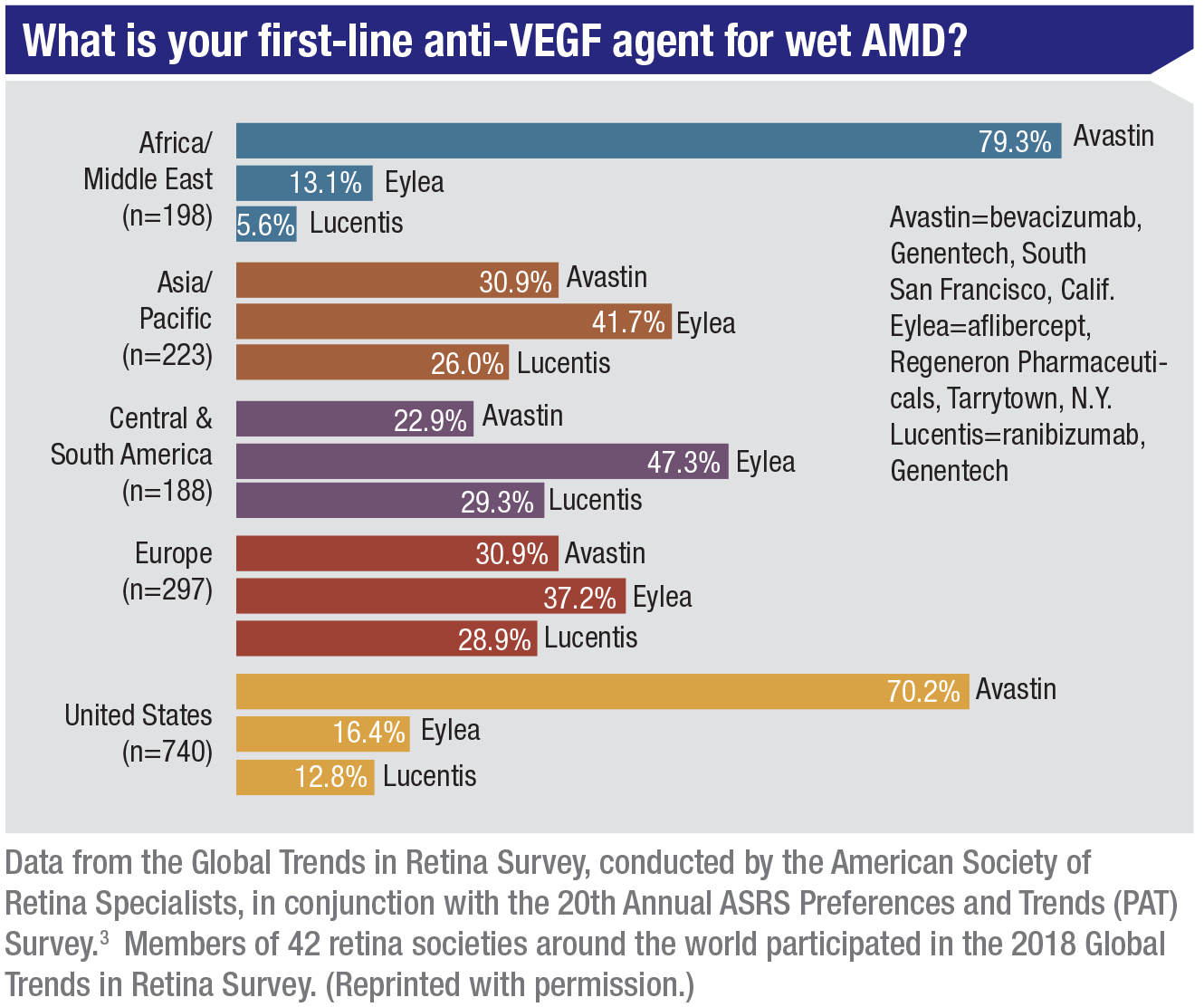
Anti Vegf 19 The State Of The Art
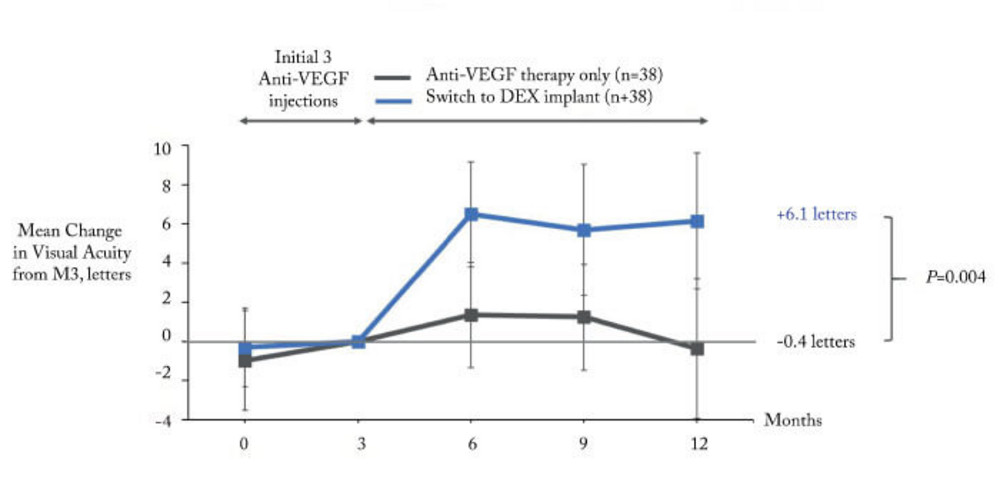
Responding To Non Responders

Anti Vegf S In Ophthalmology

Retinal Physician The Mechanism Of The Bi Specific Antibody Faricimab

Ocular Therapeutix Inc Current Report 8 K

Using The Past To Inform The Future Anti Vegf Therapy As A Road Map To Develop Novel Therapies For Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes

Therapeutic Inhibition Of Vegf Signaling And Associated Nephrotoxicities American Society Of Nephrology

Aflibercept In Pediatric Solid Tumors Moving Beyond The Trap Clinical Cancer Research
Www Cell Com Cell Pdf S0092 8674 19 6 Pdf

Mechanisms Of Vegf Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Associated Hypertension And Vascular Disease Hypertension
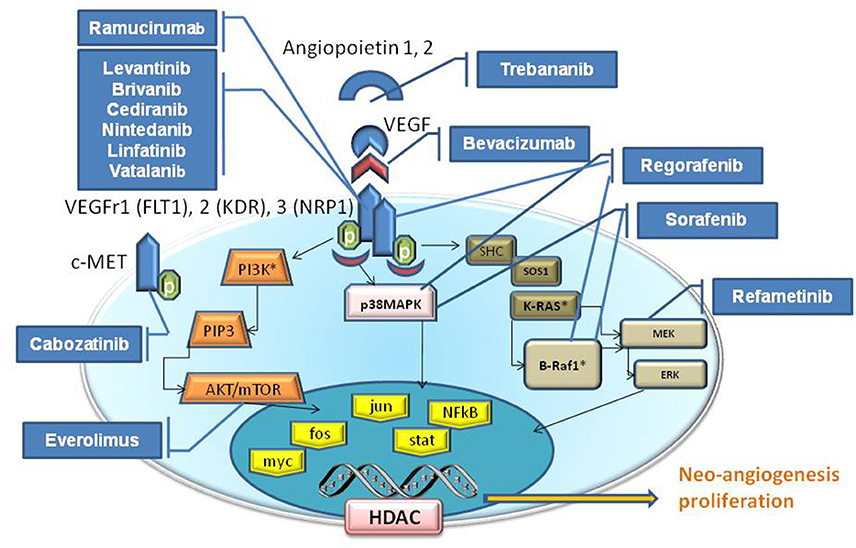
Frontiers Angiogenesis Inhibitors For The Treatment Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pharmacology

Indian Journal Of Ophthalmology Table Of Contents

Novel Treatment Strategies For Diabetic Eye Disease Retina Today
Http Ir Oncobiologics Com Static Files Dd 7472 49ba 9304 C35c50d2a2

Therapeutic Inhibition Of Vegf Signaling And Associated Nephrotoxicities American Society Of Nephrology

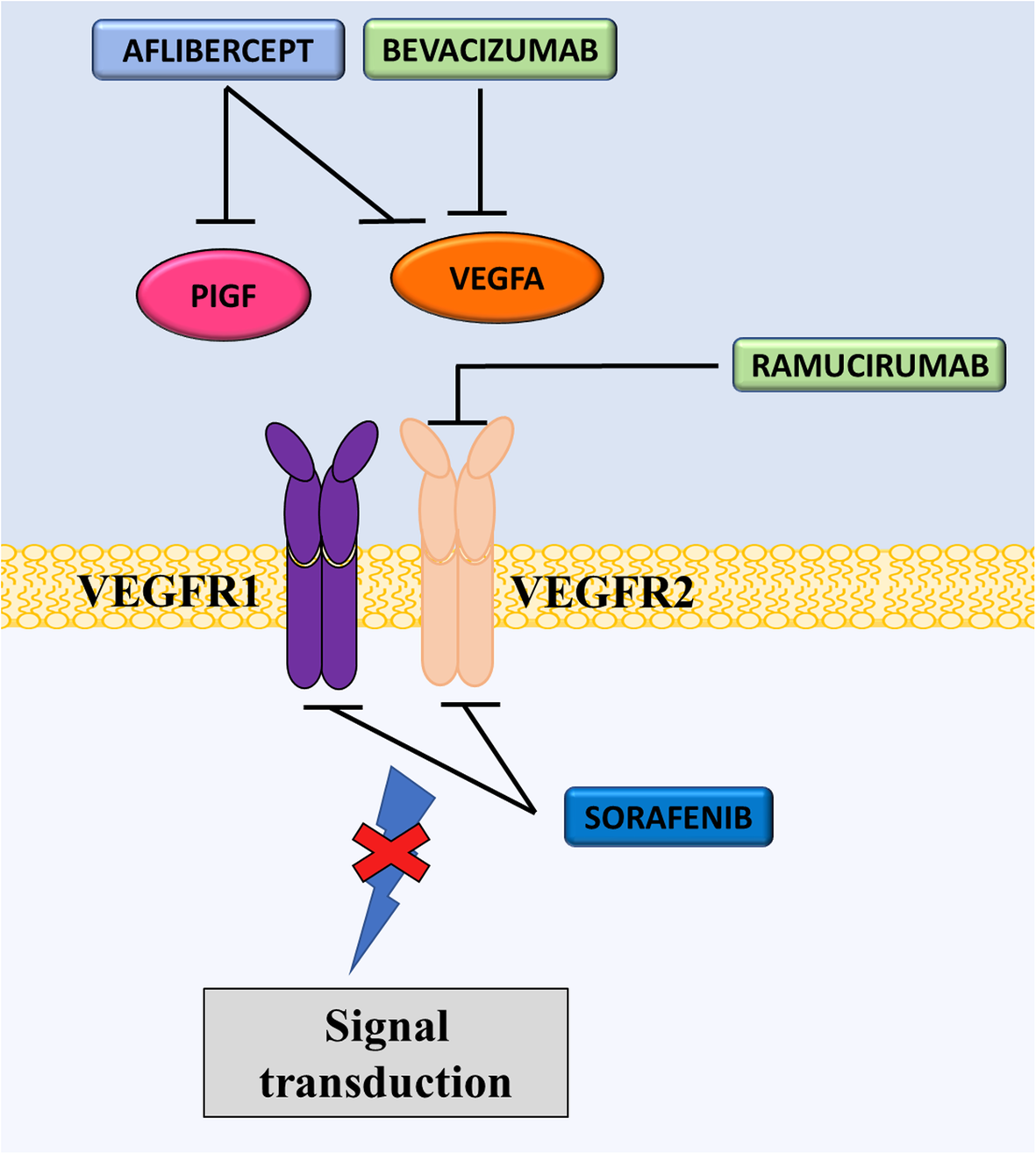
Mechanism Of Action Of Ramucirumab Vegf Vascular Endothelial Growth Download Scientific Diagram
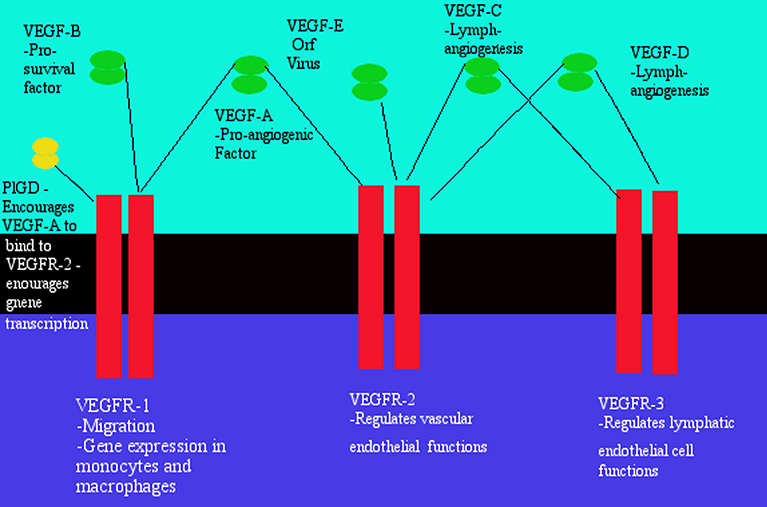
Anti Vegf Therapy In Cancer A Double Edged Sword Intechopen
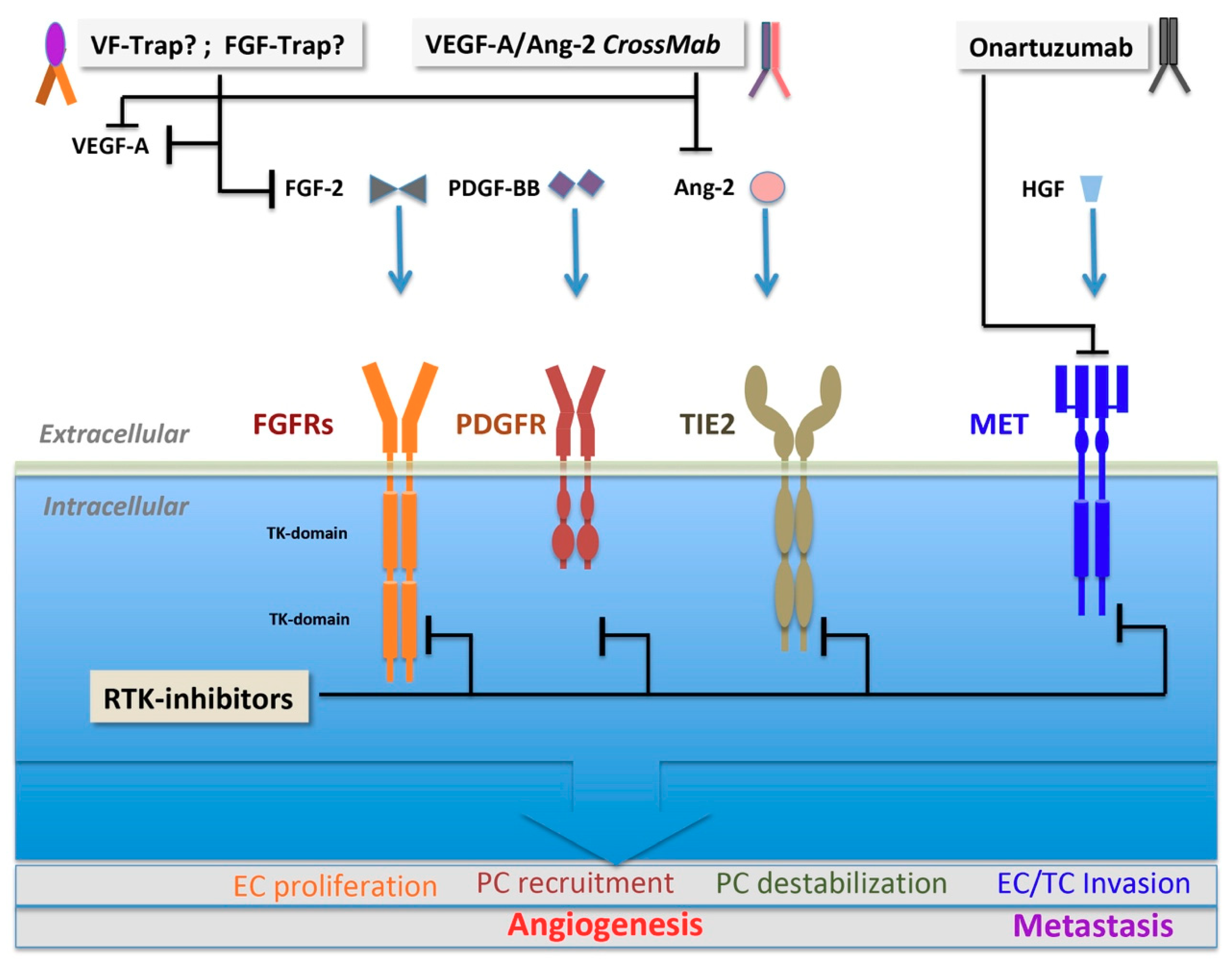
Cells Free Full Text Trends And Challenges In Tumor Anti Angiogenic Therapies Html

Vegf Bioassay
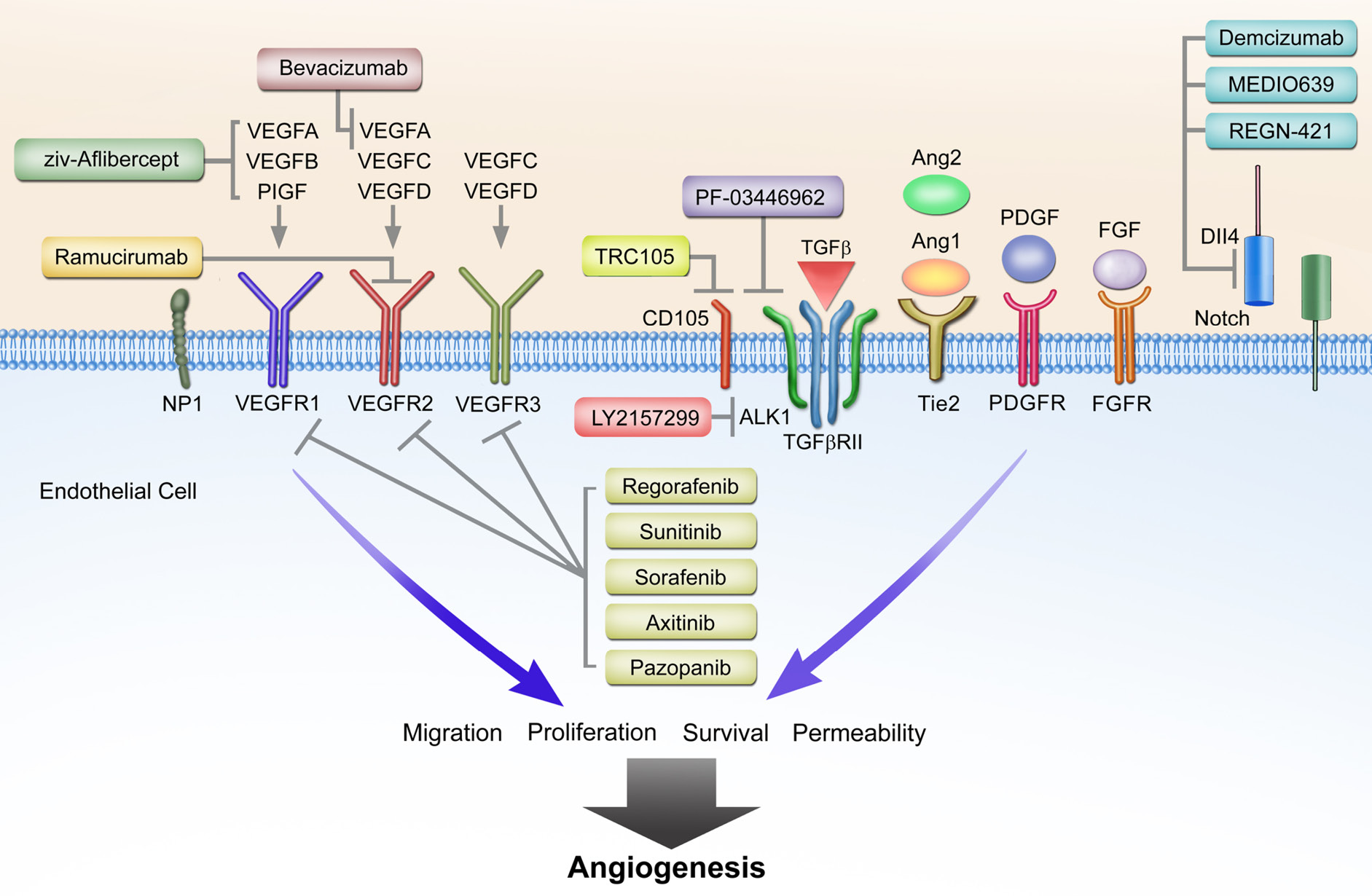
Understanding And Targeting Resistance To Anti Angiogenic Therapies Clarke Journal Of Gastrointestinal Oncology

Brolucizumab Evolution Through Preclinical And Clinical Studies And The Implications For The Management Of Neovascular Age Related Macular Degeneration Ophthalmology

Ramucirumab Successfully Targeting Angiogenesis In Gastric Cancer Clinical Cancer Research

Bevacizumab Avastin In Cancer Treatment A Review Of 15 Years Of Clinical Experience And Future Outlook Cancer Treatment Reviews



