Blink Reflex Anatomy

Vertebrobasilar Stroke Overview Of Vertebrobasilar Stroke Anatomy Of The Vertebral And Basilar Ar Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
Blink Reflex
Q Tbn And9gcsv8wltanerpi23ufbb1adqwwmizej4gkc5 8ttup25ebdisi Usqp Cau

An Explanation For Reflex Blink Hyperexcitability In Parkinson S Disease I Superior Colliculus Journal Of Neuroscience

The Corneal Reflex The Corneal Reflex Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook
The reflex helps to maintain muscles at a constant length A common example of this reflex is the knee jerk that is elicited by a rubber hammer struck against the patellar ligament in a physical exam A specialized reflex to protect the surface of the eye is the corneal reflex, or the eye blink reflex When the cornea is stimulated by a tactile.

Blink reflex anatomy. Anatomy of the blink reflex We know the corneal reflex (to a tactile stimulus) is propagated via the trigeminal nucleus and then to the motor parts of the blink reflex How would a flash light stimulus complete the reflex ark?. The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye).
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus The blink reflex also occurs when sounds greater than 40–60 dB are made Click to see full answer. Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibited by newborns upon coming of objects near it Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye It can be elicited by shining a strong light (eg flashlight, otoscope light, etc) on the eyes Blink reflex can also be elicited by a sudden movement of an object towards the eye. The blink reflex is a reflex which is designed to naturally protect the eyes Most animals with eyes have some form of this reflex, and the reflex is present from the time that an animal first opens its eyes.
R1 blink reflex and SP1 masseter inhibitory reflex Axial (left) and sagittal (right) pontine sections Statistical results of the comparison between patients with an abnormal ( n = 50) and those with a normal ( n = 125) early blink reflex (R1) and comparison between patients with an abnormal ( n = 54) and those with a normal ( n = 99) early. Blink reflex anatomy The afferent loop of the blink reflex is mediated by the first division of the trigeminal nerve (V 1 ), which synapses with both the main sensory nucleus of cranial nerve V (V M ) in the midpons and the nucleus of the spinal tract of cranial nerve V (V S ) in the medulla. Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibited by newborns upon coming of objects near it Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye It can be elicited by shining a strong light (eg flashlight, otoscope light, etc) on the eyes.
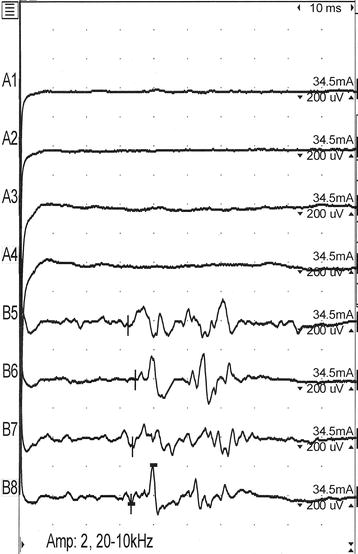
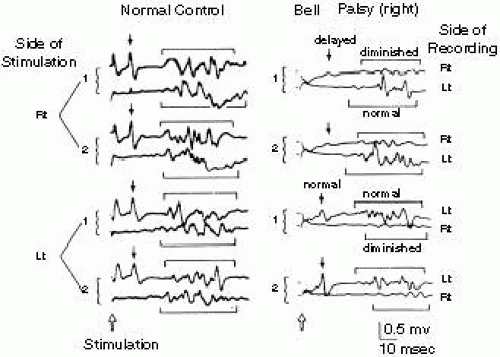
Blink reflex parameters in response to trigeminal stimulation with and without administration of a noxious compound (ingestion of hypertonic saline) and various environmental stimuli 132 Anatomy and Measurement of the Blink Reflex _____ 133 Nociceptive Blink Reflex _____ 23. The blink reflex neurophysiology and anatomy are reasonably well known The electromyography records of an electrically evoked blink reflex showed at least two components ( R 1 and R 2 components) The first or early response ( R 1 ) is brief and occurs after a latency of approximately 10 ms on the side of stimulation 19. Anatomy of the blink reflex We know the corneal reflex (to a tactile stimulus) is propagated via the trigeminal nucleus and then to the motor parts of the blink reflex How would a flash light stimulus complete the reflex ark?.
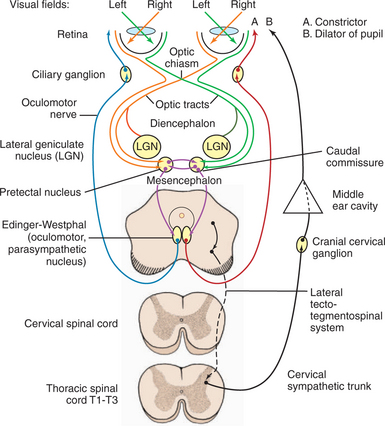
A specialized reflex to protect the surface of the eye is the corneal reflex, or the eye blink reflex When the cornea is stimulated by a tactile stimulus, or even by bright light in a related reflex, blinking is initiated. The pupillary light reflex involves sensory input through the optic nerve and motor response through the oculomotor nerve to the ciliary ganglion, which projects to the circular fibers of the iris As shown in this short animation, pupils will constrict to limit the amount of light falling on the retina under bright lighting conditions. A specialized reflex to protect the surface of the eye is the corneal reflex, or the eye blink reflex When the cornea is stimulated by a tactile stimulus, or even by bright light in a related reflex, blinking is initiated.
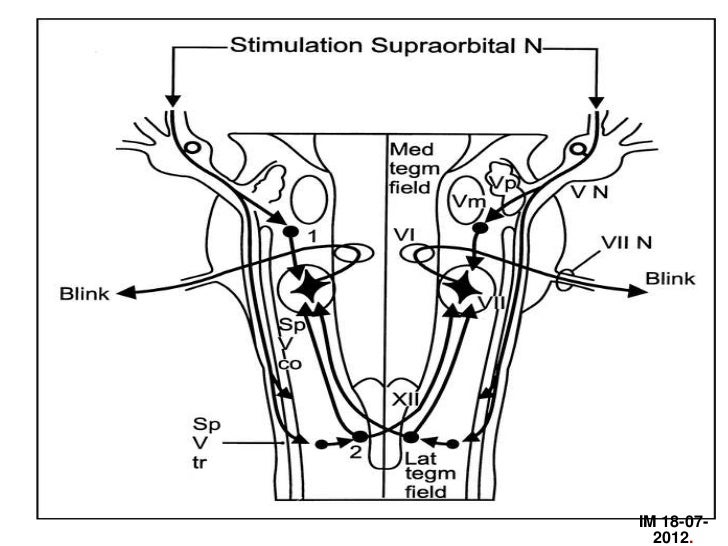
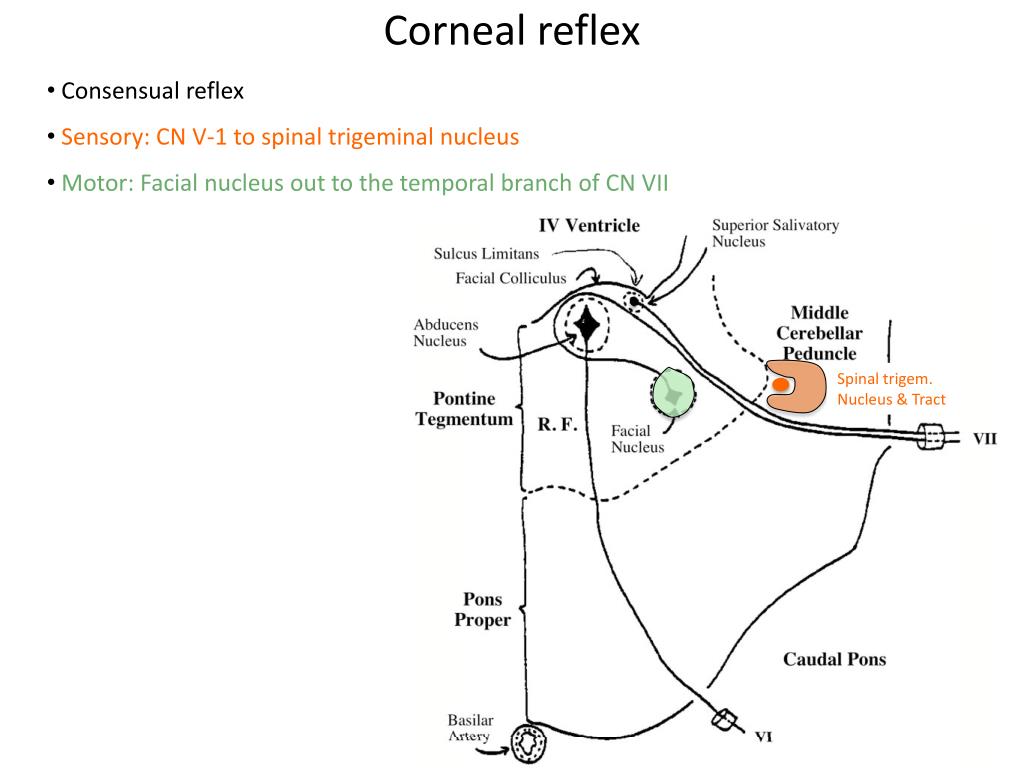
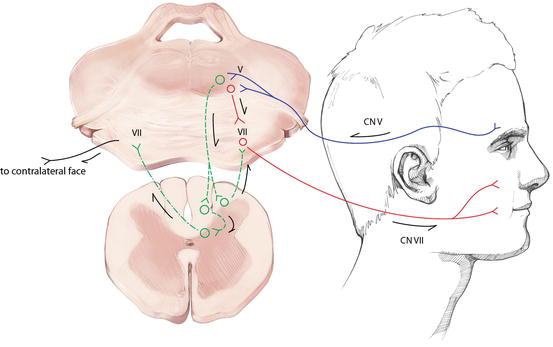
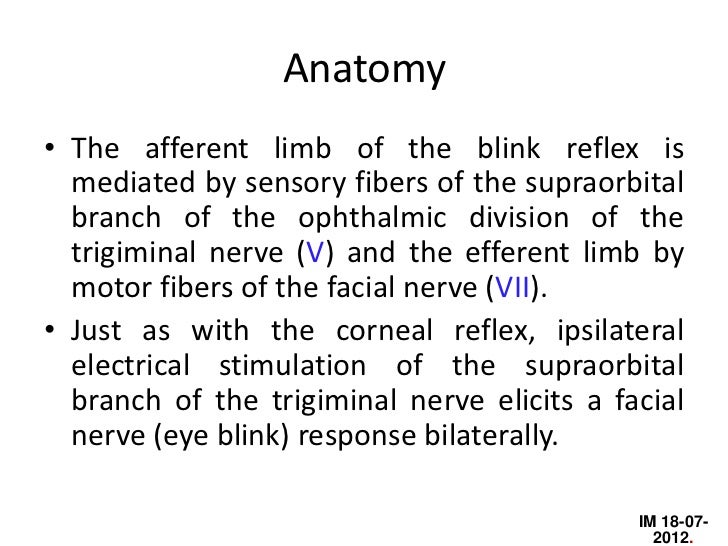
This reflex action is called the nictitating membrane response which, together with the reflex contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle, constitutes the blink reflex The retractor bulbi (RB) motoneuronal nucleus is a small cell group located in the lateral tegmentum of the caudal pons, just dorsal to the superior olivary complex. Anatomy The afferent limb of the blink reflex is mediated by sensory fibers of the supraorbital branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V 1) and the efferent limb by motor fibers of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) Just as with the corneal reflex, ipsilateral electrical stimulation of the supraorbital branch of the trigeminal nerve elicits a facial nerve (eye blink) response bilaterally. The corneal reflex causes both eyes to blink in response to tactile stimulation of the cornea Pathway Inputs are first detected by trigeminal primary afferent fibers (ie free nerve endings in the cornea, which continue through the trigeminal nerve, Gasserian ganglion, root, and spinal trigeminal tract) 2.
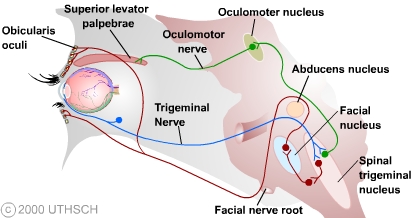
The somatic nervous system controls other reflexes, too One of the more notable ones is the cornea reflex of the eye or the blink reflex When something comes into contact with the cornea, the eye automatically blinks Reflexes are tested in physical exams to evaluate nerve function. Illustration of afferent (CN V) and efferent (CN VII) limbs of the blink reflex (Courtesy of BC Decker Inc) Vestibular reflex illustrating horizontal eye movements only. The Blink Reflex (Trigeminal V Facial VII) Stimulation of the trigeminal nerve activates a reflex pathway along the brainstem, resulting in a contraction of the orbicularis oculi The Blink Reflex reflects the integrity of the afferent and efferent pathways including the proximal segment of the facial nerve Recording Sites 2 Channel Study.
It is a semiautonomic rapid closing of the eyelid A single blink is determined by the forceful closing of the eyelid or inactivation of the levator palpebrae superioris and the activation of the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi, not the full open and close It is an essential function of the eye that helps spread tears across and remove irritants from the surface of the cornea and conjunctiva Blinking may have other functions since it occurs more often. The blink reflex and the normative data has been reported Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of the sites earlier (Ongerboer de Visser and Cruccu, 1993) The blink of lesions reflex was evoked with the subject in supine position and the eyes open Supramaximal stimulation of the supraorbital nerve was delivered transcutaneously. The blink reflex, which is also known as the corneal reflex is the reflex that is designed to ensure that your eyes do not get injured and occurs when soemthing rappidly approaches teh eye causing the rpaid oppening and closing of the eyelids The corneal reflex is driven by the autonomic nervous system and is not controlled by the human desire/thought process.
Course of Ophthalmic Nerve Ophthalmic nerve is the 1st division of trigeminal nerve It is a pure. Blinking is a bodily function;. The pathophysiology, relative anatomy, theoretical mechanisms, and history of neurostimulation for primary headache are covered in this section, Part 1 of 2 Serendipity in a blink reflex study, Cephalalgia, /, 34, 11, (9926), (14) Crossref.
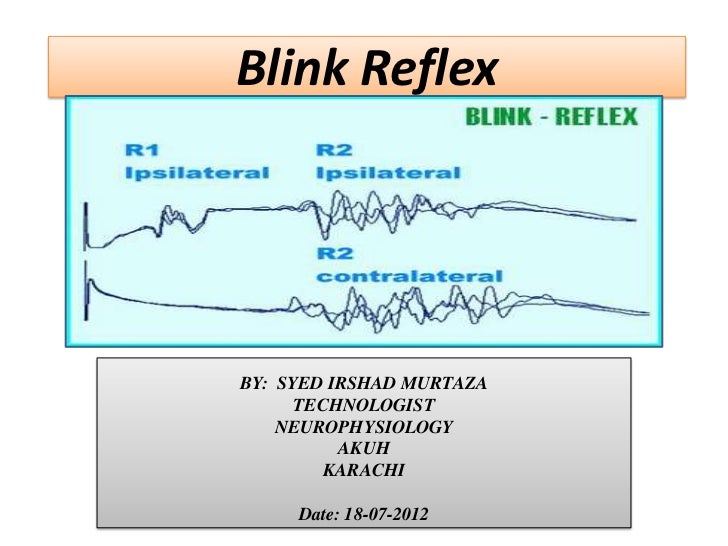
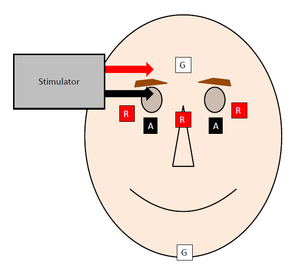
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye). Blink reflex 1 1 BLINK REFLEX DrSujin Koshy Neuro PG 2 The blink reflex is essentially the electrical correlate to corneal reflex It is useful in finding defect anywhere in the reflex arc Afferent supraorbital branch of the opthalmic division of Trigeminal nerve Efferent Motor fibers of facial nerve 3 Blink reflex anatomy 4. The blink reflex (BR) is a generalised phenomenon in mammals Its teleological protective eye function is perhaps the reason why the BR can be provoked by a multitude of stimuli As corneal and glabellar reflexes, BR has an inveterate use in the neurological exploration.
INTRODUCTION Blink reflex is essentially the electricalcorrelate of the clinically evoked cornealreflexBlink reflex is capable of evaluating the cranialnerves and their proximal segmentsThe afferent limb of blink reflex is ophthalmicdivision of trigeminal (V) nerve (which can bestimulated mechanically or electrically) andthe facial (VII) nerve mediates the efferentarc. Blink reflex 1 1 BLINK REFLEX DrSujin Koshy Neuro PG 2 The blink reflex is essentially the electrical correlate to corneal reflex It is useful in finding defect anywhere in the reflex arc Afferent supraorbital branch of the opthalmic division of Trigeminal nerve Efferent Motor fibers of facial nerve 3 Blink reflex anatomy 4. Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence 64 to per 1,000 Incidence Increased with age Overall 02 to 05 per year per 1,000 Age 01 per year per 1,000.
To test brain function, determine depth of anesthesia Describe the three eye reflexes Blink (when something comes near the eye);. The facial nerve transmits the stimulus arising in the nucleus to the orbicularis oculi muscles of the eye causing a blink response Diagrammatic Representation of Anatomy Afferent Pathways The stimulus necessary to generate a response in this test starts in the retina and causes impulses to be transmitted down the optic nerve crossing at the chiasm and synapsing in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. Corneal reflexIt is elicited by gentle stroking on the cornea with a cotton swabThis reflex mainly helps in knowing the damage peripherally to either the trigeminal nerve (V) or facial nerve (VII) nerve will disrupt the corneal blink circuit Plantar reflexabnormal reflex indicates metabolic or structural abnormality in the corticospinal system upstream from the segmental reflex.
Corneal reflex It is also known as blink reflex It is an involuntary blinking of eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (tactile, thermal or painful stimulation) Stimulation of the cornea elicits both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye)As with all reflexes it has an afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor. Using a variety of fluorescent and transganglionic tracers, the sensorimotor innervation of blinkrelated orbital and periorbital structures was studied in SpragueDawley rats The orbicularis oculi muscle surrounded the entire palpebral fissure and was innervated by motoneurons located along the dorsal cap of the ipsilateral facial motor nucleus. Corneal reflex (blink reflex) Involuntary blinking in response to corneal stimulation Afferent nasociliary branch of ophthalmic branch (V1) of trigeminal nerve (5th nerve).
Moreover, it revealed an incomplete reflex blink and an upward eye movement at around 100 ms that may correspond to Bell's phenomenon CONCLUSIONS Direct and consensual pupillary responses do not any significant temporal differences The system and method described here could prove useful for further assessment of pupillary and blink reflexes. Course of Ophthalmic Nerve Ophthalmic nerve is the 1st division of trigeminal nerve It is a pure. 1 The subject is to sit on the edge of the lab table with the legs able to swing freely (One partner will be the subject first and the other partner the tester, then you’ll switch) 2 Once the legs are relaxed and swing freely, the tester should use the side of their hand to “tap” the subject just below the kneecap.
Corneal reflex (blink reflex) Involuntary blinking in response to corneal stimulation;. Pupillary (pupils constrict in presence of bright light). The corneal reflex causes both eyes to blink in response to tactile stimulation of the cornea Pathway Inputs are first detected by trigeminal primary afferent fibers (ie free nerve endings in the cornea, which continue through the trigeminal nerve, Gasserian ganglion, root, and spinal trigeminal tract).
A specialized reflex to protect the surface of the eye is the corneal reflex, or the eye blink reflex When the cornea is stimulated by a tactile stimulus, or even by bright light in a related reflex, blinking is initiated. The blink reflex neurophysiology and anatomy are reasonably well known The electromyography records of an electrically evoked blink reflex showed at least two components ( R 1 and R 2 components) The first or early response ( R 1 ) is brief and occurs after a latency of approximately 10 ms on the side of stimulation 19. Multiple cranial nerves are involved in the process of blinking, as is the brainstem In a healthy person, the blink reflex appears in both eyes If both eyes fail to blink, it can mean that there is a problem with one of the cranial nerves or the brainstem which is inhibiting the normal processing of the reflex.
The output of a visceral reflex is a twostep pathway starting with the preganglionic fiber emerging from a lateral horn neuron in the spinal cord, or a cranial nucleus neuron in the brain stem, to a ganglion—followed by the postganglionic fiber projecting to a target effector. Blink reflex normative studies were made by many authors9,1113, although the work of Kimura et al1 is still accepted as the standard Despite many reports investigating the blink reflex in various neurological syndromes, the normative studies presented so far have not shown data for interracial comparison We do not know of normative studies. The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation (such as touching or a foreign body) of the cornea, or bright light, though could result from any peripheral stimulus Stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (response of the opposite eye).
The blink reflex can be initiated by either touch to the cornea (afferents in the trigeminal nerve) or by bright light/rapidly approaching objects (afferents in the optic nerve) is faster than spontaneous blinking. Blink reflex is absent, pupillary and corneal reflex are present;. The blink reflex abnormalities present in the 6 hydroxydopamine (6OHDA) lesioned rat model of parkinsonism mimicked those of the human with Parkinson's disease In alert rats, we monitored the long and short latency components of the orbicularis oculi electromyographic (OOemg) response evoked by el.
The corneal reflex, also called the blink reflex, is the involuntary response of blinking the eyelids when the cornea is stimulated The trigeminal nerve comprises the afferent (sensory) limb of the corneal reflex, while the facial nerve comprises the efferent (motor) limb. Corneal (when the cornea is touched);. The trigeminal reflexes include the corneal (blink) reflex, and the jaw jerk (masseter) reflex The corneal reflex, or blink reflex, is the involuntary blinking of the eyelids caused by something touching the cornea of the eye It can also result from any peripheral stimulus.
This reflex action is called the nictitating membrane response which, together with the reflex contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle, constitutes the blink reflex The retractor bulbi (RB) motoneuronal nucleus is a small cell group located in the lateral tegmentum of the caudal pons, just dorsal to the superior olivary complex.

Normal And Abnormal Lid Function Sciencedirect
Blink Reflex Springerlink

The Trigeminal And Facial Nerves

An Explanation For Reflex Blink Hyperexcitability In Parkinson S Disease Ii Nucleus Raphe Magnus Journal Of Neuroscience

Figure 46 8
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 33 6 792 Full Pdf
Corneal Reflex Testing In The Evaluation Of A Comatose Patient An Ode To Precise Semiology And Examination Skills Springerlink

Anatomy Of The Corneal Reflex Youtube

Blink Reflex Anatomy Brainstem Nerve
What Is The Blink Reflex With Pictures

Graphics For Corneal Reflex Pathway Graphics Www Graphicsbuzz Com
Q Tbn And9gcsilwa5w Jqbgozcknidn4wvg49atkdp0qujt1wfj1rexizvkpl Usqp Cau
Blink Reflex Springerlink

Blink Reflex

Usmle Tutorial The Corneal Reflex Youtube
Blink Reflex Physiopedia
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Reflex Physiology Britannica

Correlation Between Electromyographic Reflex And Mr Imaging Examinations Of The Trigeminal Nerve American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Experiment The Patellar Reflex And Reaction
Academic Oup Com Brain Article Pdf 128 2 386 Awh366 Pdf

Neural Reflexes Human Physiology Openstax Cnx

Human Eye The Visual Process Britannica
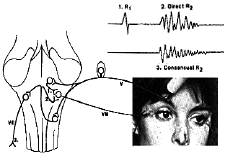
Cranial Nerves Teleemg

Corneal Reflex Wikipedia

Superficial Reflexes Flashcards Quizlet

Schematic Representation Of The Blink Reflex Pathways And Sites Of Download Scientific Diagram

Control Of Eye Movements Flashcards Quizlet
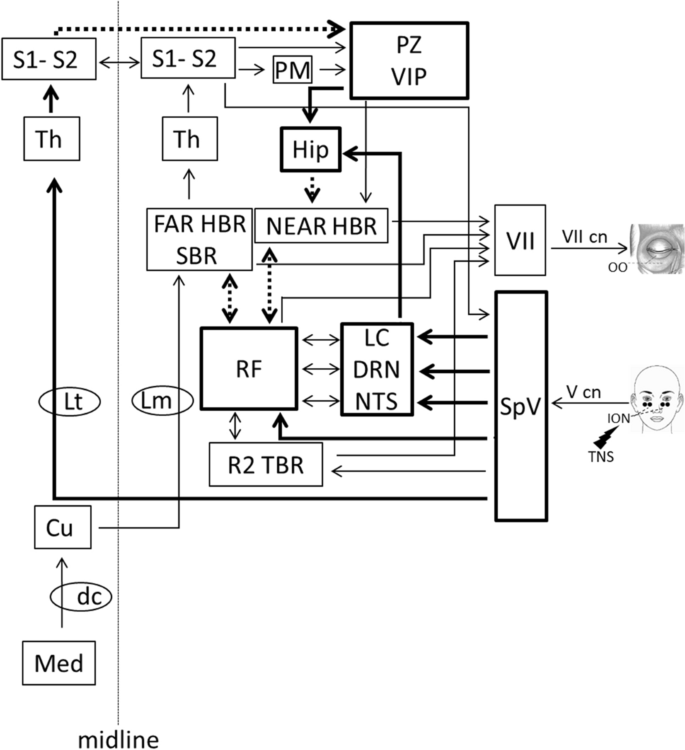
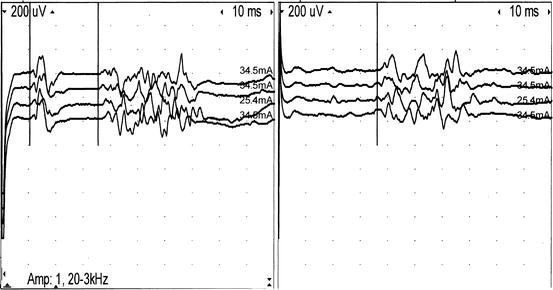
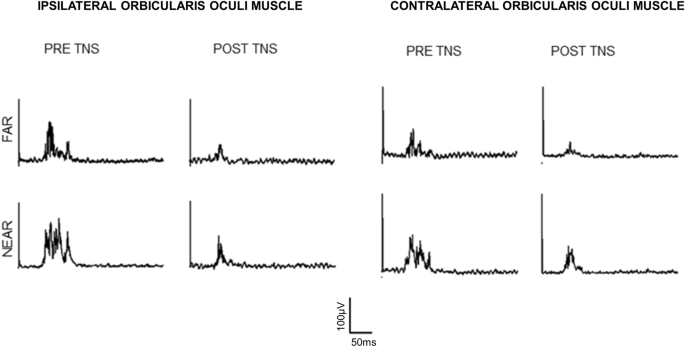
Transcutaneous Trigeminal Nerve Stimulation Modulates The Hand Blink Reflex Scientific Reports

Corneal Blink Reflex Mnemonics Afferent Vs Efferent

Schematic Representation Of The Blink Reflex Pathways And Sites Of Download Scientific Diagram

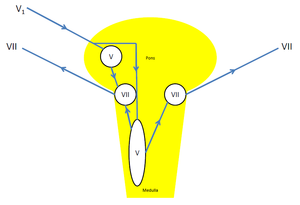
The Blink Reflex Arc The Circuit For The Oligosynaptic R1 Component Is Download Scientific Diagram

Reflex Action And Reflex Arc Concepts Solved Questions And Videos
Journals Viamedica Pl Neurologia Neurochirurgia Polska Article Download

Los Nervios Craneales I Olfatoria Olor 2 Optica Vision 3 Oculomotor Alumno Constriccion 4 Troclear M Cranial Nerves Vagus Nerve Emdr Therapy
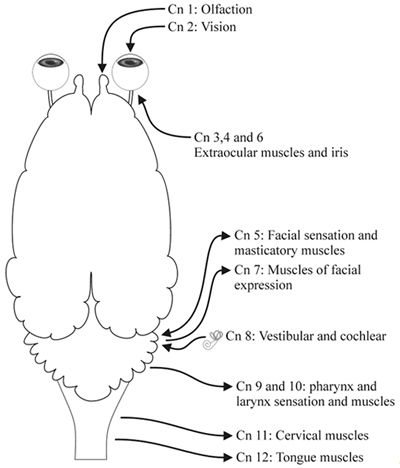
Recognition Of Common Cranial Nerve Abnormalities In Dogs Cats Acvim 08 Vin
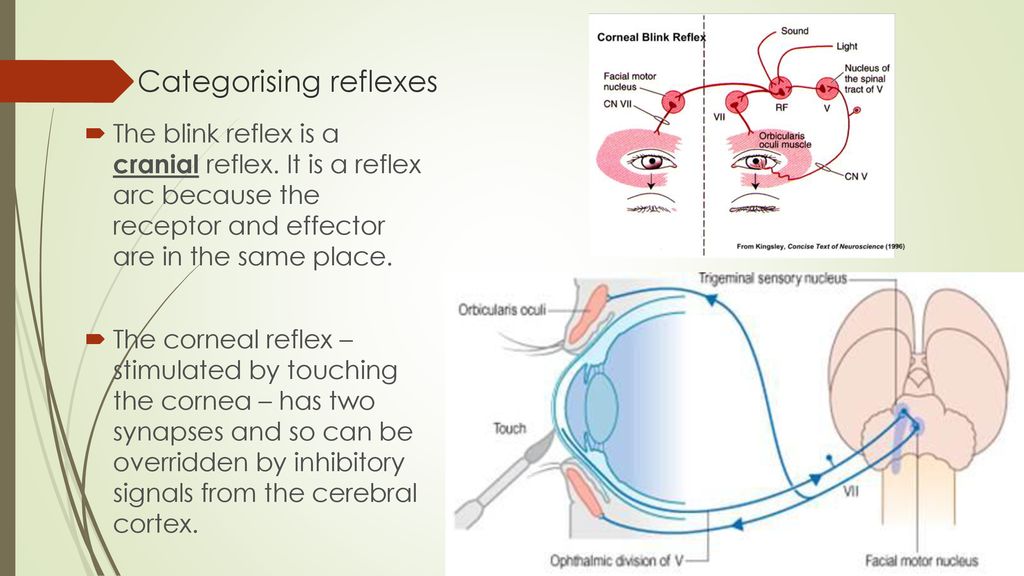
Module 5 Communication Homeostasis Energy Ppt Download

Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Late Blink Reflex Changes In Lesions Of Thalamus And Internal Capsule Neurology
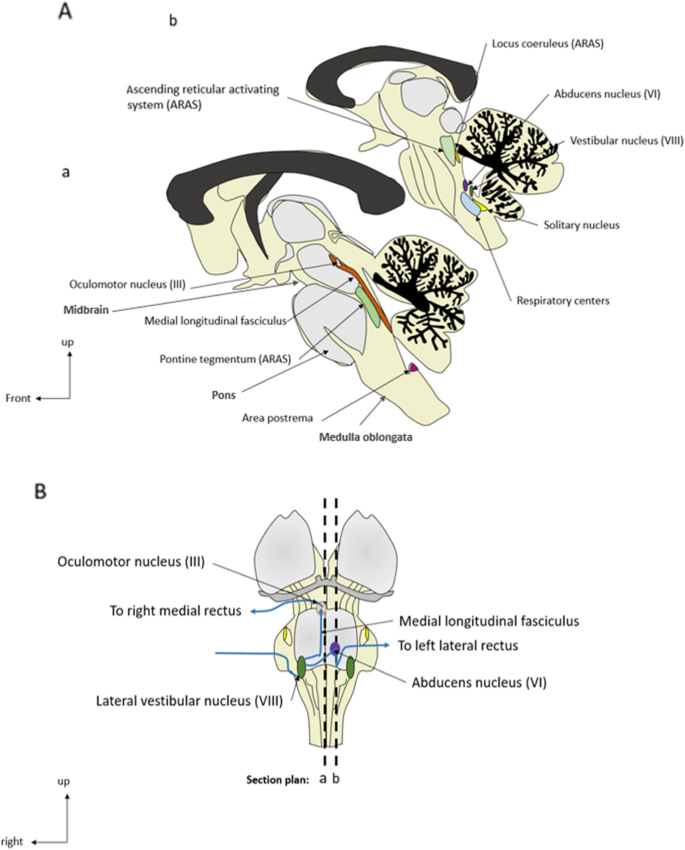
Brainstem Dysfunction In Critically Ill Patients Critical Care Full Text

Diagnostic Value Of Blink Reflex In Multisystem Atrophy Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinson Disease Sciencedirect
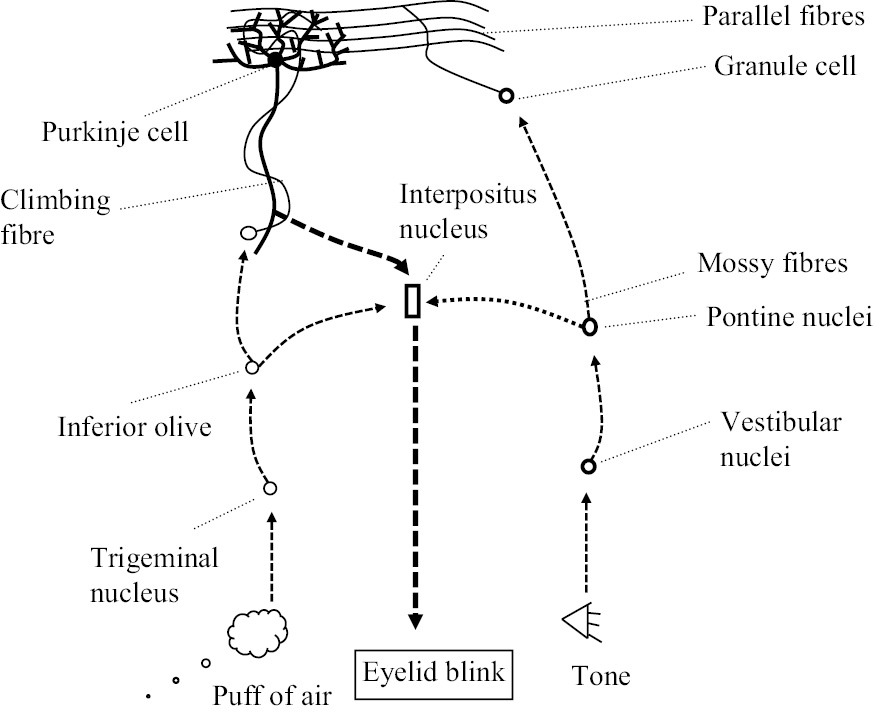
Eye Blink Conditioning Chapter 9 Behavioural Neuroscience
Neuroophthalmology Veterian Key
Late Responses And Blink Reflexes Chapter 11 Comprehensive Electromyography

Cranial Nerves And Pathways Clinical Neuroanatomy 28 Ed

Cranial Nerve Reflexes Flashcards Quizlet
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf
Blink Reflex
Pdfs Semanticscholar Org b2 3e66e250fb44d1bc063c2775f515c401 Pdf

Ocular Movements Visual Reflexes Medatrio
Transcutaneous Trigeminal Nerve Stimulation Modulates The Hand Blink Reflex Scientific Reports

Neurodiagnostic Laboratory Services Facial Nerve Study Blink Reflex Test By Juronghealth Campus Issuu

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key

Anatomy Of The Corneal Reflex Youtube
2
2

Blink Reflex
Ppt Brainstem Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Neurophysiological Aspects Of Eye And Eyelid Movements During Blinking In Humans Journal Of Neurophysiology
Ocular Motor System Section 3 Chapter 7 Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston

Reflexes And The Eye Eyewiki

Blink Reflex Responses In The Second Patient With A Lesion On The Right Download Scientific Diagram

2 Minute Neuroscience Corneal Reflex Youtube

Contralateral Dry Eye In Hemifacial Spasm A New Clinical Sign Gosal Js Das Kk Khatri D Attri G Jaiswal Ak Asian J Neurosurg

Experiment The Patellar Reflex And Reaction
Reflex And Long Latency Musculoskeletal Key
Blink Reflex Physiopedia

Reflexes And Homeostasis Principles Of Biology Openstax Cnx

Reflex Arc
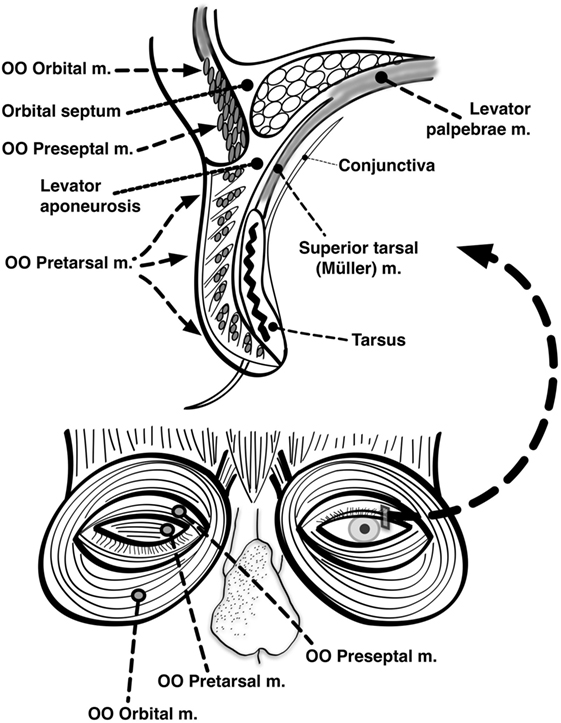
Frontiers Eyelid Dysfunction In Neurodegenerative Neurogenetic And Neurometabolic Disease Neurology

Blink Reflex By Ck Authorstream

The Corneal Reflex The Corneal Reflex Ophthalmology Notes And Synopses Facebook

The Blink Reflex And Other Cranial Nerve Reflexes Neupsy Key
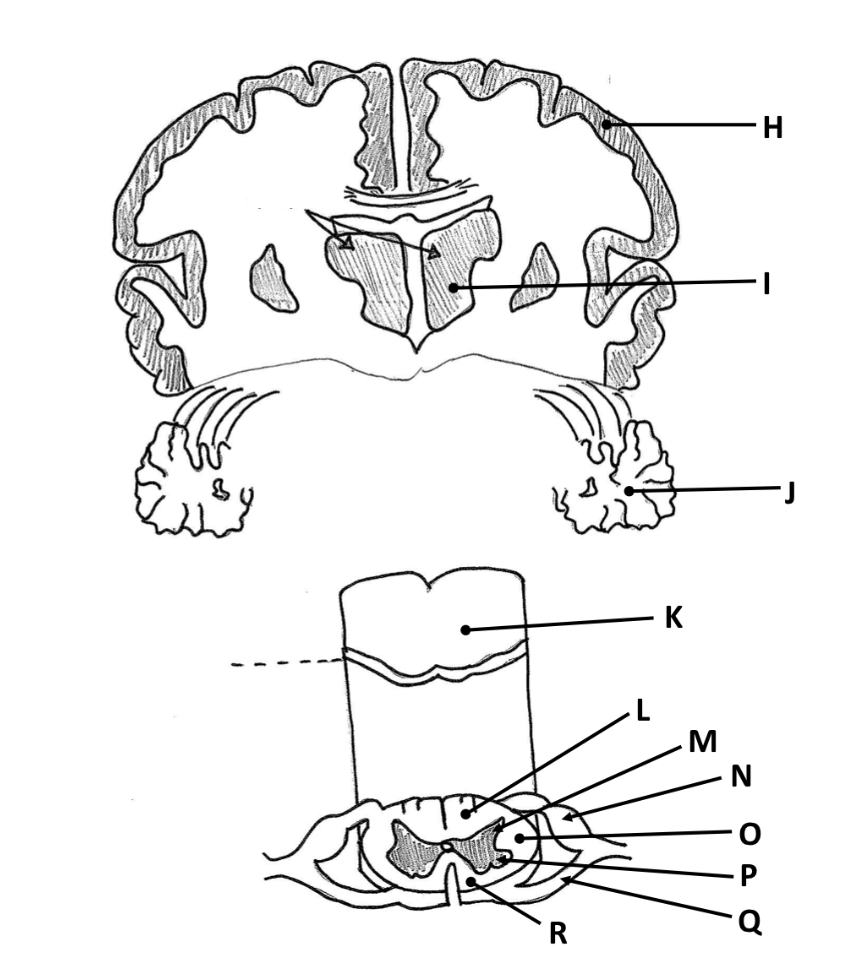
Solved Using The Figure Where Will You Find The Integrat Chegg Com

Basal Ganglia To Brainstem Pathways Influencing Reflex Open I
Blink Reflex Springerlink
Blink Reflex

Facial Nerve Wikipedia
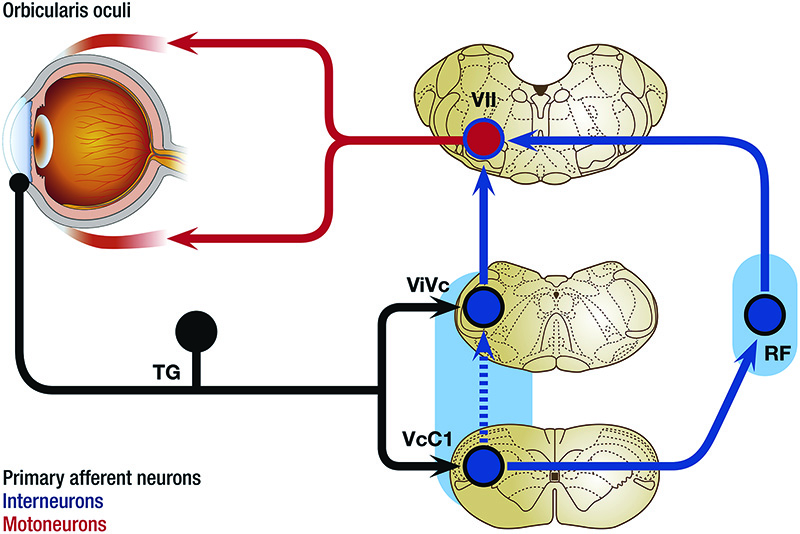
Tfos Dews Ii Report Pain And Sensation Tfos Tear Film Ocular Surface Society

Eyelid Reflex An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Q Tbn And9gcrw3in1cteamixsnggh90hkgie Kbnpfyqiziwtj7fhgxs1lxzh Usqp Cau
Q Tbn And9gcrj86uf3j5zfg 3jspwc3wmrglql95r J02qxhme8ndzzmlxqfg Usqp Cau
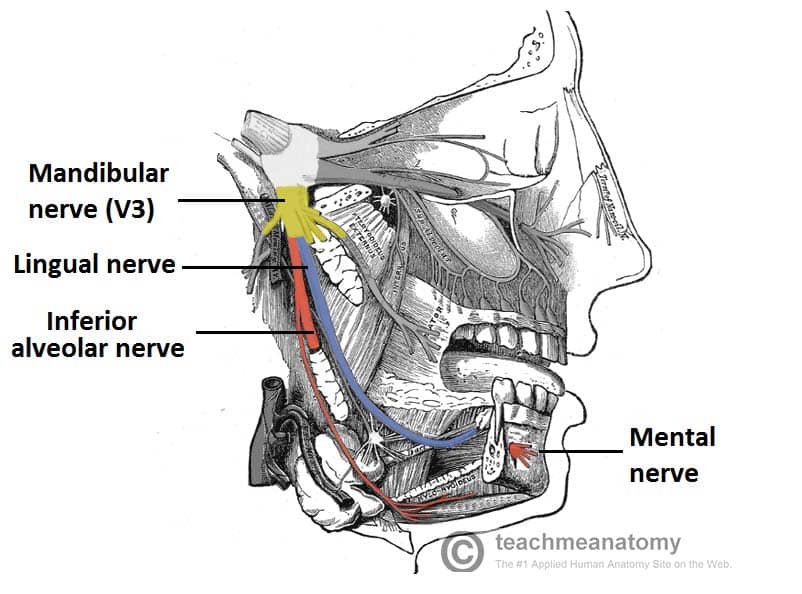
The Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Course Divisions Teachmeanatomy
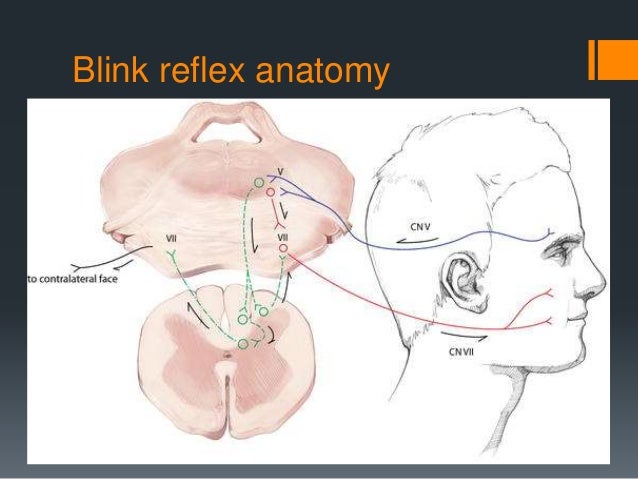
Blink Reflex 1

Figure Corneal Reflex A Diagram Of Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
Jnnp Bmj Com Content Jnnp 25 2 93 Full Pdf
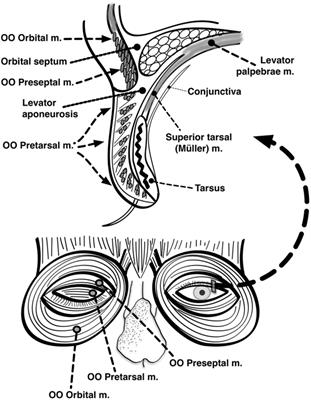
Frontiers Eyelid Dysfunction In Neurodegenerative Neurogenetic And Neurometabolic Disease Neurology

Reflexes 3 Corneal Reflex Youtube

Blink Reflex Pathway So Supraorbital Nerve St Supratrochlear Nerve Download Scientific Diagram

Blink Reflex

The Reflex Ppt Download
Http Neurothai Org Media News File 338 02 Blink Reflex And Late Responses 1 Pdf

An Explanation For Reflex Blink Hyperexcitability In Parkinson S Disease I Superior Colliculus Journal Of Neuroscience
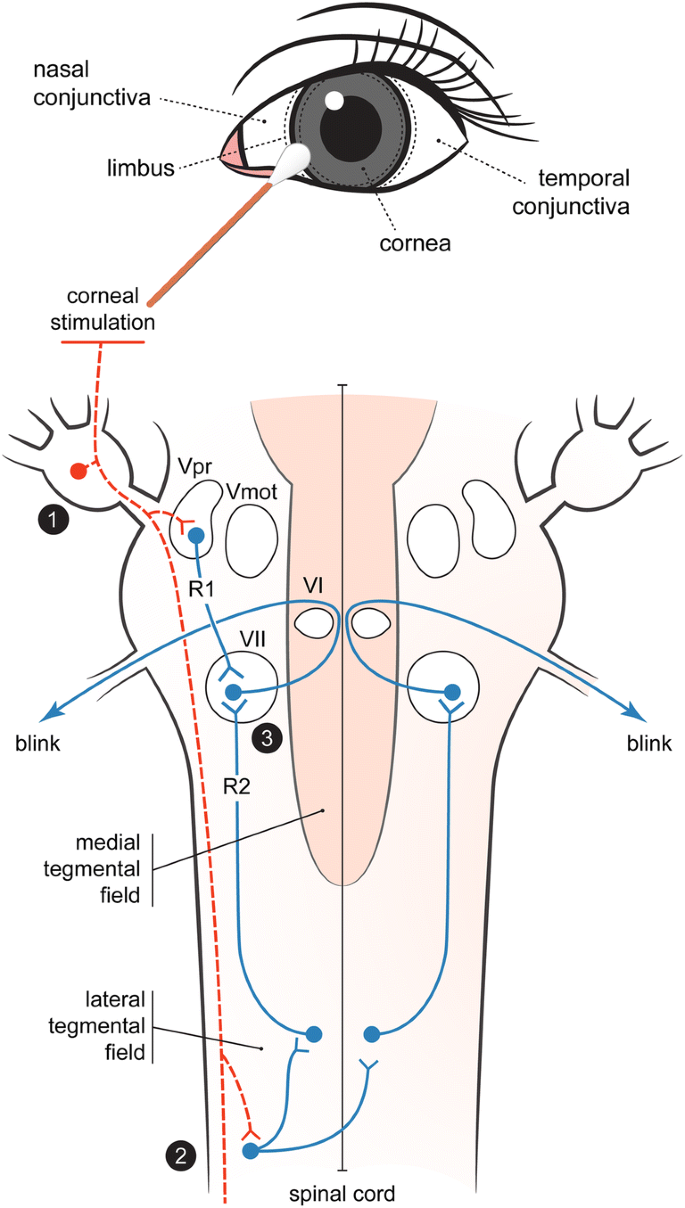
Corneal Reflex Testing In The Evaluation Of A Comatose Patient An Ode To Precise Semiology And Examination Skills Springerlink

Schematic Representation Of Various Lesions Within The Brainstem A ϫ Download Scientific Diagram

An Explanation For Reflex Blink Hyperexcitability In Parkinson S Disease Ii Nucleus Raphe Magnus Journal Of Neuroscience
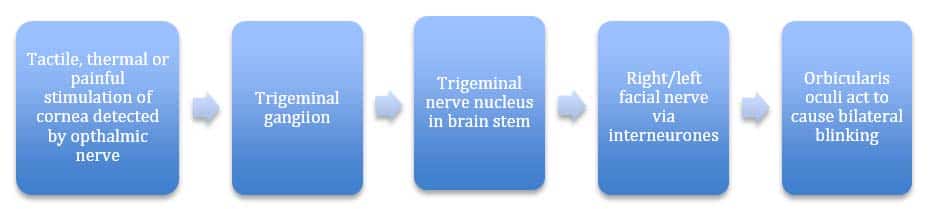
The Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Course Divisions Teachmeanatomy



