Fdg Pet Brain

Brain Defenders Alzheimers Disease Vs Ftd Fdg Pet In Addition To Clinical Findings Csf And Mri Pet Imaging Is Useful In Diagnosing Ad In Ad Fdg Pet Can Show Hypometabolism In The Temporoparietal Regions
Pet Helps Measure Awareness Of Brain Injured Patients Imaging Technology News
Brain 18f Fdg Pet In The Diagnosis Of Neurodegenerative Dementias Comparison With Perfusion Spect And With Clinical Evaluations Lacking Nuclear Imaging Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
Frontiers 18f Fdg Pet In Mouse Models Of Alzheimer S Disease Medicine
The Neurology Of Pet

Fdg Pet Shows Where Exercise Could Stall Alzheimer S
FDG PET is covered in various pediatric disorders, such as childhood epilepsy, temporal lobe epilepsy, abnormalities of neuronal migration and proliferation, and pediatric brain tumors FDG PET and PET/CT of 50 minutes after FDG injection Acquisition and Uptake Patterns The accurate interpretation of FDG PET and.

Fdg pet brain. Positron emission tomography with FDG is based on the fact that FDG, similar to glucose, is transported across the bloodbrain barrier (BBB) and cell membranes and then is phosphorylated by HK to FDG6phosphate (FDG6P), which accumlates in tissues at a rate proportional to the rate of glucose utilization (Figure 1). Positron emission tomography (PET) with 2 fluorine18fluoro2deoxyDglucose (FDG) is a highly useful imaging modality for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders ( 1 – 6 ) FDG is an analog of glucose, the main energy substrate of the brain. F18 FDGPET brain assessment in the interictal state Presurgical evaluation and the surgical treatment of nonlesional neocortical epilepsy is one of the most challenging areas in epilepsy surgery FDGPET shows hypometabolism in a majority of patients with nonlesional temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), even in the absence of hippocampal atrophy.
The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic value of positron emission tomography (PET) using (18)Ffluorodeoxyglucose ((18)FFDG) and O(2(18)Ffluoroethyl)ltyrosine ((18)FFET) in patients with brain lesions suspicious of cerebral gliomasMETHODS Fiftytwo patients with suspicion of cerebral glioma were included in this study. Heart failure patients with more severe disease showed whole‐brain and regional brain hypometabolism in 18 F‐FDG PET/CT Depressed HF patients (Beck Depression Inventory score >13) exhibited different metabolic patterns that could be used to differentiate between ‘epiphenomenal’ and ‘real’ depression. FDGPET changes in brain glucose metabolism from normal cognition to pathologically verified Alzheimer's disease Mosconi L(1), Mistur R, Switalski R, Tsui WH, Glodzik L, Li Y, Pirraglia E, De Santi S, Reisberg B, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ.
Those abbreviations stand for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)positron emission tomography (PET) The role of this procedure is to detect metabolically active malignant lesions including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, brain cancer and multiple myeloma FDGPET scan may also be used to stage and monitor the response to therapy of malignant disease. Clearly define anatomic components and boundaries FDG, utilized for PET, also can concentrate itself in normal tissue This could pose the problem of deciding if the area is truly of concern or if it correlates with “normal tissue such as the brain, muscles, salivary glands, thyroid gland, myocardium, gastrointestinal tract, and the urinary tract” (Muhammad, Tzannon & Makrilia, 10). FDG stands for fluorodeoxyglucose, a shortlived radioactive form of sugar injected into people during PET scans to show activity levels in different parts of the brain.
The still frequent use of FDG PET in the brain is of limited value due to poor lesiontobackground contrast, partially explaining disappointing results in screened cohorts 99 New PET tracers, such as TSPO ligands, might help to overcome this problem 100 and may eventually assist in radiation treatment planning. PET stands for positron emission tomography CT stands for computed tomography A PET/CT brain scan takes pictures of your brain as it works It is often done to find brain tumors or seizure sites It may also be used to help diagnose memory problems Before your scan, we will inject a radioactive tracer called 18 FDG FDG stands for 2Deoxy2. Researchers will utilize imaging techniques to monitor changes in glucose metabolism (the way the brain uses energy) as a result of liraglutide use in PD A brain imaging procedure, fluorodeoxyglucosepositron emission tomography (FDGPET) scan, will also enable researchers to better understand glucose metabolism in patients with insulin resistance and Parkinson’s disease.
A PET/CT scan is a way to take pictures of your body’s cells It allows a specially trained doctor (radiologist) to check for changes in your cells PET stands for positron emission tomography CT stands for computed tomography A PET/CT brain scan takes pictures of your brain as it works It is often. Background Florbetapir (AV45) and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET imaging are valuable techniques to detect the amyloidβ (Aβ) load and brain glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) Objective The purpose of this study is to access the characteristics of Aβ load and FDG metabolism in brain for further investigating their relationships with cognitive impairment in AD. Before your PETCT, you’ll get a radioactive medication with glucose called a tracer through an intravenous (IV) line in your arm This is done to show differences between healthy tissue and diseased tissue Your PETCT will use FDG as the tracer FDG is taken up by your cells and doesn’t stay in your body long Contrast.
1 Introduction Today, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the method of choice for the diagnosis of brain tumors, but positron emission tomography (PET) may provide significant additional clinical information in many circumstances The most widely used PET tracer is 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (18 FFDG) that has been applied successfully for tumor grading of cerebral gliomas, as a prognostic. PET imaging with 18FFDG takes advantage of the fact that the brain is normally a rapid user of glucose Standard 18FFDG PET of the brain measures regional glucose use and can be used in neuropathological diagnosis Example Brain pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease greatly decrease brain metabolism of both glucose and oxygen in tandem. PET imaging with 18FFDG takes advantage of the fact that the brain is normally a rapid user of glucose Standard 18FFDG PET of the brain measures regional glucose use and can be used in neuropathological diagnosis Examples Brain pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease greatly decrease brain metabolism of both glucose and oxygen in tandem Therefore 18FFDG PET of the brain may also be used to successfully differentiate Alzheimer's disease from other dementing processes, and also to make.
FDG PETCT (continued) Page 2 of 8 For all brain PETCTs, the patient should be in a quiet/darkened room during the uptake phase The patient should stay awake with eyes open and rest comfortably, with as little muscular activity as possible For brain PETCTs to evaluate seizures, the patient should be free of seizures for a minimum of 2 hours. Brain MR imaging, FDGPET, and EEG findings for P2, a 63yearold man with glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 encephalitis and normal brain MR imaging findings at the onset of seizures A , Axial T2weighted FLAIR image at day 12 of status epilepticus shows bilateral hippocampus and insula T2weighted hyperintense lesions. FDG PETCT (continued) Page 2 of 8 For all brain PETCTs, the patient should be in a quiet/darkened room during the uptake phase The patient should stay awake with eyes open and rest comfortably, with as little muscular activity as possible For brain PETCTs to evaluate seizures, the patient should be free of seizures for a minimum of 2 hours.
Clearly define anatomic components and boundaries FDG, utilized for PET, also can concentrate itself in normal tissue This could pose the problem of deciding if the area is truly of concern or if it correlates with “normal tissue such as the brain, muscles, salivary glands, thyroid gland, myocardium, gastrointestinal tract, and the urinary tract” (Muhammad, Tzannon & Makrilia, 10). IF FDGPET DEMENTIA EVALUATION IS INDICATED AND COVERED Criteria appropriate for all insurances using AIM (American Imaging Management) The use of FDGPET scan in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and FrontoTemporal Lobe Dementia is medically necessary and appropriate provided all of the following conditions are met. Of underlying brain pathology Since FDG is a competitive substrate with glucose for both transport and phosphorylation, it is important for tracer uptake to avoid high blood glucose levels during an FDGPET scan in subjects with diabetes In neurodegenerative brain diseases, specific brain regions degenerate and specific patterns.
The PET portion of this imaging modality relies on the accumulation of radioactive glucose analog, FDG In cancer cells, there is an overproduction of glucose transporters and, as a result, increased FDG uptake However, not all PETpositive lesions are cancer, and in many instances, PET findings can be false positive. Background Florbetapir (AV45) and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET imaging are valuable techniques to detect the amyloidβ (Aβ) load and brain glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) Objective The purpose of this study is to access the characteristics of Aβ load and FDG metabolism in brain for further investigating their relationships with cognitive impairment in AD. 2 SPECT Radiopharmaceuticals 21 Thallium1 Thallium1 (1 Tl) is a potassium analogue possessing an affinity for the sodium and potassiumactivated adenosine triphosphatase (Na K ATPase) pump and is distributed in potassiumrich organs, such as the heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, and the thyroid gland, but exhibits little uptake in the normal brain.
1 Introduction Today, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the method of choice for the diagnosis of brain tumors, but positron emission tomography (PET) may provide significant additional clinical information in many circumstances The most widely used PET tracer is 18 Ffluorodeoxyglucose (18 FFDG) that has been applied successfully for tumor grading of cerebral gliomas, as a prognostic. Objective To evaluate FDGPET as an antemortem diagnostic tool for Alzheimerrelated TAR DNAbinding protein of 43 kDa (TDP43) proteinopathy Methods We conducted a crosssectional neuroimaging–histologic analysis of patients with antemortem FDGPET and postmortem brain tissue from the Mayo Clinic Alzheimer's Disease Research Center and Study of Aging with Alzheimer spectrum pathology. FDG PET scans involve a specialized sugar that shows up on PET scans This sugar injected into your body And since most tumors will take up more of it, it allows the tumor to show up on the PET scan Besides helping to diagnose cancer, FDG PET scans can also tell you if your cancer consumes a lot of sugar (ie if it’s “glucose avid” or not).
Of underlying brain pathology Since FDG is a competitive substrate with glucose for both transport and phosphorylation, it is important for tracer uptake to avoid high blood glucose levels during an FDGPET scan in subjects with diabetes In neurodegenerative brain diseases, specific brain regions degenerate and specific patterns. All FDG PET brain scans were performed on the ECAT III (CTI, Knoxville, TN) or the GE 4096 Plus tomograph (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI) using standard techniques We administered 370 MBq (10 mCi) FDG followed by a 40min uptake period during which the patient remained quiet in a dimly lit room. Note Tumors may be difficult to detect using FDG because of the high normal uptake of sugar in the brain Preparation PET exams require careful preparations with respect to diet and exercise.
Clearly define anatomic components and boundaries FDG, utilized for PET, also can concentrate itself in normal tissue This could pose the problem of deciding if the area is truly of concern or if it correlates with “normal tissue such as the brain, muscles, salivary glands, thyroid gland, myocardium, gastrointestinal tract, and the urinary tract” (Muhammad, Tzannon & Makrilia, 10). The brain demonstrates substantial physiologic FDG avidity Malignancy involving the brain, including metastases, lymphoma, and primary gliomas, may be detected either as foci of FDG avidity greater than physiologic brain background, areas of FDG photopenia, or as lesions on the corresponding CT scan FDG PET/CT plays an important role in distinguishing recurrent malignancy from benign radiation necrosis following radiation therapy of brain malignancy. FDGPET is currently considered as an excellent tool for providing accurate rates of brain glucose metabolism in conscious rodents because it allows an accurate estimation of brain glucose patterns using methods such as voxelbased statistical analysis , , regionbased quantification by automatically segmenting brain MRI and extracting FDG.
Pet Scan FDG, Information, Cost Tweet PET scan images can provide important information about many disorders that affect the heart, lung, brain, bones, liver etc and will help the doctor plan appropriate treatment for you. Background Florbetapir (AV45) and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET imaging are valuable techniques to detect the amyloidβ (Aβ) load and brain glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) Objective The purpose of this study is to access the characteristics of Aβ load and FDG metabolism in brain for further investigating their relationships with cognitive impairment in AD. FDG PET is covered in various pediatric disorders, such as childhood epilepsy, temporal lobe epilepsy, abnormalities of neuronal migration and proliferation, and pediatric brain tumors FDG PET and PET/CT of 50 minutes after FDG injection Acquisition and Uptake Patterns The accurate interpretation of FDG PET and.
A FDGPET scan is a medical imaging procedure It involves an injection of radioactive tracer liquid inside the body that congregates at tumors and other sites where the cells divide more quickly than usual The acronym FDGPET scan stands for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)positron emission tomography (PET), where the FDG is the radioactive liquid and the PET is the scanning machinery. The purpose of this study was to compare the diagnostic value of positron emission tomography (PET) using (18)Ffluorodeoxyglucose ((18)FFDG) and O(2(18)Ffluoroethyl)ltyrosine ((18)FFET) in patients with brain lesions suspicious of cerebral gliomasMETHODS Fiftytwo patients with suspicion of cerebral glioma were included in this study. FDG PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Brain Diseases, Functional Brain Mapping and the Endeavor to Understand the Working Brain, Francesco Signorelli and Domenico Chirchiglia, IntechOpen, DOI / Available from Over 21,000 IntechOpen readers like this topic Help us write another book on this subject and reach those readers.
18 Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)PET showed bilateral hypometabolism in the lateral and midline frontal cortex, insular cortex, head of caudate nucleus, brainstem, and cerebellum , consistent with described FDGPET findings in PSP 1,2 Although not required for diagnosis of probable PSP, FDGPET may help differentiate parkinsonian syndromes In. What is a PET/CT FDG brain scan?. Objective To evaluate brain 18 Fluorodeoxyglucose PET (FDGPET) differences among patients with a clinical diagnosis of corticobasal syndrome (CBS) and distinct underling primary pathologies Methods We studied 29 patients with a diagnosis of CBS who underwent FDGPET scan and postmortem neuropathologic examination Patients were divided into subgroups on the basis of primary pathologic.
A FDGPET scan is a medical imaging procedure It involves an injection of radioactive tracer liquid inside the body that congregates at tumors and other sites where the cells divide more quickly than usual The acronym FDGPET scan stands for fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)positron emission tomography (PET), where the FDG is the radioactive liquid and the PET is the scanning machinery. Pet Scan FDG, Information, Cost Tweet PET scan images can provide important information about many disorders that affect the heart, lung, brain, bones, liver etc and will help the doctor plan appropriate treatment for you. FDG PET is covered in various pediatric disorders, such as childhood epilepsy, temporal lobe epilepsy, abnormalities of neuronal migration and proliferation, and pediatric brain tumors FDG PET and PET/CT of 50 minutes after FDG injection Acquisition and Uptake Patterns The accurate interpretation of FDG PET and.
We review the role of brain FDG PET in the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease, frontotemporal dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, and vascular dementia Characteristic spatial patterns of brain metabolism on FDG PET can help differentiate various subtypes of dementia CONCLUSION In patients with different subtypes of dementia, FDG PET/CT shows distinct spatial patterns of metabolism in the brain and can help clinicians to make a reasonably accurate and early diagnosis for appropriate. 18 Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)PET showed bilateral hypometabolism in the lateral and midline frontal cortex, insular cortex, head of caudate nucleus, brainstem, and cerebellum , consistent with described FDGPET findings in PSP 1,2 Although not required for diagnosis of probable PSP, FDGPET may help differentiate parkinsonian syndromes In. Finally, on a practical note, 18 FFDGPET imaging is an attractive future addition to the proposed workup for two reasons First, wholebody 18 FFDGPET imaging is often done in patients with paraneoplastic syndromes to screen for malignancy Such wholebody imaging can easily be extended to cover the brain without increases in radiation burden.
Abstract This handout explains a positron emission tomography (PET)/CT FDG brain scan, which allows doctors to see your brain while it is working This scan is often used to check for tumors and to find the reason for memory problems Included are how to prepare for the scan, what to expect, and how to get your results. 2 SPECT Radiopharmaceuticals 21 Thallium1 Thallium1 (1 Tl) is a potassium analogue possessing an affinity for the sodium and potassiumactivated adenosine triphosphatase (Na K ATPase) pump and is distributed in potassiumrich organs, such as the heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, and the thyroid gland, but exhibits little uptake in the normal brain. An atypical fluorodeoxyglucose positive emission tomography (FDGPET) pattern is an early marker for identifying patients with Parkinson disease (PD) at higher risk for progression to dementia.
Background Florbetapir (AV45) and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET imaging are valuable techniques to detect the amyloidβ (Aβ) load and brain glucose metabolism in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) Objective The purpose of this study is to access the characteristics of Aβ load and FDG metabolism in brain for further investigating their relationships with cognitive impairment in AD.

White Matter Brain Lesions In Infantile Onset Pompe Disease Are Not Metabolically Active Using 18f Fdg Pet Mr Imaging Neuromuscular Disorders
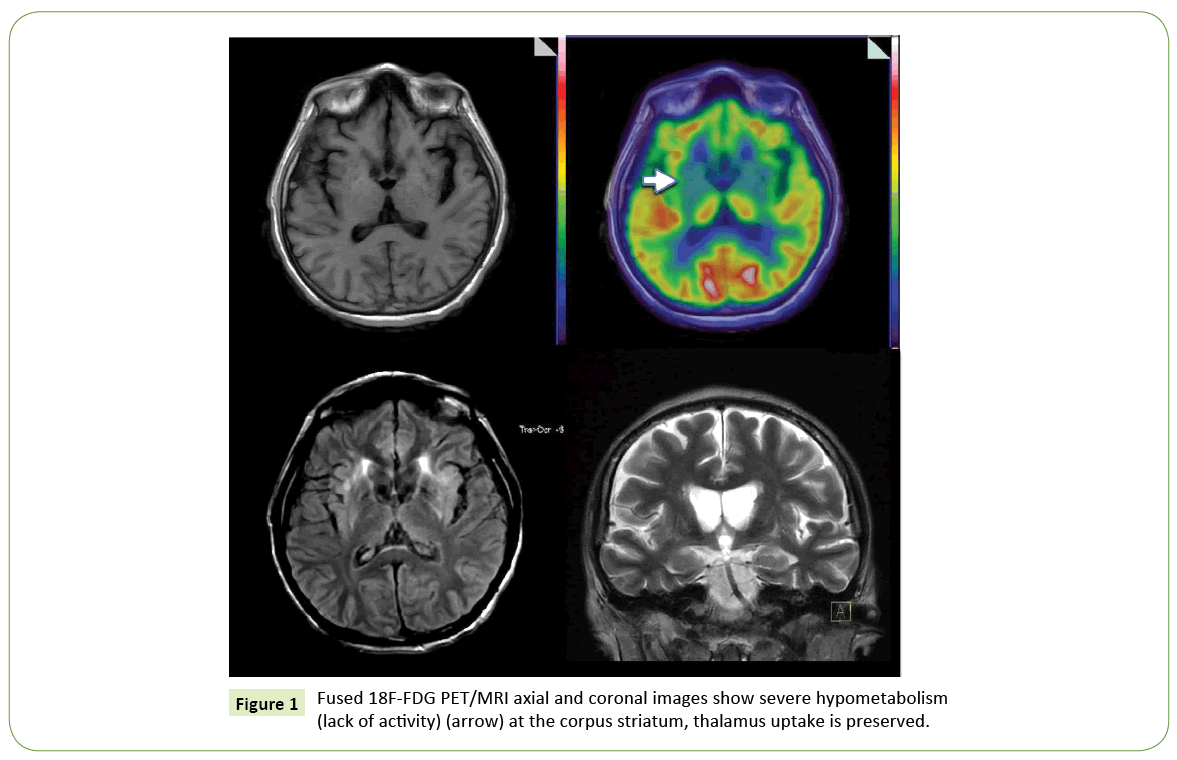
Evaluation Of Wilson Disease With 18f Fdg Pet Ct Insight Medical Publishing

Pet Brain Amyvid Scan
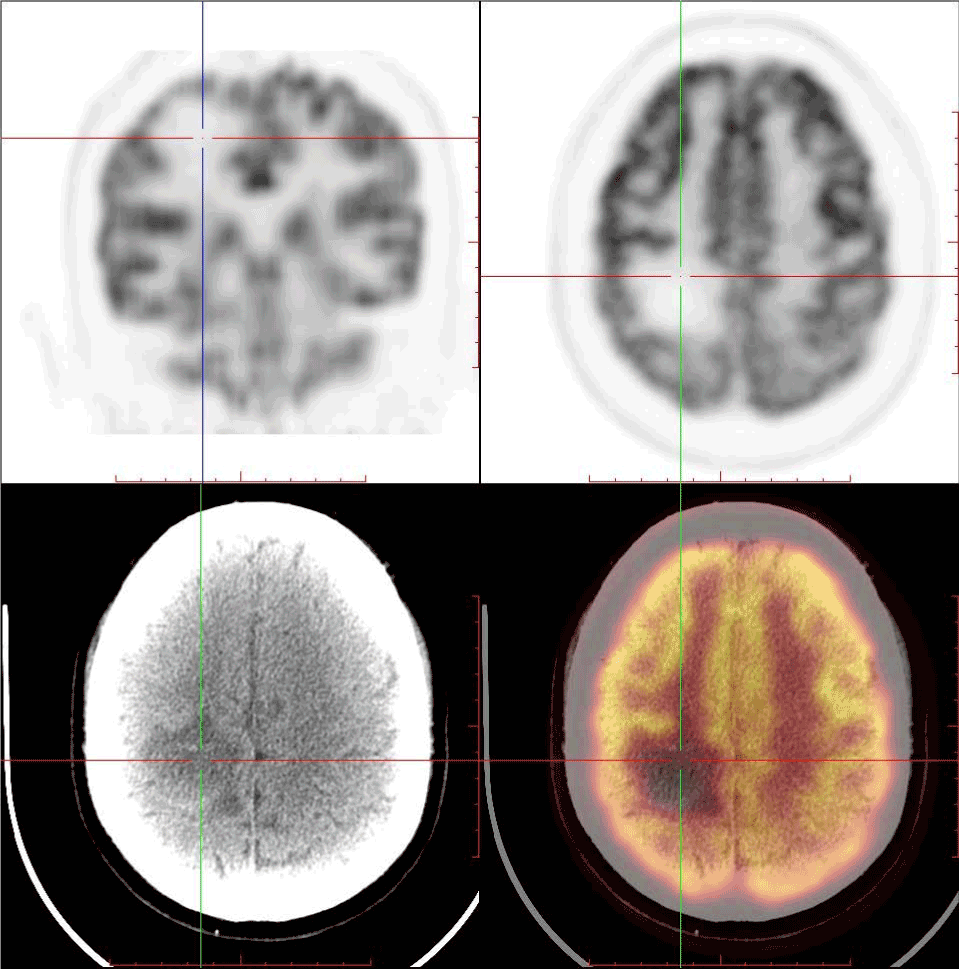
Cerebral Metastasis With Sup 18 Sup F Fdg Uptake Deficiency From Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
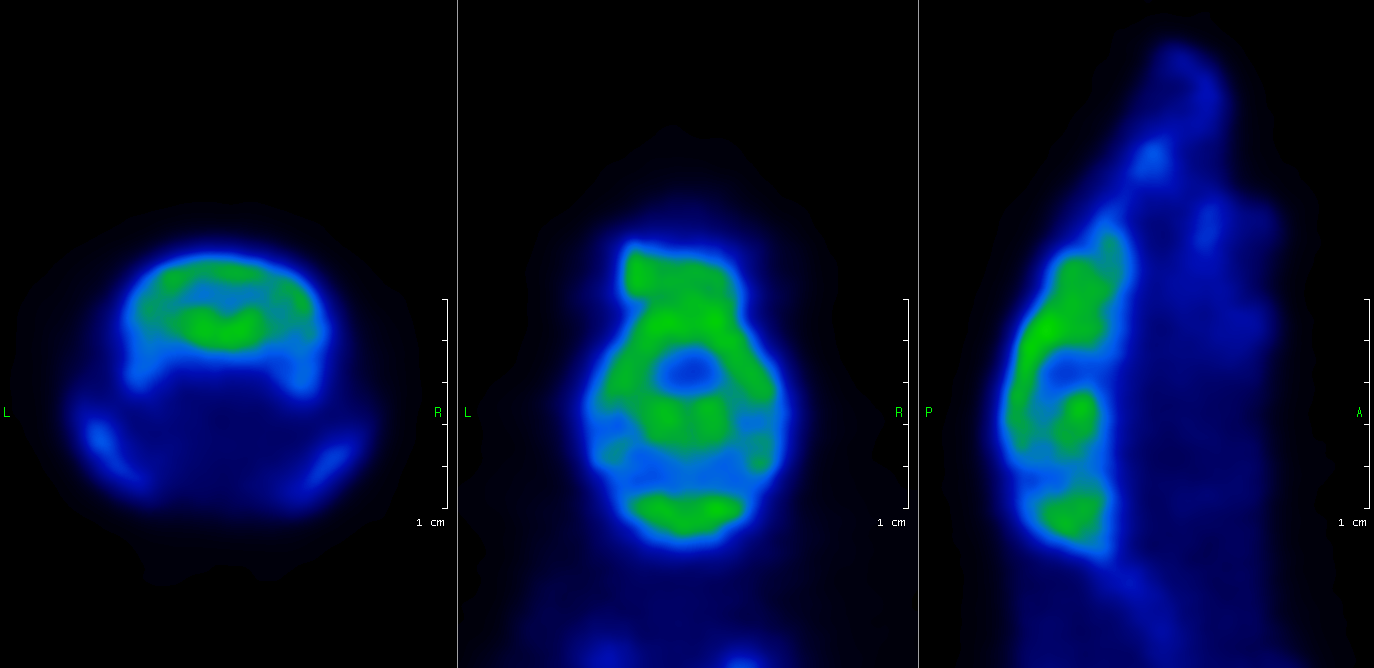
Nanoscan Pet Mri Mouse Brain Fdg Pet Cromed Research
Generative Fdg Pet And Mri Model Of Aging And Disease Progression In Alzheimer S Disease
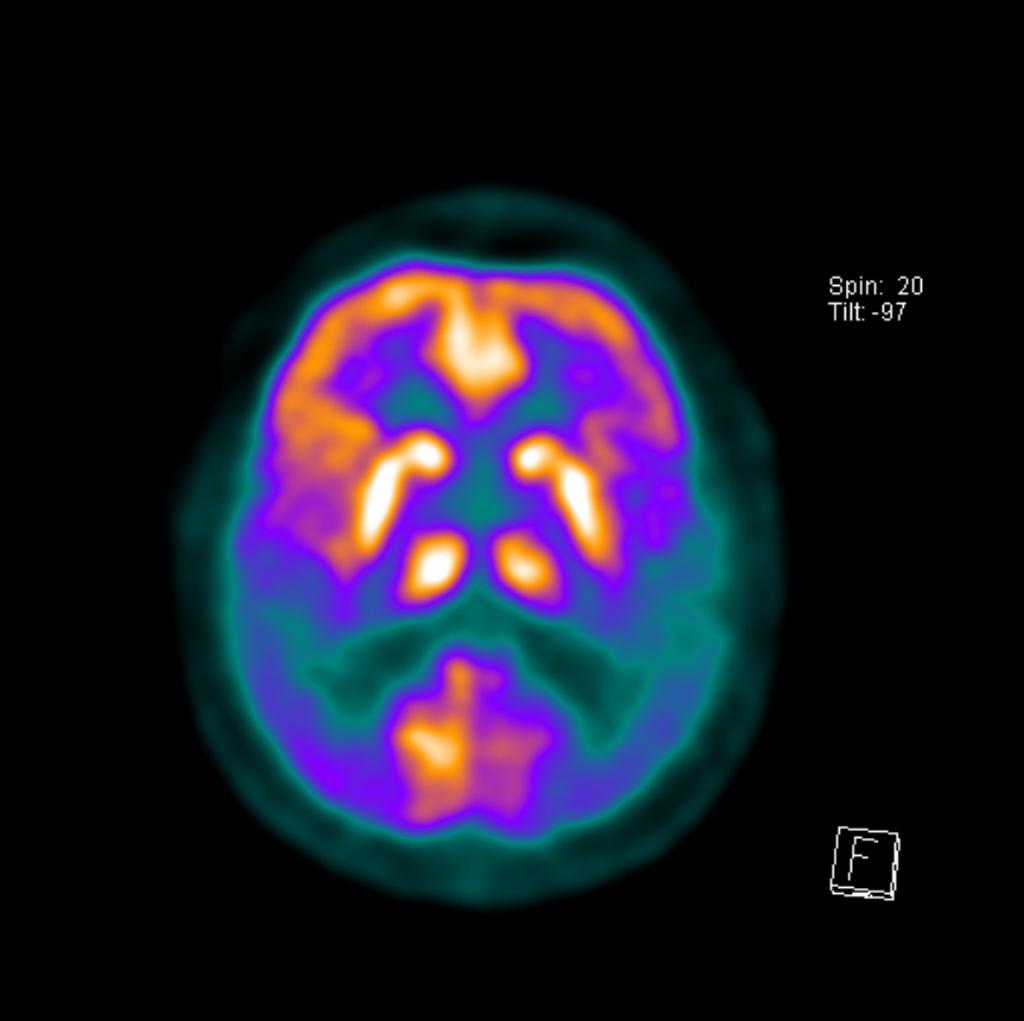
Alzheimer Disease Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Brain Pet In Suspected Dementia Patterns Of Altered Fdg Metabolism Radiographics

Fdg Pet Hypometabolism Is More Sensitive Than Mri Atrophy In Parkinson S Disease A Whole Brain Multimodal Imaging Meta Analysis Sciencedirect

Pet Brain Dementia
Brain Metastases Assessment By Fdg Pet Ct Can It Eliminate The Necessity For Dedicated Brain Imaging Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text

Abnormal Brain Metabolism On Fdg Pet Ct Is A Common Early Finding In Autoimmune Encephalitis Neurology Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation

Semi Quantitative Assessment Using 18f Fdg Tracer In Patients With Severe Brain Injury Protocol

Fdg Pet Displays Its Prowess In Dementia Detection Physics World

How To Read Brain Pet Scan For Dementia Youtube
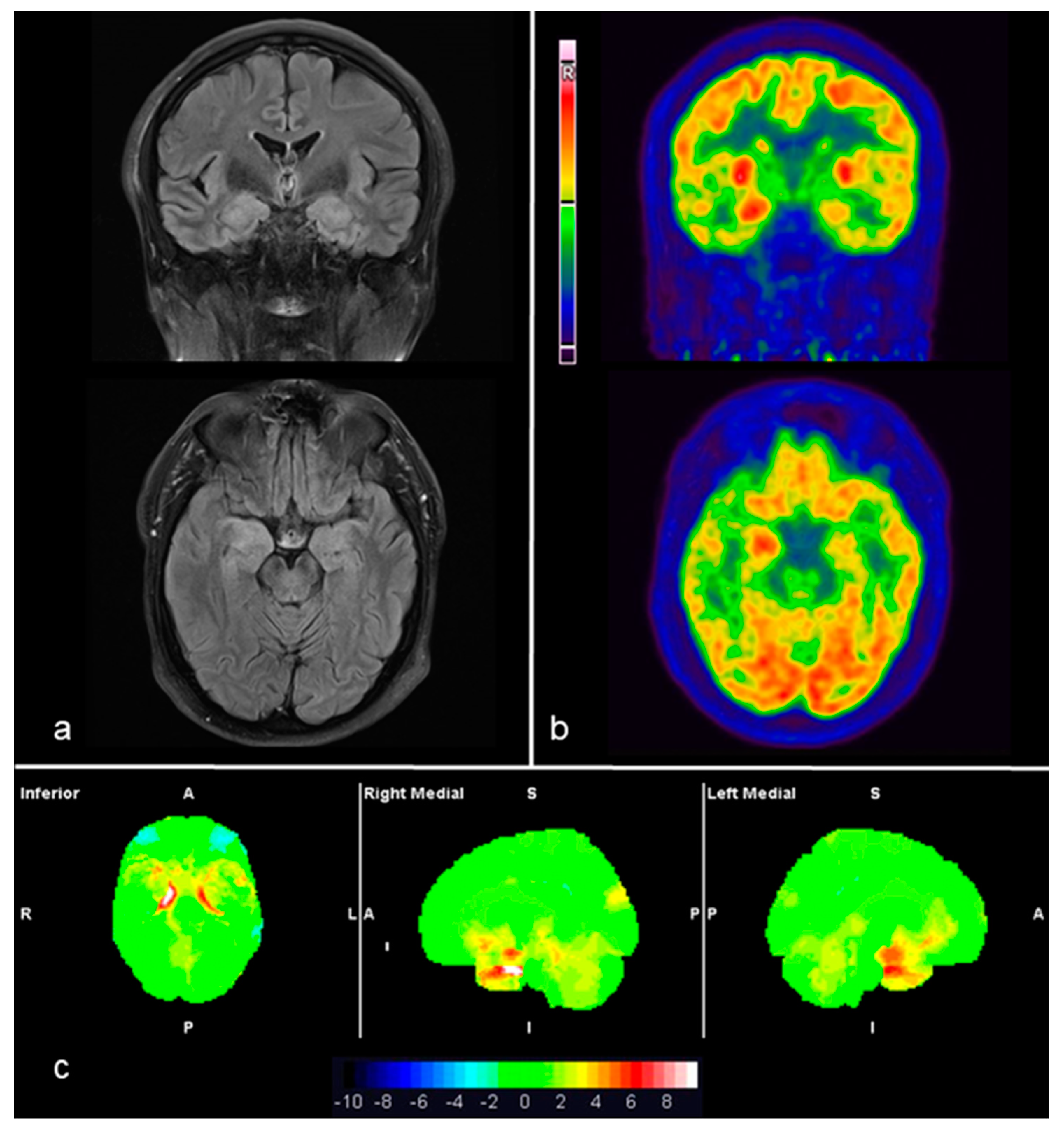
Diagnostics Free Full Text 18f Fdg Pet Imaging Patterns In Autoimmune Encephalitis Impact Of Image Analysis On The Results Html

Fdg Pet The Jagust Lab

Figure 2 From Comparison Of 18 F Fet And 18 F Fdg Pet In Brain Tumors Semantic Scholar

Pet Approaches For Diagnosis Of Dementia American Journal Of Neuroradiology
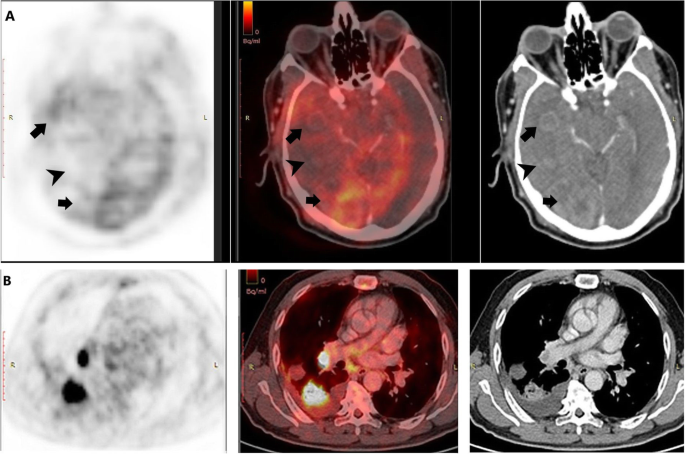
Reversible Brain Hypometabolism Associated With Central Nervous System Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Springerlink

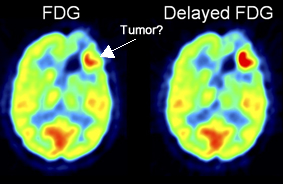
Voxel Based Analysis Of Dual Time Point 18f Fdg Pet Images For Brain Tumor Identification And Delineation Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
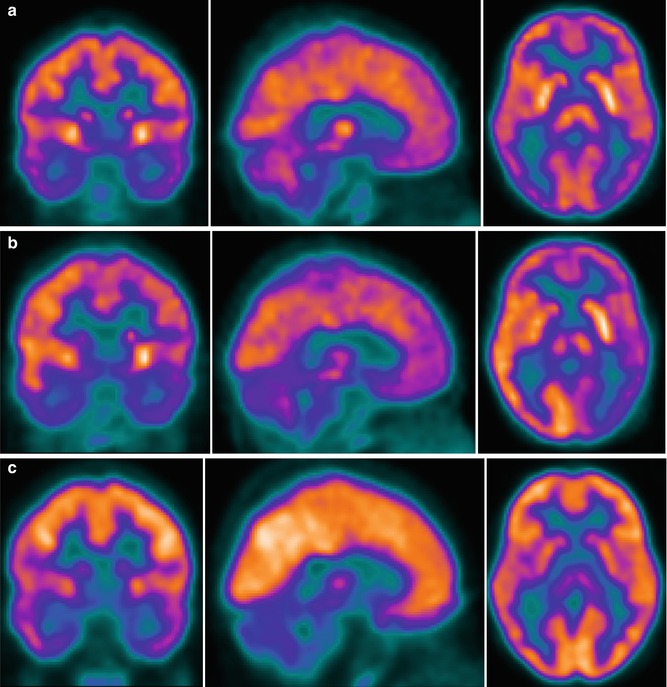
Brain 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome During And After The Acute Phase Radiology Key

Brain On Fdg Pet Ct Radiology Key

Brain Fluorodeoxyglucose Fdg Pet In Dementia Sciencedirect
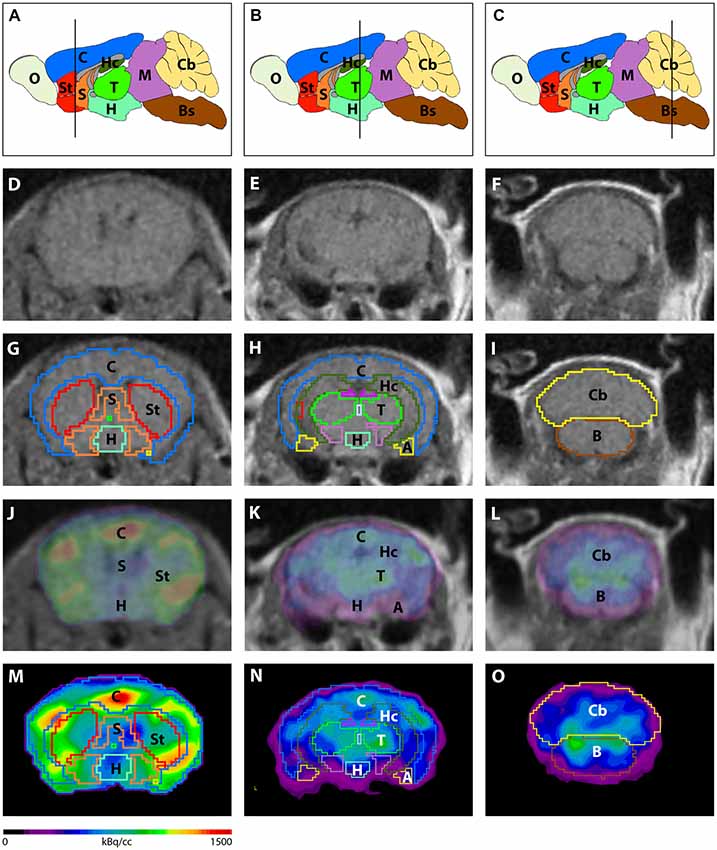
Frontiers 18f Fdg Pet Detects Drastic Changes In Brain Metabolism In The Tg4 42 Model Of Alzheimer S Disease Frontiers In Aging Neuroscience

Alzheimer S Disease Detection With Objective Statistical Evaluation Of Fdg Pet Brain Scans Essential Methodology For Early Identification Future Neurology

Pet Brain Cedars Sinai

Figure 1 From Comparison Of 18 F Fet And 18 F Fdg Pet In Brain Tumors Semantic Scholar

Inclusion Of Brain In Fdg Pet Ct Scanning Techniques In Cancer Patients Does It Obviate The Need For Dedicated Brain Imaging Semantic Scholar
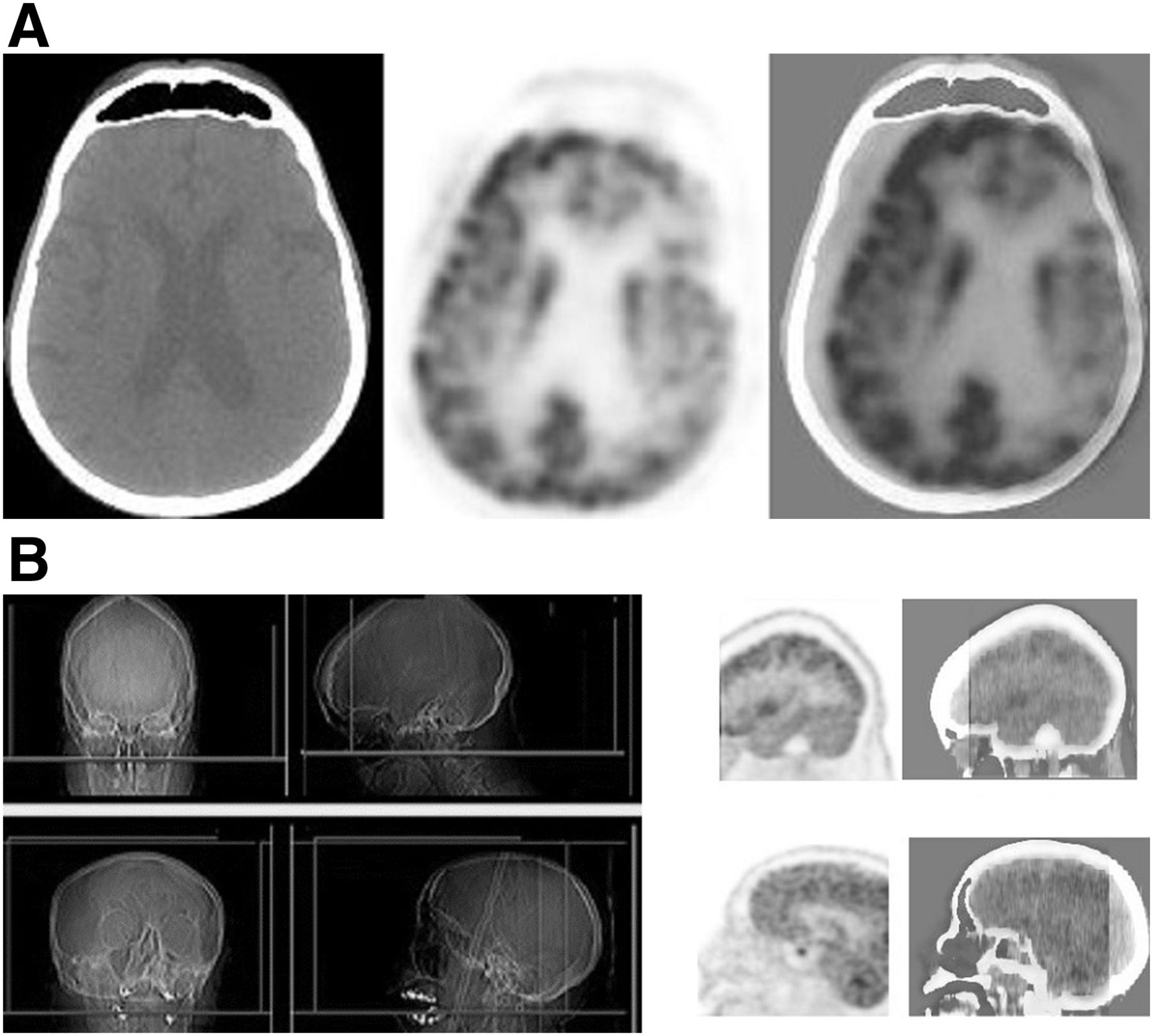
Current Status Of 18f Fdg Pet Brain Imaging In Patients With Dementia Journal Of Nuclear Medicine Technology
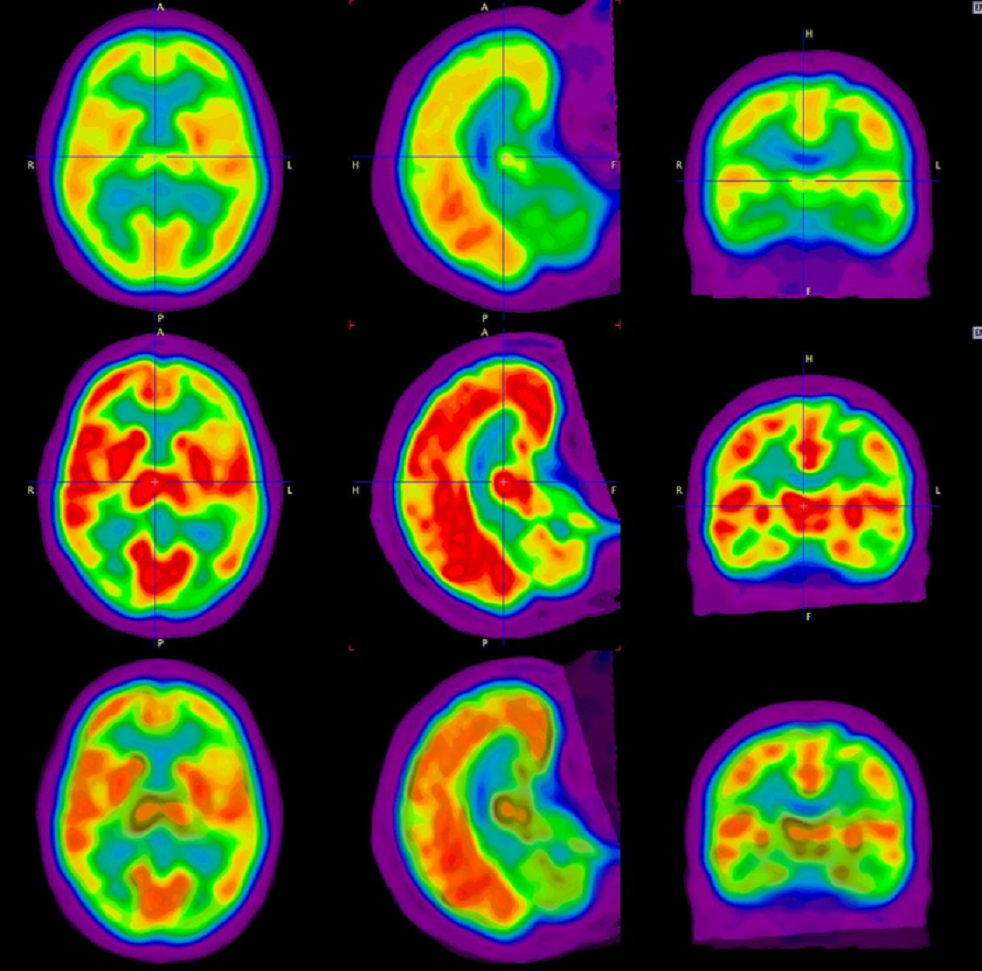
Cureus Quantitative Imaging Analysis Of Fdg Pet Ct Imaging For Detection Of Central Neurolymphomatosis In A Case Of Recurrent Diffuse B Cell Lymphoma
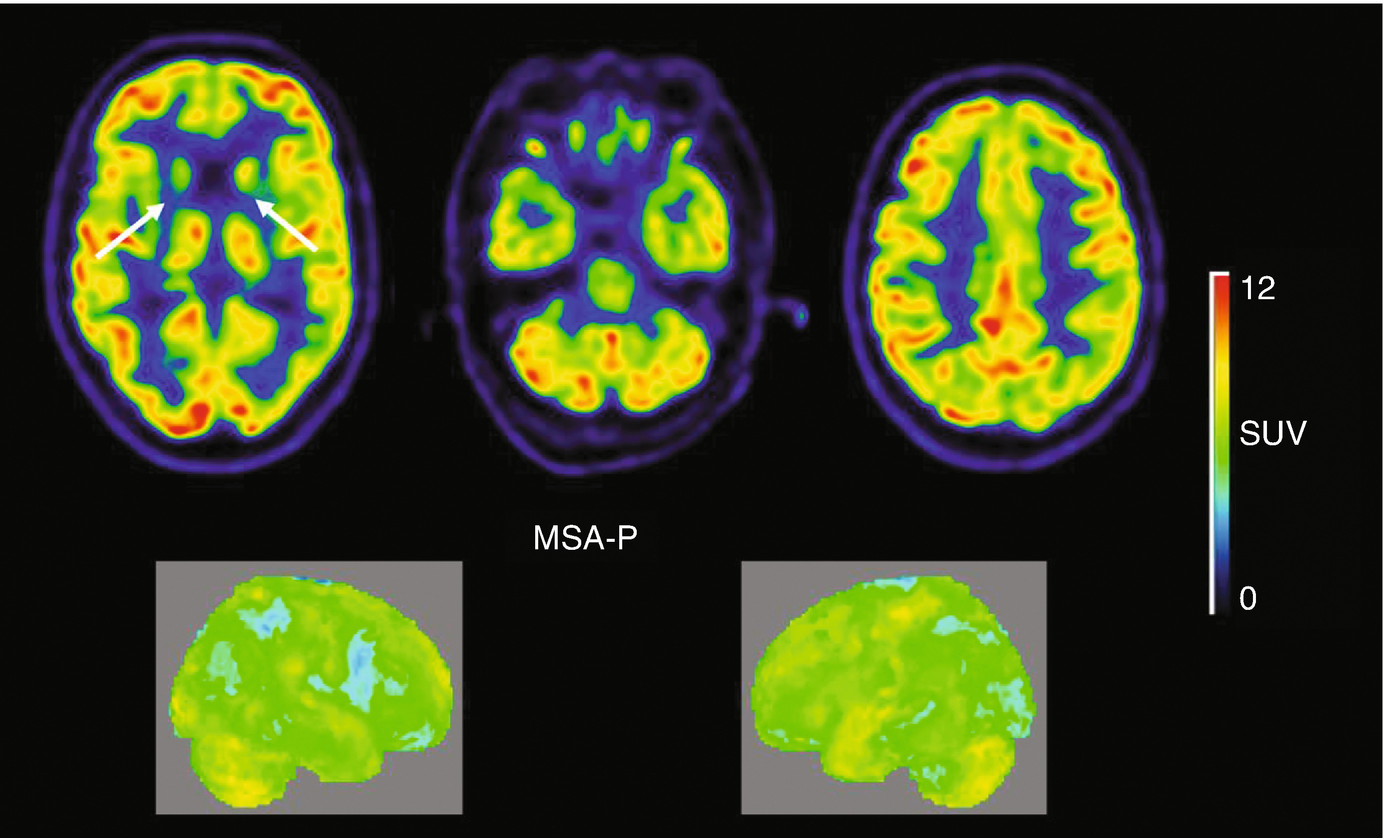
18f Fdg Pet Ct In Movement Disorders Springerlink

Fdg Pet Imaging In Neurodegenerative Brain Diseases Intechopen
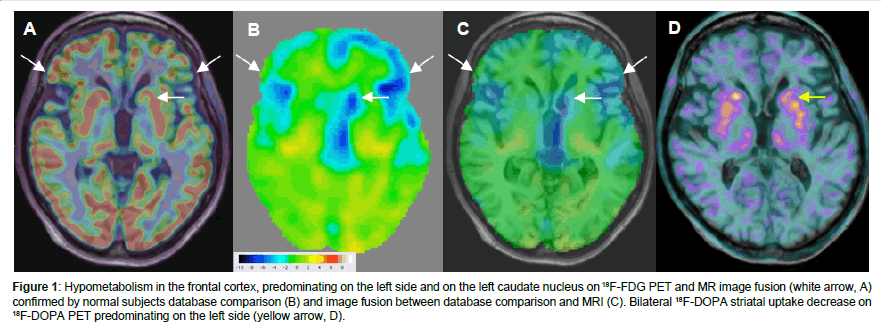
Sup 18 Sup F Fdg Pet Identified Superior Colliculi Hypometabolism In Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Omics International

A 73 Year Old Woman Confirmed The Diagnosis Of Brain Metastases A Download Scientific Diagram
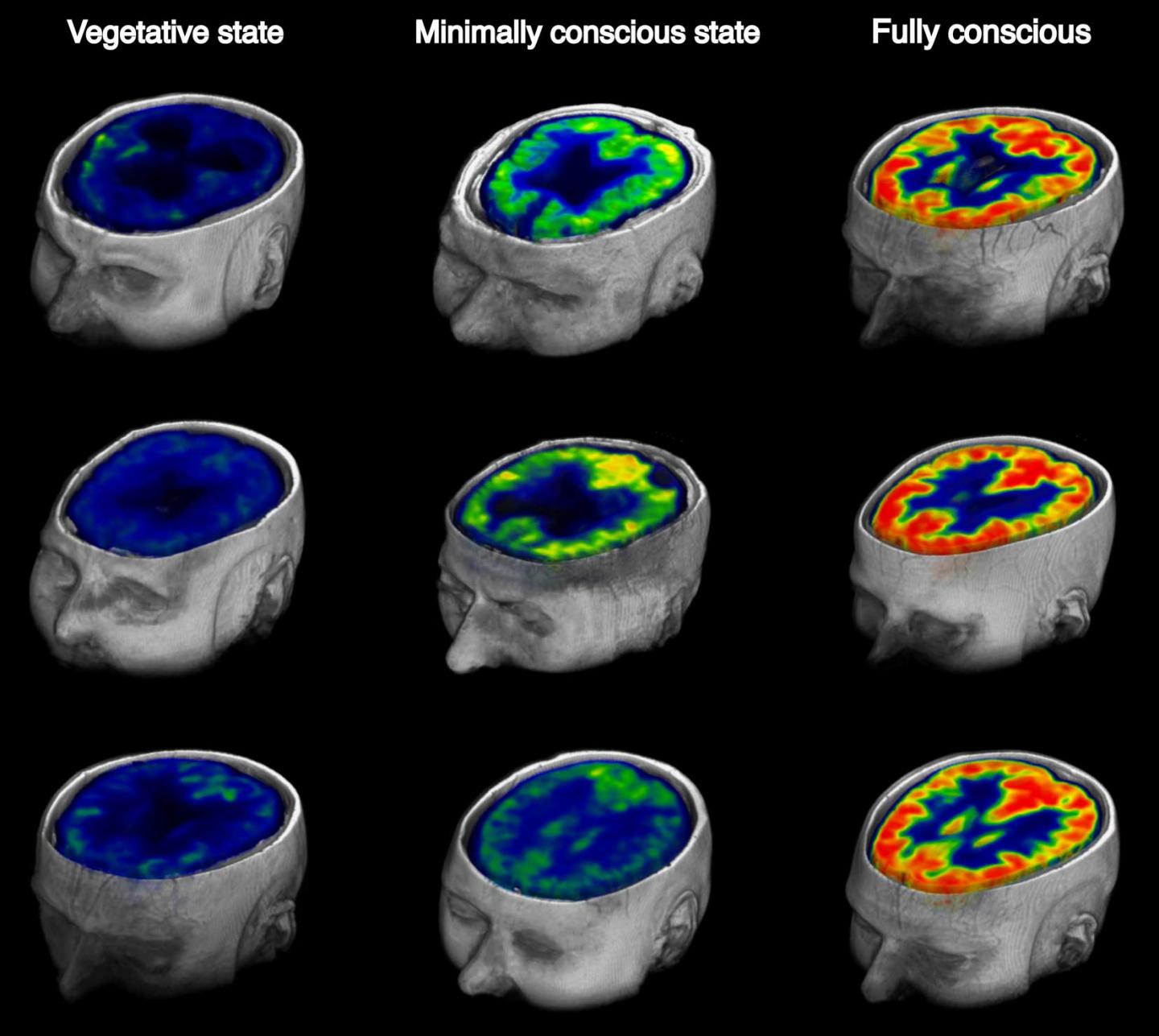
F Fdg Pet Brain Imaging Could Predict Recovery In Vegetative Patients 2 Minute Medicine

18f Fdg Pet The Early Phases And The Delivery Rate Of 18f Av45 Pet As Proxies Of Cerebral Blood Flow In Alzheimer S Disease Validation Against 15o H2o Pet Sciencedirect

Positron Emission Tomography In Autoimmune Disorders Of The Central Nervous System Intechopen
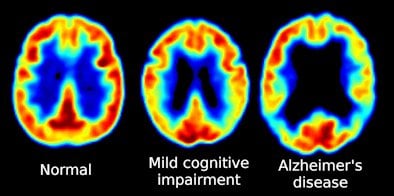
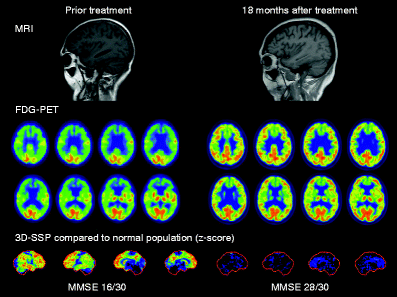
Promising Alzheimer S Drug Halts Memory Loss Neuroscience News

Fdg Pet Displays Its Prowess In Dementia Detection Physics World

History Of Pet Scanners

Positron Emission Tomography Fdg Pet Brain Scan Obtained 30 Min After Download Scientific Diagram

Alzheimer S Disease Northern California Pet Imaging Center
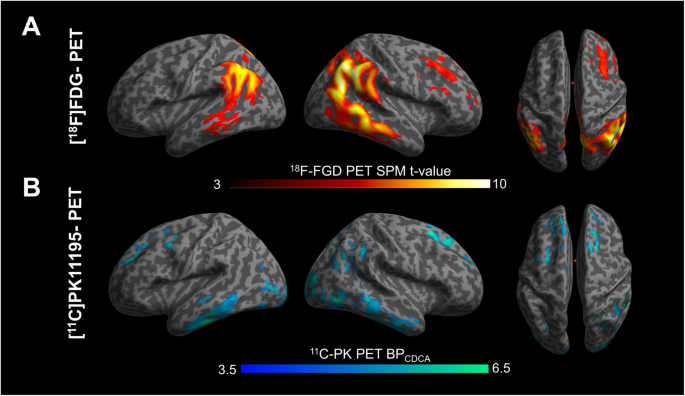
The Combined Effects Of Microglia Activation And Brain Glucose Hypometabolism In Early Onset Alzheimer S Disease Alzheimer S Research Therapy Full Text
Frontiers Fdg Pet Imaging In Mild Traumatic Brain Injury A Critical Review Frontiers In Neuroenergetics

Fdg Pet Ct Findings In A Clinically Diagnosed Case Of Childhood Autism

Role Of 18f Fdg Pet Imaging In The Diagnosis Of Autoimmune Encephalitis The Lancet Neurology

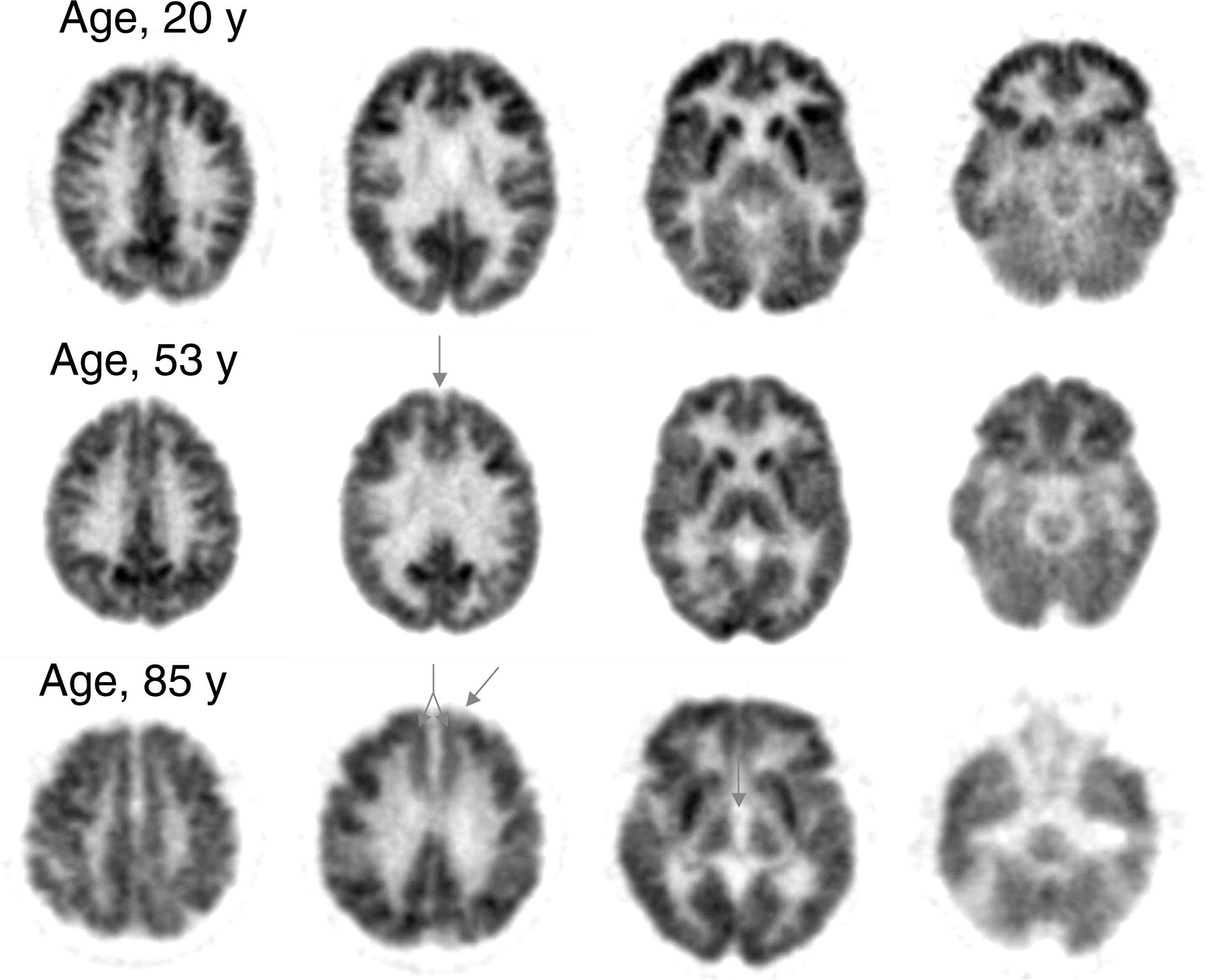
Fdg Pet Brain Glucose Metabolism As A Function Of Endocrine Aging
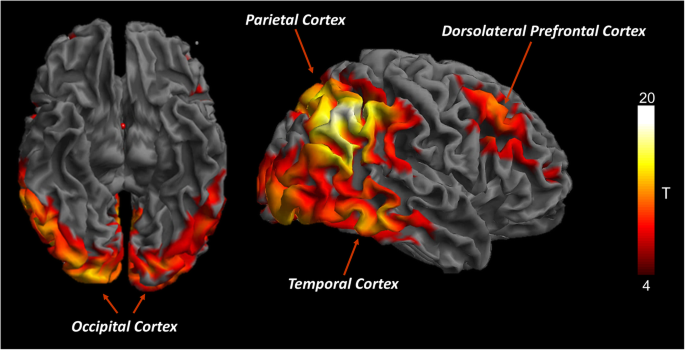
Brain Glucose Metabolism In Lewy Body Dementia Implications For Diagnostic Criteria Alzheimer S Research Therapy Full Text

Small Animal Pet Imaging

Brain 18f Fdg Pet Mri Coregistration Iconographic Essay

Metabolic Brain Changes Across Different Levels Of Cognitive Impairment In Als A 18f Fdg Pet Study Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry

Fdg Pet Brain Scan Of A Patient With Non Fluent Aphasia Open I

Local Activity Determines Functional Connectivity In The Resting Human Brain A Simultaneous Fdg Pet Fmri Study Journal Of Neuroscience

The Potential Roles Of 18f Fdg Pet In Management Of Acute Stroke Patients

Pib Fdg Pet Change Diagnosis For Dementia Patients

Global Brain Metabolism Detected By Fdg Pet In A Healthy Control Left Download Scientific Diagram

Brain 18 F Fdg Pet Is Showed The Known Spatial Pattern Of A Cerebral Download Scientific Diagram

Brain Pet In Suspected Dementia Patterns Of Altered Fdg Metabolism Radiographics
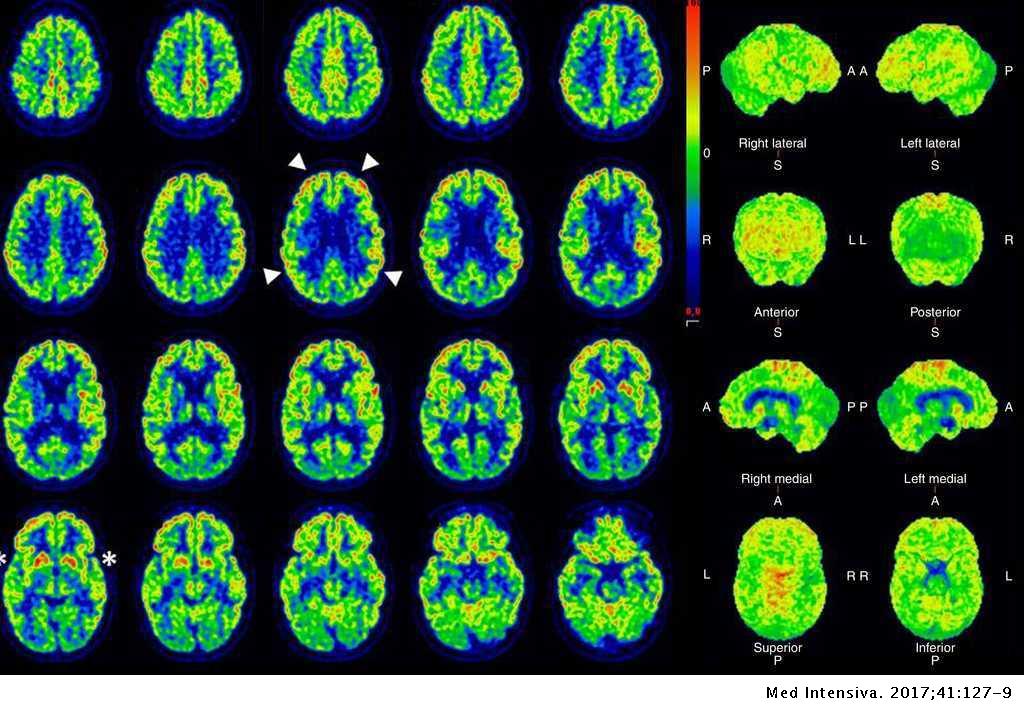
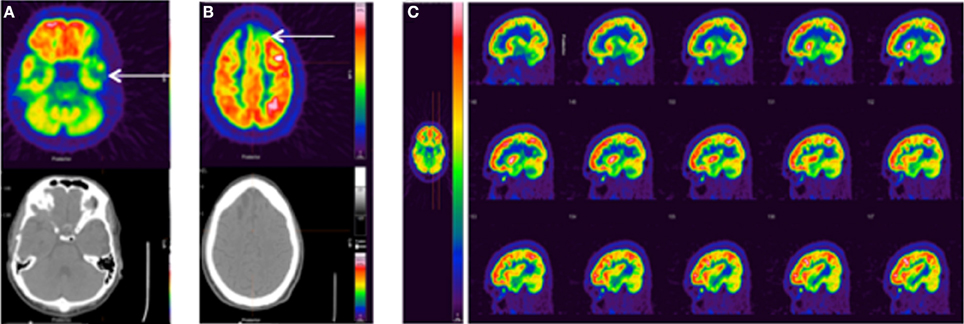
The Role Of 18f Fluorodeoxyglucose Pet Ct In Ruling Out Vegetative State Medicina Intensiva English Edition

Voxel Based Analysis Of Dual Time Point 18f Fdg Pet Images For Brain Tumor Identification And Delineation Journal Of Nuclear Medicine
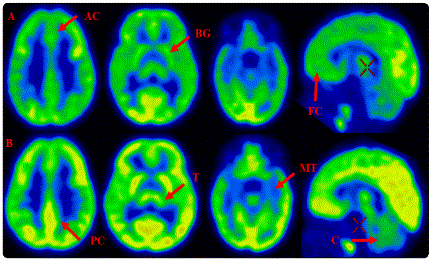
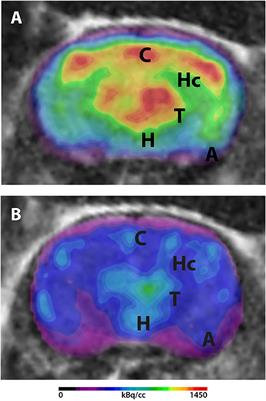
Normal Brain Glucose Metabolism Of A One Year Infant Case Report Madridge Publishers
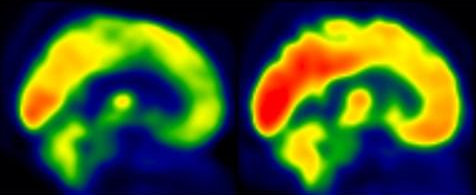
Fdg Pet Shows Where Exercise Could Stall Alzheimer S

Pet Approaches For Diagnosis Of Dementia American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Fdg Pet Imaging Reliable In Identifying Abnormalities In Parkinson Disease Neurology Advisor

Brain 18f Fdg Pet Mri Coregistration Iconographic Essay

Comparative Evaluation Of 18f Fdopa 13n Ammonia 18f Fdg Pet Ct And Mri In Primary Brain Tumors A Pilot Study
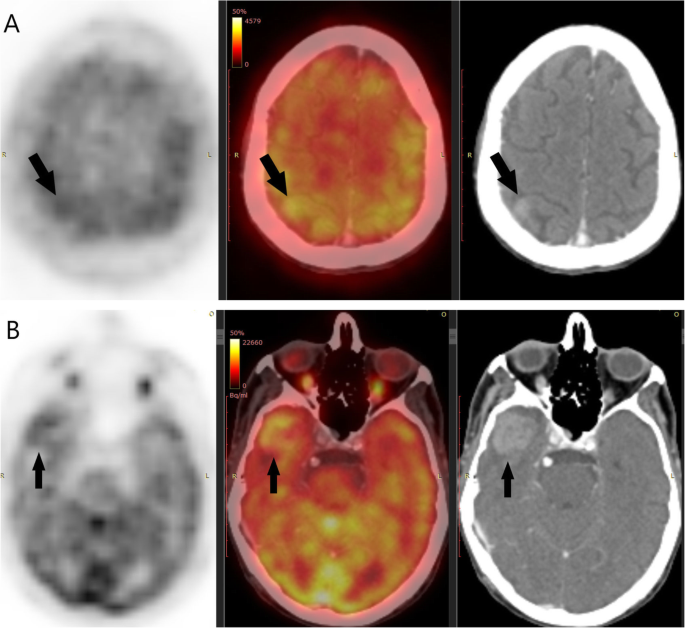
Brain Metastases Assessment By Fdg Pet Ct Can It Eliminate The Necessity For Dedicated Brain Imaging Egyptian Journal Of Radiology And Nuclear Medicine Full Text

Measuring The Brain S Amyloid Buildup Less Effective In Identifying Severity Progression Of Alzheimer S Disease Compared To Other Imaging Methods Pr News
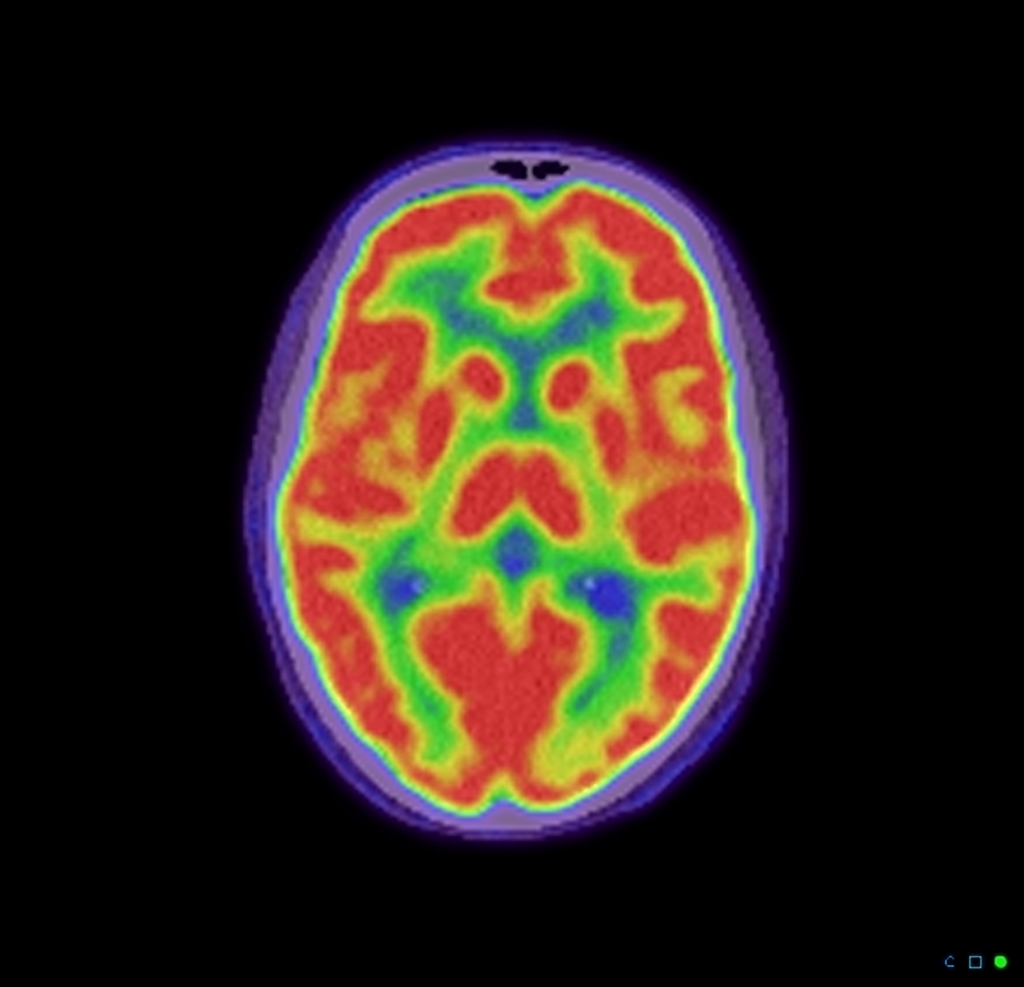
Normal Brain Pet Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
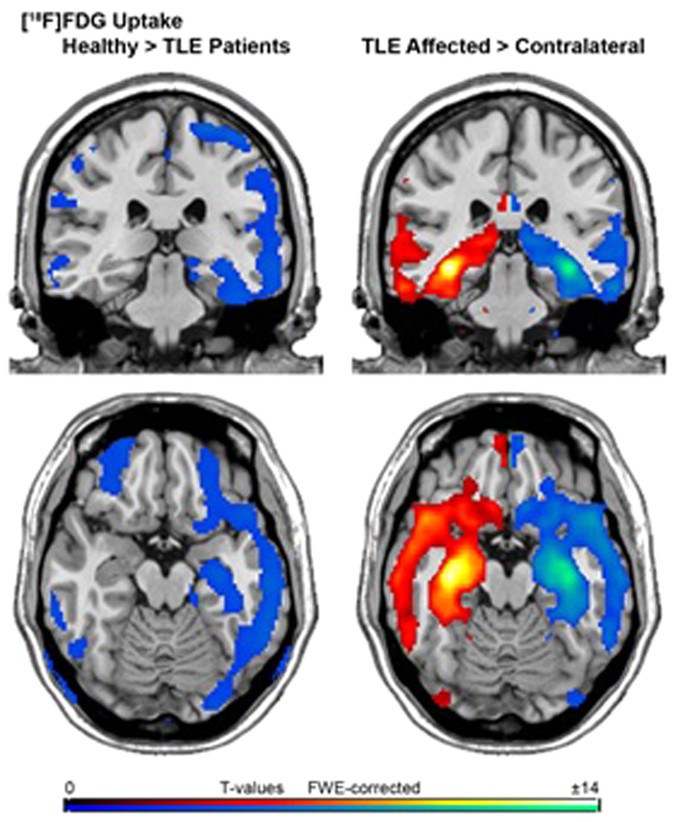
Insights Into Intrinsic Brain Networks Based On Graph Theory And Pet In Right Compared To Left Sided Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Scientific Reports

Pet Approaches For Diagnosis Of Dementia American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Pet Approaches For Diagnosis Of Dementia American Journal Of Neuroradiology
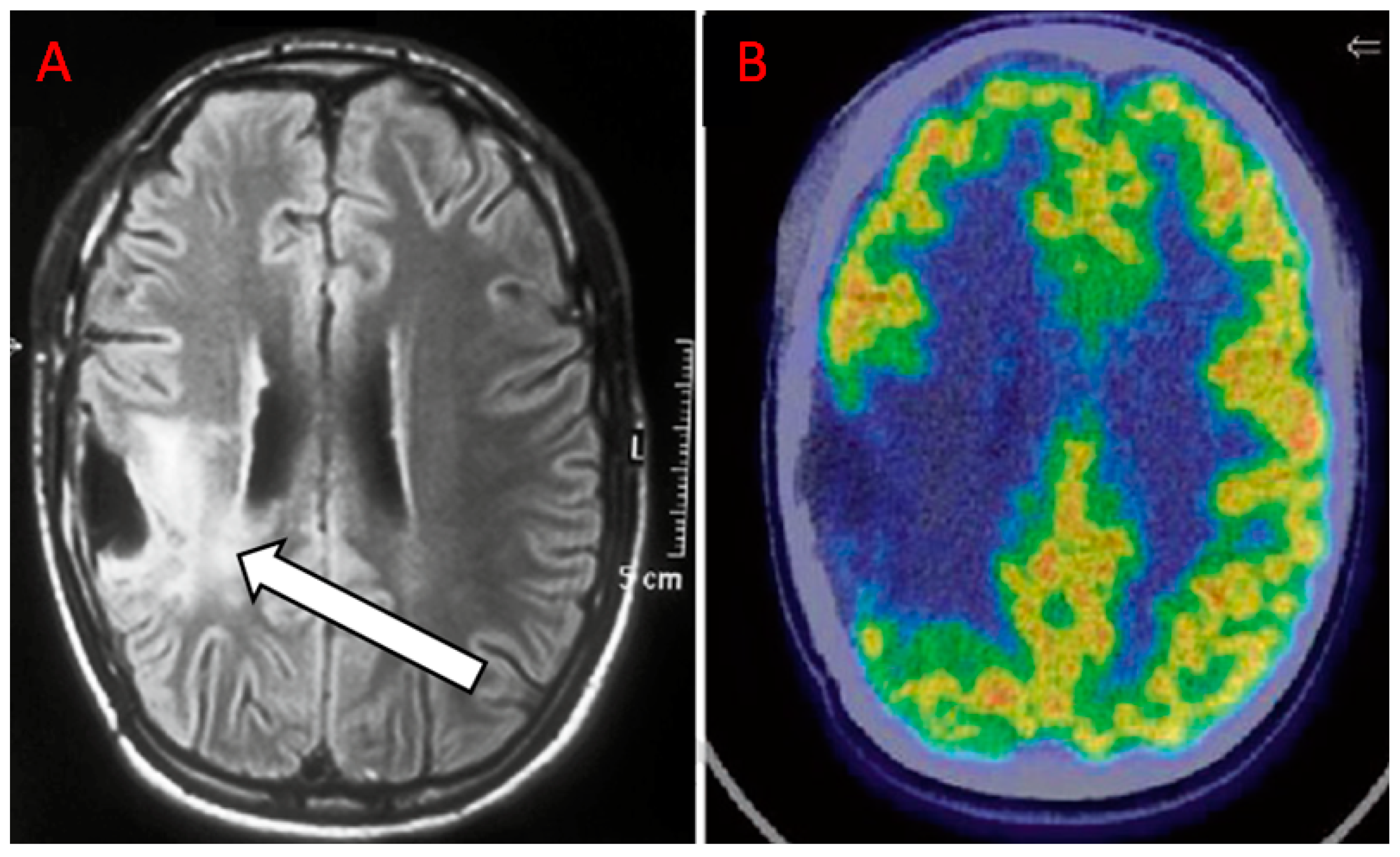
Diagnostics Free Full Text The Additional Value Of 18f Fdg Pet And Mri In Patients With Glioma A Review Of The Literature From 15 To Html

Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly

Brain Positron Emission Tomography Wikipedia
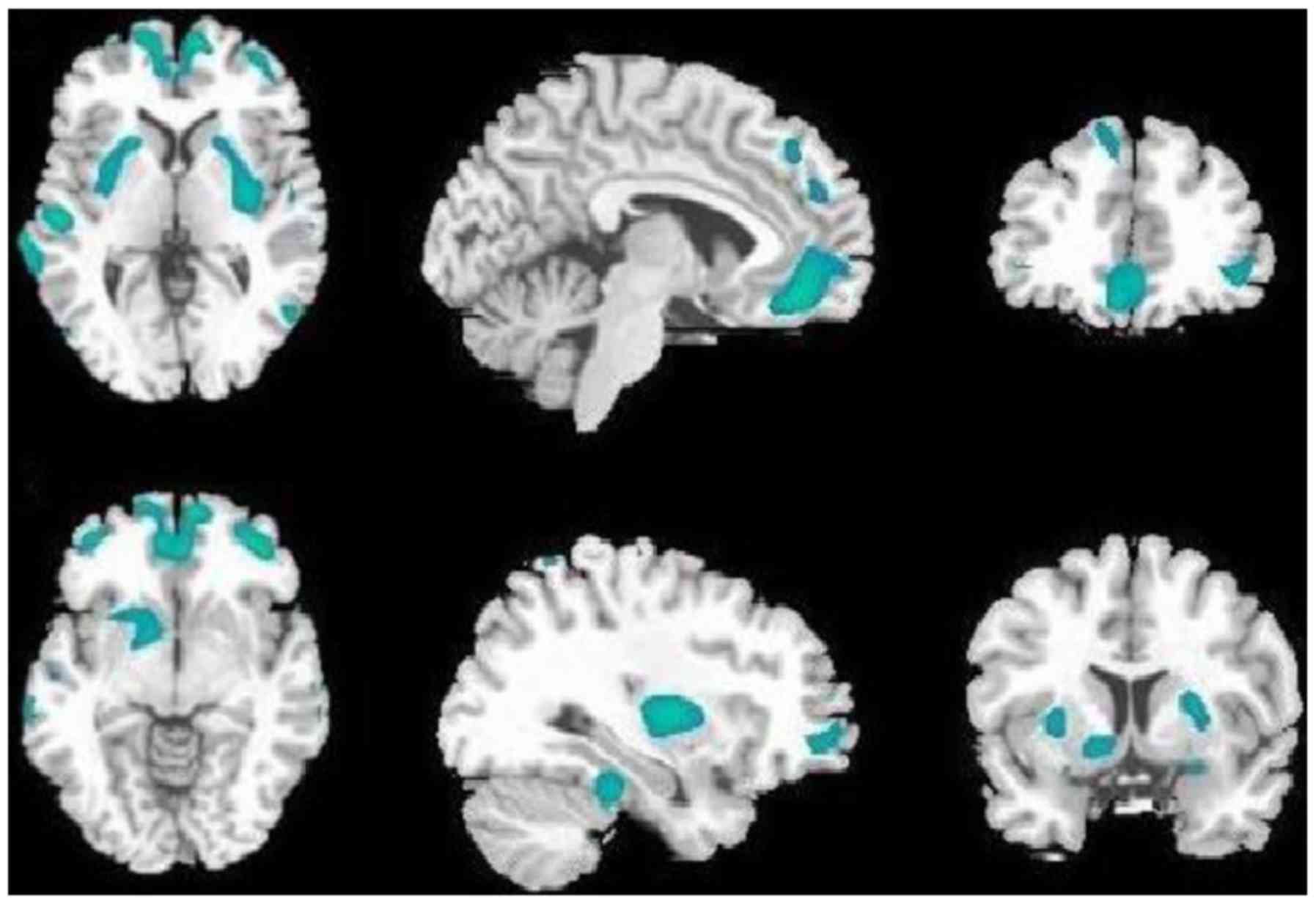
A Combined Study Of 18f Fdg Pet Ct And Fmri For Assessing Resting Cerebral Function In Patients With Major Depressive Disorder

18f Fdg Pet Algorithm Allows Early Prediction Of Alzheimer S Neurology Advisor
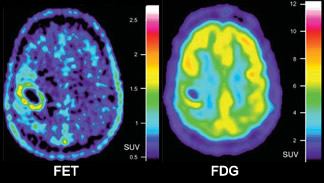
The Neurology Of Pet

Pet Ct

Pet Scans And Alzheimer S Bluegrass Regional Imaging

Congress Online

High Resolution Pet Ct Assesses Brain Stem Function In Patients With Hearing Impairment

Brain On Fdg Pet Ct Radiology Key
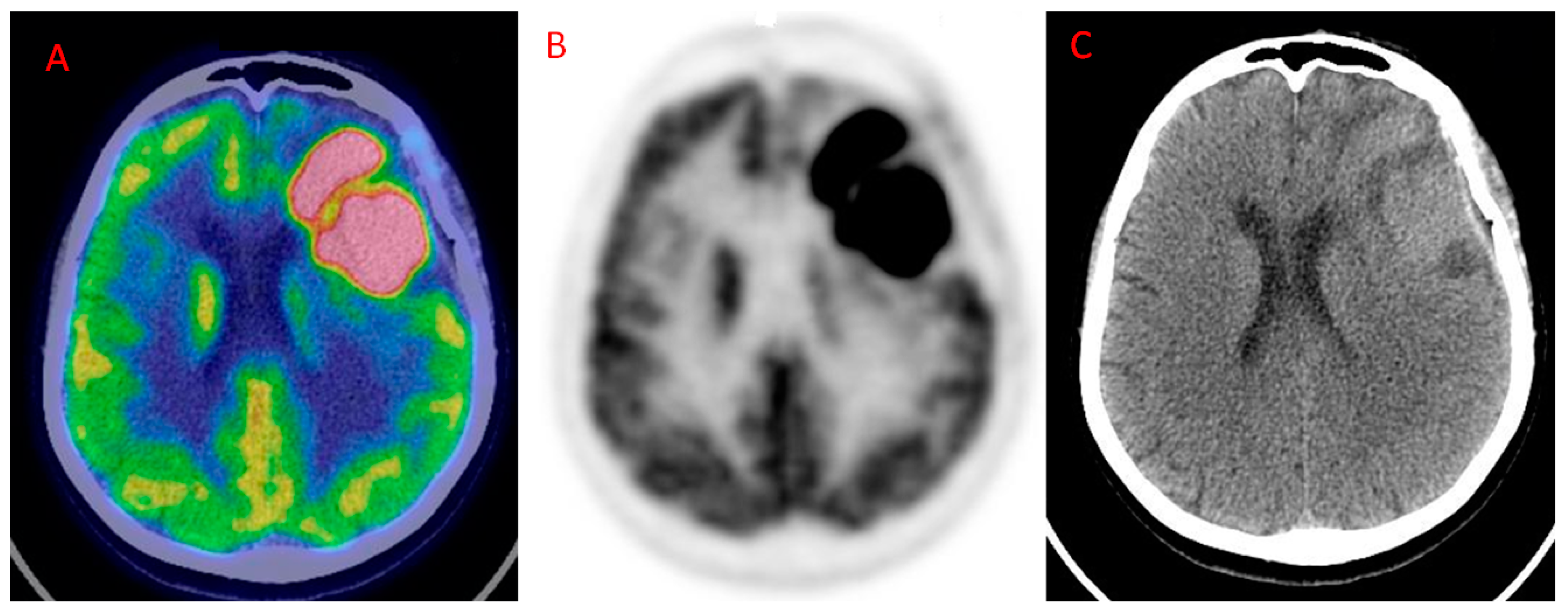
Diagnostics Free Full Text The Additional Value Of 18f Fdg Pet And Mri In Patients With Glioma A Review Of The Literature From 15 To Html

Cerebral Glucose Hypometabolism In Tick Borne Encephalitis A Pilot Study In 10 Patients Sciencedirect

Brain 18f Fdg Pet Ct Imaging In Posterior Cortical Atrophy

Integrated 18f Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging 18f Fdg Pet Mri A Multimodality Approach For Comprehensive Evaluation Of Dementia Patients A Pictorial Essay Jena A Renjen Pn Taneja S Gambhir A Negi P

Normal Distribution Of Fdg Uptake In The Brain Axial Images Of A Download Scientific Diagram



