Adenocarcinoma In Situ Histology
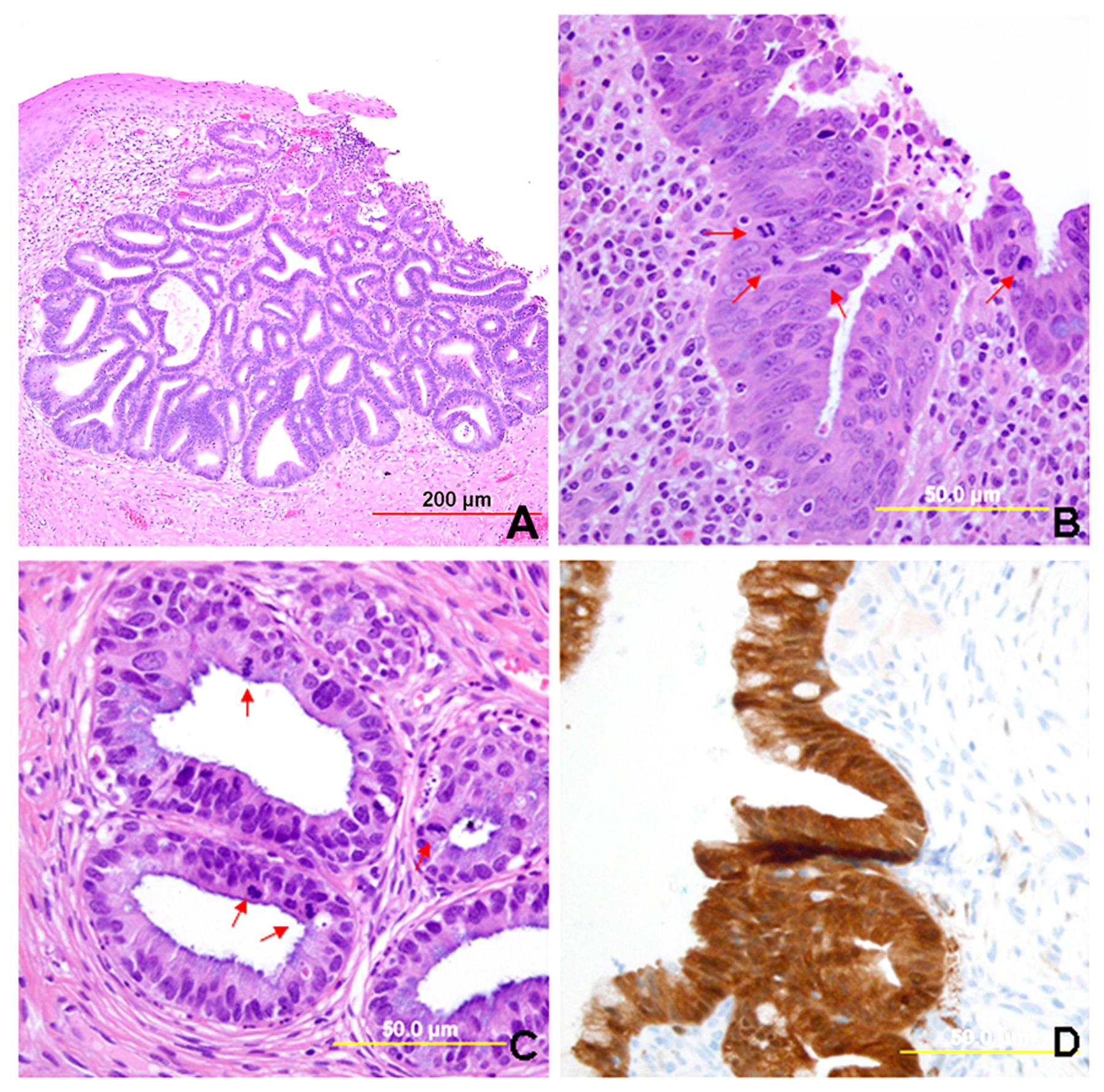
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm
Www Thoracic Org Statements Resources Lcod Adenocarcinoma Pdf

Current Trends In The Management Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Cancer Network
Types Of Breast Cancer Breast Pathology Johns Hopkins Pathology

Squamous Carcinoma In Situ Of The Larynx Mypathologyreport Ca

A Florid Variant Of Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Is Characterized By Download Scientific Diagram
Also called epidermoid carcinoma).

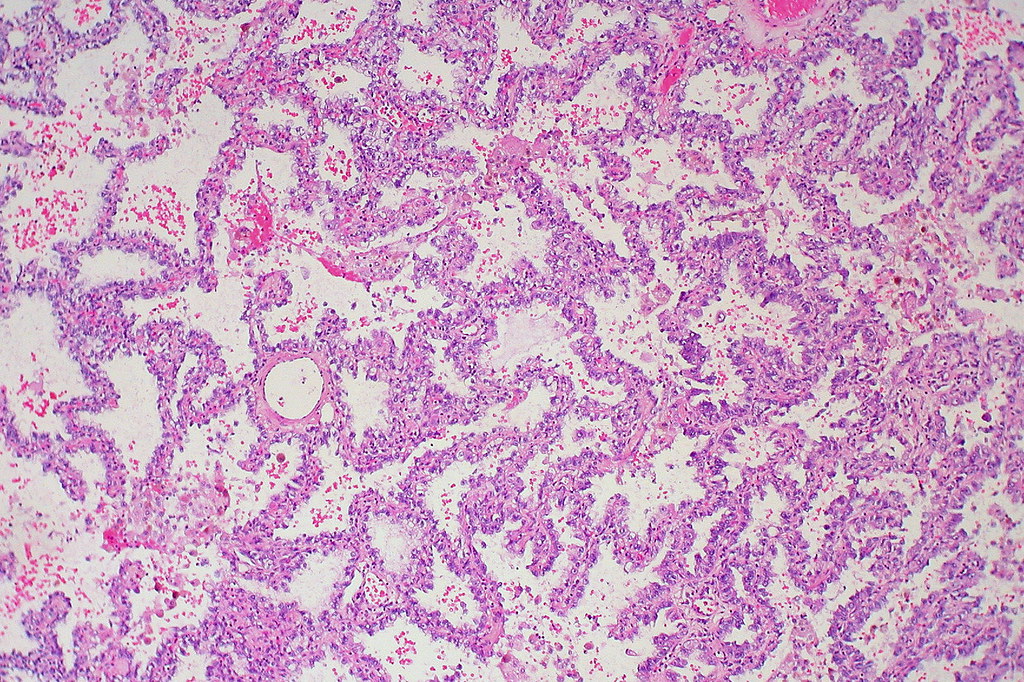
Adenocarcinoma in situ histology. Histopathology Breast Lobular carcinoma in situ. In situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (AIS)—previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a noninvasive growth pattern This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung If completely removed by surgery, the prognosis is excellent with up to 100% 5year survival Although the entity of. What is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)?.
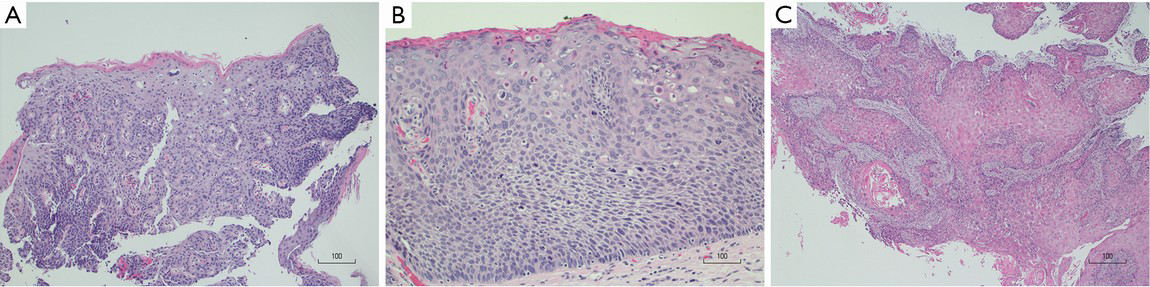
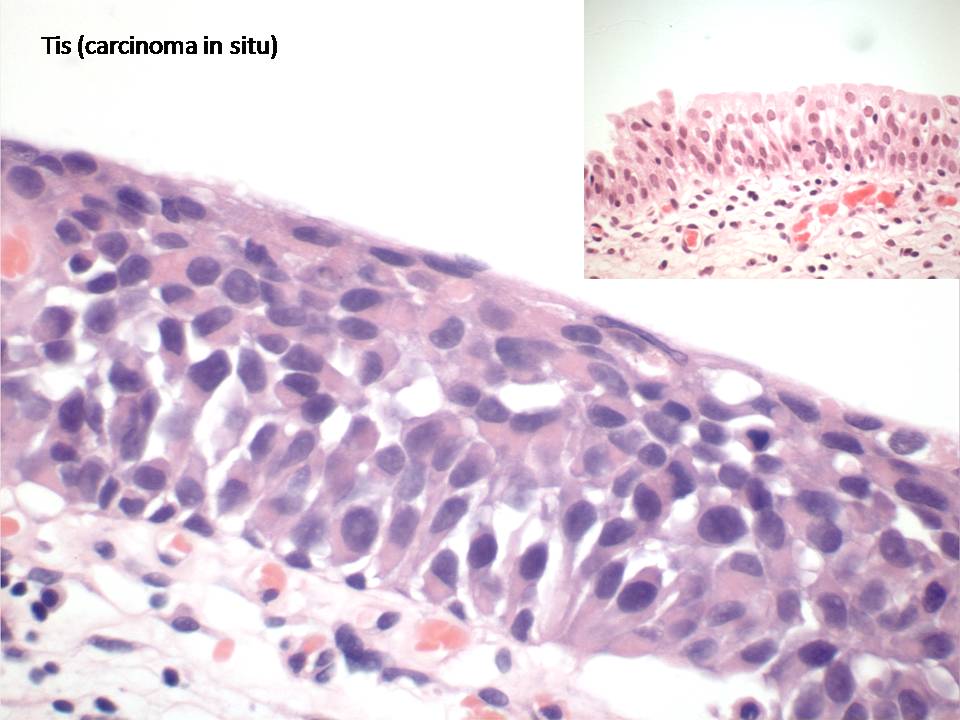
Histology of squamous cell carcinoma in situ The scanning power view of squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) reveals epidermal alteration (Figure 1) Closer inspection reveals atypia of the keratinocytes across the full thickness of the epidermis (Figures 2 and 3) There is a loss of the granular layer and overlying zones of parakeratosisSparing of the adnexal ostial epithelium is. The term carcinoma in situ is a term used to define and describe a cancer that is only present in the cells where it started and has not spread to any nearby tissues Carcinoma in situ is the earliest stage of a cancer, and is, at this stage, considered "noninvasive" With regard to staging, carcinoma in situ is considered stage 0 cancer. Primary cervical small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (SCNEC) is a rare and aggressive tumor Herein, we describe the first cytological case of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) admixed with SCNEC A 65yearold postmenopausal Japanese female presented with abnormal genital bleeding The Papanicolaou smear of the cervix demonstrated the presence of 2 distinct neoplastic components in an inflammatory background.
Insitu carcinoma with duct and lobular features means that the insitu carcinoma looks like DCIS in some ways and LCIS in some ways (when looked at under the microscope), and so the pathologist can’t call it one or the other If DCIS is left untreated, it can go on to become an invasive cancer, so it is often called a precancer Still, we don’t really understand it well. Adenocarcinoma in situ demonstrates several histological patterns papillary, glandular, cribriform, and flat Adenocarcinoma in situ can be pure or coexist with urothelial CIS or noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma In some cases, in situ adenocarcinoma is seen in association with invasive adenocarcinoma. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) More common in young women, often bilateral;.
The two major patterns seen in breast insitu carcinoma are ductal carcinoma insitu (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma insitu (LCIS) "Intraductal carcinoma" is the same as "ductal carcinoma insitu" In some cases, the insitu carcinoma can have both duct and lobular features and in some cases DCIS and LCIS may both be present at the same time 3. To make reproducible diagnoses for oral carcinoma in situ (CIS), combined immunohistochemistry directed at the positioning of squamous cell proliferation (Ki67) and differentiation (keratin (K) 13 and K19) was used, both of which support histological evaluations by providing biological evidence. Adenocarcinomas in situ (AIS) of the lung refer to a relatively new entity for a preinvasive lesion in the lung This entity partly replaces the noninvasive end of the previous term bronchoalveolar carcinoma.
• Adenocarcinoma in situ, NOS (8140) and a specific adenocarcinoma in situ or • Intraductal carcinoma, NOS (8500) and a specific intraductal carcinoma (Table 1) Note The specific histology may be identified as type, subtype, predominantly, with features of, major, with ___ differentiation, architecture or. Hepatoid Gastric Adenocarcinoma vs Hepatocellular Carcinoma;. What is adenocarcinoma of the colon?.
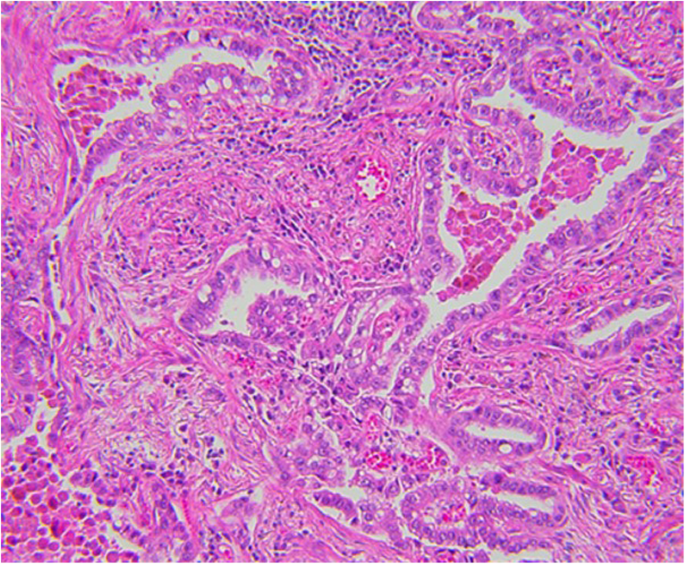
Hepatoid gastric adenocarcinoma (HGA) is commonly associated with an intestinal type carcinoma component. 3bii3 Adenocarcinoma In Situ Stratifiedtype (SMILE) Click to enlarge images SMILEs are newly described glandular intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix that are presumed to arise from the neoplastic transformation of multipotential stem cells or reserve cells. Solid Tumor Rules/HistologyLung What is the histology code and what H Rule applies for a diagnosis of well differentiated adenocarcinoma in situ (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma)?.
If the cervical biopsy specimen or endocervical curettage specimen suggests the possibility of endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, cervical conization is often used to confirm the diagnosis, excise the lesion, and exclude coexisting invasive adenocarcinoma. See Discussion Final Jul 29 19. Background Understanding the genomic landscape and immune microenvironment features of preinvasive and early invasive lung adenocarcinoma may provide critical insight and facilitate development of novel strategies for early detection and intervention Methods A total of 80 tumor tissue samples and 30 paired histologically normal lung tissue samples from 30 patients with adenocarcinoma in.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is noninvasive breast cancer that is limited to the inside of the ducts of the breast Increased use of screening mammography has resulted in a dramatic increase in the detection of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) Approximately 64,000 cases of DCIS are diagnosed annually in the United States. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is an uncommon condition in which abnormal cells form in the milk glands (lobules) in the breast LCIS isn't cancer But being diagnosed with LCIS indicates that you have an increased risk of developing breast cancer. Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in the cells that form glands making mucus to lubricate the inside of the colon and rectum This is the most common type of colon cancer What is highgrade dysplasia, intramucosal carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, or carcinoma in the lamina propria?.
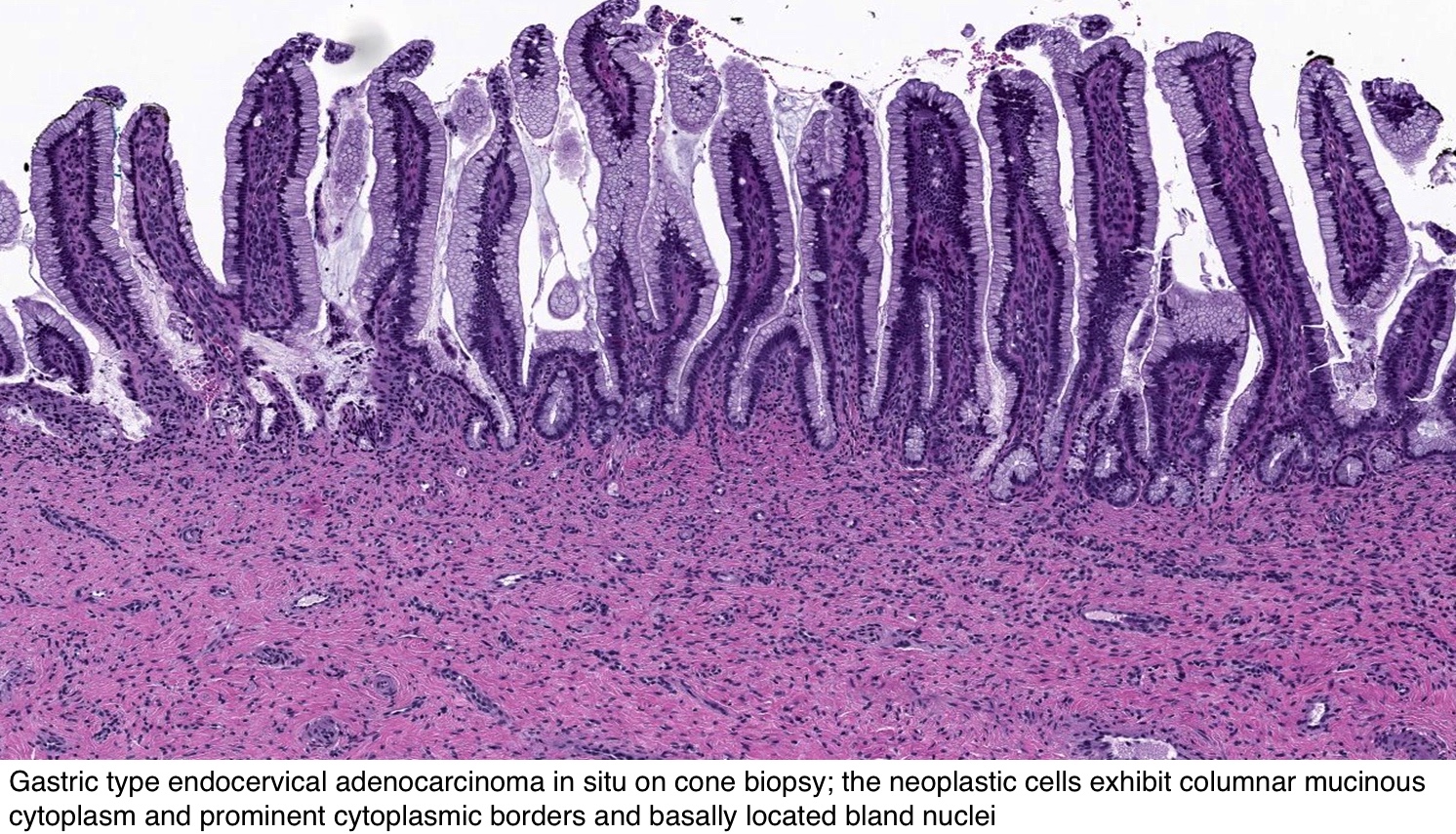
4) endocervical glandular dysplasia is not a reproducibly recognizable. The entity of endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) has been widely accepted and recognized as the precursor of invasive adenocarcinoma In addition to the usual HPVrelated type of AIS, endometrioid, 32 clear cell, 143 and intestinal (see below) types have also been described. Adenocarcinoma of the colon is the most common type of colon cancer (tumor) that occurs in the colon 6 What is “intramucosal carcinoma” or “carcinoma in situ” or “carcinoma in the lamina propria”?.
Adenocarcinoma arising in the colon or rectum;. Background Understanding the genomic landscape and immune microenvironment features of preinvasive and early invasive lung adenocarcinoma may provide critical insight and facilitate development of novel strategies for early detection and intervention Methods A total of 80 tumor tissue samples and 30 paired histologically normal lung tissue samples from 30 patients with adenocarcinoma in. Adenocarcinoma In Situ (AIS) of Cervix is a smallsized, localized, premalignant adenocarcinoma, observed in the uterine cervix, which is the lower portion of the womb AIS of Cervix only affects women It may be described as an epithelial lesion and carries a very highrisk for invasive carcinoma, if left untreated.
Background Understanding the genomic landscape and immune microenvironment features of preinvasive and early invasive lung adenocarcinoma may provide critical insight and facilitate development of novel strategies for early detection and intervention Methods A total of 80 tumor tissue samples and 30 paired histologically normal lung tissue samples from 30 patients with adenocarcinoma in. See Discussion Final Jul 29 19. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is one of several epithelial proliferative breast diseases which include epithelial hyperplasia, atypical ductal hyperplasia (), DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma ()Ductal epithelial hyperplasia without atypia confers only a slight risk of progression to IDC, about 152x greater risk then normal ductal epithelium.
Adenocarcinoma in situ 30 mm in size, atypical type II pneumocytes, purely lepidic type, non invasive (Diagn Interv Imaging 16;) Adenoid cystic carcinoma cribriform architecture and pseudocysts, PAS positive. While an adenoma with intramucosal carcinoma or carcinoma in situ or carcinoma in the lamina propria needs to be completely removed, it is not the same thing as to what is typically referred to as ""colon cancer"", since it cannot spread. The two major patterns seen in breast insitu carcinoma are ductal carcinoma insitu (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma insitu (LCIS) "Intraductal carcinoma" is the same as "ductal carcinoma insitu" In some cases, the insitu carcinoma can have both duct and lobular features and in some cases DCIS and LCIS may both be present at the same time 3.
Adenocarcinoma in situ demonstrates several histological patterns papillary, glandular, cribriform, and flat Adenocarcinoma in situ can be pure or coexist with urothelial CIS or noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma In some cases, in situ adenocarcinoma is seen in association with invasive adenocarcinoma. Other articles where Carcinoma in situ is discussed esophageal cancer Diagnosis and prognosis esophageal cancer is also called carcinoma in situ and is confined to the inner layer of epithelial cells lining the esophagus Stage I cancers have spread into the connective tissue layer below the epithelium but have not invaded the underlying muscle layer. Due to poor reproducibility, adenocarcinoma in situ is not accepted terminology in the current International Society of Gynecologic Pathologists (ISGYP) classification 4 Recently, however, a few authors have questioned this and argue for reconsideration of this concept, referring to entities such as adenocarcinoma in situ31 and endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma 32.
Adenocarcinoma is defined by the presence of invasion into lamina propria or deeper;. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is noninvasive breast cancer that is limited to the inside of the ducts of the breast Increased use of screening mammography has resulted in a dramatic increase in the detection of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) Approximately 64,000 cases of DCIS are diagnosed annually in the United States. Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma should not be used in the reporting of small biopsies and cytology Tumours with a noninvasive pattern are referred to by their pattern, eg lepidic growth , not as AIS.
General conclusions based largely on published studies include the following 1) adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) is a recognizable precursor to invasive adenocarcinoma and can be divided according to distinct histologic subtypes;. 3) AIS can be cured by simple hysterectomy and in many cases may be treated effectively by cone biopsy;. Histology of SCC Typical SCC has nests of squamous epithelial cells arising from the epidermis and extending into the dermis (figure 1) The malignant cells are often large with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and a large, often vesicular, nucleus Variable keratinisation (keratin pearls etc) is present (figure 2).
Adenocarcinoma of the colon is the most common type of colon cancer (tumor) that occurs in the colon 6 What is “intramucosal carcinoma” or “carcinoma in situ” or “carcinoma in the lamina propria”?. Arises mostly in lower third of cervix;. Primary cervical small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (SCNEC) is a rare and aggressive tumor Herein, we describe the first cytological case of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) admixed with SCNEC A 65yearold postmenopausal Japanese female presented with abnormal genital bleeding The Papanicolaou smear of the cervix demonstrated the presence of 2 distinct neoplastic components in an inflammatory background.
2) AIS is multifocal or involves multiple quadrants of the cervix in about half of cases;. Types of carcinoma in situ There are many different types of CIS and the type depends on where in the body the disease starts Squamous carcinoma in situ – Skin, mouth, larynx, lungs, cervix Adenocarcinoma in situ – Cervix, lungs, gastrointestinal tract Ductal carcinoma in situ – Breast. Ductal carcinoma in situ is a noninvasive form of cancer and is given the tumour stage pTis Nodal stage (pN) for ductal carcinoma in situ Ductal carcinoma in situ is given a nodal stage between 0 and 3 based on the number of lymph nodes that contain cancer cells, the amount of cancer cells found in the lymph node, and the location of the.
If the cervical biopsy specimen or endocervical curettage specimen suggests the possibility of endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, cervical conization is often used to confirm the diagnosis, excise the lesion, and exclude coexisting invasive adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma In Situ (AIS) of Cervix is a smallsized, localized, premalignant adenocarcinoma, observed in the uterine cervix, which is the lower portion of the womb AIS of Cervix only affects women It may be described as an epithelial lesion and carries a very highrisk for invasive carcinoma, if left untreated. Solid Tumor Rules/HistologyLung What is the histology code and what H Rule applies for a diagnosis of well differentiated adenocarcinoma in situ (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma)?.
Covered Separately Invasive carcinoma involving an adenomatous polyp;. For example, if a person has a carcinoma that has spread to the lung and the site of origin is unknown, the appropriate code is C809 (unknown primary site) M8010/3 (carcinoma) The /3 signifies the existence of a malignant neoplasm of a primary site Carcinoma in situ and CIN III Most cancer registries record carcinoma in situ arising at any. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is noninvasive breast cancer that is limited to the inside of the ducts of the breast Increased use of screening mammography has resulted in a dramatic increase in the detection of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) Approximately 64,000 cases of DCIS are diagnosed annually in the United States.
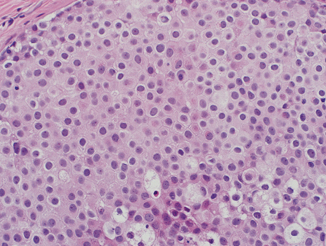
Urothelial carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a highgrade noninvasive malignancy with a high tendency of progression Although it is typically grouped with other nonmuscle invasive bladder cancers, its higher grade and aggressiveness make it a unique clinical entity. Lack of dirty necrosis;. Adenocarcinoma In Situ (AIS) of Cervix is a smallsized, localized, premalignant adenocarcinoma, observed in the uterine cervix, which is the lower portion of the womb AIS of Cervix only affects women It may be described as an epithelial lesion and carries a very highrisk for invasive carcinoma, if left untreated.
The cells of LCIS and invasive lobular carcinoma have similar appearance Tumor cells lack Ecadherin which is cell adhesion protein Cell morphology Dyscohesive cells with oval or round nuclei and small nucleoli or signet ring cell morphology with intracytoplasmic mucin. Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of colon cancer It starts out as a small polyp, or growth, that's usually harmless at first but can turn into cancer The disease can also start in your. Background Understanding the genomic landscape and immune microenvironment features of preinvasive and early invasive lung adenocarcinoma may provide critical insight and facilitate development of novel strategies for early detection and intervention Methods A total of 80 tumor tissue samples and 30 paired histologically normal lung tissue samples from 30 patients with adenocarcinoma in.
The cells of LCIS and invasive lobular carcinoma have similar appearance Tumor cells lack Ecadherin which is cell adhesion protein Cell morphology Dyscohesive cells with oval or round nuclei and small nucleoli or signet ring cell morphology with intracytoplasmic mucin. High grade intramucosal neoplasia;. Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung Dr Daniel J Bell and Dr Yuranga Weerakkody et al Adenocarcinomas in situ (AIS) of the lung refer to a relatively new entity for a preinvasive lesion in the lung This entity partly replaces the noninvasive end of the previous term bronchoalveolar carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma The 15 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors has undergone significant changes since the publication of 04 WHO Classification These changes have resulted from advances in molecular testing and radiology as well as greater use of immunohistochemistry in subtyping tumors The major changes in the 15 WHO classification of adenocarcinomas of the lung (resected tumors) are 1) Discontinuing the terms bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and mixed subtype adenocarcinoma;. Stanford Medicine » School of Medicine » Departments » Surgical Pathology Criteria » Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Navigation for This Section Surgical Pathology Criteria Diagnostic Criteria. The histopathology of colorectal cancer of the adenocarcinoma type involves analysis of tissue taken from a biopsy or surgery A pathology report contains a description of the microscopical characteristics of the tumor tissue, including both tumor cells and how the tumor invades into healthy tissues and finally if the tumor appears to be completely removed The most common form of colon cancer is adenocarcinoma, constituting between 95% to 98% of all cases of colorectal cancer Other, rarer type.
The in situ carcinomas of the breast are either ductal (also known as intraductal carcinoma) or lobular This distinction is primarily based upon the growth pattern and cytologic features of the lesions, rather than their anatomic location within the mammary ductallobular system. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) More common in young women, often bilateral;. A Apocrine ductal carcinoma in situ involving sclerosing adenosis (H&E, 10×) and b corresponding immunohistochemical (IHC) stain for musclespecific actin which highlights myoepithelium throughout, confirming in situ disease only (IHC, 10×) Biomarkers and Molecular Pathology.
For the cytology see Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (cytology) Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, also adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine endocervix, is preinvasive change of the uterine endocervix It is closely tied to HPV infection If the context is clear, it may be referred to as adenocarcinoma in situ, abbreviated AIS. Adenocarcinoma in situ of lung (AIS) (≤3 cm) has a number of subtypes the most common subtype is nonmucinous and rarely mucinous or mixed subtypes histological pattern no growth pattern other than lepidic and no feature of necrosis or invasion minimally invasive adenocarcinoma of lung (MIA) ≤3 cm. KeywordsDuctal carcinoma insitu (DCIS), molecular markers, HER2, microenvironment AbstractThe incidence of ductal carcinoma insitu (DCIS) is increasing significantly DCIS has been demonstrated to arise from terminal ductlobular units and it is generally accepted that DCIS is a precursor lesion to the majority of invasive ductal carcinoma.
Hepatoid components are identical;. May be a problem in cases with possible liver metastases;. 90% of all cervical cancers;.
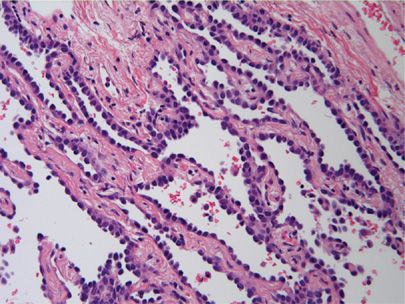
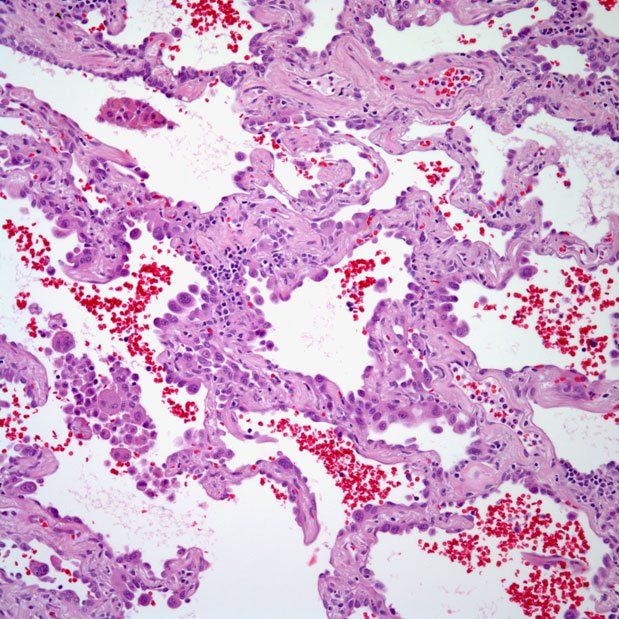
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a noninvasive breast cancer It’s stage 0 breast cancer “Ductal” means “related to the milk ducts” The milk ducts are the canals that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple openings during breastfeeding “In situ” means “in place”. Definition Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) is a localized lesion showing a pure lepidic (bronchioloalveolar) growth pattern of adenocarcinoma cells lining preexisting alveolar walls, with no evidence of stromal, lymphatic, or pleural invasion.
Pathology Of Esophageal Cancer And Barrett S Esophagus Jain Annals Of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of Lung
The Pathology Of Bronchogenic Carcinoma Thoracic Key
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
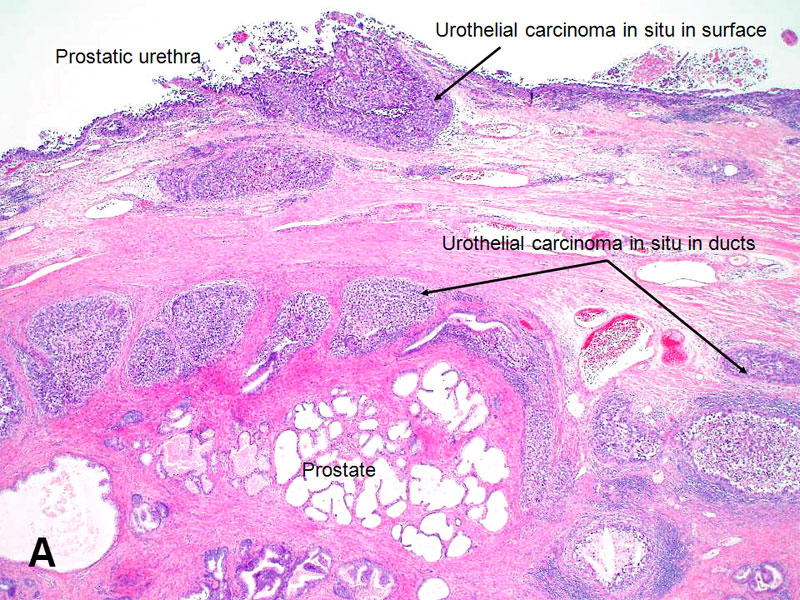
Urothelial Carcinoma Of The Prostate American Urological Association

Histopathology Images Of Carcinoma In Situ Colon By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Libre Pathology
Slide Show Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Pathology Cancer Network

Severe Squamous Dysplasia Or Carcinoma In Situ Causing Laryngeal Leukoplakia Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
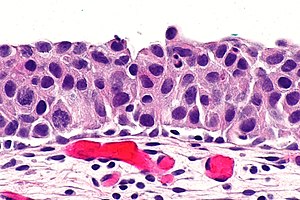
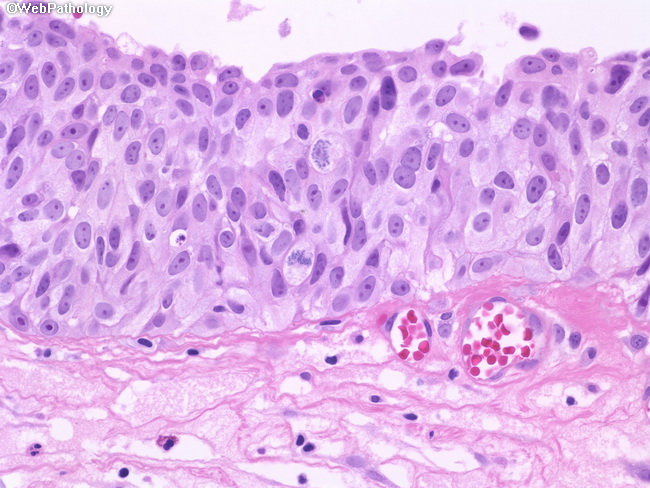
Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ Libre Pathology
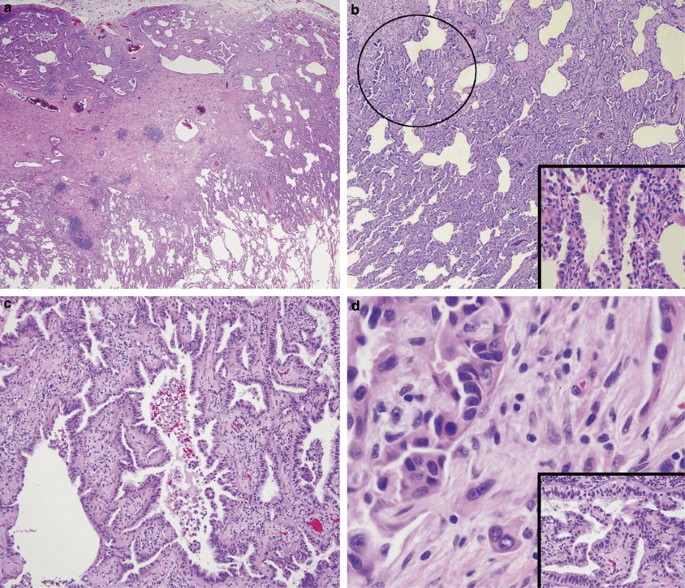
Assessment Of Invasion In Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification Including Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma Modern Pathology
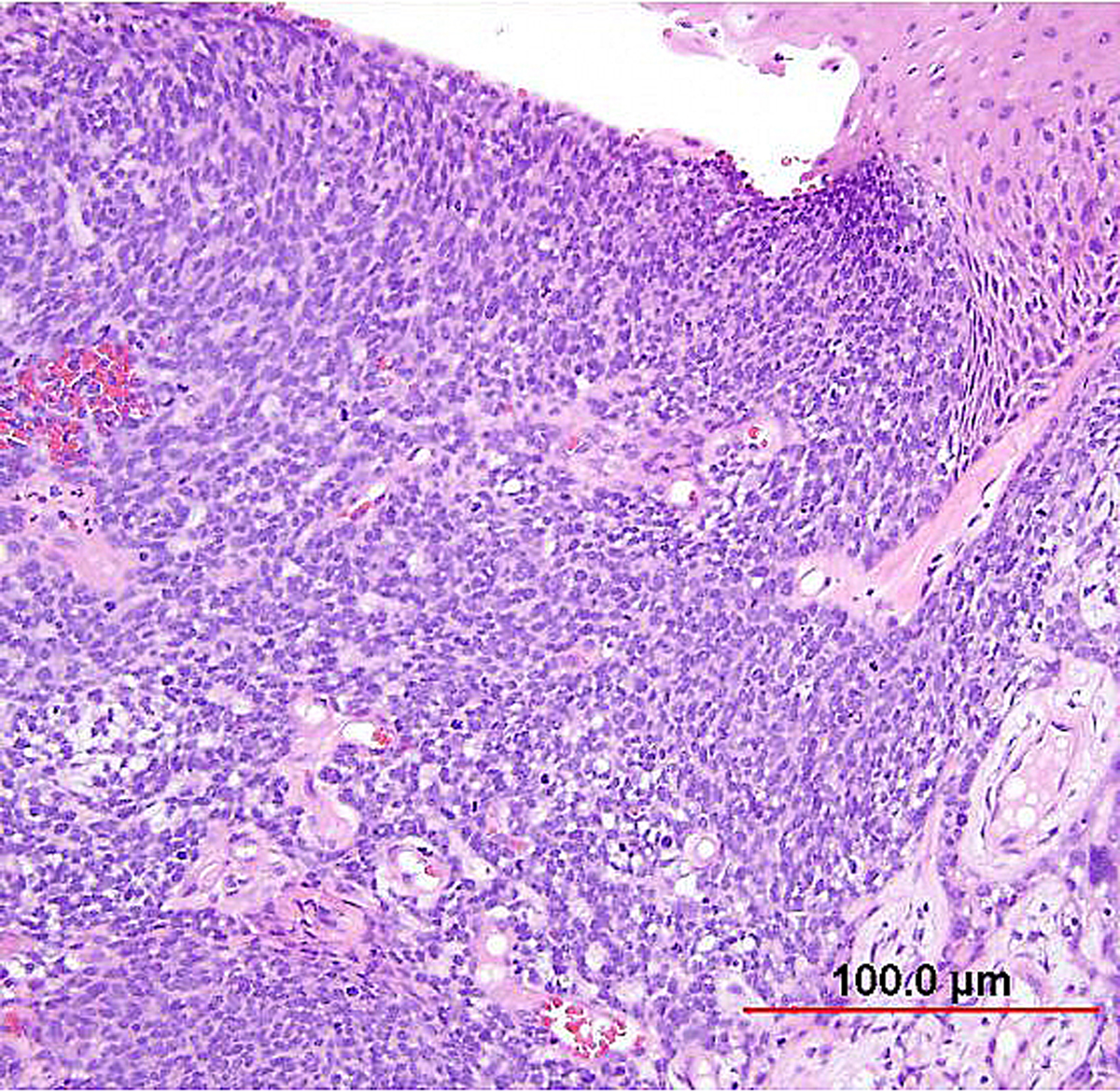
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Of Breast Update 19 Pathology

The New Iaslc Ats Ers Lung Adenocarcinoma Classification From A Clinical Perspective Current Concepts And Future Prospects Zugazagoitia Journal Of Thoracic Disease
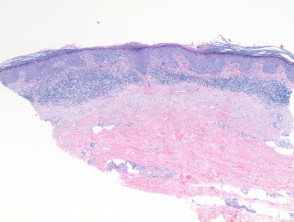
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Pathology Dermnet Nz

Carcinoma In Situ Of The Oral Mucosa Its Pathological Diagnostic Concept Based On The Recognition Of Histological Varieties Proposed In The Jsop Oral Cis Catalog Sciencedirect

Breast Carcinoma In Situ Lobular Ductal Lcis Dcis Teachmesurgery

Severe Squamous Dysplasia Or Carcinoma In Situ Causing Laryngeal Leukoplakia Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
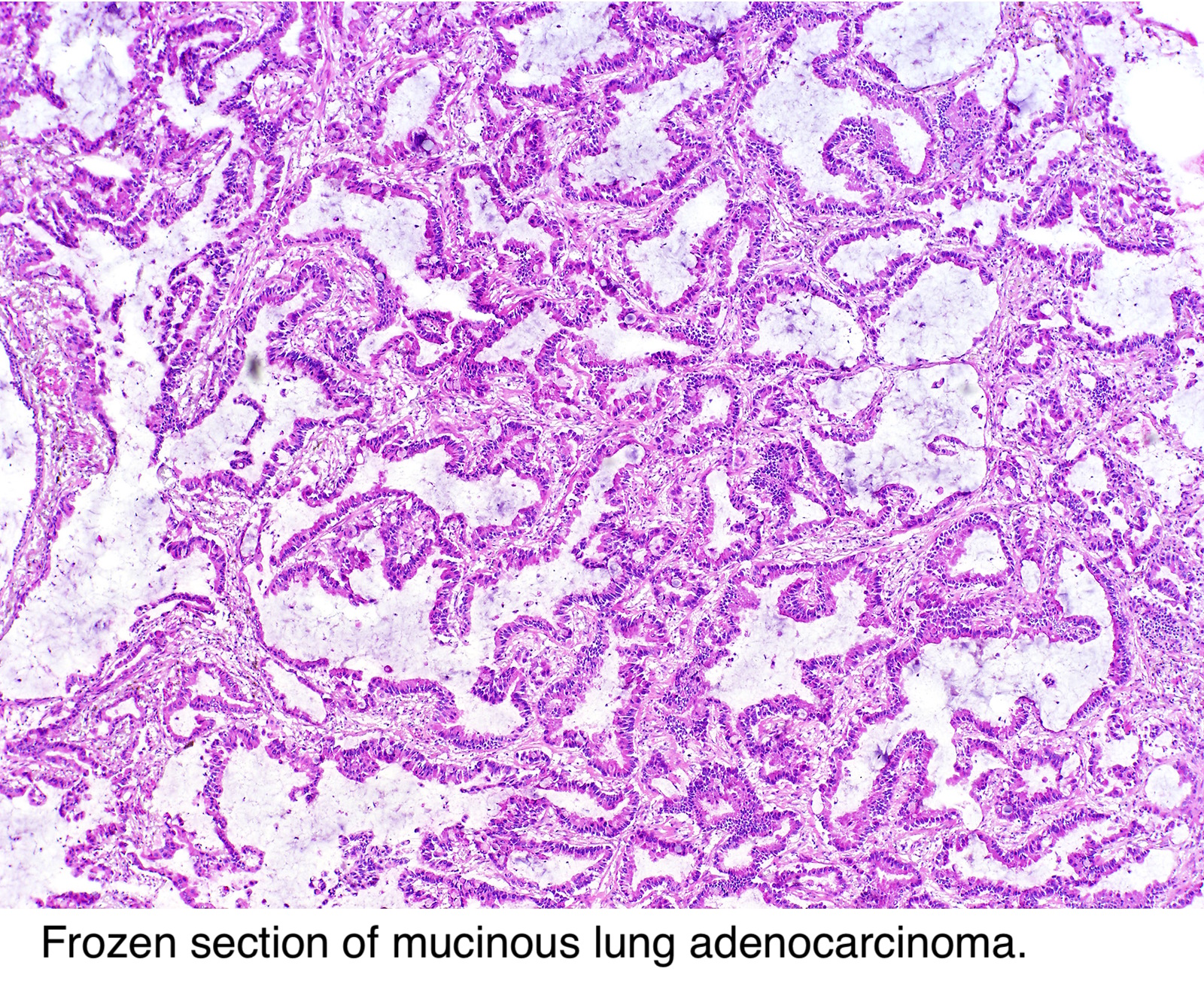
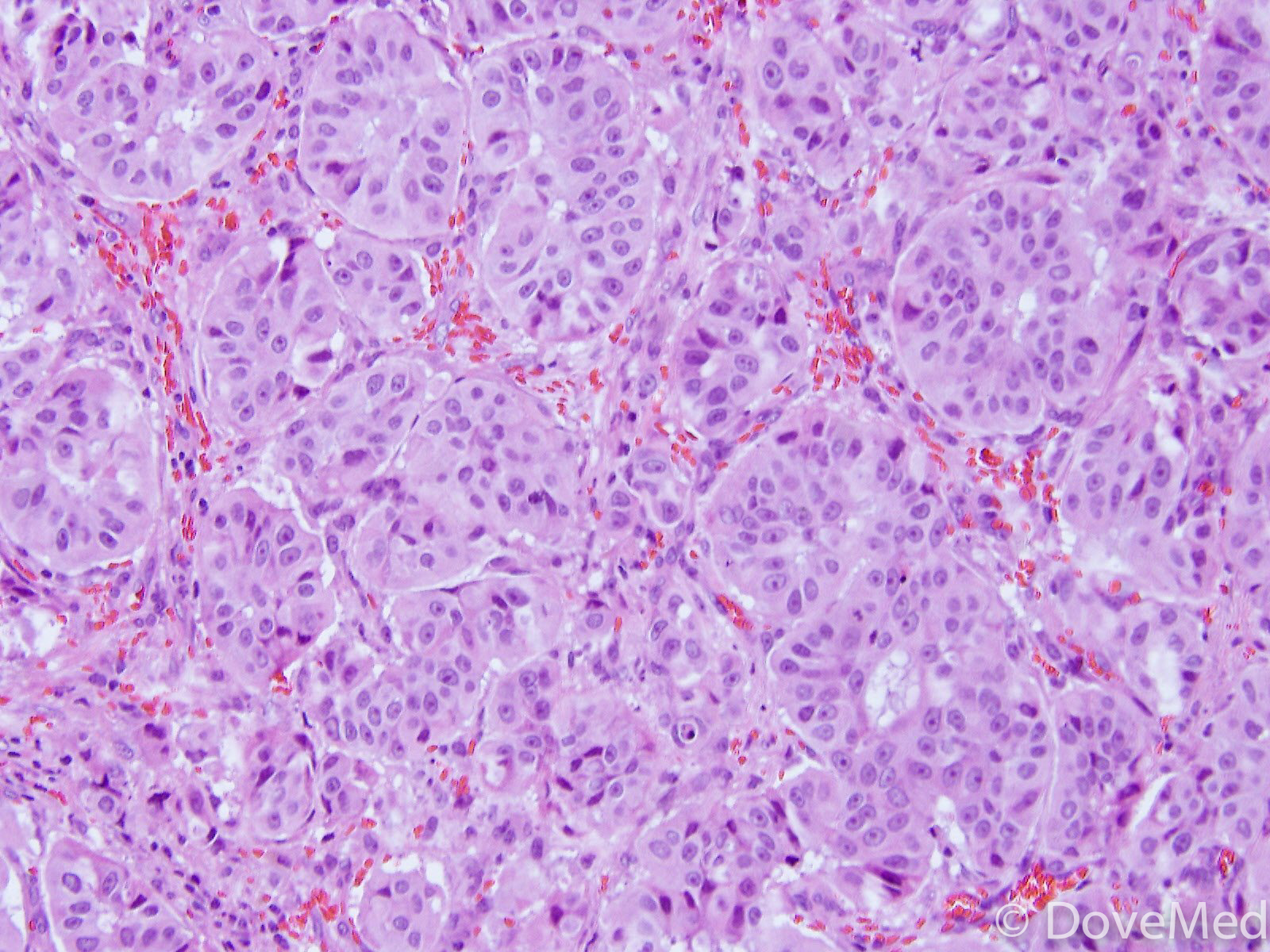
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
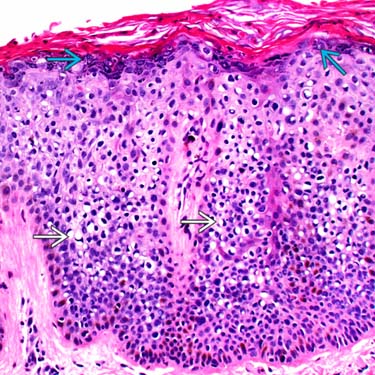
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Bowen Disease Basicmedical Key
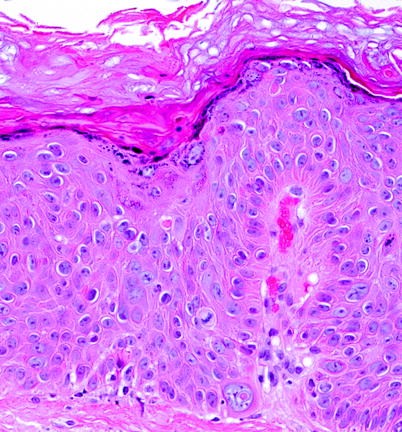
Clinical Differential Diagnosis Of Histological Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Springerlink

Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ Diagnostic Update Pathology

Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Surgical Pathology Clinics
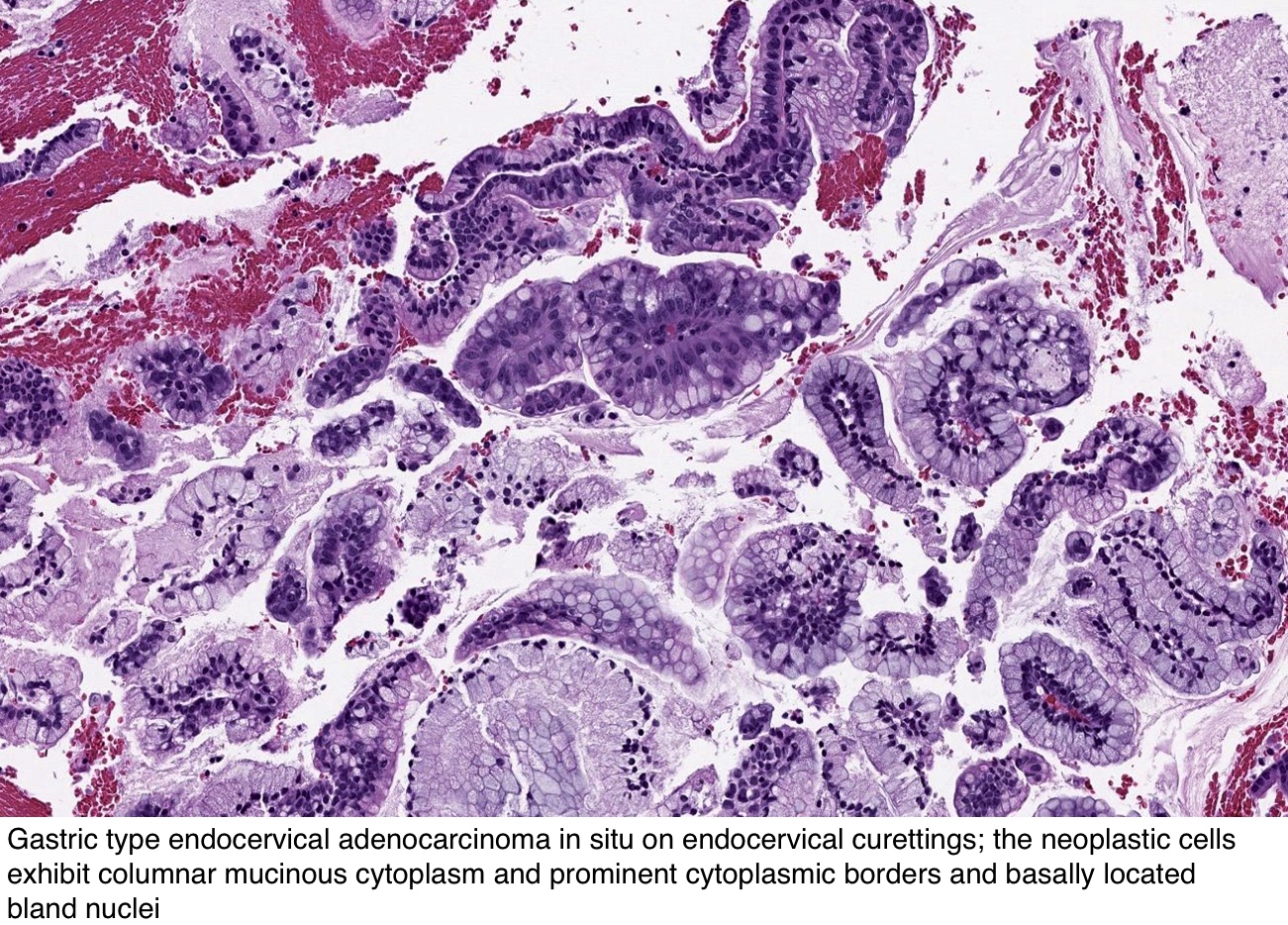
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
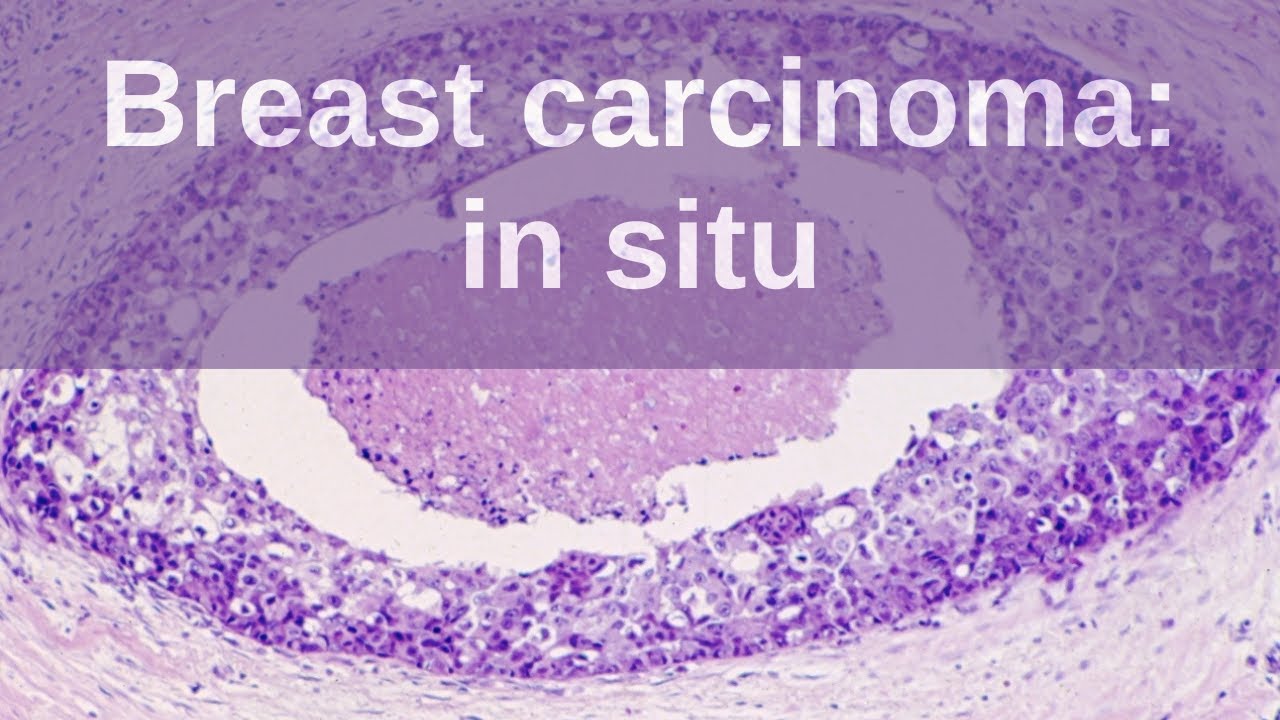
Breast Carcinoma In Situ Pathology Mini Tutorial Youtube

High Grade Ta Urothelial Carcinoma And Carcinoma In Situ Of The Bladder Urology
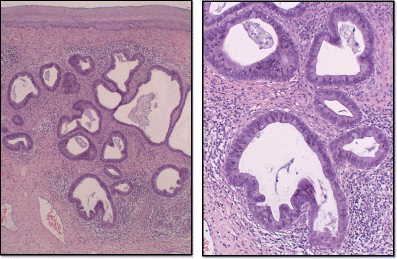
Cervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Update And Management Springerlink
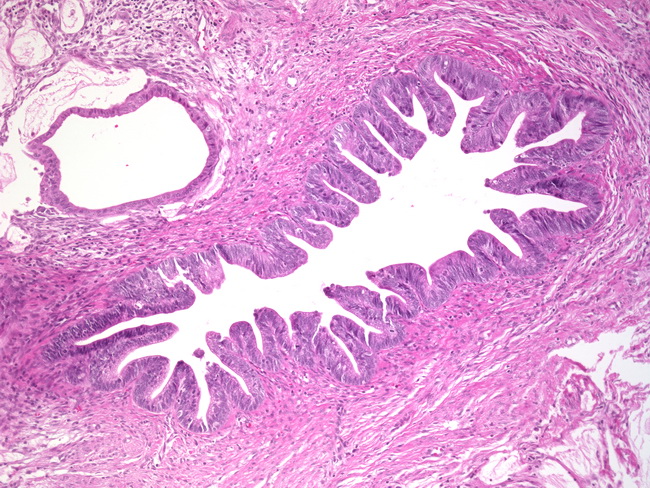
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
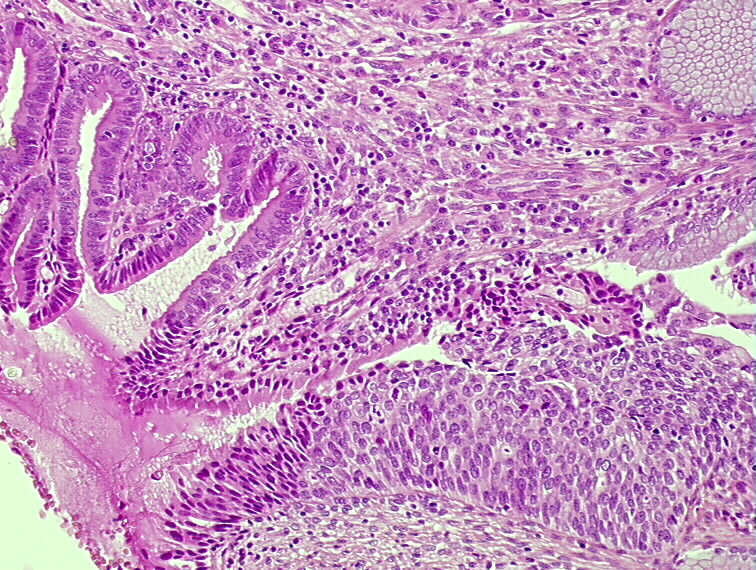
Histopathology Of The Uterine Cervix Digital Atlas
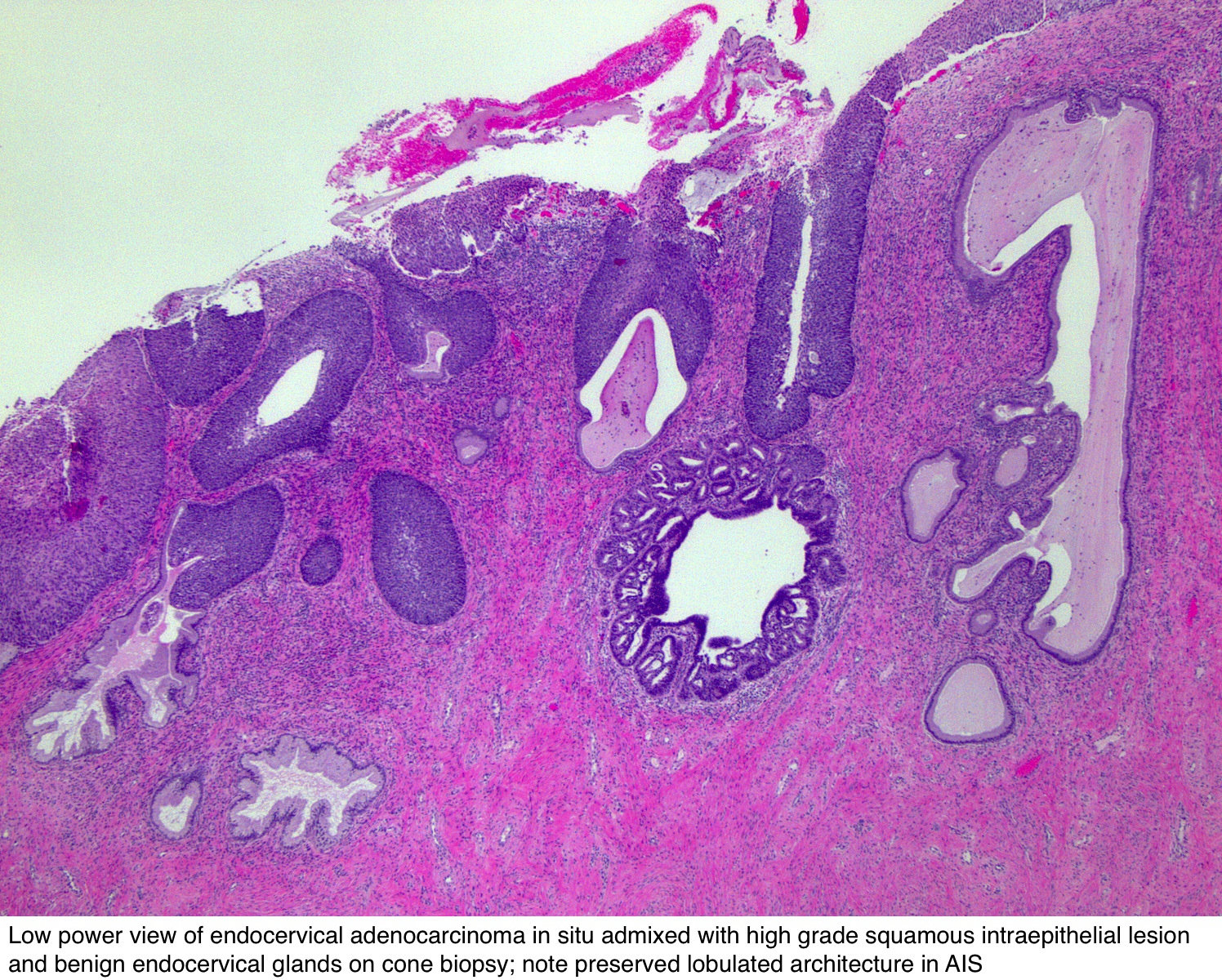
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
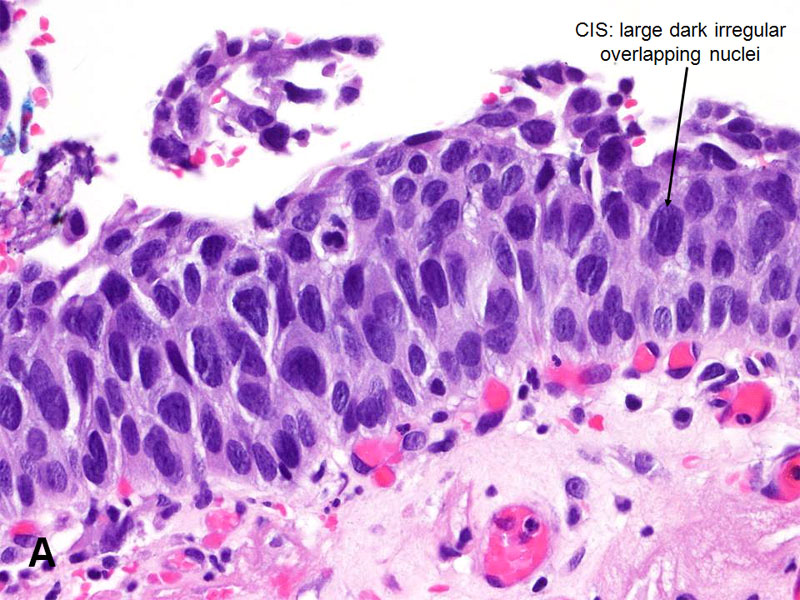
Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ American Urological Association
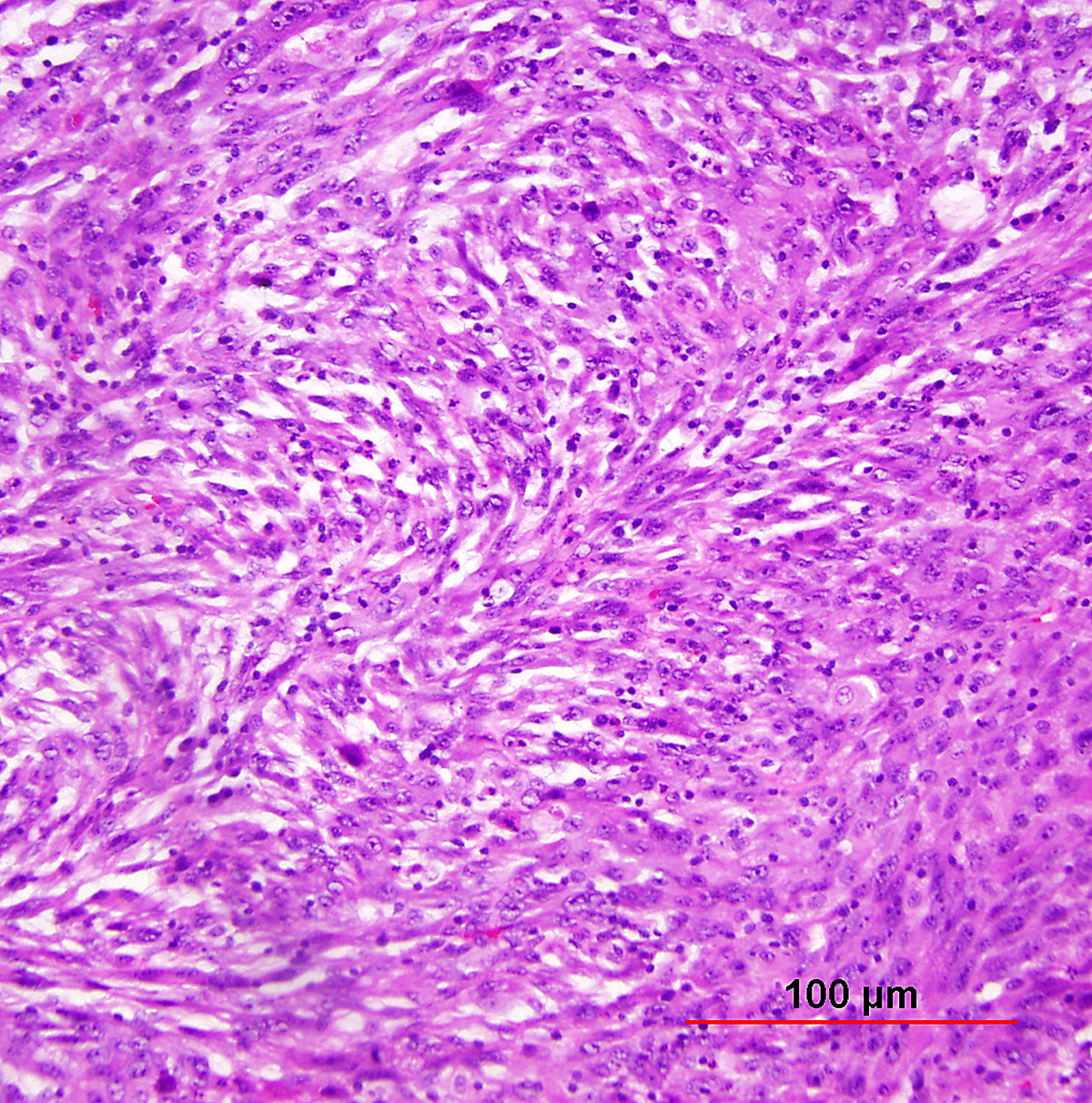
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma Overview
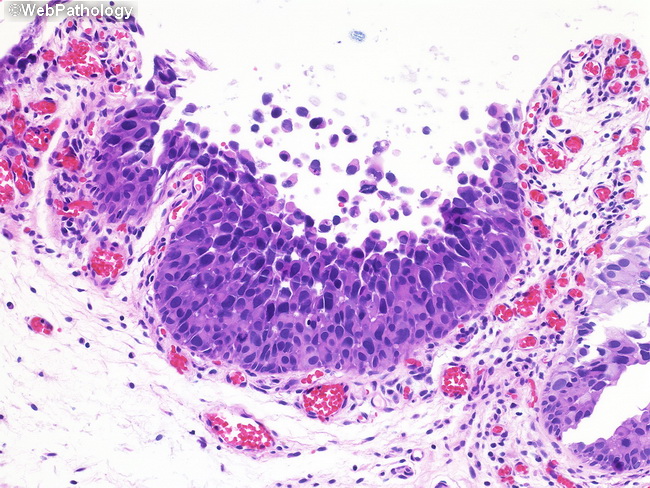
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
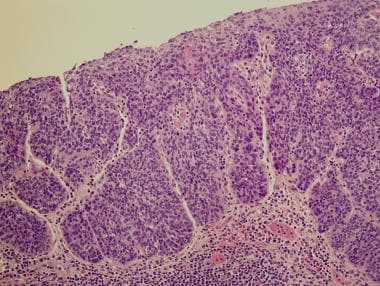
Pathologic Findings In Squamous Cell Bladder Carcinoma Overview Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Gross Findings In Squamous Cell Carcinoma Microscopic Findings In Squamous Cell Carcinoma
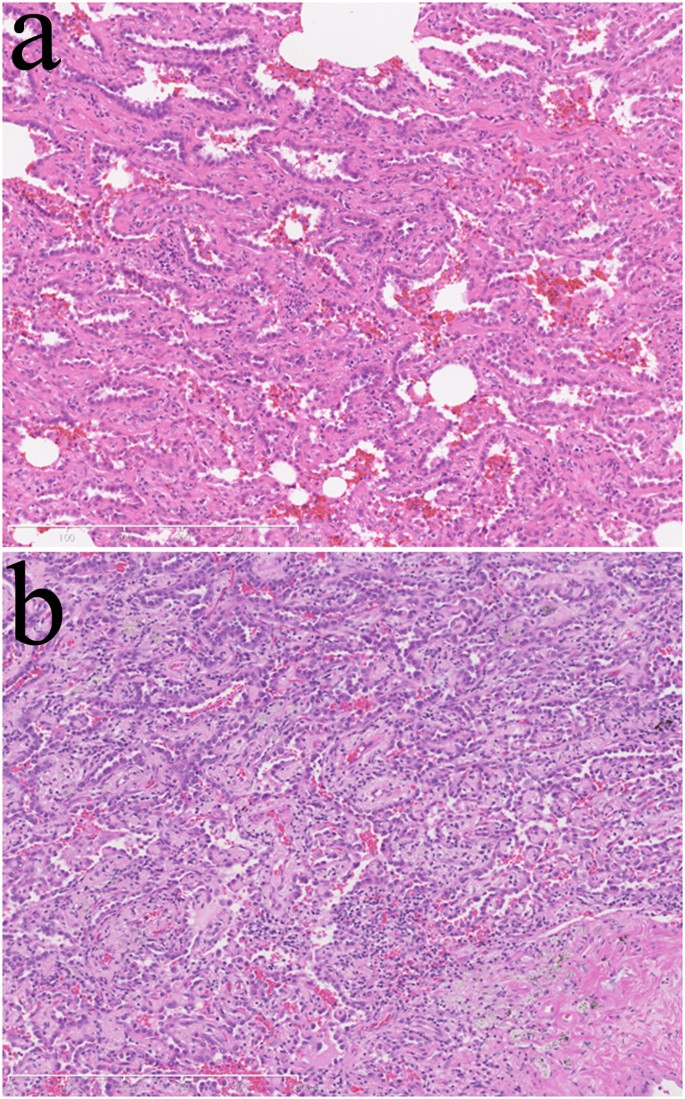
Bronchioloalveolar Invasion In Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Is Associated With Expression Of Transforming Growth Factor B1 World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text
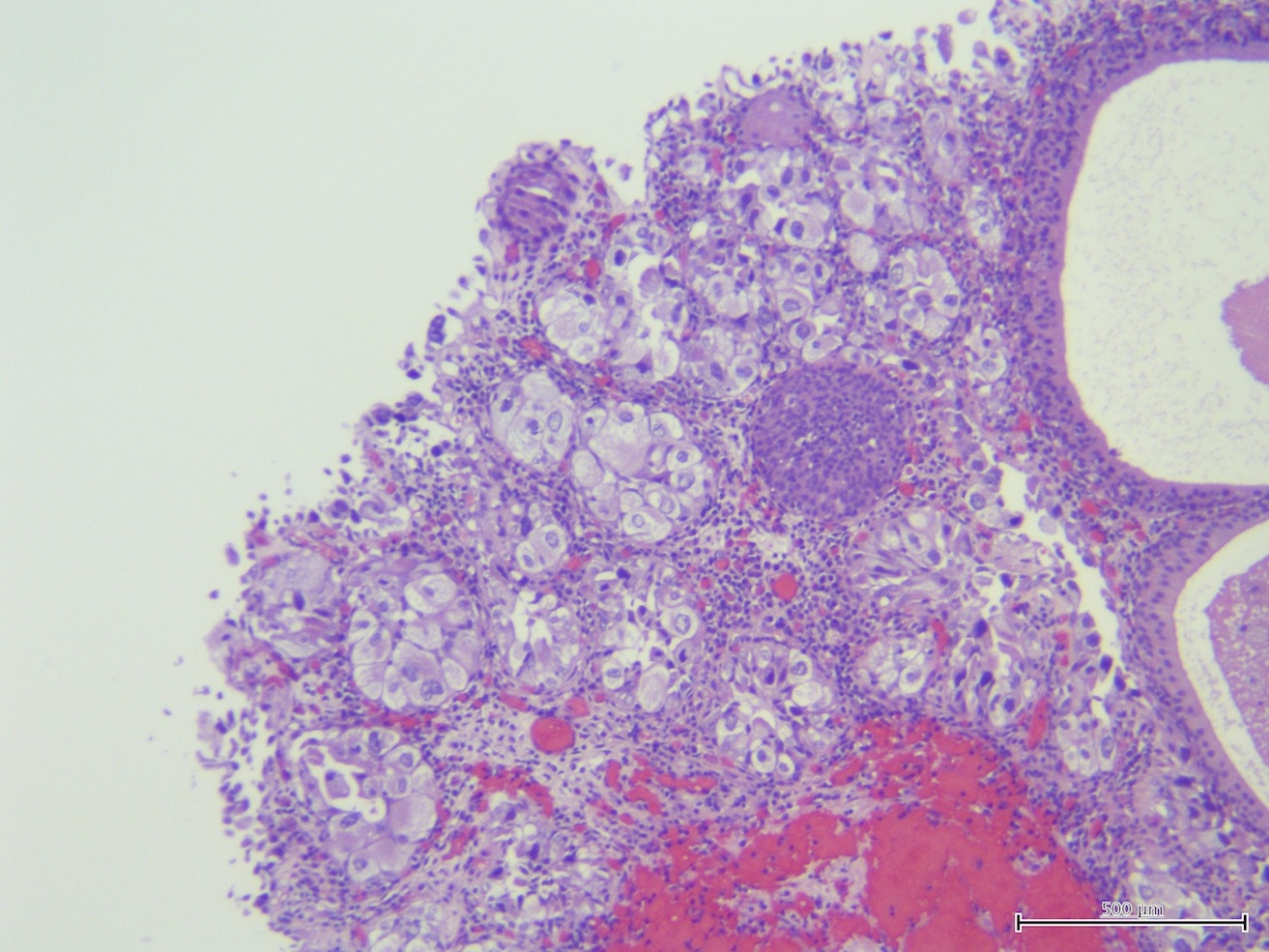
Pathology Outlines Carcinoma In Situ

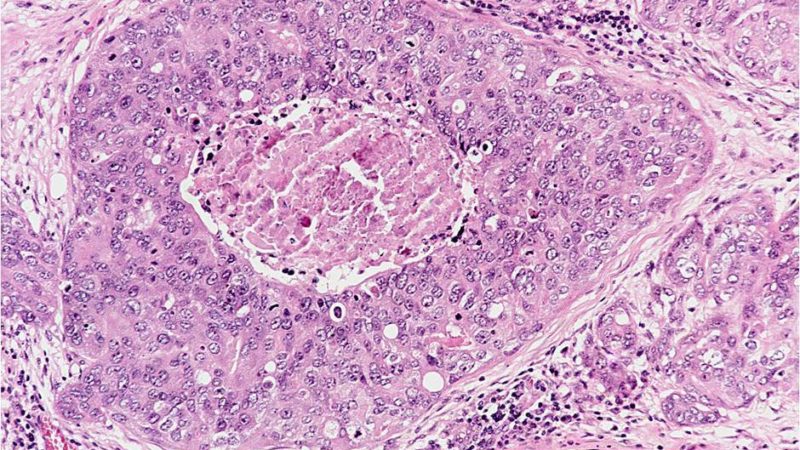
Molecular And Histological Correlations In Liver Cancer Journal Of Hepatology
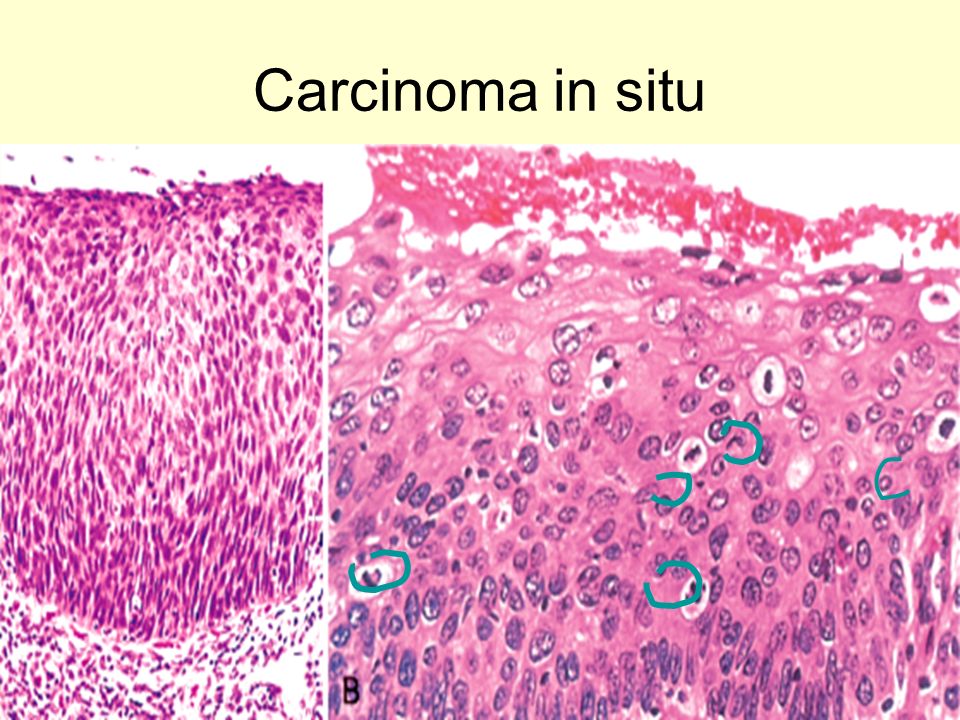
Tumor 2 Pathology And Histology Ppt Video Online Download

Cervical Cancer Histology

Pin On Pathology
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Pathology

Histology Of Cervical Cancer
Adenocarcinoma Of The Lung From Bac To The Future Insights Into Imaging Full Text

Pathology Of Cancers Of The Female Genital Tract Prat 18 International Journal Of Gynecology Amp Obstetrics Wiley Online Library

Adenocarcinoma Situ Lung Lepidic Growth Pattern Stock Photo Edit Now

Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Wikipedia
3
Pathology Of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Features And Diagnostic Challenges Oncohema Key
Q Tbn And9gcspyq3lm 6ukmkoyebdjii26k3tynaz69jdywli7asehpiebqpk Usqp Cau
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ

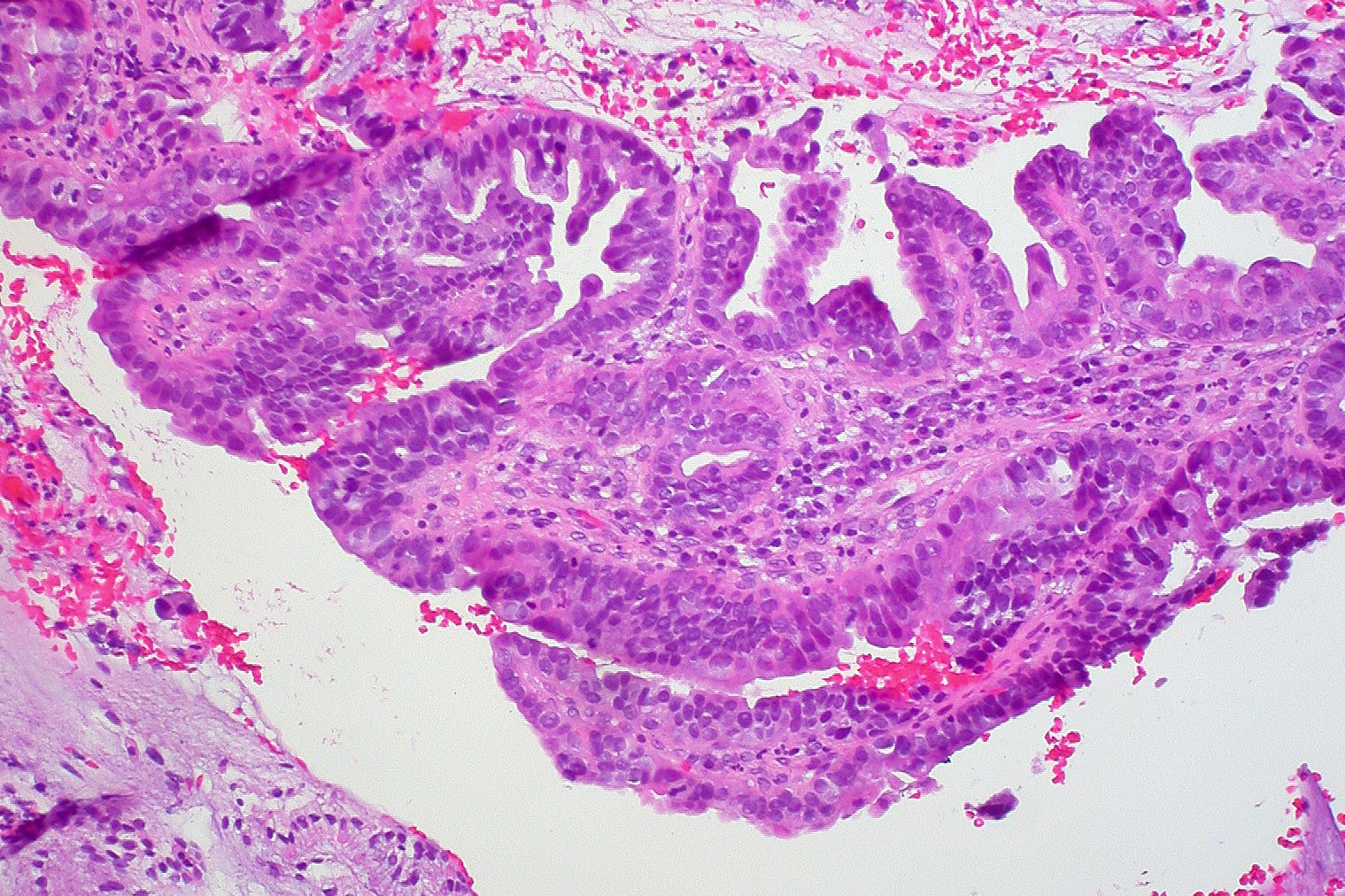
Cervix Image Atlas Adenocarcinoma In Situ Endocervical Type Sunnybrook Hospital

Severe Squamous Dysplasia Or Carcinoma In Situ Causing Laryngeal Leukoplakia Iowa Head And Neck Protocols

Journal Of Pathology And Translational Medicine

Adenocarcinoma In Situ Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma And Invasive Adenocarcinoma Of Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Cervix Image Atlas Adenocarcinoma In Situ Endocervical Type Sunnybrook Hospital

Precursor Lesions Of The Urinary Bladder Mckenney 19 Histopathology Wiley Online Library
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Dcis Pathological Features Differential Diagnosis Prognostic Factors And Specimen Evaluation Modern Pathology
3

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The Changing Incidence Of Carcinoma In Situ Of The Bladder Worldwide Intechopen

The Histology Of Tongue A Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ And B Download Scientific Diagram

Prognostic Considerations Of The New World Health Organization Classification Of Lung Adenocarcinoma European Respiratory Society
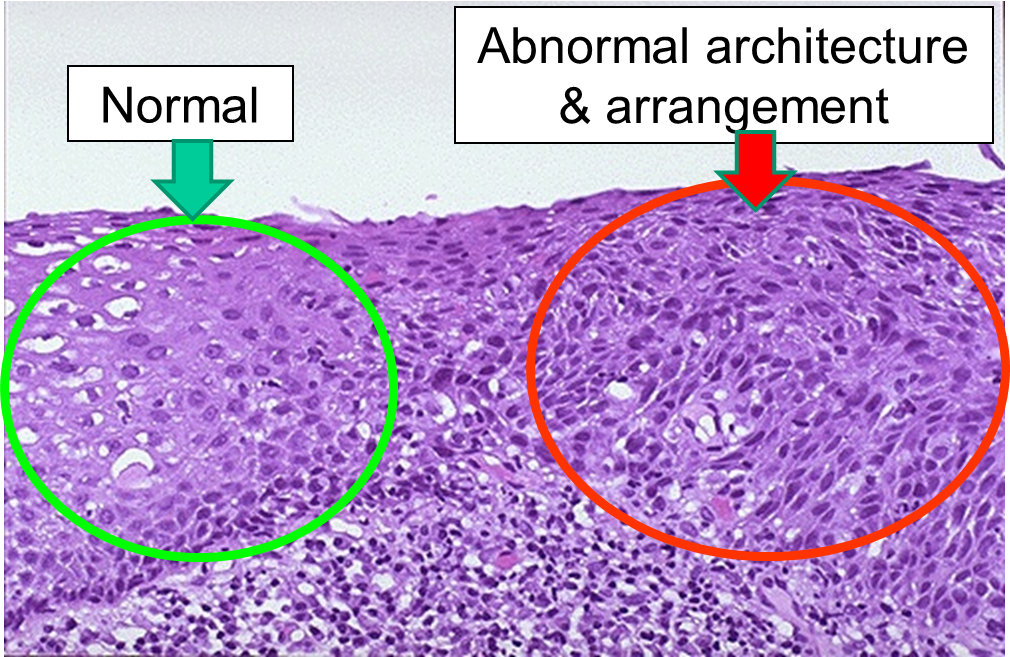
Evolution Of A Cancer
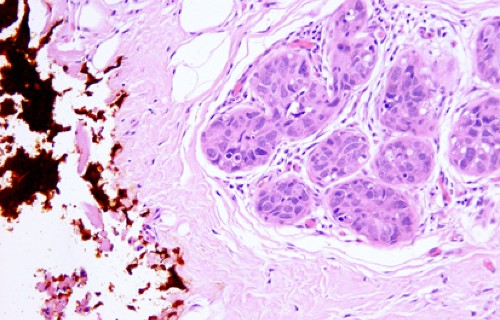
File Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Cervix Jpg Wikimedia Commons
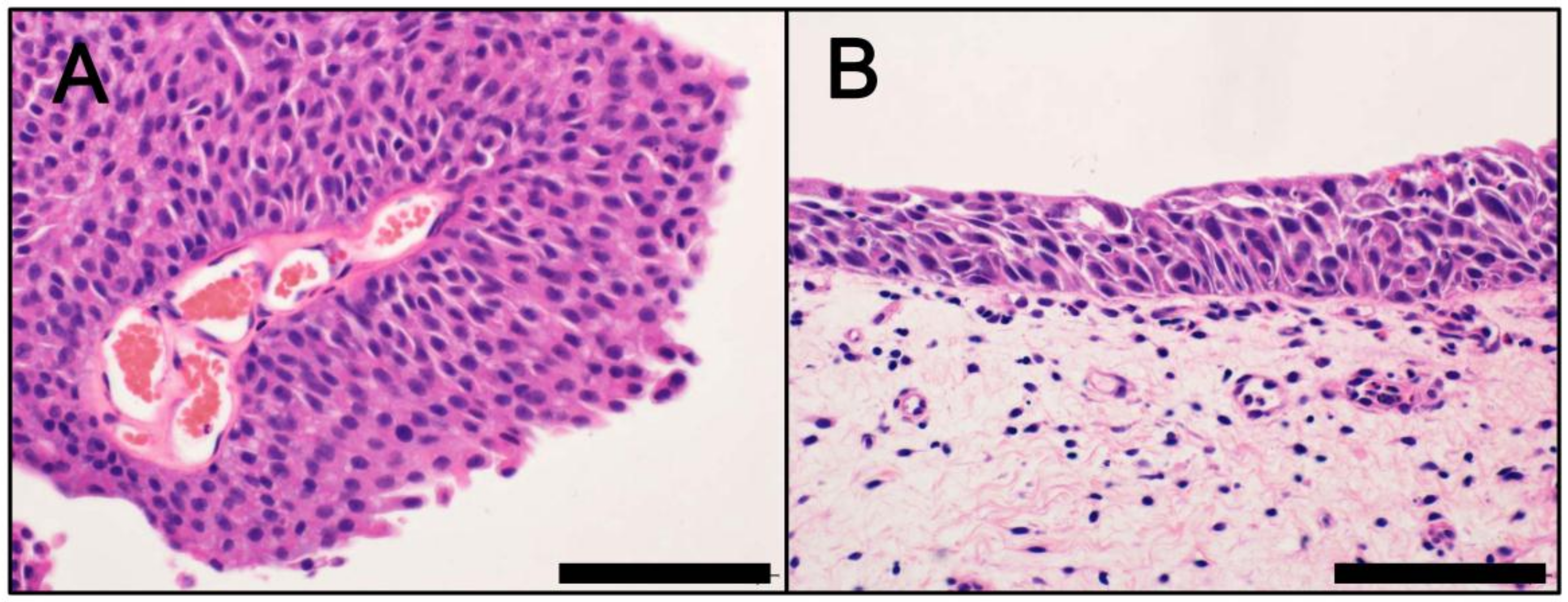
Cancers Free Full Text Bladder Cancer New Insights Into Its Molecular Pathology Html

Histopathology Images Of Carcinoma In Situ Colon By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra
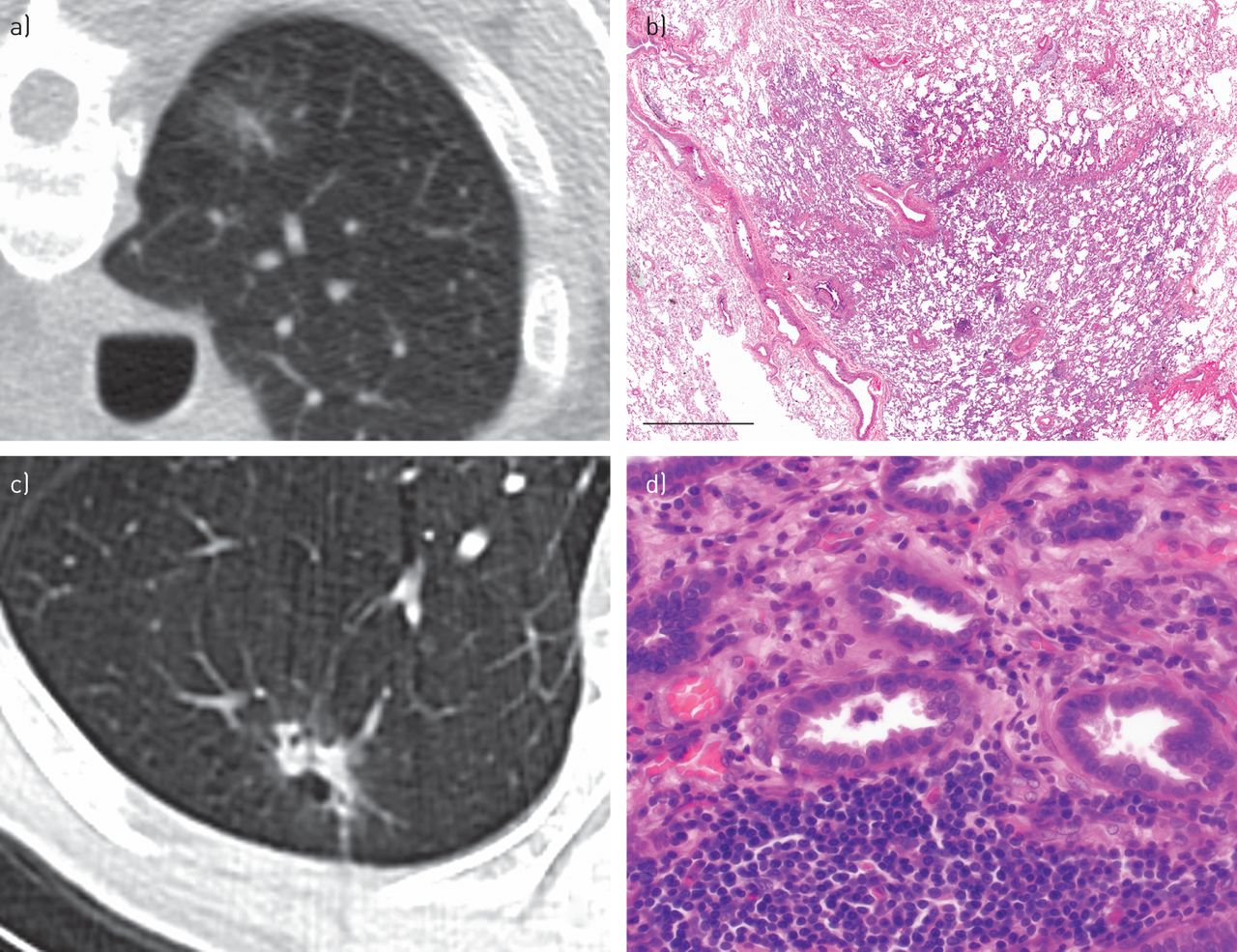
Prognostic Considerations Of The New World Health Organization Classification Of Lung Adenocarcinoma European Respiratory Society
1

Pulmonary Pathology

Carcinoma In Situ Of The Oral Mucosa Its Pathological Diagnostic Concept Based On The Recognition Of Histological Varieties Proposed In The Jsop Oral Cis Catalog Sciencedirect
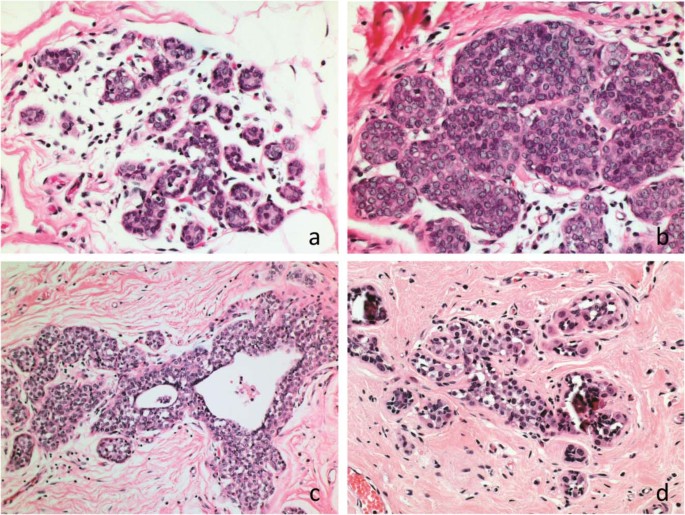
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Diagnostic Criteria And Molecular Correlates Modern Pathology
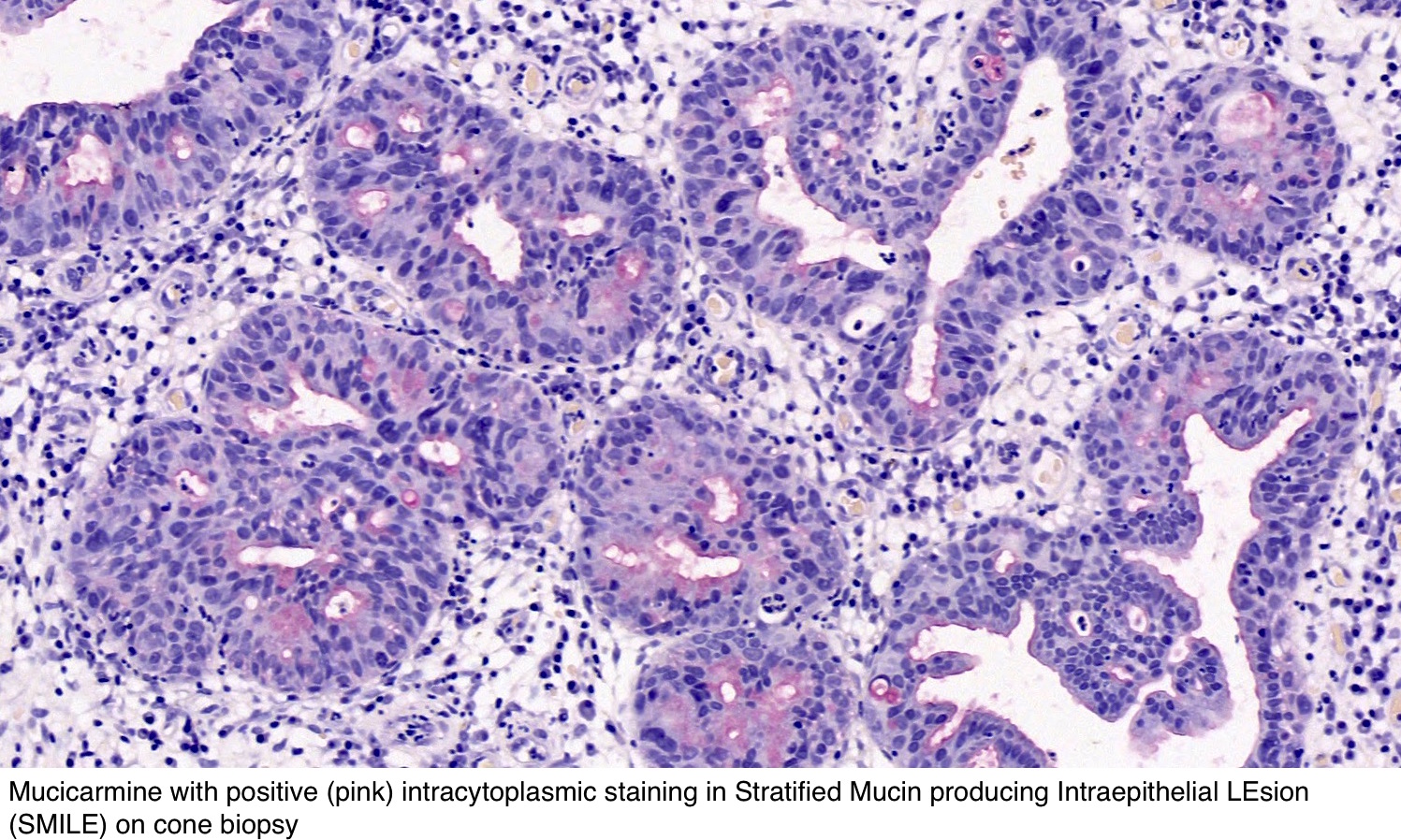
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images

Breast Cancer Histology Lobular Carcinoma Situ Stock Photo Edit Now

Diagnosis Of Lung Adenocarcinoma In Situ And Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma From Intraoperative Frozen Sections An Analysis Of 136 Cases Journal Of Clinical Pathology
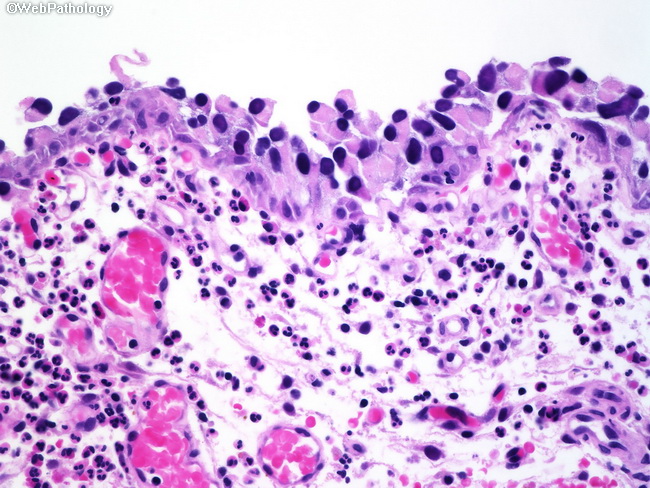
Ocular Pathology What Is Carcinoma In Situ Of The Conjunctiva

Histopathology Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Youtube
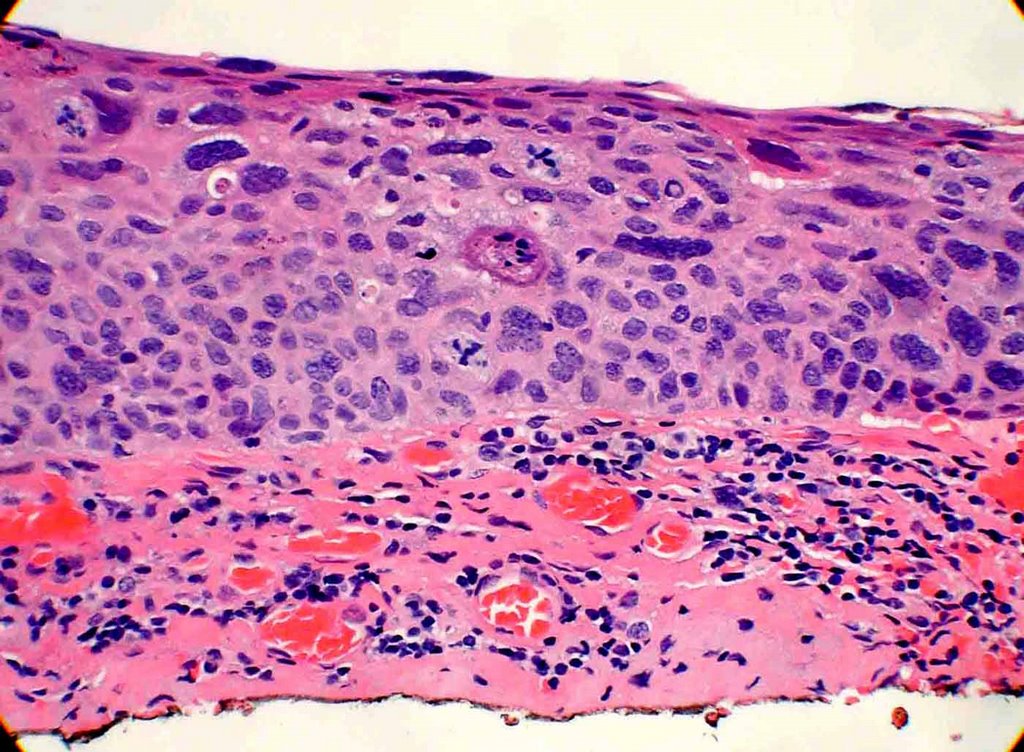
P 3pat1 Lung Cancer Pathology Pulmonary Flashcards Memorang

The Pivotal Role Of Pathology In The Management Of Lung Cancer Davidson Journal Of Thoracic Disease

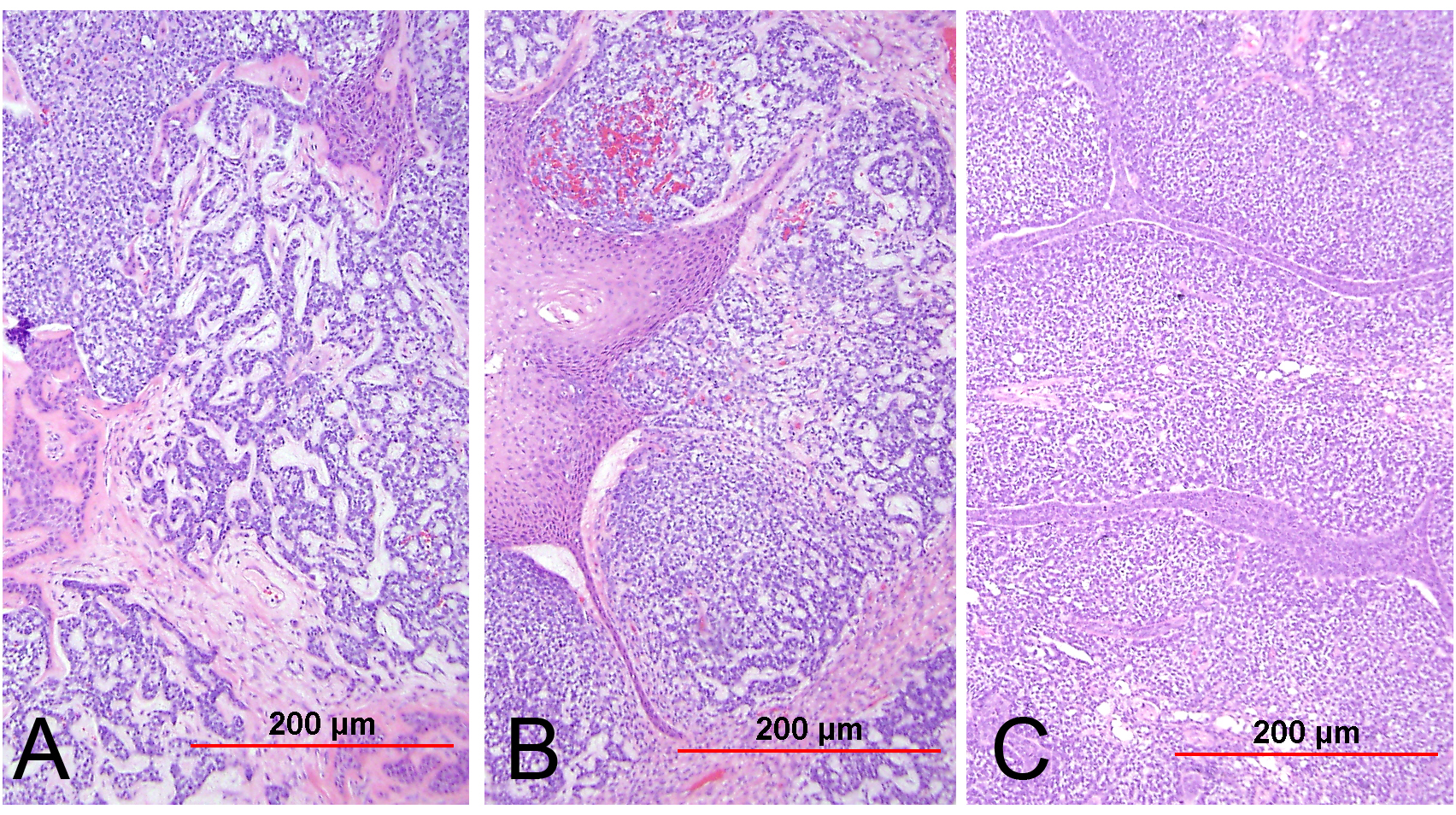
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Non Mucinous A This Tumor Shows A Download Scientific Diagram
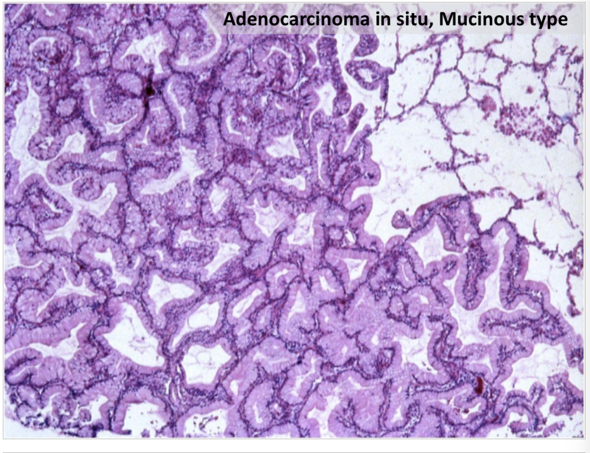
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm

Histopathology Images Of Adenocarcinoma In Situ Cervix By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas
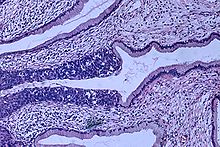
Carcinoma In Situ Wikipedia
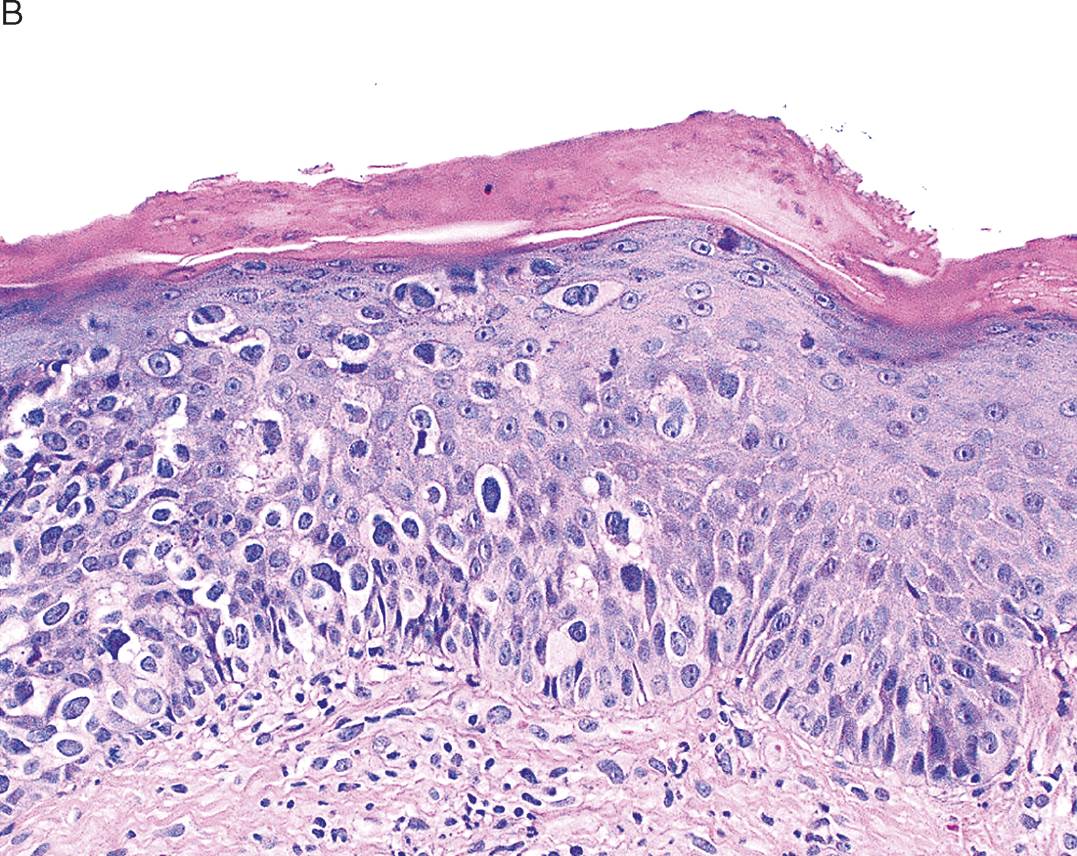
Cutaneous Tumors And Tumor Like Conditions Chapter 8 Silverberg S Principles And Practice Of Surgical Pathology And Cytopathology
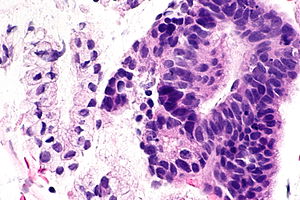
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma In Situ Libre Pathology

File Adenocarcinoma In Situ Of The Cervix Jpg Wikimedia Commons
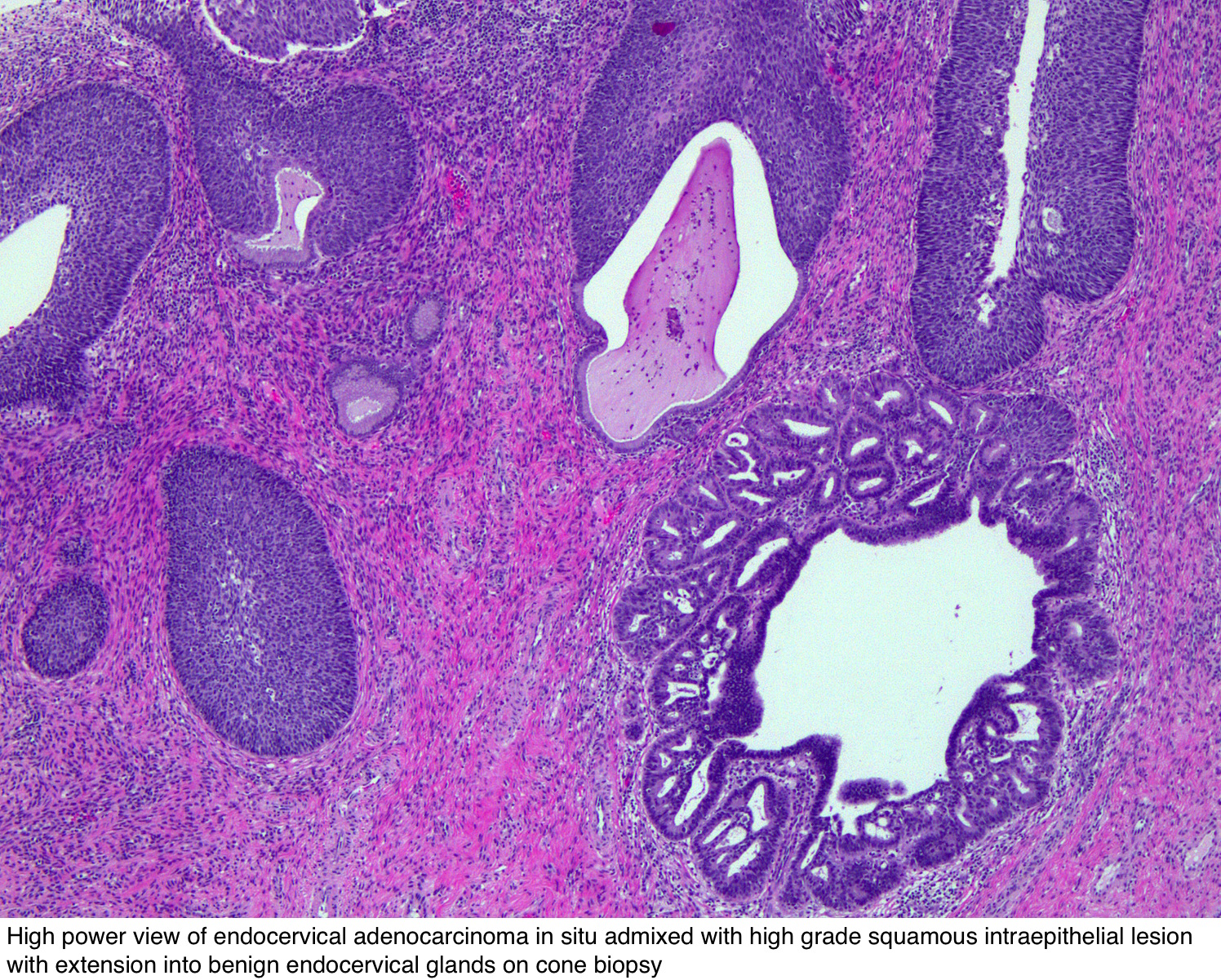
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma In Situ
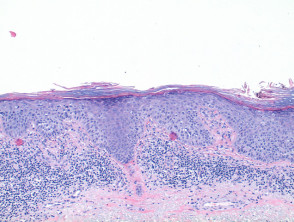
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Pathology Dermnet Nz
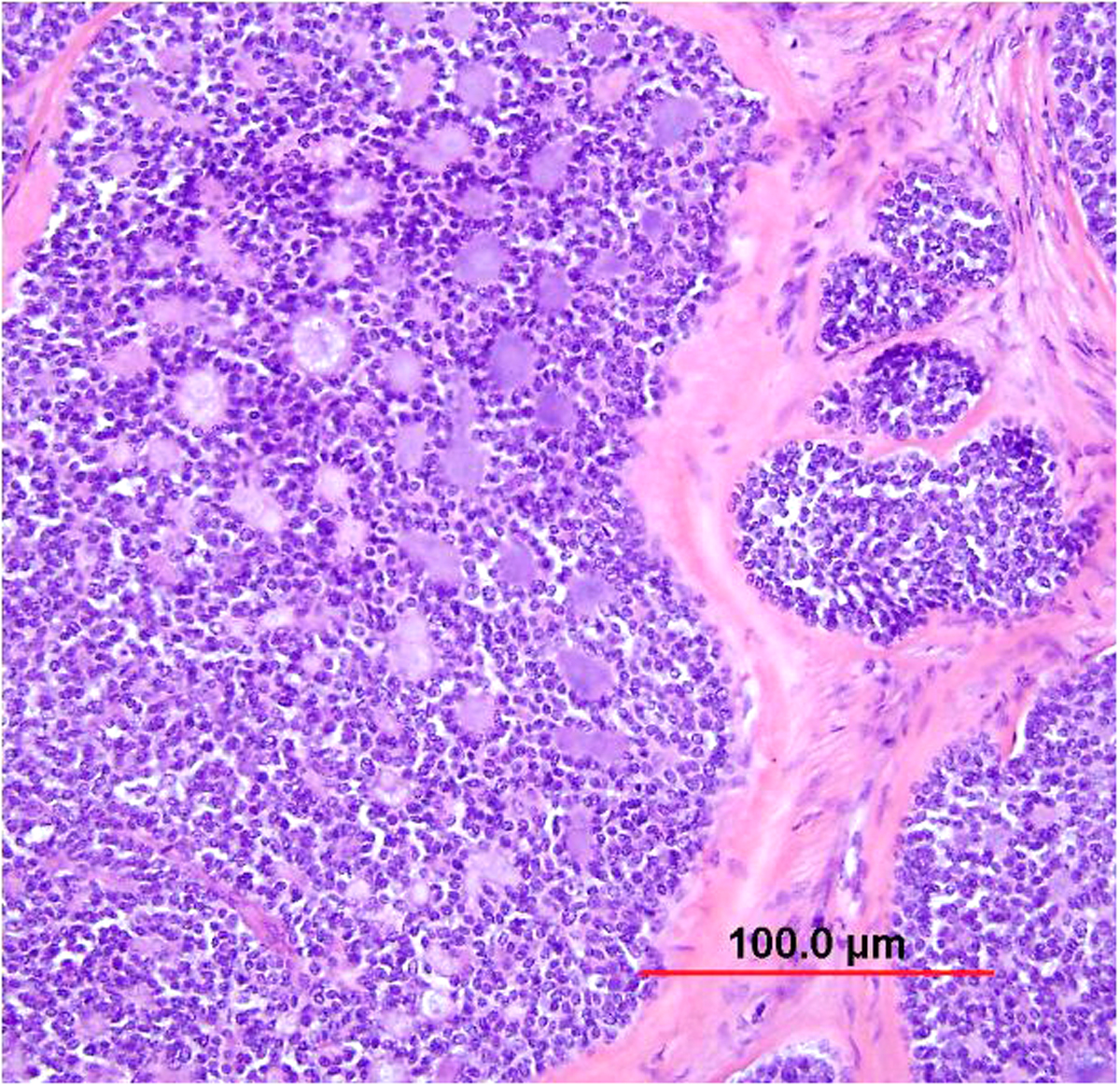
Pathology Of Cervical Carcinoma Glowm
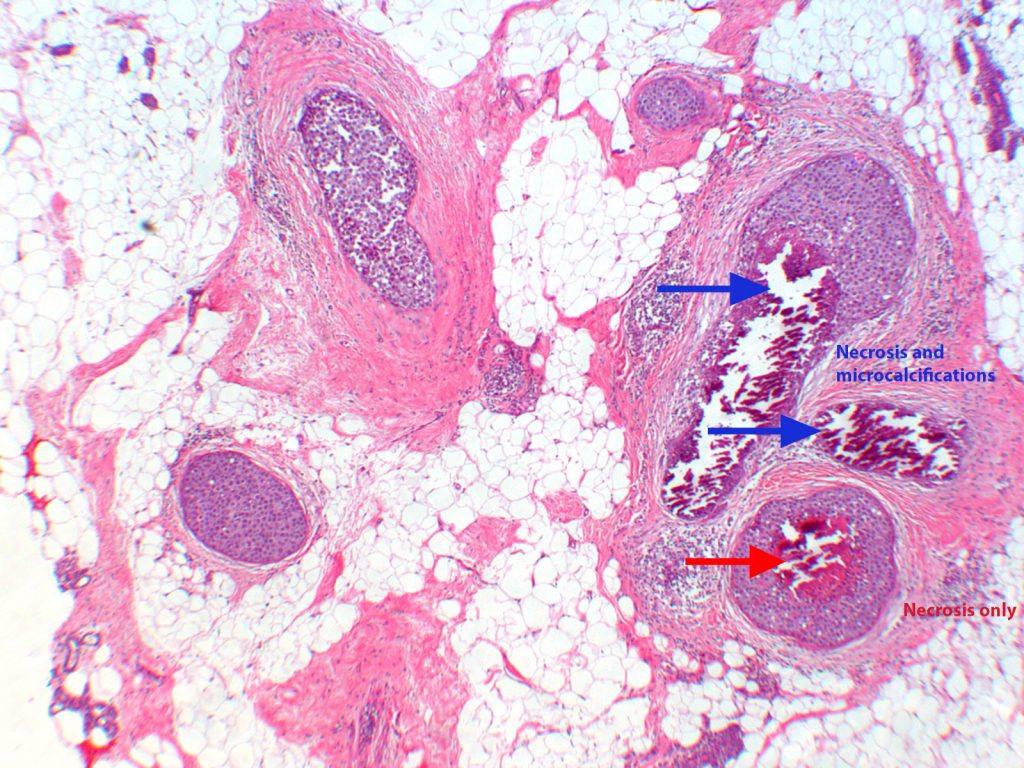
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ J B Askew Jr M D P A
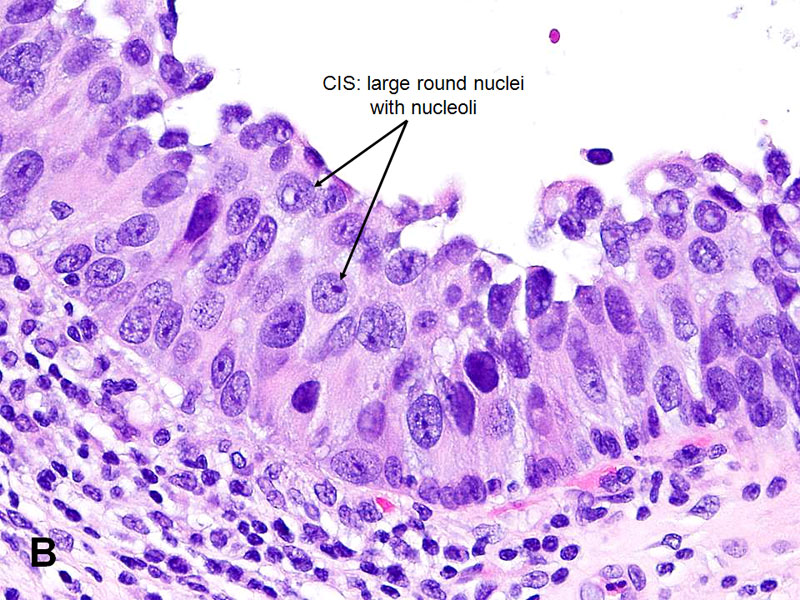
Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ American Urological Association

Adenocarcinoma In Situ An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images

Dcis Vs Lcis Pathology Student

Morphologic And Molecular Features Of Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ The American Journal Of Pathology

Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ Atlas



